Washington, D.C.— The Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) announces the establishment of two SFI Climate Smart Forestry Initiative Advisory Committees, one in the United States and one in Canada, to shape the activities and outputs of the SFI Climate Smart Forestry (SFI CSF) Initiative on climate-informed forest management practices, science syntheses, and knowledge sharing across North America. In 2024, SFI launched the Climate Smart Forestry Initiative to advance Objective 9 (Climate Smart Forestry) of the SFI 2022 Forest Management Standard. Objective 9 requires organizations certified to the SFI Forest Management Standard to consider and implement actions to reduce the negative effects of climate change and adapt to changing conditions. The SFI CSF Initiative is a collaborative effort to identify and implement climate-informed, data-driven forestry practices that address climate change through adaptive management, enhanced carbon storage, and increased forest resilience.
 The December edition — issued by FSC Canada — includes several major updates: the Canadian home-improvement and construction retailer RONA has become the first such retailer in Canada to use DoorDash for distribution; there’s news that Chantiers Chibougamau reaffirmed its commitment to FSC certification; Esri donated $1.65 million worth of geospatial technology to FSC; and there are recap highlights from the 2025 General Assembly in Panama. The newsletter also announces the launch of a new registry for certificate holders (ES Registry), publishes a new “Advice Note” on Indicator 55 of the Risk Assessment Framework, and opens two major consultations — one on Indigenous Cultural Landscapes and another to revise FSC’s Chain-of-Custody standards.
The December edition — issued by FSC Canada — includes several major updates: the Canadian home-improvement and construction retailer RONA has become the first such retailer in Canada to use DoorDash for distribution; there’s news that Chantiers Chibougamau reaffirmed its commitment to FSC certification; Esri donated $1.65 million worth of geospatial technology to FSC; and there are recap highlights from the 2025 General Assembly in Panama. The newsletter also announces the launch of a new registry for certificate holders (ES Registry), publishes a new “Advice Note” on Indicator 55 of the Risk Assessment Framework, and opens two major consultations — one on Indigenous Cultural Landscapes and another to revise FSC’s Chain-of-Custody standards.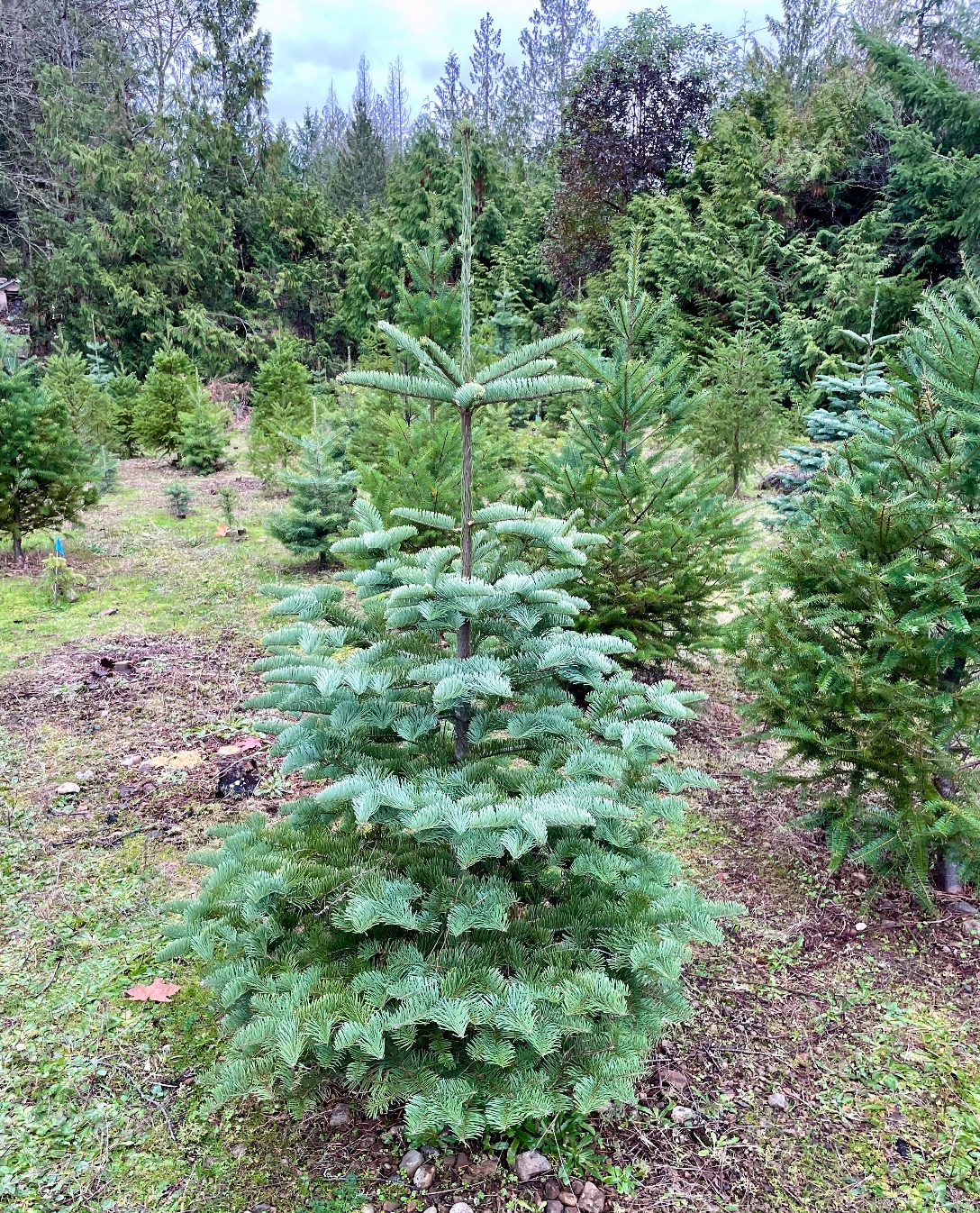 Modern-day circumstances are slowly transforming the Christmas tree farming industry. …weather is a challenge Michael Cormack faces on the Christmas tree farm he owns and operates in Ontario. … “Mother nature is a big, big factor in the business,” Cormack said. “This year in July, we were averaging over 29 C. So we had trees from two to three years ago that just died. … Four years ago, we had a tornado here that wiped out a bunch of our stuff.” …Another major factor is the cost of living crisis. …“Right now many of the farms are owned by elderly growers, and they’re aging out. So we’re losing a lot of farms year after year, which is unfortunate,” said Kelsey Leonard, founder and director of the Christmas Tree Lab at the University of Waterloo. …U.S. tariffs are also likely to have an impact on the costs associated with growing Christmas trees this year, Leonard said.
Modern-day circumstances are slowly transforming the Christmas tree farming industry. …weather is a challenge Michael Cormack faces on the Christmas tree farm he owns and operates in Ontario. … “Mother nature is a big, big factor in the business,” Cormack said. “This year in July, we were averaging over 29 C. So we had trees from two to three years ago that just died. … Four years ago, we had a tornado here that wiped out a bunch of our stuff.” …Another major factor is the cost of living crisis. …“Right now many of the farms are owned by elderly growers, and they’re aging out. So we’re losing a lot of farms year after year, which is unfortunate,” said Kelsey Leonard, founder and director of the Christmas Tree Lab at the University of Waterloo. …U.S. tariffs are also likely to have an impact on the costs associated with growing Christmas trees this year, Leonard said. FORT ST. JOHN, B.C. — The B.C. Ministry of Forests is encouraged that the Government of Canada has taken a huge step to amp up aerial firefighting capacity. Anthony Housefather, parliamentary secretary to Eleanor Olszewski, federal minister of emergency management and community resilience and minister responsible for Prairies economic development, recently highlighted a new multi-million-dollar investment of over $257.6 million for four years to Natural Resources Canada. The funds will be used to lease firefighting aircrafts, which can include waterbombers or other aircrafts to deliver water or fire retardant drops in hard-to-reach areas. …The Ministry of Forests will be hosting a
FORT ST. JOHN, B.C. — The B.C. Ministry of Forests is encouraged that the Government of Canada has taken a huge step to amp up aerial firefighting capacity. Anthony Housefather, parliamentary secretary to Eleanor Olszewski, federal minister of emergency management and community resilience and minister responsible for Prairies economic development, recently highlighted a new multi-million-dollar investment of over $257.6 million for four years to Natural Resources Canada. The funds will be used to lease firefighting aircrafts, which can include waterbombers or other aircrafts to deliver water or fire retardant drops in hard-to-reach areas. …The Ministry of Forests will be hosting a  Joshua Wright says a yellow cedar tree he photographed last year was the largest he’d ever seen in a decade of hiking around Vancouver Island. …Wright measured the cedar’s diameter at 2.79 metres, a size that should have ensured protection for the tree, along with a one-hectare buffer under provincial law. But when he returned to the area south of Gold River in June, Wright says the tree had been felled as part of a logging operation approved by the province. …the area where Wright documented the yellow cedar overlaps significantly with a category of old-growth representing the largest trees left standing. …Yet the deferrals required support from First Nations to go ahead, and at the time, there was no significant funding to help communities offset foregone revenues. …the yellow cedar was felled in an area where Matchlee Ltd. Partnership, majority owned by Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nation, holds a non-renewable forest licence.
Joshua Wright says a yellow cedar tree he photographed last year was the largest he’d ever seen in a decade of hiking around Vancouver Island. …Wright measured the cedar’s diameter at 2.79 metres, a size that should have ensured protection for the tree, along with a one-hectare buffer under provincial law. But when he returned to the area south of Gold River in June, Wright says the tree had been felled as part of a logging operation approved by the province. …the area where Wright documented the yellow cedar overlaps significantly with a category of old-growth representing the largest trees left standing. …Yet the deferrals required support from First Nations to go ahead, and at the time, there was no significant funding to help communities offset foregone revenues. …the yellow cedar was felled in an area where Matchlee Ltd. Partnership, majority owned by Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nation, holds a non-renewable forest licence.

 A BC Resource Sector Coalition says current federal and provincial policymaking has become unpredictable enough to justify an immediate pause on all implementation and action under Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act (DRIPA). …“We write to you on behalf of thousands of British Columbians whose livelihoods, communities, and futures are tied to the natural resource sector. Today, those livelihoods are at risk,” the letter begins. “A series of federal and provincial policy decisions have destabilized the industries that sustain our province and are eroding the economic foundations of British Columbia.” …The coalition is composed of a cross-industry membership spanning land and marine activity: BCCA, Geoduck Underwater Harvesters Association, ICBA, Deep Sea Trawlers Association of BC, Guide Outfitters Association of British Columbia, Pacific Prawn Fishermen’s Association, North West Loggers Association, and the Council of Marine Carriers.
A BC Resource Sector Coalition says current federal and provincial policymaking has become unpredictable enough to justify an immediate pause on all implementation and action under Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act (DRIPA). …“We write to you on behalf of thousands of British Columbians whose livelihoods, communities, and futures are tied to the natural resource sector. Today, those livelihoods are at risk,” the letter begins. “A series of federal and provincial policy decisions have destabilized the industries that sustain our province and are eroding the economic foundations of British Columbia.” …The coalition is composed of a cross-industry membership spanning land and marine activity: BCCA, Geoduck Underwater Harvesters Association, ICBA, Deep Sea Trawlers Association of BC, Guide Outfitters Association of British Columbia, Pacific Prawn Fishermen’s Association, North West Loggers Association, and the Council of Marine Carriers.




 Prince George residents had better pay attention to last week’s report showing that unelected bureaucrats in Victoria are playing politics when they decide how much can be logged up here. I’ve been informed that our unelected Office of the Chief Forester, currently led by Shane Berg, is figuring out the Annual Allowable Cut (AAC) in the Prince George Timber Supply Area for the next 10 years. The process, known as a Timber Supply Review (TSR), masquerades as scientific and expert-driven, but in reality it’s politics. The amount we log is largely pre-determined and the game is how to manipulate the models and forests to achieve it. That’s why we get glyphosate with our blueberries and fertilizer-poisoned cattle. It’s why we don’t thin the plantations or do more selective logging. …The Office of Chief Forester prioritizes the “timber supply” over diverse, fire-resistant forests, as if the two are mutually exclusive.
Prince George residents had better pay attention to last week’s report showing that unelected bureaucrats in Victoria are playing politics when they decide how much can be logged up here. I’ve been informed that our unelected Office of the Chief Forester, currently led by Shane Berg, is figuring out the Annual Allowable Cut (AAC) in the Prince George Timber Supply Area for the next 10 years. The process, known as a Timber Supply Review (TSR), masquerades as scientific and expert-driven, but in reality it’s politics. The amount we log is largely pre-determined and the game is how to manipulate the models and forests to achieve it. That’s why we get glyphosate with our blueberries and fertilizer-poisoned cattle. It’s why we don’t thin the plantations or do more selective logging. …The Office of Chief Forester prioritizes the “timber supply” over diverse, fire-resistant forests, as if the two are mutually exclusive. I am writing to express my concern for the fate of B.C.’s remaining old growth forests, including the globally rare and at-risk Inland Temperate Rainforest. Most of this endangered forest is still not protected, and thus all creatures who dwell therein are equally unprotected. The Valhalla Wilderness Society … is putting forth a plan to protect the remaining intact Inland Temperate Rainforests through its three park proposals: the Rainbow-Jordan Wilderness proposal; the Selkirk Mountains Ancient Forest Park proposal; and the Quesnel Lake Wilderness proposal. This protection is crucial for the survival of these rare temperate rainforests. David Eby, you are undoubtedly well informed as to the many scientific reasons for protecting more forest, especially old growth forests…Importantly, only the BC Park Act and the BC Protected Areas Act can provide secure protection to preserve forest for future generations. Please adopt and implement the VWS park proposals as quickly as possible.
I am writing to express my concern for the fate of B.C.’s remaining old growth forests, including the globally rare and at-risk Inland Temperate Rainforest. Most of this endangered forest is still not protected, and thus all creatures who dwell therein are equally unprotected. The Valhalla Wilderness Society … is putting forth a plan to protect the remaining intact Inland Temperate Rainforests through its three park proposals: the Rainbow-Jordan Wilderness proposal; the Selkirk Mountains Ancient Forest Park proposal; and the Quesnel Lake Wilderness proposal. This protection is crucial for the survival of these rare temperate rainforests. David Eby, you are undoubtedly well informed as to the many scientific reasons for protecting more forest, especially old growth forests…Importantly, only the BC Park Act and the BC Protected Areas Act can provide secure protection to preserve forest for future generations. Please adopt and implement the VWS park proposals as quickly as possible. 
 The Forest History Association of BC is hosting its 43rd Annual General Meeting tonight, December 1, 2025 at 7:00 pm PST. All members are warmly invited to attend this virtual gathering and take part in shaping the direction of the organization for the coming year. The AGM will include key updates on current projects, board activities and election, and ongoing efforts to preserve and share BC’s forest and community history. For those interested in learning more about the FHABC’s mission—promoting research, storytelling, and education about the province’s rich forest heritage—visit their objectives
The Forest History Association of BC is hosting its 43rd Annual General Meeting tonight, December 1, 2025 at 7:00 pm PST. All members are warmly invited to attend this virtual gathering and take part in shaping the direction of the organization for the coming year. The AGM will include key updates on current projects, board activities and election, and ongoing efforts to preserve and share BC’s forest and community history. For those interested in learning more about the FHABC’s mission—promoting research, storytelling, and education about the province’s rich forest heritage—visit their objectives 


 B.C. has invited stakeholders, experts, Indigenous partners and government representatives from throughout the country to a wildfire symposium in Vancouver on Dec. 5, 2025. The focus will be the 2025 wildfire season, wildfire technology, active forest management and national readiness for future wildfires. The symposium includes advancing discussions on a national leadership strategy and stronger collaboration that will shape the framework of wildfire resiliency in Canada. Enhancing a national framework for wildfire resilience, including the challenges and opportunities people and communities are facing, is one intended outcome for the upcoming symposium on wildfires to be hosted in B.C. After the second-worst wildfire season nationally, B.C. is leading the symposium to bring together national and international experts, provincial, federal and territorial governments, as well as key industry and Indigenous partners, with the goal of sharing best practices and considering mitigation and preparation steps for 2026.
B.C. has invited stakeholders, experts, Indigenous partners and government representatives from throughout the country to a wildfire symposium in Vancouver on Dec. 5, 2025. The focus will be the 2025 wildfire season, wildfire technology, active forest management and national readiness for future wildfires. The symposium includes advancing discussions on a national leadership strategy and stronger collaboration that will shape the framework of wildfire resiliency in Canada. Enhancing a national framework for wildfire resilience, including the challenges and opportunities people and communities are facing, is one intended outcome for the upcoming symposium on wildfires to be hosted in B.C. After the second-worst wildfire season nationally, B.C. is leading the symposium to bring together national and international experts, provincial, federal and territorial governments, as well as key industry and Indigenous partners, with the goal of sharing best practices and considering mitigation and preparation steps for 2026.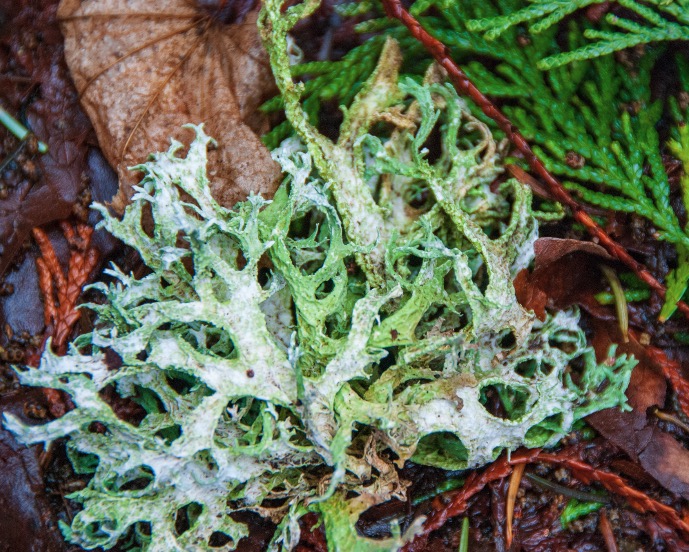 Researchers with the Nature Trust of New Brunswick are on the hunt for four different types of lichens and they’ve found one – in an unusual spot. The scaly fringe lichen, known scientifically as heterodermia squamulosa, was found between Alma and Riverside-Albert, east of Fundy National Park. “As far as I know, it’s the most eastern recorded occurrence of the species to date,” said Ilana Urquhart, a conservation coordinator with the Nature Trust. …Urquhart said lichens can be a good indicator of a healthy environment that can support a variety of species. “We might not directly see what the importance of them is, but they’re often found in areas that are really rich, that are biodiverse.” The biggest threat to lichens is habitat loss, according to Urquhart, which can be caused by logging and harvesting.
Researchers with the Nature Trust of New Brunswick are on the hunt for four different types of lichens and they’ve found one – in an unusual spot. The scaly fringe lichen, known scientifically as heterodermia squamulosa, was found between Alma and Riverside-Albert, east of Fundy National Park. “As far as I know, it’s the most eastern recorded occurrence of the species to date,” said Ilana Urquhart, a conservation coordinator with the Nature Trust. …Urquhart said lichens can be a good indicator of a healthy environment that can support a variety of species. “We might not directly see what the importance of them is, but they’re often found in areas that are really rich, that are biodiverse.” The biggest threat to lichens is habitat loss, according to Urquhart, which can be caused by logging and harvesting. Retired federal wildlife surveyor Erich Reeder… has seen centuries-old forests targeted for destruction as President Donald Trump’s administration accelerates logging on federal lands nationwide. Earlier this year, loggers cleared out most of the forest in Galagher Canyon, part of a federal timber sale an hour south of Eugene, Oregon. …“The Trump administration is ordering the last of our publicly-owned mature and old-growth forests to be cut off and sold,” Reeder, 59, said. …Legal and political battles are heating up between Trump, who is eager to bolster the timber industry as part of his effort to create thousands of jobs and reduce the risk of wildfire, and environmentalists who are keen to protect ancient forests and the endangered wildlife that depend on them. …At least 27 court battles over federal logging and endangered species are unfolding from California to Washington, DC. Seven cases are challenging logging in eastern states.
Retired federal wildlife surveyor Erich Reeder… has seen centuries-old forests targeted for destruction as President Donald Trump’s administration accelerates logging on federal lands nationwide. Earlier this year, loggers cleared out most of the forest in Galagher Canyon, part of a federal timber sale an hour south of Eugene, Oregon. …“The Trump administration is ordering the last of our publicly-owned mature and old-growth forests to be cut off and sold,” Reeder, 59, said. …Legal and political battles are heating up between Trump, who is eager to bolster the timber industry as part of his effort to create thousands of jobs and reduce the risk of wildfire, and environmentalists who are keen to protect ancient forests and the endangered wildlife that depend on them. …At least 27 court battles over federal logging and endangered species are unfolding from California to Washington, DC. Seven cases are challenging logging in eastern states. The Washington Forest Protection Association (WFPA) announced last week that it would file litigation against Washington state. The lawsuit will challenge a new buffer rule by the Washington State Forest Practices Board. The new rule expands the required no-cut buffers around non-fish-bearing streams in the state, requiring forestland owners to leave more trees uncut. WFPA states that it believes the new rule is a result of the Washington state Department of Ecology “misinterpreting” a federal water temperature standard. The statement added that the financial cost of implementing the rule is so large that it “justifies a judicial review.” The group also painted the creation of the new rule as a break from the state’s tradition of collaboration with other stakeholders. …“The rule overreaches the law, ignores on-the-ground realities, adds costly and unnecessary regulations, and offers little to no benefit for salmon recovery.”
The Washington Forest Protection Association (WFPA) announced last week that it would file litigation against Washington state. The lawsuit will challenge a new buffer rule by the Washington State Forest Practices Board. The new rule expands the required no-cut buffers around non-fish-bearing streams in the state, requiring forestland owners to leave more trees uncut. WFPA states that it believes the new rule is a result of the Washington state Department of Ecology “misinterpreting” a federal water temperature standard. The statement added that the financial cost of implementing the rule is so large that it “justifies a judicial review.” The group also painted the creation of the new rule as a break from the state’s tradition of collaboration with other stakeholders. …“The rule overreaches the law, ignores on-the-ground realities, adds costly and unnecessary regulations, and offers little to no benefit for salmon recovery.” As the US Forest Service considers the future management of the Tongass National Forest, I hope that Alaska’s congressional delegation will listen to what Southeast Alaskans already know: Wild salmon are one of the Tongass’ most valuable resources. If we leave the trees standing and protect the habitat that fish need, the Tongass will continue to generate billions of dollars in natural dividends, in turn supporting thousands of fishing jobs and providing millions of pounds of nutritious seafood year after year. …For decades, Southeast Alaska’s communities and fishermen have fought industrial logging in the Tongass. …The harmful impacts of industrial logging on Southeast Alaska’s salmon watersheds and our natural dividends are not hypothetical. Protecting the Tongass is the most cost-effective way to improve ecosystem productivity and ensure the well-being for all who call Southeast home.
As the US Forest Service considers the future management of the Tongass National Forest, I hope that Alaska’s congressional delegation will listen to what Southeast Alaskans already know: Wild salmon are one of the Tongass’ most valuable resources. If we leave the trees standing and protect the habitat that fish need, the Tongass will continue to generate billions of dollars in natural dividends, in turn supporting thousands of fishing jobs and providing millions of pounds of nutritious seafood year after year. …For decades, Southeast Alaska’s communities and fishermen have fought industrial logging in the Tongass. …The harmful impacts of industrial logging on Southeast Alaska’s salmon watersheds and our natural dividends are not hypothetical. Protecting the Tongass is the most cost-effective way to improve ecosystem productivity and ensure the well-being for all who call Southeast home.  TROY, Montana — Vincent Logging, a family-owned logging company in Libby is working with Hecla Mining Company to manage its forested lands for wildlife habitat. It’s a 15-hundred acre research project to determine which management techniques provide the best habitat for endangered species. …It’s forest land in the Bull Lake area on Hecla Mining property near Troy. “We’re going to create grizzly bear habitat or enhance existing habitat for the bear,” he said. “Doing so, will enhance habitat for all the other critters that are living in here or that might live in here. We’re also studying it for success or failure at the same time.” Chas said thinning small diameter trees opens the area to create more plants that grizzlies like to eat. Larger diameter trees and thickets are left untouched to create a safe haven for the bears.
TROY, Montana — Vincent Logging, a family-owned logging company in Libby is working with Hecla Mining Company to manage its forested lands for wildlife habitat. It’s a 15-hundred acre research project to determine which management techniques provide the best habitat for endangered species. …It’s forest land in the Bull Lake area on Hecla Mining property near Troy. “We’re going to create grizzly bear habitat or enhance existing habitat for the bear,” he said. “Doing so, will enhance habitat for all the other critters that are living in here or that might live in here. We’re also studying it for success or failure at the same time.” Chas said thinning small diameter trees opens the area to create more plants that grizzlies like to eat. Larger diameter trees and thickets are left untouched to create a safe haven for the bears. ARIZONA — For the first time in months, Forest Service timber managers last week attended a Natural Resources Working Group meeting on the continuing effort to restore Northern Arizona forests and protect communities including Payson, Show Low, Pinetop and Pine. Local officials and logging operators said they are still searching for ways to handle millions of tons of low-value brush, slash and small trees that crowd the region’s overgrown ponderosa pine forests. The group, formed through the Eastern Arizona Counties Organization, meets regularly with industry representatives and Forest Service staff. …The Four Forest Restoration Initiative (4FRI) completed about 18,000 acres of thinning in the past year. Mass layoffs and the shutdown limited collaboration and fieldwork. …Pascal Berlioux, executive director of the Eastern Arizona Counties Organization, said a major problem was reduced production at the Lignetics plant in Show Low, which normally buys large amounts of biomass for wood-pellet manufacturing.
ARIZONA — For the first time in months, Forest Service timber managers last week attended a Natural Resources Working Group meeting on the continuing effort to restore Northern Arizona forests and protect communities including Payson, Show Low, Pinetop and Pine. Local officials and logging operators said they are still searching for ways to handle millions of tons of low-value brush, slash and small trees that crowd the region’s overgrown ponderosa pine forests. The group, formed through the Eastern Arizona Counties Organization, meets regularly with industry representatives and Forest Service staff. …The Four Forest Restoration Initiative (4FRI) completed about 18,000 acres of thinning in the past year. Mass layoffs and the shutdown limited collaboration and fieldwork. …Pascal Berlioux, executive director of the Eastern Arizona Counties Organization, said a major problem was reduced production at the Lignetics plant in Show Low, which normally buys large amounts of biomass for wood-pellet manufacturing. It was no surprise that everyone on the timber panel at this month’s Alaska Resource Development Council conference had the same message: The industry needs a larger supply of trees to cut. And a steady, bankable supply, said Joe Young, of Tok, who started Young’s Timber in Alaska’s Interior more than 30 years ago. …The Nov. 13 industry panel at the annual conference held in Anchorage also talked about demand for their product and the challenges in meeting that demand. Juneau attorney Jim Clark, said the Trump administration’s move to rescind the Roadless Rule, which has been around since 2001, could help open areas of the Tongass National Forest to logging. …The lack of timber sales, financial pressures and opposition from conservation groups have knocked down Alaska timber industry jobs from almost 4,000 in 1990 to about 700 in 2015 and just 360 in 2024, according to Alaska Department of Labor statistics.
It was no surprise that everyone on the timber panel at this month’s Alaska Resource Development Council conference had the same message: The industry needs a larger supply of trees to cut. And a steady, bankable supply, said Joe Young, of Tok, who started Young’s Timber in Alaska’s Interior more than 30 years ago. …The Nov. 13 industry panel at the annual conference held in Anchorage also talked about demand for their product and the challenges in meeting that demand. Juneau attorney Jim Clark, said the Trump administration’s move to rescind the Roadless Rule, which has been around since 2001, could help open areas of the Tongass National Forest to logging. …The lack of timber sales, financial pressures and opposition from conservation groups have knocked down Alaska timber industry jobs from almost 4,000 in 1990 to about 700 in 2015 and just 360 in 2024, according to Alaska Department of Labor statistics.

 As the American West warms due to climate change, wildfires are increasingly burning in higher-elevation mountains, charring the watersheds where the region’s vital snowpack accumulates. A new study has found that in the immediate aftermath of fires across the region, the snowpack disappears earlier in burned areas. This change can threaten forest health and affect the downstream farms, cities and species that rely on the snowpack for their water, according to other research. Scientists who study the effects of wildfires on the snowpack and streamflows are finding that the story is complex and nuanced. The impacts can vary greatly across the West’s diverse ecosystems and topography. Plus, each wildfire burns differently, so the severity of the blaze is another critical factor. …Published in the Sept. 17 issue of
As the American West warms due to climate change, wildfires are increasingly burning in higher-elevation mountains, charring the watersheds where the region’s vital snowpack accumulates. A new study has found that in the immediate aftermath of fires across the region, the snowpack disappears earlier in burned areas. This change can threaten forest health and affect the downstream farms, cities and species that rely on the snowpack for their water, according to other research. Scientists who study the effects of wildfires on the snowpack and streamflows are finding that the story is complex and nuanced. The impacts can vary greatly across the West’s diverse ecosystems and topography. Plus, each wildfire burns differently, so the severity of the blaze is another critical factor. …Published in the Sept. 17 issue of 
 The total forest area in the world is 4.1 billion hectares, or 32 per cent of Earth’s total surface area. The tropics are home to the majority of the world’s forests – 45 per cent – while the rest is mainly found in boreal, temperate and subtropical zones. Since 1990, 489 million hectares of forest have been lost to deforestation… While the rate of deforestation is actually slowing, so is the rate of forest expansion, dropping from 9.88 million hectares per year from 2000-2015 to 6.78 million hectares per year in the decade to 2025. Below are the top five countries with the biggest forests as of 2025, according to forest area:
The total forest area in the world is 4.1 billion hectares, or 32 per cent of Earth’s total surface area. The tropics are home to the majority of the world’s forests – 45 per cent – while the rest is mainly found in boreal, temperate and subtropical zones. Since 1990, 489 million hectares of forest have been lost to deforestation… While the rate of deforestation is actually slowing, so is the rate of forest expansion, dropping from 9.88 million hectares per year from 2000-2015 to 6.78 million hectares per year in the decade to 2025. Below are the top five countries with the biggest forests as of 2025, according to forest area:

 The European Parliament has approved measures to simplify the EU Deforestation Regulation adopted in 2023, which aims to ensure that products sold in the EU are not sourced from deforested land, according to the European Parliament. The new position grants companies an additional year to comply with the regulation. Large operators and traders must apply the obligations from 30 December 2026, and micro and small enterprises from 30 June 2027. The extension is designed to support a smooth transition and allow upgrades to the IT system used for electronic due diligence statements. Parliament agreed that the responsibility for submitting due diligence statements should rest with businesses that first place products on the EU market, not with later traders. Micro and small primary operators will now be required to file only a single simplified declaration instead of full due diligence reports.
The European Parliament has approved measures to simplify the EU Deforestation Regulation adopted in 2023, which aims to ensure that products sold in the EU are not sourced from deforested land, according to the European Parliament. The new position grants companies an additional year to comply with the regulation. Large operators and traders must apply the obligations from 30 December 2026, and micro and small enterprises from 30 June 2027. The extension is designed to support a smooth transition and allow upgrades to the IT system used for electronic due diligence statements. Parliament agreed that the responsibility for submitting due diligence statements should rest with businesses that first place products on the EU market, not with later traders. Micro and small primary operators will now be required to file only a single simplified declaration instead of full due diligence reports. Illinois — Four-legged reinforcements may be enlisted to help battle invasive buckthorn in Lake County forest preserves. The idea is in the formative stage, but forest district commissioners appear amenable to launching a pilot program to determine if grazing goats or sheep can help manage the pesky invaders. Buckthorn and other woody invasive species are considered among the greatest threats to natural areas across the region, and in Lake County comprise more than 52% of all trees, according to the Lake County Forest Preserve District. …“While grazing is not anticipated to fully replace herbicides or other invasive control practices, it could provide a potential alternative to accomplish objectives in a cost-effective manner,” according to information being presented this week to forest board committees. The pilot agreement likely would allow six to eight sheep or goats to graze on two or three acres of district land for up to four years.
Illinois — Four-legged reinforcements may be enlisted to help battle invasive buckthorn in Lake County forest preserves. The idea is in the formative stage, but forest district commissioners appear amenable to launching a pilot program to determine if grazing goats or sheep can help manage the pesky invaders. Buckthorn and other woody invasive species are considered among the greatest threats to natural areas across the region, and in Lake County comprise more than 52% of all trees, according to the Lake County Forest Preserve District. …“While grazing is not anticipated to fully replace herbicides or other invasive control practices, it could provide a potential alternative to accomplish objectives in a cost-effective manner,” according to information being presented this week to forest board committees. The pilot agreement likely would allow six to eight sheep or goats to graze on two or three acres of district land for up to four years.  Conservative Forestry Critic Ward Stamer wants to decrease regulation of the logging industry and an increase to the annual allowable cut. Logging proponents love to cite how important and valuable the industry is to B.C. communities. The reality, however, is quite different. Here are some figures that show clearly – in almost every metric – that logging is less valuable to B.C. communities and the B.C. economy than tourism. … These figures of the logging industry are from 2022 and the tourism figures are from 2022 and 2023, so they are roughly comparable. Tourism employed over 125,700 people; logging and related industry employed approximately 100,000. Tourism resulted in $5.9 billion in wages and salaries in 2023, 11.8 per cent higher than in 2022; Logging and related industries resulted in approximately $9.1 billion. There were 16,860 tourism businesses in operation in 2023, mostly in small communities, many of them remote and, increasingly, more of them Indigenous owned.
Conservative Forestry Critic Ward Stamer wants to decrease regulation of the logging industry and an increase to the annual allowable cut. Logging proponents love to cite how important and valuable the industry is to B.C. communities. The reality, however, is quite different. Here are some figures that show clearly – in almost every metric – that logging is less valuable to B.C. communities and the B.C. economy than tourism. … These figures of the logging industry are from 2022 and the tourism figures are from 2022 and 2023, so they are roughly comparable. Tourism employed over 125,700 people; logging and related industry employed approximately 100,000. Tourism resulted in $5.9 billion in wages and salaries in 2023, 11.8 per cent higher than in 2022; Logging and related industries resulted in approximately $9.1 billion. There were 16,860 tourism businesses in operation in 2023, mostly in small communities, many of them remote and, increasingly, more of them Indigenous owned.