 Biomass professionals from across Canada gathered for a virtual celebration this week as the winners of the inaugural Canadian Biomass Awards were announced. Awards were handed out in five special categories, recognizing the work of both individuals and organizations across the country.
Biomass professionals from across Canada gathered for a virtual celebration this week as the winners of the inaugural Canadian Biomass Awards were announced. Awards were handed out in five special categories, recognizing the work of both individuals and organizations across the country.
- Lifetime Achievement Award: Rob McCurdy, Burkhard Fink and John Swaan
- Community Project of the Year: Village of Fort Simpson
- Thought Leader of the Year: Liezl van Wyk, Drax Group Canada
- Champion of the Year: Gordon Murray, Wood Pellet Assn of Canada
- Company of the Year: Ecostrat
Additional coverage by Central Chilcotin Rehabilitation Ltd: Williams Lake Local Recognized at 2024 Canadian Biomass Awards

 Two years ago, BBC journalists visited Canada to investigate the wood pellet industry. Their findings, broadcast in the documentary Drax: The Green Energy Scandal exposed, sent shockwaves through climate politics in the UK. …In February 2024, the BBC published a follow-up story. …Drax did not dispute these findings or that it is still sourcing wood from old-growth forests, but it claimed to be undertaking work to stop sourcing wood from official “old-growth priority deferral areas.” …However, it is primarily up to Canadian authorities, not foreign nations, to investigate and regulate the country’s biomass industry. British authorities do not have the resources to effectively monitor biomass sourcing in foreign countries, as the National Audit Office has made clear. …Source countries such as Canada profit from industrial logging, leading to concerns about conflicts of interest with regulatory enforcement. …Canada’s problems go beyond one company. Current logging practices risk ecosystem collapse.
Two years ago, BBC journalists visited Canada to investigate the wood pellet industry. Their findings, broadcast in the documentary Drax: The Green Energy Scandal exposed, sent shockwaves through climate politics in the UK. …In February 2024, the BBC published a follow-up story. …Drax did not dispute these findings or that it is still sourcing wood from old-growth forests, but it claimed to be undertaking work to stop sourcing wood from official “old-growth priority deferral areas.” …However, it is primarily up to Canadian authorities, not foreign nations, to investigate and regulate the country’s biomass industry. British authorities do not have the resources to effectively monitor biomass sourcing in foreign countries, as the National Audit Office has made clear. …Source countries such as Canada profit from industrial logging, leading to concerns about conflicts of interest with regulatory enforcement. …Canada’s problems go beyond one company. Current logging practices risk ecosystem collapse. Nearly a dozen environmental groups are calling on the federal government to expand its review of Canada’s forestry sector emissions, saying the current scope fails to address their concerns about underreporting. In an open letter, the groups say the federal government’s review must consider how forestry emissions are estimated in the first place. The letter, signed by representatives from 11 environmental groups including Nature Canada, says the review’s scope undermines its credibility. The letter comes after the federal environment commissioner issued a report last year recommending Ottawa initiate an independent review to look at how it estimates and reports on emission related to logging. In response to that report, the government agreed that independent review was important but noted that the science underlying its carbon reporting was peer-reviewed.
Nearly a dozen environmental groups are calling on the federal government to expand its review of Canada’s forestry sector emissions, saying the current scope fails to address their concerns about underreporting. In an open letter, the groups say the federal government’s review must consider how forestry emissions are estimated in the first place. The letter, signed by representatives from 11 environmental groups including Nature Canada, says the review’s scope undermines its credibility. The letter comes after the federal environment commissioner issued a report last year recommending Ottawa initiate an independent review to look at how it estimates and reports on emission related to logging. In response to that report, the government agreed that independent review was important but noted that the science underlying its carbon reporting was peer-reviewed.


 Natural gas made its debut in the City of Vancouver over a century ago… Today, it’s the primary way B.C. powers its buildings, and a major problem for B.C.’s pursuit to cut its emissions by 40 per cent in a mere six years. …Fortis has its own plan to cut pollution while keeping the gas lines flowing. The company’s “Clean Growth Pathway” projects a scenario where growing appetites for gas and electricity can coexist by supercharging its supply of “low-carbon gases” like renewable natural gas, hydrogen and syngas, a type of gas produced from non-fossil sources via thermal conversion. …Fortis also has plans to use syngas, likely to be produced from wood, to bolster its supply. …Syngas can’t be delivered into pipelines like RNG, but it can be used directly in some industrial facilities, like a lumber mill that uses wood-produced syngas to power a pulp mill next door, for example.
Natural gas made its debut in the City of Vancouver over a century ago… Today, it’s the primary way B.C. powers its buildings, and a major problem for B.C.’s pursuit to cut its emissions by 40 per cent in a mere six years. …Fortis has its own plan to cut pollution while keeping the gas lines flowing. The company’s “Clean Growth Pathway” projects a scenario where growing appetites for gas and electricity can coexist by supercharging its supply of “low-carbon gases” like renewable natural gas, hydrogen and syngas, a type of gas produced from non-fossil sources via thermal conversion. …Fortis also has plans to use syngas, likely to be produced from wood, to bolster its supply. …Syngas can’t be delivered into pipelines like RNG, but it can be used directly in some industrial facilities, like a lumber mill that uses wood-produced syngas to power a pulp mill next door, for example. Bodies and minds are just as affected by climate change as sea ice and forests, says University of Alberta scientist Sherilee Harper. “Climate change impacts everything we care about,” she said. “It’s not just an environmental issue.” That’s why Harper, along with 30 or so colleagues from disciplines as wide-ranging as economics and epidemiology, have banded together into what she calls Canada’s first university hub to shift the view of climate change from an environmental problem to a threat to human health. “The hub is about helping people see that every climate change decision is a health decision,” said Harper. …Wildfire smoke, which last summer gave Canada some of the worst air quality on the globe. …There are mental health impacts as well, from the acute stress suffered by those forced to flee by flames. …Such hubs already exist in the U.S., the U.K. and Australia, Harper said.
Bodies and minds are just as affected by climate change as sea ice and forests, says University of Alberta scientist Sherilee Harper. “Climate change impacts everything we care about,” she said. “It’s not just an environmental issue.” That’s why Harper, along with 30 or so colleagues from disciplines as wide-ranging as economics and epidemiology, have banded together into what she calls Canada’s first university hub to shift the view of climate change from an environmental problem to a threat to human health. “The hub is about helping people see that every climate change decision is a health decision,” said Harper. …Wildfire smoke, which last summer gave Canada some of the worst air quality on the globe. …There are mental health impacts as well, from the acute stress suffered by those forced to flee by flames. …Such hubs already exist in the U.S., the U.K. and Australia, Harper said.


 Renewable energy comes from matter that nature produces and replenishes constantly. The power generated through this source does not significantly threaten the environment, especially in comparison with fossil fuels… according to the United Nations. Renewable energy derived from wind, solar, geothermal, hydrokinetic, and hydro energy has a much lower environmental impact than fossil fuels. It harnesses the power of readily available elements and does not diminish with use. …And because wind and sunlight are inherently free, there are no ongoing feedstock costs. Bioenergy, otherwise known as biomass energy, is, however, different. This kind of power involves using living matter or matter that was recently been alive. …Trees are also used, most oftenfrom the forests of the U.S. South, including pine and hardwood species. …Supporters argue that bioenergy is a climate-friendly, sustainable power source that helps local economies. The truth is that wood pellet plants are as dirty and problematic as coal plants.
Renewable energy comes from matter that nature produces and replenishes constantly. The power generated through this source does not significantly threaten the environment, especially in comparison with fossil fuels… according to the United Nations. Renewable energy derived from wind, solar, geothermal, hydrokinetic, and hydro energy has a much lower environmental impact than fossil fuels. It harnesses the power of readily available elements and does not diminish with use. …And because wind and sunlight are inherently free, there are no ongoing feedstock costs. Bioenergy, otherwise known as biomass energy, is, however, different. This kind of power involves using living matter or matter that was recently been alive. …Trees are also used, most oftenfrom the forests of the U.S. South, including pine and hardwood species. …Supporters argue that bioenergy is a climate-friendly, sustainable power source that helps local economies. The truth is that wood pellet plants are as dirty and problematic as coal plants. 
 …To an extent not widely appreciated, the world is now warming at a pace that scientists did not expect and, alarmingly, do not fully understand. At a Financial Times conference this month, Jim Skea, the chair of the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, said last year’s spike in temperatures was “quicker than we all anticipated”. “Ocean temperatures were just off the scale in terms of historic records and we still need to do more work to explain it.” …Gavin Schmidt, director of Nasa’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York City warned that the… surprising heat revealed that “an unprecedented knowledge gap” had opened up for the first time since satellite data began to give scientists a real-time view of the climate system about 40 years ago. This gap may mean we have a shakier grasp of what lies ahead — which is worrying when it comes to forecasting drought and rainfall patterns.
…To an extent not widely appreciated, the world is now warming at a pace that scientists did not expect and, alarmingly, do not fully understand. At a Financial Times conference this month, Jim Skea, the chair of the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, said last year’s spike in temperatures was “quicker than we all anticipated”. “Ocean temperatures were just off the scale in terms of historic records and we still need to do more work to explain it.” …Gavin Schmidt, director of Nasa’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York City warned that the… surprising heat revealed that “an unprecedented knowledge gap” had opened up for the first time since satellite data began to give scientists a real-time view of the climate system about 40 years ago. This gap may mean we have a shakier grasp of what lies ahead — which is worrying when it comes to forecasting drought and rainfall patterns. 
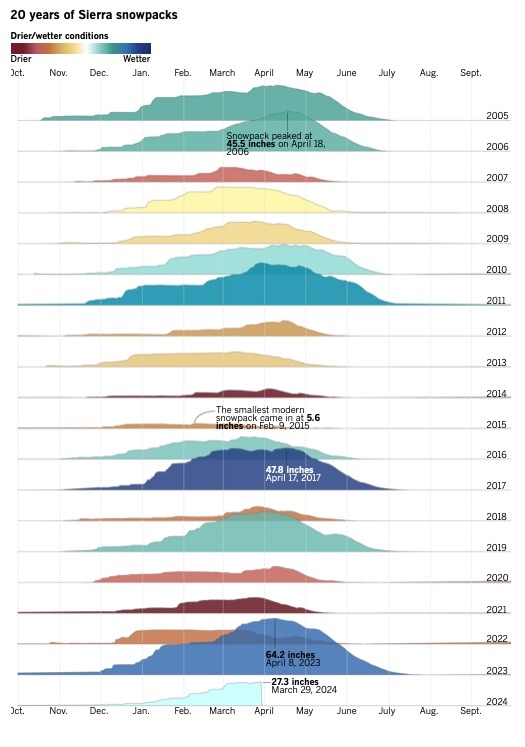 The Sierra snowpack has reached its seasonal peak. The snowpack plays an important role in providing water to millions of Californians. Throughout the winter months, snow accumulates on the high peaks of the Sierra Nevada and slowly melts in the spring and early summer. The runoff fills dozens of major reservoirs downstream. Last year’s epic snowpack helped relieve a yearslong drought, reaching an eye-popping 252% of normal on April 8. By that date, the mountains held an average equivalent of 64.2 inches of water. The current snowpack now holds a healthy 27.3 inches of water on average after a series of winter storms alleviated concerns that California was facing a “snow drought.” The California Department of Water Resources tracks the snow water equivalent in the Sierra using a network of 130 electronic sensors. …This graphic plots a 20-year history of the Sierra snowpack, showing wet years interspersed with severe droughts.
The Sierra snowpack has reached its seasonal peak. The snowpack plays an important role in providing water to millions of Californians. Throughout the winter months, snow accumulates on the high peaks of the Sierra Nevada and slowly melts in the spring and early summer. The runoff fills dozens of major reservoirs downstream. Last year’s epic snowpack helped relieve a yearslong drought, reaching an eye-popping 252% of normal on April 8. By that date, the mountains held an average equivalent of 64.2 inches of water. The current snowpack now holds a healthy 27.3 inches of water on average after a series of winter storms alleviated concerns that California was facing a “snow drought.” The California Department of Water Resources tracks the snow water equivalent in the Sierra using a network of 130 electronic sensors. …This graphic plots a 20-year history of the Sierra snowpack, showing wet years interspersed with severe droughts.
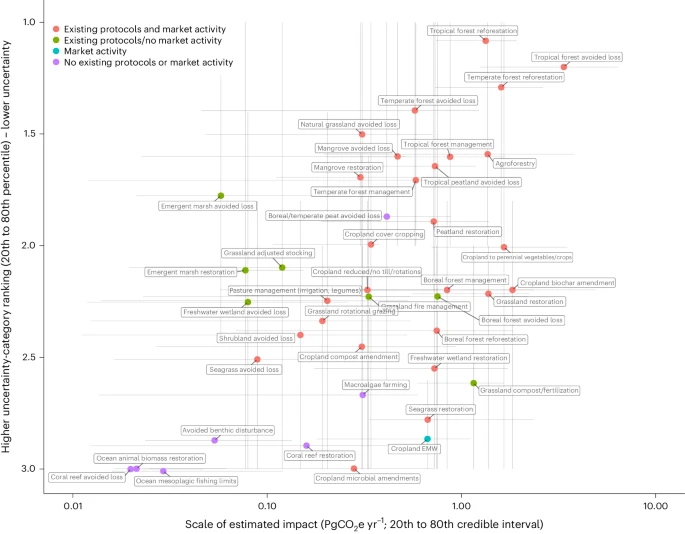
 U.S. scientists and policy experts with a broad range of expertise in the fields of climate and ecosystem sciences have outlined key recommendations aimed at bolstering the scientific foundation for implementation of nature-based climate solutions (NbCS) across the nation. These solutions, which include strategies like protecting carbon-dense forests and wetlands, improving land management, and restoring natural ecosystems, are crucial for enhancing carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The stakes are very high—getting NbCS right could mean the difference between achieving long-term global greenhouse gas reduction goals or missing those targets and further destabilizing the climate system. Although NbCS strategies have potential, on the ground implementation of NbCS has been controversial, often outpacing the scientific understanding of their long-term benefits. The group calls for a more robust, evidence-based approach for NbCS so they can be deployed when and where they are most likely to succeed as climate solutions.
U.S. scientists and policy experts with a broad range of expertise in the fields of climate and ecosystem sciences have outlined key recommendations aimed at bolstering the scientific foundation for implementation of nature-based climate solutions (NbCS) across the nation. These solutions, which include strategies like protecting carbon-dense forests and wetlands, improving land management, and restoring natural ecosystems, are crucial for enhancing carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The stakes are very high—getting NbCS right could mean the difference between achieving long-term global greenhouse gas reduction goals or missing those targets and further destabilizing the climate system. Although NbCS strategies have potential, on the ground implementation of NbCS has been controversial, often outpacing the scientific understanding of their long-term benefits. The group calls for a more robust, evidence-based approach for NbCS so they can be deployed when and where they are most likely to succeed as climate solutions.
 Nearly five years ago, New York state passed an ambitious climate law intended to reduce and counteract fossil fuel emissions contributing to climate change. Storing carbon dioxide, a gas released from burning fuel, is key to achieving the goals outlined in the Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act. Much of that can be accomplished through protecting carbon-absorbing forests across the state. Although the Adirondacks has millions of acres of forest, most land in the state is privately owned. Which puts a critical network of interconnected properties at risk of development. To achieve goals set in the climate act, experts say the state needs to roughly double the size of its carbon sink by fostering new forests and avoiding further loss. Researchers with the SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry developed an accounting system with detailed satellite imagery to help agencies identify where forests are most vulnerable.
Nearly five years ago, New York state passed an ambitious climate law intended to reduce and counteract fossil fuel emissions contributing to climate change. Storing carbon dioxide, a gas released from burning fuel, is key to achieving the goals outlined in the Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act. Much of that can be accomplished through protecting carbon-absorbing forests across the state. Although the Adirondacks has millions of acres of forest, most land in the state is privately owned. Which puts a critical network of interconnected properties at risk of development. To achieve goals set in the climate act, experts say the state needs to roughly double the size of its carbon sink by fostering new forests and avoiding further loss. Researchers with the SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry developed an accounting system with detailed satellite imagery to help agencies identify where forests are most vulnerable.

 In March, Enviva, the world’s largest woody biomass producer for industrial energy, declared bankruptcy. That cataclysmic collapse triggered a rush of political and economic maneuvering in the US, and in Europe. …While Enviva publicly claims it will survive the bankruptcy, a whistleblower in touch with sources inside the company says it will continue failing to meet its wood pellet contract obligations, and that its production facilities — plagued by chronic systemic manufacturing problems — will continue underperforming. Enviva and the forestry industry appear now to be lobbying the Biden administration, hoping to tap into millions in renewable energy credits under the Inflation Reduction Act — a move environmentalists are resisting. …Meanwhile, some EU nations are scrambling to find new sources of wood pellets to meet their sustainable energy pledges under the Paris agreement. The UK’s Drax, an Enviva pellet user, is positioning itself to greatly increase its pellet production in the U.S. South.
In March, Enviva, the world’s largest woody biomass producer for industrial energy, declared bankruptcy. That cataclysmic collapse triggered a rush of political and economic maneuvering in the US, and in Europe. …While Enviva publicly claims it will survive the bankruptcy, a whistleblower in touch with sources inside the company says it will continue failing to meet its wood pellet contract obligations, and that its production facilities — plagued by chronic systemic manufacturing problems — will continue underperforming. Enviva and the forestry industry appear now to be lobbying the Biden administration, hoping to tap into millions in renewable energy credits under the Inflation Reduction Act — a move environmentalists are resisting. …Meanwhile, some EU nations are scrambling to find new sources of wood pellets to meet their sustainable energy pledges under the Paris agreement. The UK’s Drax, an Enviva pellet user, is positioning itself to greatly increase its pellet production in the U.S. South.
 The Scottish Government has confirmed that wood burning stoves can still be installed in new houses but only “to provide emergency heating, where a need can be justified.” Changes to the building standards – the regulations governing the requirements for all building in Scotland – came in last week, forbidding the use of ‘direct emission heating systems.’ Effectively, that means that new houses and conversions are not allowed to use gas or oil boilers, or any form of bioenergy where electricity or heat is generated from organic matter such as wood. Instead, housebuilders are expected to use what are known as ‘zero DEH’ systems such as heat pumps, solar thermal storage systems or electric storage heaters. …A Scottish Government spokesperson said: “Heating our homes and buildings represents about a fifth of Scotland’s carbon emissions so tackling the climate emergency requires us to address these emissions.
The Scottish Government has confirmed that wood burning stoves can still be installed in new houses but only “to provide emergency heating, where a need can be justified.” Changes to the building standards – the regulations governing the requirements for all building in Scotland – came in last week, forbidding the use of ‘direct emission heating systems.’ Effectively, that means that new houses and conversions are not allowed to use gas or oil boilers, or any form of bioenergy where electricity or heat is generated from organic matter such as wood. Instead, housebuilders are expected to use what are known as ‘zero DEH’ systems such as heat pumps, solar thermal storage systems or electric storage heaters. …A Scottish Government spokesperson said: “Heating our homes and buildings represents about a fifth of Scotland’s carbon emissions so tackling the climate emergency requires us to address these emissions.
 Another month, another global heat record that has left climate scientists scratching their heads and hoping this is an El Niño-related hangover rather than a symptom of worse-than-expected planetary health. Global surface temperatures in March were 0.1C higher than the previous record for the month, set in 2016, and 1.68C higher than the pre-industrial average, according to data released on Tuesday by the Copernicus Climate Change Service. This is the 10th consecutive monthly record in a warming phase that has shattered all previous records. Over the past 12 months, average global temperatures have been 1.58C above pre-industrial levels. This, at least temporarily, exceeds the 1.5C benchmark set as a target in the Paris climate agreement but that landmark deal will not be considered breached unless this trend continues on a decadal scale. …The sharp increase in temperatures over the past year has surprised many scientists, and prompted concerns about a possible acceleration of heating.
Another month, another global heat record that has left climate scientists scratching their heads and hoping this is an El Niño-related hangover rather than a symptom of worse-than-expected planetary health. Global surface temperatures in March were 0.1C higher than the previous record for the month, set in 2016, and 1.68C higher than the pre-industrial average, according to data released on Tuesday by the Copernicus Climate Change Service. This is the 10th consecutive monthly record in a warming phase that has shattered all previous records. Over the past 12 months, average global temperatures have been 1.58C above pre-industrial levels. This, at least temporarily, exceeds the 1.5C benchmark set as a target in the Paris climate agreement but that landmark deal will not be considered breached unless this trend continues on a decadal scale. …The sharp increase in temperatures over the past year has surprised many scientists, and prompted concerns about a possible acceleration of heating.




