 The U.S. Department of Commerce will start annual administrative reviews of existing antidumping and countervailing duty measures on key wood imports on March 9, 2026, and it plans to issue final results by January 31, 2027, the department said in a notice. The reviews cover Canadian softwood lumber under the antidumping order A-122-857 and the countervailing duty order C-122-858 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025. They also cover Chinese certain hardwood plywood products under antidumping order A-570-051 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025, and Chinese wooden bedroom furniture under antidumping order A-570-890 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025. Commerce said it may limit the number of companies examined and then select respondents using U.S. import data or quantity-and-value questionnaires. It said it intends to place the data or questionnaires on the record within five days after publication of the initiation notice and make respondent selection decisions within 35 days after publication.
The U.S. Department of Commerce will start annual administrative reviews of existing antidumping and countervailing duty measures on key wood imports on March 9, 2026, and it plans to issue final results by January 31, 2027, the department said in a notice. The reviews cover Canadian softwood lumber under the antidumping order A-122-857 and the countervailing duty order C-122-858 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025. They also cover Chinese certain hardwood plywood products under antidumping order A-570-051 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025, and Chinese wooden bedroom furniture under antidumping order A-570-890 for January 1, 2025, through December 31, 2025. Commerce said it may limit the number of companies examined and then select respondents using U.S. import data or quantity-and-value questionnaires. It said it intends to place the data or questionnaires on the record within five days after publication of the initiation notice and make respondent selection decisions within 35 days after publication.

 US President Trump’s administration on Wednesday launched a trade investigation into excess industrial capacity in 16 major trading partners in a move to rebuild tariff pressure after the U.S. Supreme Court tore down the centerpiece of Trump’s trade policy last month. Canada is not named as one of the targets of the new probe. US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer said the Section 301 unfair trade practices investigation could lead to new tariffs imposed against China, the European Union, India, Japan, Mexico and South Korea by this summer. Other trading partners subject to the excess capacity probe include Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Cambodia, Singapore, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Switzerland and Norway. Trump and his team have made clear they’re seeking to replace the hundreds of billions of dollars in lost revenues after the Supreme Court’s February ruling. In this case, the administration is starting investigations under Section 301 of the Trade Act.
US President Trump’s administration on Wednesday launched a trade investigation into excess industrial capacity in 16 major trading partners in a move to rebuild tariff pressure after the U.S. Supreme Court tore down the centerpiece of Trump’s trade policy last month. Canada is not named as one of the targets of the new probe. US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer said the Section 301 unfair trade practices investigation could lead to new tariffs imposed against China, the European Union, India, Japan, Mexico and South Korea by this summer. Other trading partners subject to the excess capacity probe include Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Cambodia, Singapore, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Switzerland and Norway. Trump and his team have made clear they’re seeking to replace the hundreds of billions of dollars in lost revenues after the Supreme Court’s February ruling. In this case, the administration is starting investigations under Section 301 of the Trade Act. Fiber and glass are among the packaging substrates hardest hit by February closure and layoff announcements. Here are the North American facilities that have announced downsizing efforts:
Fiber and glass are among the packaging substrates hardest hit by February closure and layoff announcements. Here are the North American facilities that have announced downsizing efforts: The escalating crisis in the Middle East could extend transport times for Finnish forest industry products to Asia by several weeks. At the same time, freight costs may rise, and container availability could become increasingly uncertain. Iran has announced the closure of the Strait of Hormuz. According to international reporting, several major shipping lines have also paused or reduced traffic through the Suez Canal, redirecting vessels around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope on routes to Asia. The Strait of Hormuz is a critical artery for global oil trade, and disruptions there primarily push up energy prices. For Finland’s forest industry, however, access through the Suez Canal is more directly decisive. Approximately 20 percent of the forest industry’s exports go to Asia, and the majority of those shipments pass through the Suez Canal, says Maarit Lindström, Director and Chief Economist at Metsäteollisuus ry.
The escalating crisis in the Middle East could extend transport times for Finnish forest industry products to Asia by several weeks. At the same time, freight costs may rise, and container availability could become increasingly uncertain. Iran has announced the closure of the Strait of Hormuz. According to international reporting, several major shipping lines have also paused or reduced traffic through the Suez Canal, redirecting vessels around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope on routes to Asia. The Strait of Hormuz is a critical artery for global oil trade, and disruptions there primarily push up energy prices. For Finland’s forest industry, however, access through the Suez Canal is more directly decisive. Approximately 20 percent of the forest industry’s exports go to Asia, and the majority of those shipments pass through the Suez Canal, says Maarit Lindström, Director and Chief Economist at Metsäteollisuus ry.  The US Department of Commerce preliminarily determined that hardwood and decorative plywood from China was sold in the US at less than fair value during the period Oct. 1, 2024, through March 31, 2025, and it also made a preliminary affirmative determination of critical circumstances. Starting March 2, 2026, the publication date of the Commerce Department notice in the Federal Register, US Customs and Border Protection will begin suspending liquidation and collecting cash deposits on covered entries at the applicable rates. The notice sets an estimated weighted-average dumping margin of 187.27% for the China-wide entity and an adjusted cash-deposit rate of 185.96% for the listed producer-exporter combinations as well as for the China-wide entity. …Commerce said it plans to issue its final determination by May 10, 2026, within 75 days of the preliminary decision’s Feb. 24 signature date, after which the US International Trade Commission will decide whether the U.S. industry was materially injured by the imports.
The US Department of Commerce preliminarily determined that hardwood and decorative plywood from China was sold in the US at less than fair value during the period Oct. 1, 2024, through March 31, 2025, and it also made a preliminary affirmative determination of critical circumstances. Starting March 2, 2026, the publication date of the Commerce Department notice in the Federal Register, US Customs and Border Protection will begin suspending liquidation and collecting cash deposits on covered entries at the applicable rates. The notice sets an estimated weighted-average dumping margin of 187.27% for the China-wide entity and an adjusted cash-deposit rate of 185.96% for the listed producer-exporter combinations as well as for the China-wide entity. …Commerce said it plans to issue its final determination by May 10, 2026, within 75 days of the preliminary decision’s Feb. 24 signature date, after which the US International Trade Commission will decide whether the U.S. industry was materially injured by the imports.
 The outsized impact that oil prices have on the global economy means higher fuel and energy prices are all but guaranteed for many countries, not just those in the conflict region. …In the forest products sector, softwood lumber trade is one of the most directly exposed segments. Europe accounts for about one-third of the global softwood supply. Sweden and Finland are among Europe’s top exporters, along with Germany and Austria. …Lumber shipments out of Europe rely heavily on shipping routes through the Mediterranean, the Suez Canal, and the Gulf. Shipping costs are expected to escalate as fuel prices and risk premiums rise. Spikes in freight and insurance, along with rising energy costs in production and transport, could quickly start to make Nordic lumber less competitive while tightening margins. …Prolonged disruption in that region could force Nordic lumber producers to redirect volumes to Europe, North Africa, and Asia, causing price pressures in those markets.
The outsized impact that oil prices have on the global economy means higher fuel and energy prices are all but guaranteed for many countries, not just those in the conflict region. …In the forest products sector, softwood lumber trade is one of the most directly exposed segments. Europe accounts for about one-third of the global softwood supply. Sweden and Finland are among Europe’s top exporters, along with Germany and Austria. …Lumber shipments out of Europe rely heavily on shipping routes through the Mediterranean, the Suez Canal, and the Gulf. Shipping costs are expected to escalate as fuel prices and risk premiums rise. Spikes in freight and insurance, along with rising energy costs in production and transport, could quickly start to make Nordic lumber less competitive while tightening margins. …Prolonged disruption in that region could force Nordic lumber producers to redirect volumes to Europe, North Africa, and Asia, causing price pressures in those markets.
 WASHINGTON — The widening conflict in the Middle East following joint U.S.-Israeli strikes against Iran is introducing fresh uncertainty into global markets, with potential downstream effects for furniture importers, who despite relying more heavily on Asia-based sourcing than directly in the region are still exposed to volatility across the global supply chain. Analysts told Reuters that a broader regional conflict could disrupt global trade routes, supply chains and commodity prices, all of which have implications downstream for furniture importers by heaping pressure on both costs and capacity. Three potential effects of the ongoing unrest in the Middle East that could spill over for furniture companies include higher fuel costs and landed container prices, container capacity pressures, and risks and longer-term supply chain strains. Over the longer term, the conflict underscores the need to reassess geographic concentration risk.
WASHINGTON — The widening conflict in the Middle East following joint U.S.-Israeli strikes against Iran is introducing fresh uncertainty into global markets, with potential downstream effects for furniture importers, who despite relying more heavily on Asia-based sourcing than directly in the region are still exposed to volatility across the global supply chain. Analysts told Reuters that a broader regional conflict could disrupt global trade routes, supply chains and commodity prices, all of which have implications downstream for furniture importers by heaping pressure on both costs and capacity. Three potential effects of the ongoing unrest in the Middle East that could spill over for furniture companies include higher fuel costs and landed container prices, container capacity pressures, and risks and longer-term supply chain strains. Over the longer term, the conflict underscores the need to reassess geographic concentration risk.
 OTTAWA — The Canadian minister responsible for Canada-United States trade said Wednesday that Mexico was keen to maintain a trilateral agreement under the free trade pact between the three North American neighbors that is up for review this year. “I am reassured by the Mexican economy secretary … his desire to work with Canada and to ensure that the review of CUSMA results in a strengthened and ongoing trilateral trade arrangement,” Dominic LeBlanc said in a press conference from Mexico. LeBlanc is heading a group of over 370 delegates to Mexico for a six-day trade mission amid fears that U.S. President Donald Trump could ditch the decades-old three-way free trade agreement between the U.S., Mexico, and Canada when it comes up for review later this year. “The Mexicans have very similar interests to Canada,” LeBlanc said. “We both remain absolutely committed to the trilateral free trade agreement and working together as this review process unfolds,” he added.
OTTAWA — The Canadian minister responsible for Canada-United States trade said Wednesday that Mexico was keen to maintain a trilateral agreement under the free trade pact between the three North American neighbors that is up for review this year. “I am reassured by the Mexican economy secretary … his desire to work with Canada and to ensure that the review of CUSMA results in a strengthened and ongoing trilateral trade arrangement,” Dominic LeBlanc said in a press conference from Mexico. LeBlanc is heading a group of over 370 delegates to Mexico for a six-day trade mission amid fears that U.S. President Donald Trump could ditch the decades-old three-way free trade agreement between the U.S., Mexico, and Canada when it comes up for review later this year. “The Mexicans have very similar interests to Canada,” LeBlanc said. “We both remain absolutely committed to the trilateral free trade agreement and working together as this review process unfolds,” he added.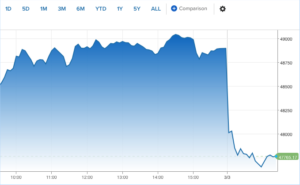 US equities tumbled on Tuesday, undoing a Monday equity comeback, as oil prices spiked again and traders began to worry the U.S.-Iran conflict could drag on longer than anticipated. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 1,238 points, or 2.5%. If that holds, it would mark the blue-chip index’s first 1,000-point decline since April 10, 2025. The S&P 500 slipped 2.2%, while the Nasdaq Composite was down 2.3%. Brent crude oil, the international benchmark, topped $84 a barrel, up 8% Tuesday following a 6% spike Monday. WTI crude jumped 8% to above $77 a barrel after a 6% jump as well on Monday. Iranian Revolutionary Guard commander said the Strait of Hormuz — the world’s most vital transit route for crude oil — is closed and that Iran would set ablaze ships attempting the route, Reuters reported, citing Iranian media.
US equities tumbled on Tuesday, undoing a Monday equity comeback, as oil prices spiked again and traders began to worry the U.S.-Iran conflict could drag on longer than anticipated. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 1,238 points, or 2.5%. If that holds, it would mark the blue-chip index’s first 1,000-point decline since April 10, 2025. The S&P 500 slipped 2.2%, while the Nasdaq Composite was down 2.3%. Brent crude oil, the international benchmark, topped $84 a barrel, up 8% Tuesday following a 6% spike Monday. WTI crude jumped 8% to above $77 a barrel after a 6% jump as well on Monday. Iranian Revolutionary Guard commander said the Strait of Hormuz — the world’s most vital transit route for crude oil — is closed and that Iran would set ablaze ships attempting the route, Reuters reported, citing Iranian media.
 Japan’s housing starts fell 0.4% yoy in January 2026, easing from a 1.3% drop in the previous month and beating market expectations of a 1.6% decline. It marked the third consecutive month of contraction, though the pace was the mildest since July 2024. Rental housing starts declined at a slower rate (-1.5% vs -3.4% in December). Meanwhile, owner-occupied homes rebounded (6.6% vs -1.8%), as did prefabricated housing (5.1% vs -6.1%). Starts for two-by-four homes also accelerated (8.7% vs 2.8%). In contrast, built-for-sale housing fell 4.8%, reversing a 1.9% increase in December.
Japan’s housing starts fell 0.4% yoy in January 2026, easing from a 1.3% drop in the previous month and beating market expectations of a 1.6% decline. It marked the third consecutive month of contraction, though the pace was the mildest since July 2024. Rental housing starts declined at a slower rate (-1.5% vs -3.4% in December). Meanwhile, owner-occupied homes rebounded (6.6% vs -1.8%), as did prefabricated housing (5.1% vs -6.1%). Starts for two-by-four homes also accelerated (8.7% vs 2.8%). In contrast, built-for-sale housing fell 4.8%, reversing a 1.9% increase in December. Drax Group Plc’s profit declined last year but exceeded analyst estimates, helping lift the shares to their highest level in almost two decades despite significant impairment charges. Adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization totaled £947 million ($1.3 billion), beating analyst estimates for £913.7 million. Citigroup Inc. analyst Jenny Ping cited lower pellet costs and record generation at its main biomass plant as supporting the result. The figure was still 11% lower than a year earlier, which Drax attributed to weaker power prices. The company’s share price rose as much as 6.2% to the highest since October 2006 before paring gains. …Drax reaffirmed its target of £600 million to £700 million of annual adjusted EBITDA after 2027 and said it expects 2026 earnings to align with analyst forecasts of about £662 million. The company also expects to return £1 billion to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks from 2025 until 2031, with £2 billion invested in growth areas.
Drax Group Plc’s profit declined last year but exceeded analyst estimates, helping lift the shares to their highest level in almost two decades despite significant impairment charges. Adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization totaled £947 million ($1.3 billion), beating analyst estimates for £913.7 million. Citigroup Inc. analyst Jenny Ping cited lower pellet costs and record generation at its main biomass plant as supporting the result. The figure was still 11% lower than a year earlier, which Drax attributed to weaker power prices. The company’s share price rose as much as 6.2% to the highest since October 2006 before paring gains. …Drax reaffirmed its target of £600 million to £700 million of annual adjusted EBITDA after 2027 and said it expects 2026 earnings to align with analyst forecasts of about £662 million. The company also expects to return £1 billion to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks from 2025 until 2031, with £2 billion invested in growth areas. Visit Canada Wood’s Market News for these stories and more:
Visit Canada Wood’s Market News for these stories and more:


 HCM CITY — Canadian Wood Vietnam, part of Forestry Innovation Investment (FII) – a provincial agency of the Government of British Columbia (B.C.), Canada, has recently reaffirmed its commitment to the Vietnamese wood industry by maintaining a consistent presence across key industry platforms. Canadian Wood Vietnam is dedicated to enhancing networking activities, sharing information, and fostering professional exchanges within Việt Nam’s wood and furniture industry. In addition to promoting trade, Canadian Wood Vietnam works closely with manufacturers in Việt Nam by offering technical support, training programmes, and facilitating market development initiatives that link businesses with reputable Canadian softwood suppliers and provide valuable insights into softwood species from British Columbia (B.C.), Canada. These ongoing efforts aim to assist Vietnamese manufacturers in strengthening their product development capabilities, refining design applications, and enhancing value creation.
HCM CITY — Canadian Wood Vietnam, part of Forestry Innovation Investment (FII) – a provincial agency of the Government of British Columbia (B.C.), Canada, has recently reaffirmed its commitment to the Vietnamese wood industry by maintaining a consistent presence across key industry platforms. Canadian Wood Vietnam is dedicated to enhancing networking activities, sharing information, and fostering professional exchanges within Việt Nam’s wood and furniture industry. In addition to promoting trade, Canadian Wood Vietnam works closely with manufacturers in Việt Nam by offering technical support, training programmes, and facilitating market development initiatives that link businesses with reputable Canadian softwood suppliers and provide valuable insights into softwood species from British Columbia (B.C.), Canada. These ongoing efforts aim to assist Vietnamese manufacturers in strengthening their product development capabilities, refining design applications, and enhancing value creation. 
.jpg)


 As the EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) nears implementation this year, furniture giant IKEA may need stronger traceability systems to prove its timber isn’t linked to post-2020 deforestation. Although nearly all IKEA wood is FSC-certified or recycled, past investigations show this voluntary scheme can miss illegal or unsustainable logging. The EUDR requires geolocation data and stricter due diligence than existing certifications or regulations, but repeated delays and possible rule changes have created uncertainty for companies like IKEA preparing to comply. Industry watchdogs say high-profile companies like IKEA can “do more” to champion the landmark regulation and implement leading wood traceability systems, rather than relying solely on existing — voluntary— certification schemes.
As the EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) nears implementation this year, furniture giant IKEA may need stronger traceability systems to prove its timber isn’t linked to post-2020 deforestation. Although nearly all IKEA wood is FSC-certified or recycled, past investigations show this voluntary scheme can miss illegal or unsustainable logging. The EUDR requires geolocation data and stricter due diligence than existing certifications or regulations, but repeated delays and possible rule changes have created uncertainty for companies like IKEA preparing to comply. Industry watchdogs say high-profile companies like IKEA can “do more” to champion the landmark regulation and implement leading wood traceability systems, rather than relying solely on existing — voluntary— certification schemes.






 Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington.
Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington.
 A new study with EFI contribution,
A new study with EFI contribution,  With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe.
With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe.