 MEDFORD, Oregon- An explosion and fire broke out late Saturday night at the Roseburg Forest Products facility in northwest Medford, prompting a second-alarm response from fire crews. According to the Medford Fire Department, the initial call came in after a reported explosion at the facility. When firefighters arrived, they found flames rapidly spreading across the plant’s conveyor system, raw material storage areas, and elevated platforms. Crews worked through the night alongside facility staff to bring the blaze under control, with additional units called in to help contain the fire and extinguish persistent hot spots. No injuries were reported, and all personnel were safely accounted for. An investigation by fire officials determined the cause of the fire to be accidental.
MEDFORD, Oregon- An explosion and fire broke out late Saturday night at the Roseburg Forest Products facility in northwest Medford, prompting a second-alarm response from fire crews. According to the Medford Fire Department, the initial call came in after a reported explosion at the facility. When firefighters arrived, they found flames rapidly spreading across the plant’s conveyor system, raw material storage areas, and elevated platforms. Crews worked through the night alongside facility staff to bring the blaze under control, with additional units called in to help contain the fire and extinguish persistent hot spots. No injuries were reported, and all personnel were safely accounted for. An investigation by fire officials determined the cause of the fire to be accidental.
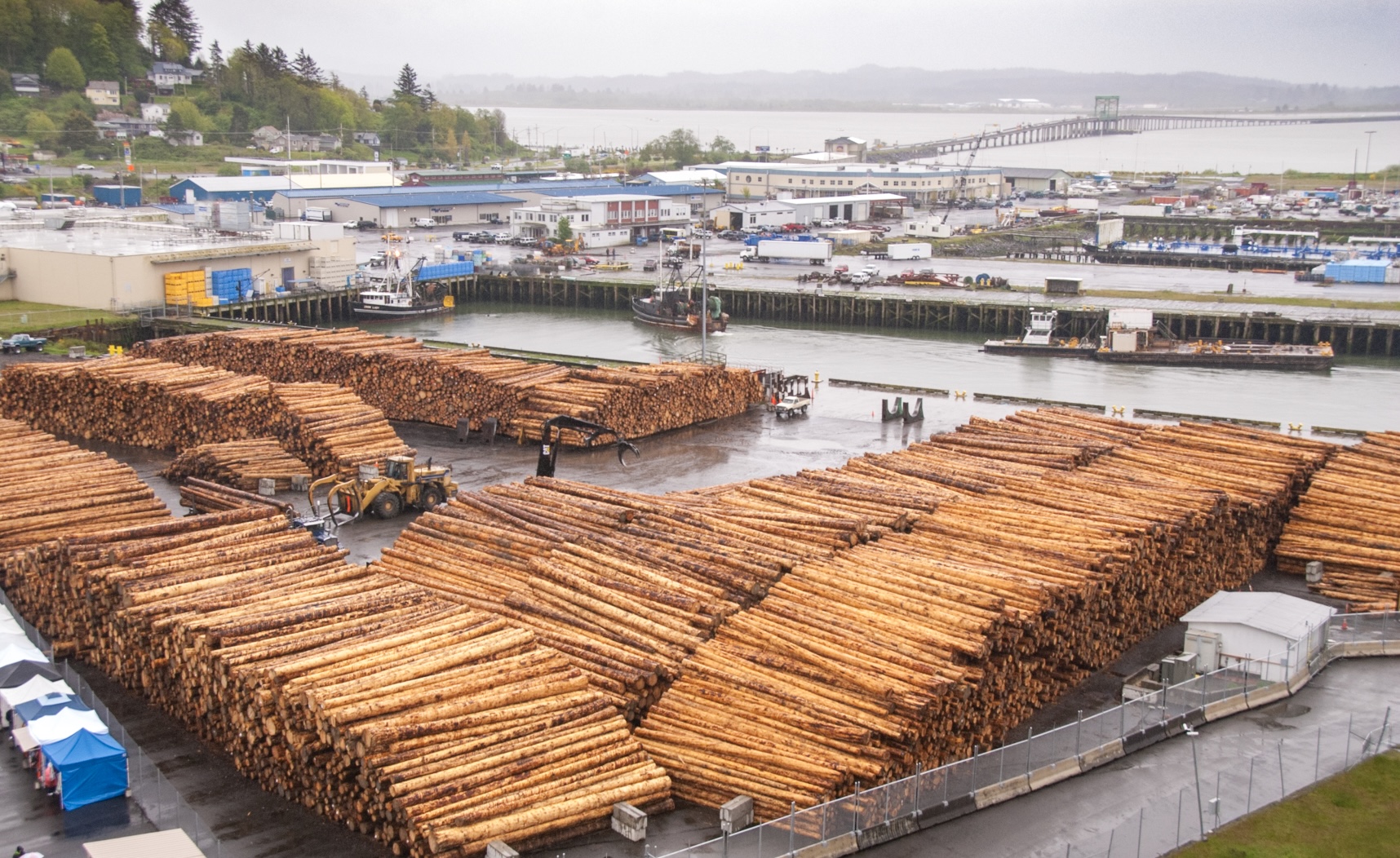

 SKAMANIA COUNTY, Washington — Sawmills have been closing across the Pacific Northwest over the past 30 years. There is just one left in Skamania County, down from six during its logging heyday. Limited log supply from the region’s national forests has cut off their raw material, while cheap lumber from Canada has taken market share for their finished product. Owners of the remaining mills have high hopes that President Trump will deliver relief by increasing logging in national forests and raising trade protections against Canadian exports. Although the latter can be achieved with a stroke of the president’s pen, meaningfully boosting the federal timber harvest could take years and be impeded by litigation and red tape. …US sawyers have argued successfully in trade cases that their Canadian competitors are supplied with subsidized government logs, and that they offer two-by-fours over the border for less than they sell them at home. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
SKAMANIA COUNTY, Washington — Sawmills have been closing across the Pacific Northwest over the past 30 years. There is just one left in Skamania County, down from six during its logging heyday. Limited log supply from the region’s national forests has cut off their raw material, while cheap lumber from Canada has taken market share for their finished product. Owners of the remaining mills have high hopes that President Trump will deliver relief by increasing logging in national forests and raising trade protections against Canadian exports. Although the latter can be achieved with a stroke of the president’s pen, meaningfully boosting the federal timber harvest could take years and be impeded by litigation and red tape. …US sawyers have argued successfully in trade cases that their Canadian competitors are supplied with subsidized government logs, and that they offer two-by-fours over the border for less than they sell them at home. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
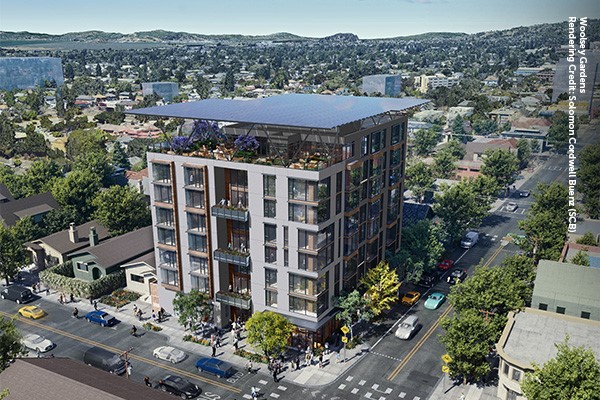
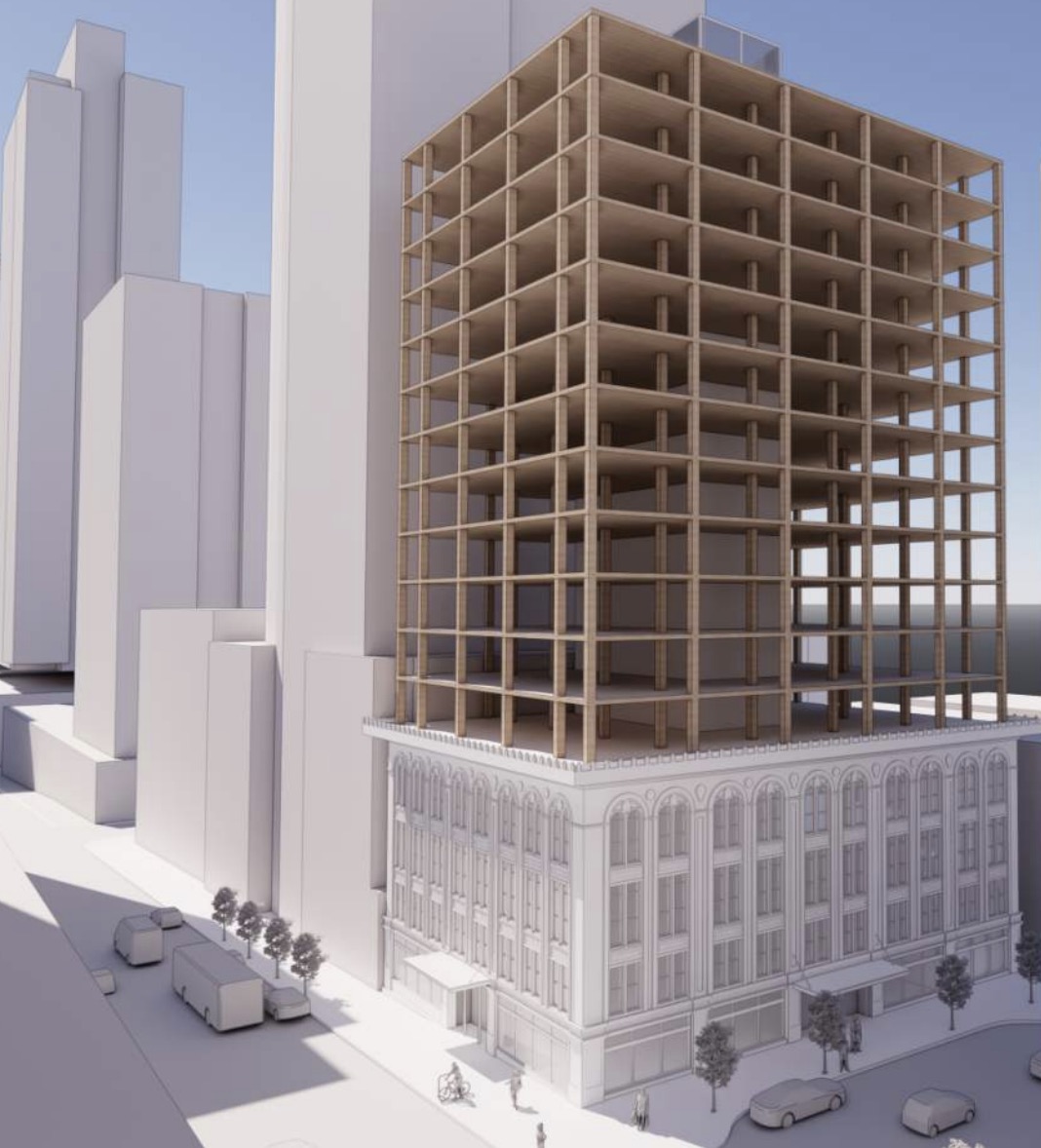

 A Seattle proposal to add more housing above the historic Doyle Building near Pike Place Market is bringing out significant opposition, with nearby condominium owners seeking to utilize the only point of leverage they have: the city’s landmarks board. Clark/Barnes architects are working with the owners of the four-story building….
A Seattle proposal to add more housing above the historic Doyle Building near Pike Place Market is bringing out significant opposition, with nearby condominium owners seeking to utilize the only point of leverage they have: the city’s landmarks board. Clark/Barnes architects are working with the owners of the four-story building…. 

 WASHINGTON STATE — Washington’s rural counties and school districts are preparing to start the school year without millions of dollars from a program meant to offset reduced revenue from logging on federal lands. The Secure Rural Schools program expired at the end of 2023 after Congress failed to renew it. Democratic and Republican lawmakers, along with local officials, are pushing US House leadership to bring a bill renewing the program to the floor. The lapsed program helps pay for roads and schools, providing $7 billion in payments to more than 700 counties and 4,400 school districts across 40 states since it was enacted in 2000. …Counties and schools have received logging revenue from the federal government for roads and schools since 1906. Federal law currently mandates that all counties annually receive 25% of the seven-year average of revenue generated by that county’s forests.
WASHINGTON STATE — Washington’s rural counties and school districts are preparing to start the school year without millions of dollars from a program meant to offset reduced revenue from logging on federal lands. The Secure Rural Schools program expired at the end of 2023 after Congress failed to renew it. Democratic and Republican lawmakers, along with local officials, are pushing US House leadership to bring a bill renewing the program to the floor. The lapsed program helps pay for roads and schools, providing $7 billion in payments to more than 700 counties and 4,400 school districts across 40 states since it was enacted in 2000. …Counties and schools have received logging revenue from the federal government for roads and schools since 1906. Federal law currently mandates that all counties annually receive 25% of the seven-year average of revenue generated by that county’s forests.  In May, the White House Office of Budget and Management sent Congress President Trump’s proposed budget for discretionary spending for upcoming fiscal year 2026. Among the budget’s many cuts is a proposal to eliminate all funding for the Collaborative Forest Landscape Restoration Program, designed to make timber projects run more smoothly. The Collaborative is a decades-long experiment to get conservationists, the timber industry and U.S. Forest Service back to the proverbial table after the timber wars of years past. Collaboratives have been widely credited with incorporating conservationist’s environmental concerns in the design of timber harvests and, consequently, reducing environmental litigation known to slow down harvests. The CFLRP has been lauded by some for helping implement forest thinning and restoration projects meant to both reduce wildfire risk and increase timber production and jobs in rural communities.
In May, the White House Office of Budget and Management sent Congress President Trump’s proposed budget for discretionary spending for upcoming fiscal year 2026. Among the budget’s many cuts is a proposal to eliminate all funding for the Collaborative Forest Landscape Restoration Program, designed to make timber projects run more smoothly. The Collaborative is a decades-long experiment to get conservationists, the timber industry and U.S. Forest Service back to the proverbial table after the timber wars of years past. Collaboratives have been widely credited with incorporating conservationist’s environmental concerns in the design of timber harvests and, consequently, reducing environmental litigation known to slow down harvests. The CFLRP has been lauded by some for helping implement forest thinning and restoration projects meant to both reduce wildfire risk and increase timber production and jobs in rural communities. The Trump administration has announced plans to rescind the 2001 Roadless Rule, changing the political and timber industry landscape in the Tongass National Forest for the third time in five years. The Roadless Rule prevents logging, road building and mining on national forest lands. It was last repealed in 2020 and restored in 2023, and has been subject to decades of debate. Timber operators say the rescission could help a dying industry – if it passes through Congress. The U.S. Forest Service owns approximately 78% of the land in Southeast Alaska, meaning timber operators are dependent on the federal agency for a majority of their supply. Kirk Dahlstrom, co-owner of Viking Lumber Co. in Klawock, said the agency is nine years behind on offering timber supply for the Southeast industry. He said his business will not survive if land management remains under Forest Service control. “We got starved to almost nothing.”
The Trump administration has announced plans to rescind the 2001 Roadless Rule, changing the political and timber industry landscape in the Tongass National Forest for the third time in five years. The Roadless Rule prevents logging, road building and mining on national forest lands. It was last repealed in 2020 and restored in 2023, and has been subject to decades of debate. Timber operators say the rescission could help a dying industry – if it passes through Congress. The U.S. Forest Service owns approximately 78% of the land in Southeast Alaska, meaning timber operators are dependent on the federal agency for a majority of their supply. Kirk Dahlstrom, co-owner of Viking Lumber Co. in Klawock, said the agency is nine years behind on offering timber supply for the Southeast industry. He said his business will not survive if land management remains under Forest Service control. “We got starved to almost nothing.” The Trump administration has proposed drastically limiting the public’s say in how federal lands are used at a time when the president is pushing to fast-track logging, mining and oil extraction. That’s raising concerns amongst conservationists and environmental advocates, who worry that the changes could have a profound impact on Oregonians’ relationship with the lands around them. More than half the land in Oregon is federally owned, as is about 29% of land in Washington. …Under President Donald Trump, 16 federal agencies are now considering rule changes that could curtail or drastically limit this public input, which is required under the National Environmental Policy Act, known as NEPA. Those proposed changes were announced in early July. The public has until Monday to provide input on the changes for the U.S Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. …Data shows that public comments can make a difference.
The Trump administration has proposed drastically limiting the public’s say in how federal lands are used at a time when the president is pushing to fast-track logging, mining and oil extraction. That’s raising concerns amongst conservationists and environmental advocates, who worry that the changes could have a profound impact on Oregonians’ relationship with the lands around them. More than half the land in Oregon is federally owned, as is about 29% of land in Washington. …Under President Donald Trump, 16 federal agencies are now considering rule changes that could curtail or drastically limit this public input, which is required under the National Environmental Policy Act, known as NEPA. Those proposed changes were announced in early July. The public has until Monday to provide input on the changes for the U.S Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. …Data shows that public comments can make a difference.

 The Washington Forest Practices Board is proposing new legislation pushed by the Washington Department of Ecology that will affect all of us financially. The Washington Forest Practices Board (FPB) is supposedly an “independent” state agency responsible for establishing rules that govern forest practices in Washington state. It’s chaired by the Commissioner of Public Lands Dave Upthegrove. …The FPB is proposing streams that are perennial with no fish should have the existing no-harvest buffers changed from 50 feet each side of the stream to 75 feet (or more). The proposal affects not only the stream buffer width, but the length of stream buffer and volume of restricted trees. Why does it affect you? All timber harvests are taxed by the state of Washington — 4% of the net log value goes back to the county the trees were harvested in. …You are affected by this proposed change in law that does nothing for fish.
The Washington Forest Practices Board is proposing new legislation pushed by the Washington Department of Ecology that will affect all of us financially. The Washington Forest Practices Board (FPB) is supposedly an “independent” state agency responsible for establishing rules that govern forest practices in Washington state. It’s chaired by the Commissioner of Public Lands Dave Upthegrove. …The FPB is proposing streams that are perennial with no fish should have the existing no-harvest buffers changed from 50 feet each side of the stream to 75 feet (or more). The proposal affects not only the stream buffer width, but the length of stream buffer and volume of restricted trees. Why does it affect you? All timber harvests are taxed by the state of Washington — 4% of the net log value goes back to the county the trees were harvested in. …You are affected by this proposed change in law that does nothing for fish. The Trump administration’s tumultuous relationship with China is proving to be a major issue for some companies in Alaska’s forest products industry. That includes in Haines, where a timber sale that was supposed to kick off this spring has stalled amid China’s ban on US log imports. China announced the ban in March, citing concerns over pests like bark and longhorn beetles in US shipments. The move came the same day that China imposed retaliatory tariffs on certain US agricultural products amid President Donald Trump’s global trade war. The decision has had sweeping effects on companies that harvest logs in Alaska and ship them overseas. …The trade disputes have also hit Canadian lumber company Transpac Group. The company in March largely shut down its site on Afognak Island, just north of Kodiak, citing the ban and failed efforts to divert its product to other markets.
The Trump administration’s tumultuous relationship with China is proving to be a major issue for some companies in Alaska’s forest products industry. That includes in Haines, where a timber sale that was supposed to kick off this spring has stalled amid China’s ban on US log imports. China announced the ban in March, citing concerns over pests like bark and longhorn beetles in US shipments. The move came the same day that China imposed retaliatory tariffs on certain US agricultural products amid President Donald Trump’s global trade war. The decision has had sweeping effects on companies that harvest logs in Alaska and ship them overseas. …The trade disputes have also hit Canadian lumber company Transpac Group. The company in March largely shut down its site on Afognak Island, just north of Kodiak, citing the ban and failed efforts to divert its product to other markets. MISSOULA — in the Blue Mountain area in Missoula, trees with a blue ring painted around them are slated for removal as part of a larger plan to restore the forest to its pre-colonial state — a state that was more fire-resistant. The plan involves several agencies collaborating to achieve this goal. …The Blue Mountain Area consists of land owned by the U.S. Forest Service, Missoula County, the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) and private land owners. They will implement forest treatments to change the forest, as the current state of it is extremely fire-prone. …The ultimate goal of all the agencies is to create open areas with ponderosa pine scattered about. To achieve this, agencies are looking at a combination of mechanized and non-mechanized vegetation management; clearing the forest floor, often through prescribed burning, and removing species like Douglas fir.
MISSOULA — in the Blue Mountain area in Missoula, trees with a blue ring painted around them are slated for removal as part of a larger plan to restore the forest to its pre-colonial state — a state that was more fire-resistant. The plan involves several agencies collaborating to achieve this goal. …The Blue Mountain Area consists of land owned by the U.S. Forest Service, Missoula County, the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) and private land owners. They will implement forest treatments to change the forest, as the current state of it is extremely fire-prone. …The ultimate goal of all the agencies is to create open areas with ponderosa pine scattered about. To achieve this, agencies are looking at a combination of mechanized and non-mechanized vegetation management; clearing the forest floor, often through prescribed burning, and removing species like Douglas fir. Throughout her two decades working on forestry issues, Jasmine Minbashian has often found herself at odds with the US Forest Service and the timber industry. Her environmental activism started during the second wave of Pacific Northwest “Timber Wars”. …She joined the North Central Washington Forest Health Collaborative in 2019. …The group is one of 19 forest collaboratives focused on public lands in Washington and Oregon that emerged in the wake of the “Timber Wars” in an attempt to find agreement around contentious forestry issues. …These forest collaboratives, touted as a model of consensus-driven conservation, have quietly become influential engines for federal forest management decisions across the West. But critics worry the groups are too aligned with timber interests that prioritize commercial logging, and that they helped pave the way for the Trump administration’s latest effort to expand logging on public lands throughout the country by skirting environmental protection laws.
Throughout her two decades working on forestry issues, Jasmine Minbashian has often found herself at odds with the US Forest Service and the timber industry. Her environmental activism started during the second wave of Pacific Northwest “Timber Wars”. …She joined the North Central Washington Forest Health Collaborative in 2019. …The group is one of 19 forest collaboratives focused on public lands in Washington and Oregon that emerged in the wake of the “Timber Wars” in an attempt to find agreement around contentious forestry issues. …These forest collaboratives, touted as a model of consensus-driven conservation, have quietly become influential engines for federal forest management decisions across the West. But critics worry the groups are too aligned with timber interests that prioritize commercial logging, and that they helped pave the way for the Trump administration’s latest effort to expand logging on public lands throughout the country by skirting environmental protection laws. There are obvious benefits to logging, grazing, prescribed burns, and mechanical thinning of California’s forests. When you suppress wildfires for what is now over a century, then overregulate and suppress any other means to thin the forest, you get overcrowded and unhealthy forests. California’s trees now have 5 to 10 times more than a historically normal density. They’re competing for an insufficient share of light, water and nutrients, leading to disease, infestations, dehydration and death. Up through the 1980s, California harvested 6 billion board feet per year of timber; the annual harvest is now 25% of that. We have turned our forests into tinderboxes. …For the sake of California’s water supply, its energy security, the safety of people living in the forests, and the health of our trees and wildlife, Californian needs to revive its logging industry. …It will also enable something counterintuitive: precious and endangered wildlife can thrive in a responsibly managed forest.
There are obvious benefits to logging, grazing, prescribed burns, and mechanical thinning of California’s forests. When you suppress wildfires for what is now over a century, then overregulate and suppress any other means to thin the forest, you get overcrowded and unhealthy forests. California’s trees now have 5 to 10 times more than a historically normal density. They’re competing for an insufficient share of light, water and nutrients, leading to disease, infestations, dehydration and death. Up through the 1980s, California harvested 6 billion board feet per year of timber; the annual harvest is now 25% of that. We have turned our forests into tinderboxes. …For the sake of California’s water supply, its energy security, the safety of people living in the forests, and the health of our trees and wildlife, Californian needs to revive its logging industry. …It will also enable something counterintuitive: precious and endangered wildlife can thrive in a responsibly managed forest. Wildfires are getting more catastrophic and expensive. For the last decade, Oregon policymakers haven’t been able to agree on how to pay for them. And while lawmakers emerged from this year’s legislative session with a plan to fund wildfire prevention, there’s still no dedicated funding to fight large fires like the Cram Fire, which has burned nearly 100,000 acres in Central Oregon. The total wildfire budget for the next two years is less than the state spent last year alone. And in some cases, costs that used to be borne by insurance plans and private landowners are now the responsibility of all Oregonians. A similar phrase cropped up during multiple interviews with policymakers: The consensus lawmakers reached this year is a good “first step.” What’s less clear is if it’s enough. ….“Oregonians writ large, are going to be the ones to pay for it,” said Casey Kulla, with Oregon Wild.
Wildfires are getting more catastrophic and expensive. For the last decade, Oregon policymakers haven’t been able to agree on how to pay for them. And while lawmakers emerged from this year’s legislative session with a plan to fund wildfire prevention, there’s still no dedicated funding to fight large fires like the Cram Fire, which has burned nearly 100,000 acres in Central Oregon. The total wildfire budget for the next two years is less than the state spent last year alone. And in some cases, costs that used to be borne by insurance plans and private landowners are now the responsibility of all Oregonians. A similar phrase cropped up during multiple interviews with policymakers: The consensus lawmakers reached this year is a good “first step.” What’s less clear is if it’s enough. ….“Oregonians writ large, are going to be the ones to pay for it,” said Casey Kulla, with Oregon Wild.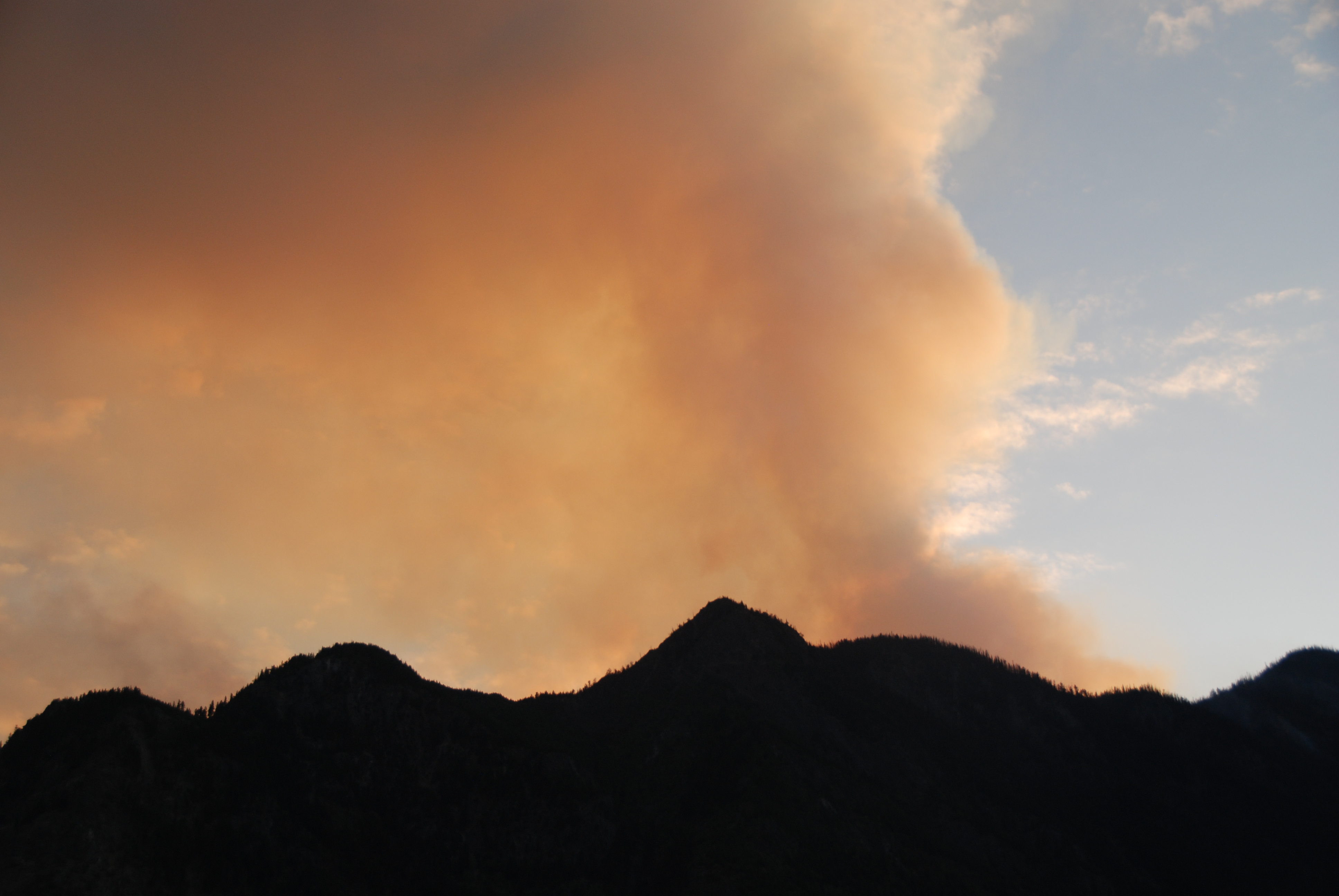 Thousands of lightning strikes have been recorded in California recently as portions of the state gear up for more storms, bringing with them potential wildfires. The state’s northern half saw 1,681 lightning strikes between Sunday, July 27, and Monday, July 28, Cal Fire reported, sparking 23 wildfires. Cal Fire units Lassen-Modoc, Shasta-Trinity, and Siskiyou responded to 14 new fires, none of which grew significantly, Cal Fire said as of July 28. Yet, this month, more lightning strikes in short periods have occurred in the state. The U.S. Forest Service Shasta-Trinity National Forest reported on July 26 that Northern California experienced 18,863 lightning strikes due to storms in the area the evening before. …The National Interagency Fire Center has tracked the number of fires in Northern California and Southern California caused by lightning in recent years, showing that thousands of fires in the state and nationwide are caused by nature.
Thousands of lightning strikes have been recorded in California recently as portions of the state gear up for more storms, bringing with them potential wildfires. The state’s northern half saw 1,681 lightning strikes between Sunday, July 27, and Monday, July 28, Cal Fire reported, sparking 23 wildfires. Cal Fire units Lassen-Modoc, Shasta-Trinity, and Siskiyou responded to 14 new fires, none of which grew significantly, Cal Fire said as of July 28. Yet, this month, more lightning strikes in short periods have occurred in the state. The U.S. Forest Service Shasta-Trinity National Forest reported on July 26 that Northern California experienced 18,863 lightning strikes due to storms in the area the evening before. …The National Interagency Fire Center has tracked the number of fires in Northern California and Southern California caused by lightning in recent years, showing that thousands of fires in the state and nationwide are caused by nature. The U.S. Forest Service will abandon its nine regional offices as its parent Department of Agriculture consolidates out of Washington, D.C., according to a memo released on Thursday by Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins. “President Trump was elected to make real change in Washington, and we are doing just that by moving our key services outside the beltway and into great American cities across the country,” Rollins said in a statement announcing the reorganization. “We will do so through a transparent and common-sense process that preserves USDA’s critical health and public safety services the American public relies on. We will do right by the great American people who we serve and with respect to the thousands of hardworking USDA employees who so nobly serve their country.” The reorganization plan left many Forest Service experts wondering what the benefit would be, including former Forest Service Chief Dale Bosworth, who served during the George W. Bush administration.
The U.S. Forest Service will abandon its nine regional offices as its parent Department of Agriculture consolidates out of Washington, D.C., according to a memo released on Thursday by Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins. “President Trump was elected to make real change in Washington, and we are doing just that by moving our key services outside the beltway and into great American cities across the country,” Rollins said in a statement announcing the reorganization. “We will do so through a transparent and common-sense process that preserves USDA’s critical health and public safety services the American public relies on. We will do right by the great American people who we serve and with respect to the thousands of hardworking USDA employees who so nobly serve their country.” The reorganization plan left many Forest Service experts wondering what the benefit would be, including former Forest Service Chief Dale Bosworth, who served during the George W. Bush administration. Since the mid-1990s, so-called blooms of bark beetles have affected nearly 80% of Colorado’s 4.2 million acres of pine forest, reducing decades-old trees into firewood. In the process, they’ve literally laid the groundwork for some of the state’s most devastating forest fires, from the 2016 Beaver Creek Fire in Walden to the 2020 East Troublesome Fire in Grand County. Despite rendering postcard views into wildfire fodder, West does not call these beetles a pest. Like fire, they’re just a part of nature here, filling a vital biological niche in their native habitat. In the long term, experts say they even make forests healthier. “Bark beetles serve as the ecological sanitizers of the forest,” said West, who helps manage Colorado’s 24 million acres of state forestland. One paper,
Since the mid-1990s, so-called blooms of bark beetles have affected nearly 80% of Colorado’s 4.2 million acres of pine forest, reducing decades-old trees into firewood. In the process, they’ve literally laid the groundwork for some of the state’s most devastating forest fires, from the 2016 Beaver Creek Fire in Walden to the 2020 East Troublesome Fire in Grand County. Despite rendering postcard views into wildfire fodder, West does not call these beetles a pest. Like fire, they’re just a part of nature here, filling a vital biological niche in their native habitat. In the long term, experts say they even make forests healthier. “Bark beetles serve as the ecological sanitizers of the forest,” said West, who helps manage Colorado’s 24 million acres of state forestland. One paper,  If state funding for forest health and wildfire prevention isn’t ramped back up in the next legislative session, it could hinder efforts to prevent severe fires in the coming years, Washington’s top public lands official and others warned this week. The state Legislature approved House Bill 1168 in 2021, which committed $500 million over eight years to the state Department of Natural Resources for wildfire preparedness and response. State spending had largely kept up with that target until this year, with the department receiving $115 million in the last two-year budget and $130 million in the one before that. Then this year, as lawmakers confronted a budget shortfall, they slashed the wildfire preparedness funding to just $60 million for the next two years. The Department of Natural Resources says it’s prepared for this fire season and has money left over from past years. But the funding rollback has sparked concerns.
If state funding for forest health and wildfire prevention isn’t ramped back up in the next legislative session, it could hinder efforts to prevent severe fires in the coming years, Washington’s top public lands official and others warned this week. The state Legislature approved House Bill 1168 in 2021, which committed $500 million over eight years to the state Department of Natural Resources for wildfire preparedness and response. State spending had largely kept up with that target until this year, with the department receiving $115 million in the last two-year budget and $130 million in the one before that. Then this year, as lawmakers confronted a budget shortfall, they slashed the wildfire preparedness funding to just $60 million for the next two years. The Department of Natural Resources says it’s prepared for this fire season and has money left over from past years. But the funding rollback has sparked concerns. The state’s top public lands official is urging lawmakers to restore the spending to previous levels after they cut it by about half this year. If state funding for forest health and wildfire prevention isn’t ramped back up in the next legislative session, it could hinder efforts to prevent severe fires in the coming years, Washington’s top public lands official and others warned this week. The state Legislature approved House Bill 1168 in 2021, which committed $500 million over eight years to the state Department of Natural Resources for wildfire preparedness and response. State spending had largely kept up with that target until this year, with the department receiving $115 million in the last two-year budget and $130 million in the one before that. Then this year, as lawmakers confronted a budget shortfall, they slashed the wildfire preparedness funding to just $60 million for the next two years.
The state’s top public lands official is urging lawmakers to restore the spending to previous levels after they cut it by about half this year. If state funding for forest health and wildfire prevention isn’t ramped back up in the next legislative session, it could hinder efforts to prevent severe fires in the coming years, Washington’s top public lands official and others warned this week. The state Legislature approved House Bill 1168 in 2021, which committed $500 million over eight years to the state Department of Natural Resources for wildfire preparedness and response. State spending had largely kept up with that target until this year, with the department receiving $115 million in the last two-year budget and $130 million in the one before that. Then this year, as lawmakers confronted a budget shortfall, they slashed the wildfire preparedness funding to just $60 million for the next two years. 
 The restoration of gray wolves in Yellowstone National Park has helped revive an aspen tree population unique to the region, a new study has found. Quaking aspen, one of the few deciduous tree species in the northern Rocky Mountain ecosystem, is once again thriving, after suffering severe decline during the 20th century, according to a new study. “This is a remarkable case of ecological restoration,” lead author, Luke Painter, at Oregon State University’s College of Agricultural Sciences, said. The decline in aspen growth occurred in tandem with a surge in Rocky Mountain elk, which had lost a key predator following the elimination of wolves from the region by 1930. …At the same time… aspen recovery hasn’t been uniform across northern Yellowstone — and the growth is subject to numerous potential threats including climate change and encroachment of coniferous trees, are possible such factors. And other herbivores have increased in the region.
The restoration of gray wolves in Yellowstone National Park has helped revive an aspen tree population unique to the region, a new study has found. Quaking aspen, one of the few deciduous tree species in the northern Rocky Mountain ecosystem, is once again thriving, after suffering severe decline during the 20th century, according to a new study. “This is a remarkable case of ecological restoration,” lead author, Luke Painter, at Oregon State University’s College of Agricultural Sciences, said. The decline in aspen growth occurred in tandem with a surge in Rocky Mountain elk, which had lost a key predator following the elimination of wolves from the region by 1930. …At the same time… aspen recovery hasn’t been uniform across northern Yellowstone — and the growth is subject to numerous potential threats including climate change and encroachment of coniferous trees, are possible such factors. And other herbivores have increased in the region.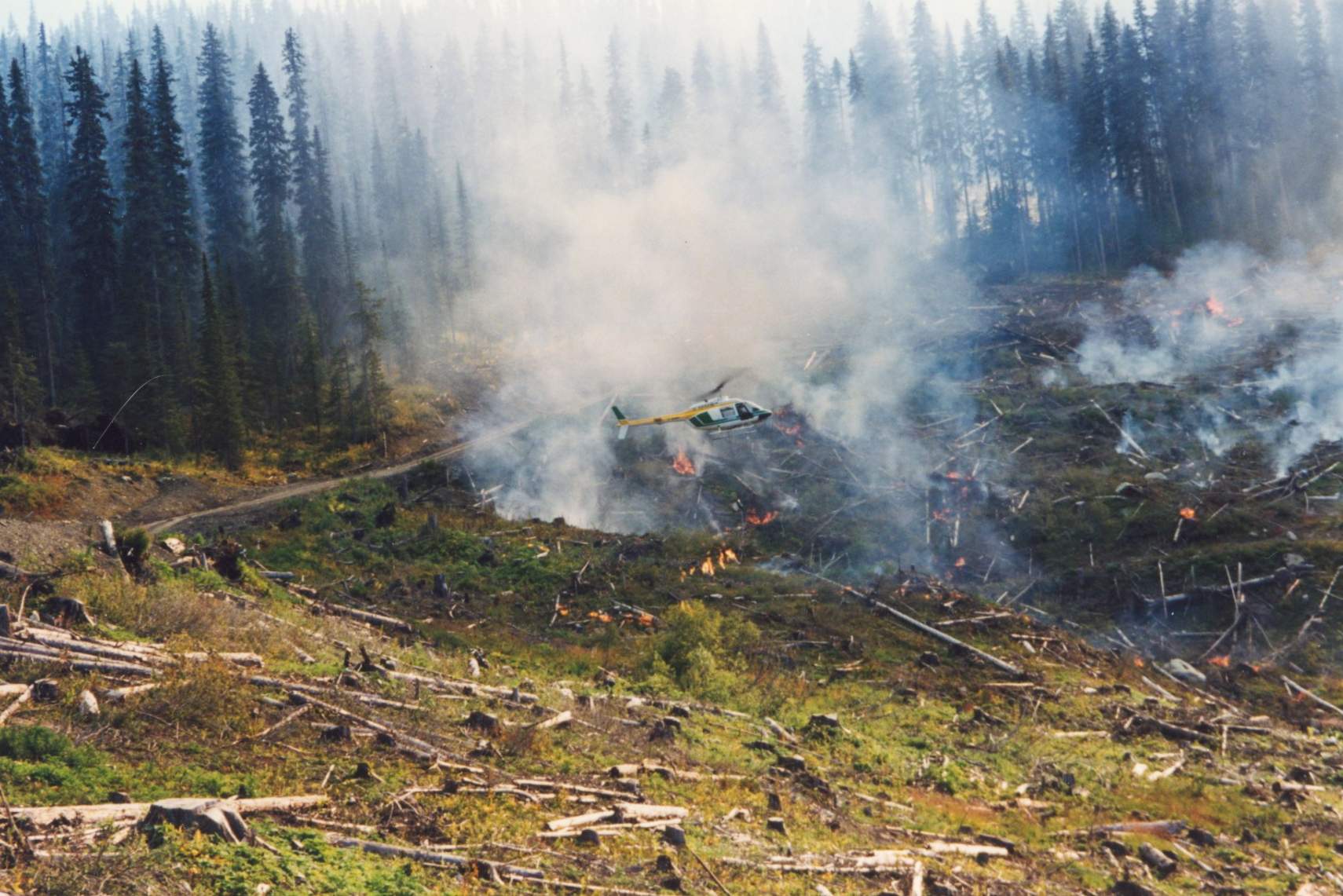 Western Washington state is one of the wettest places in the country. In the North Cascade mountains and on the Olympic Peninsula, lush cedars, ferns and mosses form classic Pacific Northwest rainforests. But even here, climate change is making wildfires more likely. And the state is figuring out how to respond. “It used to be that it really wasn’t until mid-August that fuels dried out in western Washington,” said Derek Churchill, a forest health scientist at the Washington Department of Natural Resources. “Now it’s July or earlier.” In fact, last month human activity started a wildfire in the Olympic national forest. As of Tuesday, it had grown to more than 5,100 acres and some campgrounds were under evacuation orders… But global warming is changing fire patterns in the state. Washington’s summers are growing longer, hotter and drier, resulting in an extended fire season with more desiccated fuel available. [A free account is required to read this article]
Western Washington state is one of the wettest places in the country. In the North Cascade mountains and on the Olympic Peninsula, lush cedars, ferns and mosses form classic Pacific Northwest rainforests. But even here, climate change is making wildfires more likely. And the state is figuring out how to respond. “It used to be that it really wasn’t until mid-August that fuels dried out in western Washington,” said Derek Churchill, a forest health scientist at the Washington Department of Natural Resources. “Now it’s July or earlier.” In fact, last month human activity started a wildfire in the Olympic national forest. As of Tuesday, it had grown to more than 5,100 acres and some campgrounds were under evacuation orders… But global warming is changing fire patterns in the state. Washington’s summers are growing longer, hotter and drier, resulting in an extended fire season with more desiccated fuel available. [A free account is required to read this article] Fires, storms and the potential for near-record high temperatures across the western US are in the offing for the coming week. The Gifford Fire, about 125 miles northwest of Los Angeles, had burned 113,648 acres and was 21% contained through Saturday, according to Cal Fire. So far, 809 people have been evacuated and the Los Padres National Forest was closed because of the flames. There are 3,935 fire crews and support staff on the scene, and at least seven have been injured, according to a joint statement by Cal Fire, the US Forest Service and several local agencies. The Gifford blaze is the largest of 14 fires across the state. …Large wildfires in Colorado have also caused air quality to drop there, the U.S. National Weather Service said. …Meanwhile, smoke from forest fires in Canada has once again crossed into the US, causing air quality alerts to be posted in Minnesota and parts of Wisconsin.
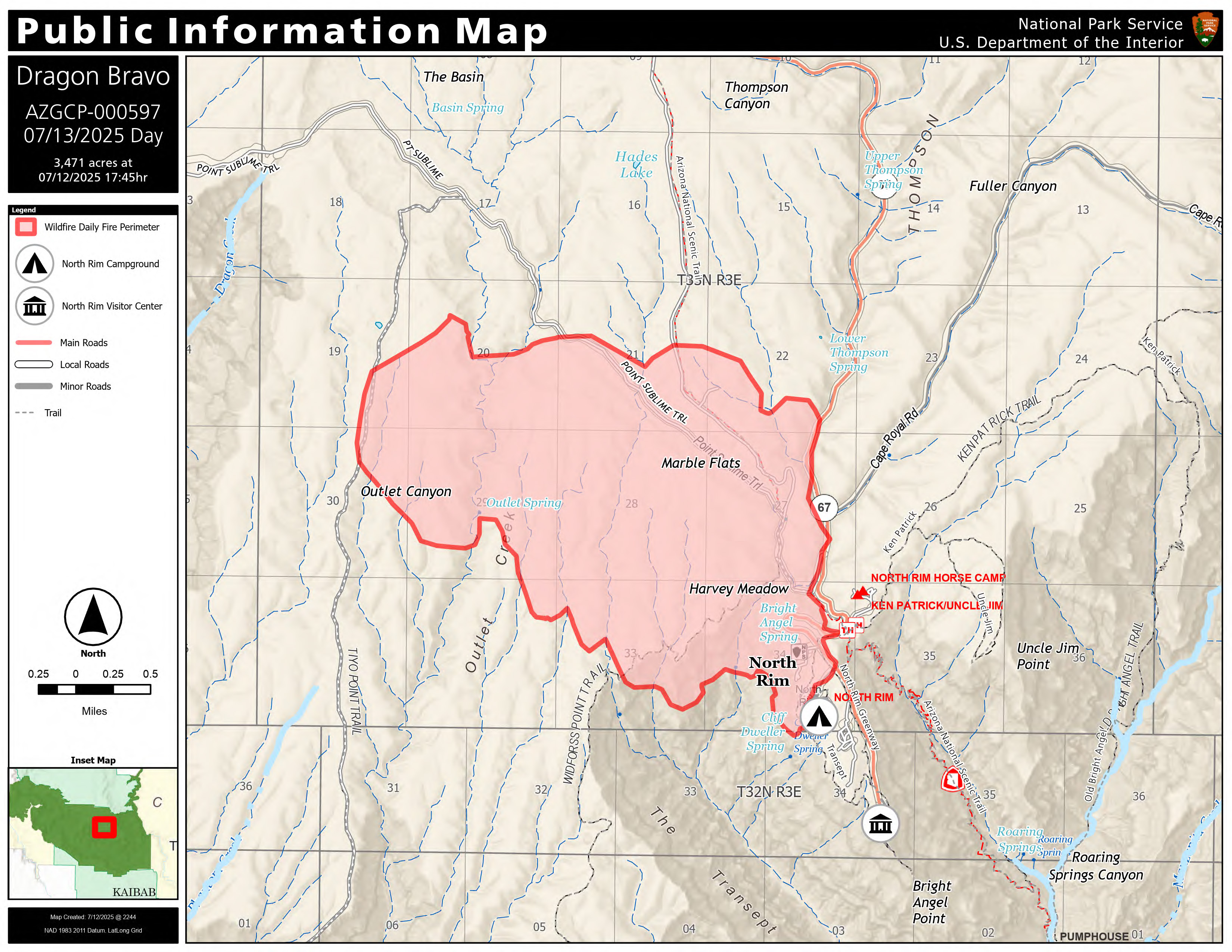
Fires, storms and the potential for near-record high temperatures across the western US are in the offing for the coming week. The Gifford Fire, about 125 miles northwest of Los Angeles, had burned 113,648 acres and was 21% contained through Saturday, according to Cal Fire. So far, 809 people have been evacuated and the Los Padres National Forest was closed because of the flames. There are 3,935 fire crews and support staff on the scene, and at least seven have been injured, according to a joint statement by Cal Fire, the US Forest Service and several local agencies. The Gifford blaze is the largest of 14 fires across the state. …Large wildfires in Colorado have also caused air quality to drop there, the U.S. National Weather Service said. …Meanwhile, smoke from forest fires in Canada has once again crossed into the US, causing air quality alerts to be posted in Minnesota and parts of Wisconsin. Arizona’s fire season keeps smoldering and flaring, thanks to a schizo monsoon and a dry winter. The 125,000-acre Dragon Bravo Fire continues to grow, with the 1,200 firefighters managing just 13% containment after nearly a month of trying. The National Weather Service had predicted a normal to wet monsoon after a bone-dry winter, based largely on sea-surface temperatures in the Pacific. But as a global warming trend driven by heat-trapping pollutants pumps energy into the atmosphere, patterns of drought, heat and storm tracks have become harder and harder to predict. So the monsoon has splashed and sputtered, with a week of storms giving way to a week of hot, dry weather – extending the fire season well into the period when fire crews would normally shift to other areas. Fortunately, the extended forecast calls for a chance the monsoon will gust back to life next week.
Arizona’s fire season keeps smoldering and flaring, thanks to a schizo monsoon and a dry winter. The 125,000-acre Dragon Bravo Fire continues to grow, with the 1,200 firefighters managing just 13% containment after nearly a month of trying. The National Weather Service had predicted a normal to wet monsoon after a bone-dry winter, based largely on sea-surface temperatures in the Pacific. But as a global warming trend driven by heat-trapping pollutants pumps energy into the atmosphere, patterns of drought, heat and storm tracks have become harder and harder to predict. So the monsoon has splashed and sputtered, with a week of storms giving way to a week of hot, dry weather – extending the fire season well into the period when fire crews would normally shift to other areas. Fortunately, the extended forecast calls for a chance the monsoon will gust back to life next week.
 …The National Weather Service issued red flag warnings from 2 p.m. to 11 p.m. July 29 due to thunderstorms producing abundant lightning and wind gusts up to 50-60 mph, in combination with dry fuels, the alert said. A red flag warning means that critical fire weather conditions are either occurring now, or will occur shortly. NWS also issued a fire weather advisory from 2 p.m. to 11 p.m. July 29 due to potential lightning from thunderstorms that could spark new fires and wind gusts that could impact new and existing fires. …The Piper Fire sparked on July 28 from thunderstorms 3 miles northeast of Skookum Creek Campground in the Three Sisters Wilderness. It was estimated to be 20 acres as of July 28. …The High Horn Fire in Malheur County had burned 120 acres as of July 28. …The Skyline Fire, also burning in Malheur County, had burned 38.5 acres as of July 28.
…The National Weather Service issued red flag warnings from 2 p.m. to 11 p.m. July 29 due to thunderstorms producing abundant lightning and wind gusts up to 50-60 mph, in combination with dry fuels, the alert said. A red flag warning means that critical fire weather conditions are either occurring now, or will occur shortly. NWS also issued a fire weather advisory from 2 p.m. to 11 p.m. July 29 due to potential lightning from thunderstorms that could spark new fires and wind gusts that could impact new and existing fires. …The Piper Fire sparked on July 28 from thunderstorms 3 miles northeast of Skookum Creek Campground in the Three Sisters Wilderness. It was estimated to be 20 acres as of July 28. …The High Horn Fire in Malheur County had burned 120 acres as of July 28. …The Skyline Fire, also burning in Malheur County, had burned 38.5 acres as of July 28.