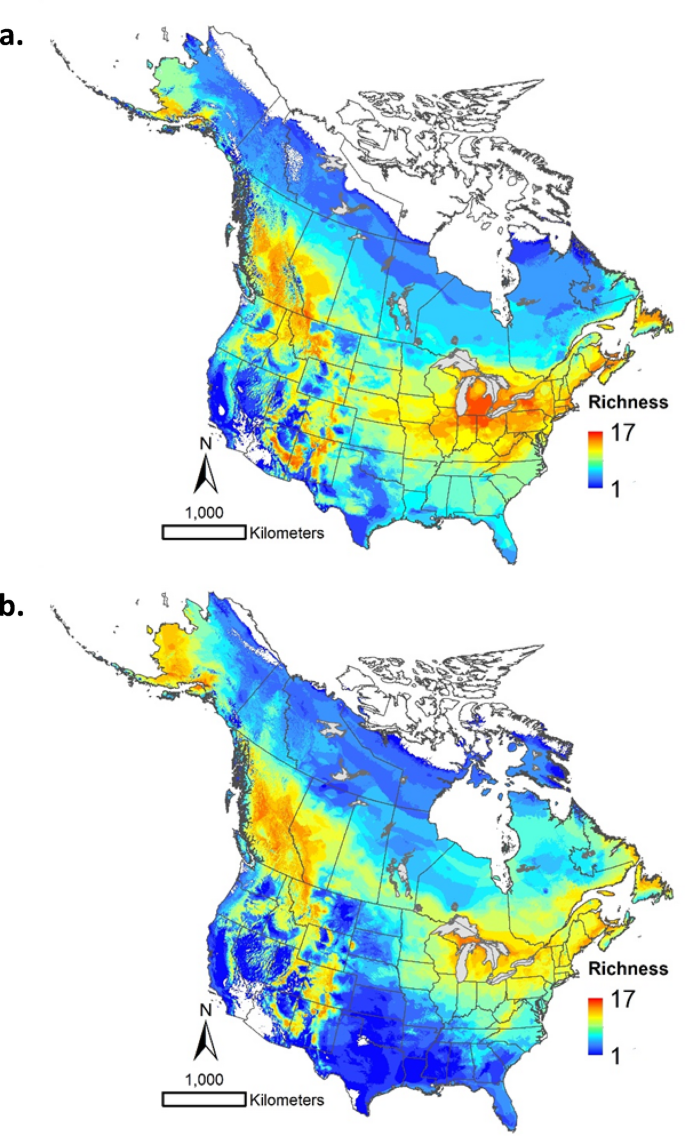
 Insects and diseases are important disturbance agents in Canadian forests and there is concern that their impacts will intensify under climate change. Here we report on an effort to model and map the climate niches of more than 4000 forest insect and fungus species in Canada – including high-profile pest species that are already, or may soon become, established in the country. This work employs occurrence data from historical, national-scale forest insect and disease surveys. …We further employ national forest inventory products (gridded maps) to summarize forest host volumes at risk of infestation by selected insect and disease species. …We demonstrate use of the products through examples, including brown spruce longhorn beetle, southern pine beetle, oak wilt, and map overlays that show hotspots for bark beetles under current and projected climate. We hope this tool will help pest managers to better understand how these species may respond to projected climate change.
Insects and diseases are important disturbance agents in Canadian forests and there is concern that their impacts will intensify under climate change. Here we report on an effort to model and map the climate niches of more than 4000 forest insect and fungus species in Canada – including high-profile pest species that are already, or may soon become, established in the country. This work employs occurrence data from historical, national-scale forest insect and disease surveys. …We further employ national forest inventory products (gridded maps) to summarize forest host volumes at risk of infestation by selected insect and disease species. …We demonstrate use of the products through examples, including brown spruce longhorn beetle, southern pine beetle, oak wilt, and map overlays that show hotspots for bark beetles under current and projected climate. We hope this tool will help pest managers to better understand how these species may respond to projected climate change.
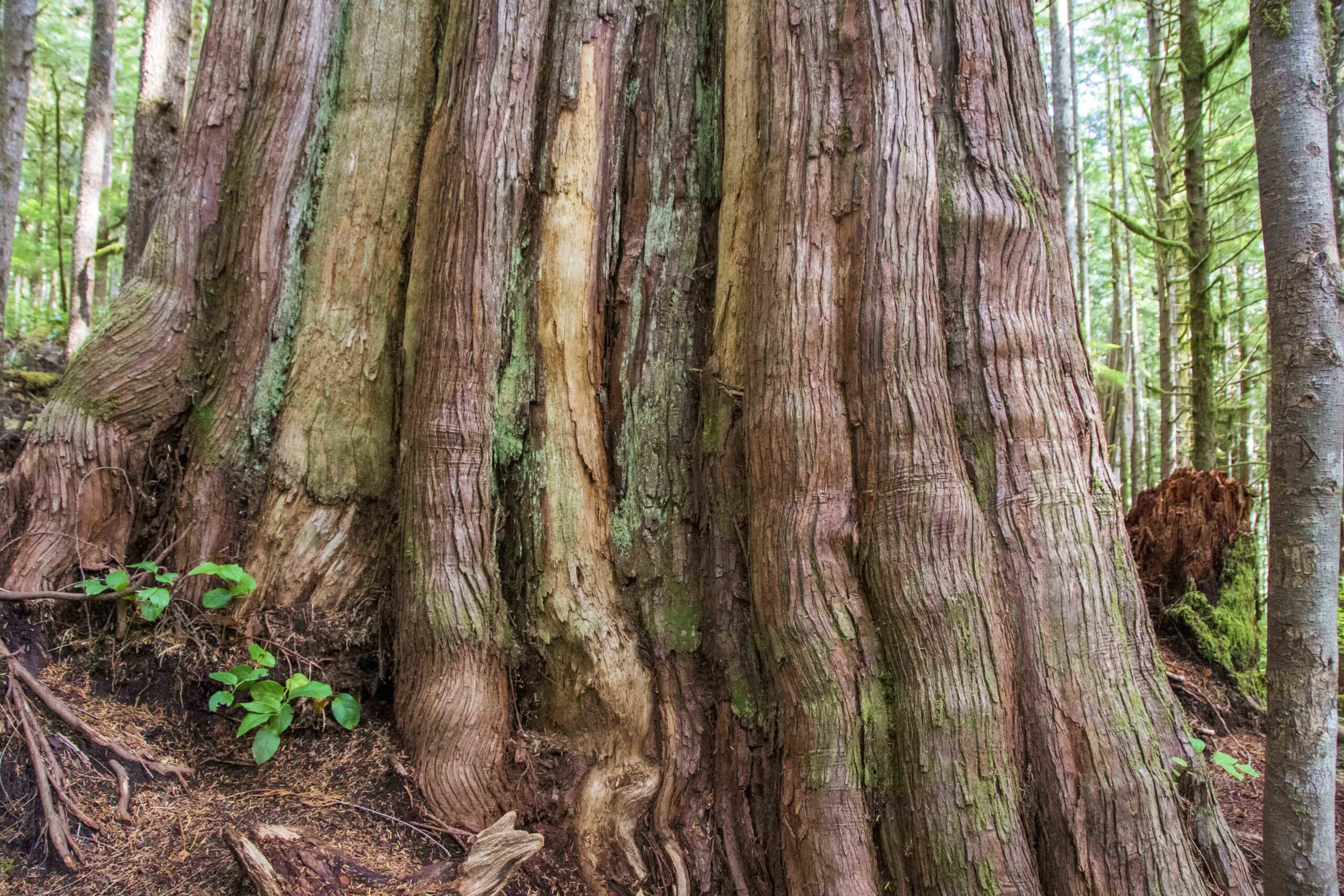
 A proactive new tool that can help preserve old forests in British Columbia has been developed by University of Alberta researchers. A new study gives crucial insight into where to focus conservation measures, by identifying areas of old-growth forest in areas predicted to be stable in the face of climate change. The approach shifts the focus toward what can still be protected, says Nick Pochailo, who led the study…. “Old-growth forests located in areas of potential climatic stability offer exceptional long-term conservation value. By identifying these places, land managers can prioritize and plan conservation efforts more effectively.” …old-growth forests account for about 25 per cent of BC’s forested areas. They’ve shrunk from 25 million hectares to about half that due to logging, wildfires, and pests like the mountain pine beetle… computer models predict how these ecosystems might shift by the 2050s, then mapped the changes to geographically pinpoint areas most likely to survive.
A proactive new tool that can help preserve old forests in British Columbia has been developed by University of Alberta researchers. A new study gives crucial insight into where to focus conservation measures, by identifying areas of old-growth forest in areas predicted to be stable in the face of climate change. The approach shifts the focus toward what can still be protected, says Nick Pochailo, who led the study…. “Old-growth forests located in areas of potential climatic stability offer exceptional long-term conservation value. By identifying these places, land managers can prioritize and plan conservation efforts more effectively.” …old-growth forests account for about 25 per cent of BC’s forested areas. They’ve shrunk from 25 million hectares to about half that due to logging, wildfires, and pests like the mountain pine beetle… computer models predict how these ecosystems might shift by the 2050s, then mapped the changes to geographically pinpoint areas most likely to survive. 
 The Province is responding to a potential case of chronic wasting disease (CWD) in a male white-tailed deer harvested east of Enderby. CWD is an infectious and fatal disease affecting species in the cervid family, such as deer, elk, moose and caribou. Initial testing by the provincial animal health laboratory detected prions (which are abnormal proteins) that may indicate CWD in the deer sample. The sample has been submitted to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) for further testing, as the CFIA is Canada’s authority for confirming CWD. Results are expected by early December. The hunter who submitted the sample has been notified of the potential detection. The Province will update the public if the CFIA confirms the sample to be positive for CWD. This is the first potential detection in the Okanagan and the first identified outside B.C.’s existing CWD management zone in the Kootenay region.
The Province is responding to a potential case of chronic wasting disease (CWD) in a male white-tailed deer harvested east of Enderby. CWD is an infectious and fatal disease affecting species in the cervid family, such as deer, elk, moose and caribou. Initial testing by the provincial animal health laboratory detected prions (which are abnormal proteins) that may indicate CWD in the deer sample. The sample has been submitted to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) for further testing, as the CFIA is Canada’s authority for confirming CWD. Results are expected by early December. The hunter who submitted the sample has been notified of the potential detection. The Province will update the public if the CFIA confirms the sample to be positive for CWD. This is the first potential detection in the Okanagan and the first identified outside B.C.’s existing CWD management zone in the Kootenay region. A First Nation in north-central B.C. says it is banning the use of herbicides across all of its territory, which includes Prince George and the Robson Valley. The Lheidli T’enneh First Nation says the ban is being put into place because of the negative impacts herbicides, and glyphosate in particular, have had on the environment and wildlife for which they are stewards. “It is our duty to disallow toxic chemicals in our territory that reduce biodiversity and have negative impacts on our members’ health, wellbeing and the environment where we exercise our living rights and traditions,” Lheidli T’enneh Elected Chief Dolleen Logan said in a statement. She also says the nation expects both government and private industry workers operating in the region to adhere to the ban. It was not immediately clear if the ban would also apply to private and municipal property. More details coming Tuesday morning.
A First Nation in north-central B.C. says it is banning the use of herbicides across all of its territory, which includes Prince George and the Robson Valley. The Lheidli T’enneh First Nation says the ban is being put into place because of the negative impacts herbicides, and glyphosate in particular, have had on the environment and wildlife for which they are stewards. “It is our duty to disallow toxic chemicals in our territory that reduce biodiversity and have negative impacts on our members’ health, wellbeing and the environment where we exercise our living rights and traditions,” Lheidli T’enneh Elected Chief Dolleen Logan said in a statement. She also says the nation expects both government and private industry workers operating in the region to adhere to the ban. It was not immediately clear if the ban would also apply to private and municipal property. More details coming Tuesday morning. The new allowable annual cut (AAC) for Tree Farm Licence (TFL) 49 near Vernon has been chopped. The cut, which is the maximum amount of timber that can be harvested each year, is now 150,500 cubic metres, and takes effect immediately. That’s a 26.2% reduction from the previous AAC. “That decision reflects a return to sustainable harvest levels following wildfire impacts in 2021 and 2023,” said the
The new allowable annual cut (AAC) for Tree Farm Licence (TFL) 49 near Vernon has been chopped. The cut, which is the maximum amount of timber that can be harvested each year, is now 150,500 cubic metres, and takes effect immediately. That’s a 26.2% reduction from the previous AAC. “That decision reflects a return to sustainable harvest levels following wildfire impacts in 2021 and 2023,” said the  For more than 80 years, the annual
For more than 80 years, the annual  Sponsors enjoy high-profile recognition before, during, and after the convention, ensuring your brand stays top of mind among key industry players. Tracey Russell, Vice President-Equipment, Inland Truck & Equipment Ltd. is a regular at the Convention, “We sponsor the TLA Convention + Trade Show every year because it’s one of the best opportunities for exposure and relationship building – connections that have made a lasting impact on our business and our brand.”
Sponsors enjoy high-profile recognition before, during, and after the convention, ensuring your brand stays top of mind among key industry players. Tracey Russell, Vice President-Equipment, Inland Truck & Equipment Ltd. is a regular at the Convention, “We sponsor the TLA Convention + Trade Show every year because it’s one of the best opportunities for exposure and relationship building – connections that have made a lasting impact on our business and our brand.”
 The return of cold and snow at the close of the year typically signal the end of the wildfire season. …Zombie fires, sometimes betrayed by a plume of steam emerging from the bubbling ground in the frozen forest, were once a rare occurrence in the boreal regions that stretch across the far north through Siberia, Canada and Alaska. But in a rapidly heating world, they are becoming increasingly common. The overwintering burns are small – and often hard to detect – but they are transforming fires into multi-year events. …“It is a massive problem,” says Lori Daniels, a professor at the University of BC. Current estimates show that only about 15% of the northern hemisphere is underlain by permafrost, yet these frozen soils contain roughly twice as much carbon than is now in the atmosphere. By burning slowly and at a lower temperature, they release vastly more particulate pollution and greenhouse gas emissions than flaming fires.
The return of cold and snow at the close of the year typically signal the end of the wildfire season. …Zombie fires, sometimes betrayed by a plume of steam emerging from the bubbling ground in the frozen forest, were once a rare occurrence in the boreal regions that stretch across the far north through Siberia, Canada and Alaska. But in a rapidly heating world, they are becoming increasingly common. The overwintering burns are small – and often hard to detect – but they are transforming fires into multi-year events. …“It is a massive problem,” says Lori Daniels, a professor at the University of BC. Current estimates show that only about 15% of the northern hemisphere is underlain by permafrost, yet these frozen soils contain roughly twice as much carbon than is now in the atmosphere. By burning slowly and at a lower temperature, they release vastly more particulate pollution and greenhouse gas emissions than flaming fires.


 The crowd stretched from the doors of City Hall to the Ward Street sidewalk in Nelson to hear guest speaker David Suzuki and other forest ecology advocates at a rally held Nov. 18 in Nelson. …The Broken Promises rally was held simultaneously in Nelson, Victoria, Vernon, Revelstoke, Smithers, Courtenay, Parksville, and Powell River to protest what is seen as provincial government backtracking on the protection of old growth forests, biodiversity and watersheds, and continuing with timber volume as the only priority. …Speaker Suzanne Simard said failure to use that foresight, to respect all life and give back more than we receive, has resulted in climate change, biodiversity loss, and land degradation. …She said the province should stop clearcutting and creating tree plantations that are flammable and subject to erosion. …Slocan Valley ecologist and forester Herb Hammond spoke about secondary forests… That’s where we should get our wood and our employment…
The crowd stretched from the doors of City Hall to the Ward Street sidewalk in Nelson to hear guest speaker David Suzuki and other forest ecology advocates at a rally held Nov. 18 in Nelson. …The Broken Promises rally was held simultaneously in Nelson, Victoria, Vernon, Revelstoke, Smithers, Courtenay, Parksville, and Powell River to protest what is seen as provincial government backtracking on the protection of old growth forests, biodiversity and watersheds, and continuing with timber volume as the only priority. …Speaker Suzanne Simard said failure to use that foresight, to respect all life and give back more than we receive, has resulted in climate change, biodiversity loss, and land degradation. …She said the province should stop clearcutting and creating tree plantations that are flammable and subject to erosion. …Slocan Valley ecologist and forester Herb Hammond spoke about secondary forests… That’s where we should get our wood and our employment…




%20(6).jpg)
 OTTAWA — The Carney government will still pay to help plant a previously announced 52 million trees in New Brunswick, even though hardly any of them are in the ground and the program’s funding has been cancelled. The recent federal budget scrapped a program to plant two billion trees across the country by 2031 in order to find hundreds of millions of dollars in savings. It was a climate change initiative first announced by former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the 2019 election campaign with $3.2 billion over 10 years earmarked to carry it out. New Brunswick was one of the last provinces to reach an agreement for its cut of that money. It didn’t sign on until March 2024. A few months after that, the feds and the New Brunswick government announced $71.6 million to plant more than 52 million trees on Crown lands across the province over the next eight years. [A Telegraph-Journal subscription is required for full access]
OTTAWA — The Carney government will still pay to help plant a previously announced 52 million trees in New Brunswick, even though hardly any of them are in the ground and the program’s funding has been cancelled. The recent federal budget scrapped a program to plant two billion trees across the country by 2031 in order to find hundreds of millions of dollars in savings. It was a climate change initiative first announced by former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the 2019 election campaign with $3.2 billion over 10 years earmarked to carry it out. New Brunswick was one of the last provinces to reach an agreement for its cut of that money. It didn’t sign on until March 2024. A few months after that, the feds and the New Brunswick government announced $71.6 million to plant more than 52 million trees on Crown lands across the province over the next eight years. [A Telegraph-Journal subscription is required for full access]


 The timber industry built around the Tongass National Forest in Alaska got a boost from the Trump administration’s latest trade deal with China. In settling part of its trade battles, China agreed to accept imports of US sawlogs for the first time since banning them in March due to worries about insect pests. The resumption of exports — effective Nov. 12 — would help companies like Alcan Forest Products in Ketchikan, which for years has sold unprocessed logs to China. The latest agreement lasts one year, said Tessa Axelson, executive director of the Alaska Forest Association. A 10% tariff on products from both countries would still apply. …Southeast Alaska’s timber industry relies heavily on the nearly 17-million-acre Tongass, although most of the forest is off-limits to logging. Federal law allows the export of unprocessed logs, a practice long banned elsewhere to protect the domestic lumber processing industry. [to access the full story an E&ENews subscription is required]
The timber industry built around the Tongass National Forest in Alaska got a boost from the Trump administration’s latest trade deal with China. In settling part of its trade battles, China agreed to accept imports of US sawlogs for the first time since banning them in March due to worries about insect pests. The resumption of exports — effective Nov. 12 — would help companies like Alcan Forest Products in Ketchikan, which for years has sold unprocessed logs to China. The latest agreement lasts one year, said Tessa Axelson, executive director of the Alaska Forest Association. A 10% tariff on products from both countries would still apply. …Southeast Alaska’s timber industry relies heavily on the nearly 17-million-acre Tongass, although most of the forest is off-limits to logging. Federal law allows the export of unprocessed logs, a practice long banned elsewhere to protect the domestic lumber processing industry. [to access the full story an E&ENews subscription is required]
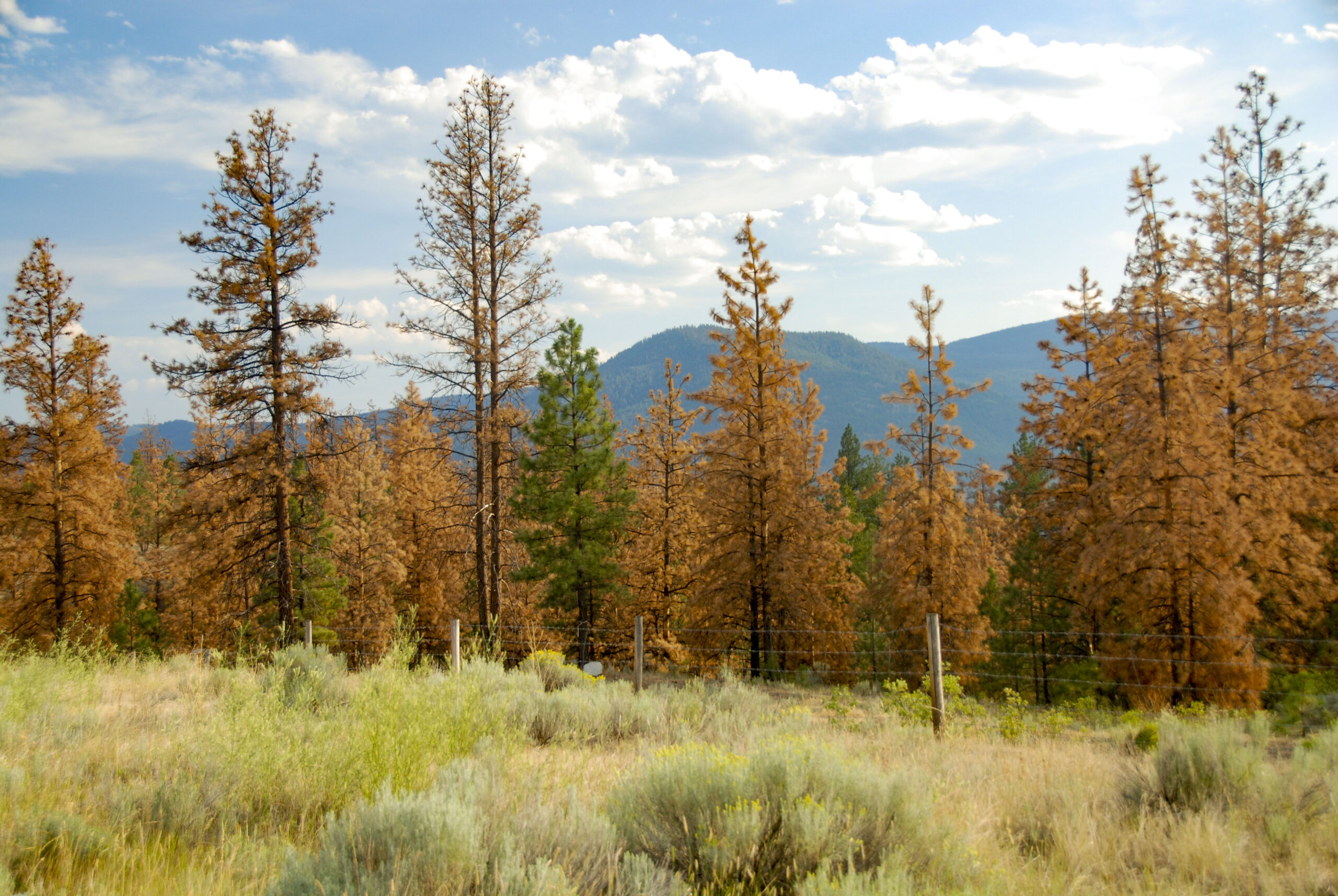

 Kremmling, Colorado — The Mill in Kremmling is contributing to the natural carbon-storing success of trees in Routt County by purchasing and reusing standing dead trees logged during wildfire mitigation projects and turned into usable wood products. The company’s goal is to support the local economy and Colorado’s timber industry by creating a demand for forest products sourced entirely from fire mitigation projects, said Lisa Hara, owner and CEO at The Mill. Some 90% of the trees processed at The Mill come from Routt County, with 10% from Jefferson County for Douglas fir wood, Hara said. “We help Routt County by creating a demand for materials that come directly from fire mitigation and watershed projects,” said Hara, who purchased The Mill in spring 2023. “Instead of being treated as waste, this wood becomes a resource, one that supports forest health and rural jobs at the same time.”
Kremmling, Colorado — The Mill in Kremmling is contributing to the natural carbon-storing success of trees in Routt County by purchasing and reusing standing dead trees logged during wildfire mitigation projects and turned into usable wood products. The company’s goal is to support the local economy and Colorado’s timber industry by creating a demand for forest products sourced entirely from fire mitigation projects, said Lisa Hara, owner and CEO at The Mill. Some 90% of the trees processed at The Mill come from Routt County, with 10% from Jefferson County for Douglas fir wood, Hara said. “We help Routt County by creating a demand for materials that come directly from fire mitigation and watershed projects,” said Hara, who purchased The Mill in spring 2023. “Instead of being treated as waste, this wood becomes a resource, one that supports forest health and rural jobs at the same time.”
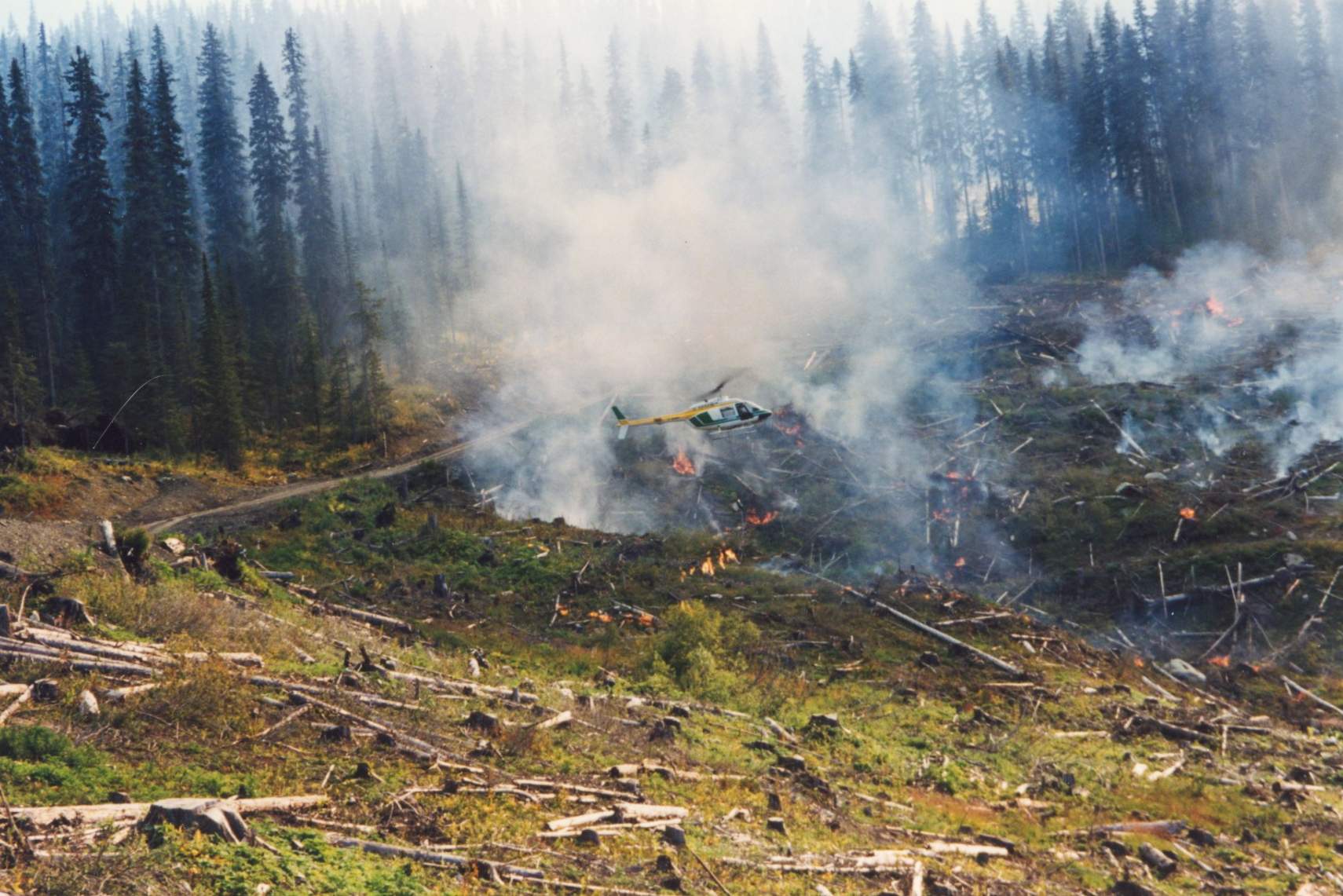
 Oregon — Deschutes County is preparing to deploy $3.4 million for wildfire mitigation projects to reduce the likelihood of catastrophic wildfire in La Pine. The money comes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and is part of a $200 million funding package to assist fire-prone areas across the country. Work is expected to begin in the spring on a variety of projects ranging from fuels reduction to community education, according to Lauren Street, a natural resources specialist with Deschutes County. The project is expected to continue for five years. La Pine was one of 58 recipients nationwide to benefit from community wildfire defense grants. The grants are funded by the Biden-era bipartisan infrastructure law of 2021. Elsewhere in Oregon, the Sweet Home Fire and Ambulance District is set to receive $8.7 million, the largest grant for any project in the state.
Oregon — Deschutes County is preparing to deploy $3.4 million for wildfire mitigation projects to reduce the likelihood of catastrophic wildfire in La Pine. The money comes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and is part of a $200 million funding package to assist fire-prone areas across the country. Work is expected to begin in the spring on a variety of projects ranging from fuels reduction to community education, according to Lauren Street, a natural resources specialist with Deschutes County. The project is expected to continue for five years. La Pine was one of 58 recipients nationwide to benefit from community wildfire defense grants. The grants are funded by the Biden-era bipartisan infrastructure law of 2021. Elsewhere in Oregon, the Sweet Home Fire and Ambulance District is set to receive $8.7 million, the largest grant for any project in the state.
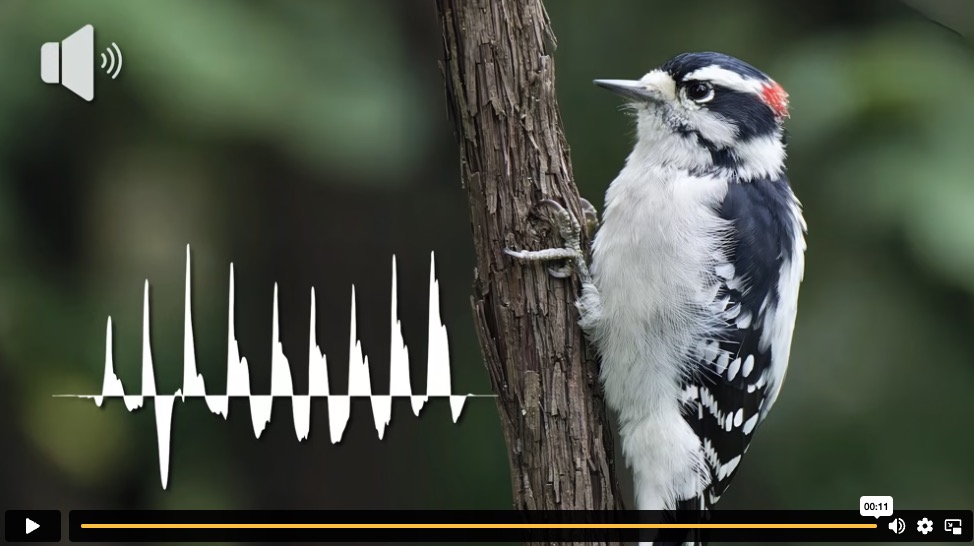
 PROVIDENCE, R.I. — It’s one of nature’s mysteries: How can woodpeckers, the smallest of which weigh less than an ounce, drill permanent holes into massive trees using only their tiny heads? New research shows that there’s much more at play, anatomically: When a woodpecker bores into wood, it uses not only its head but its entire body, as well as its breathing. In a study published in the Journal of Experimental Biology, a team led by biologists at Brown University reveals how woodpeckers combine breathing and whole-body coordination to drill into trees with extraordinary force. “These findings expand our understanding of the links between respiration, muscle physiology and behavior to perform extreme motor feats and meet ecological challenges,” said lead author Nicholas Antonson… The team studied downy woodpeckers, the smallest species of woodpeckers in North America, which populate forested areas throughout the United States and Canada.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. — It’s one of nature’s mysteries: How can woodpeckers, the smallest of which weigh less than an ounce, drill permanent holes into massive trees using only their tiny heads? New research shows that there’s much more at play, anatomically: When a woodpecker bores into wood, it uses not only its head but its entire body, as well as its breathing. In a study published in the Journal of Experimental Biology, a team led by biologists at Brown University reveals how woodpeckers combine breathing and whole-body coordination to drill into trees with extraordinary force. “These findings expand our understanding of the links between respiration, muscle physiology and behavior to perform extreme motor feats and meet ecological challenges,” said lead author Nicholas Antonson… The team studied downy woodpeckers, the smallest species of woodpeckers in North America, which populate forested areas throughout the United States and Canada.


