Many Canadians may not realize we are soon entering National Forest Week, a time to reflect on forests’ vital role in our history, economy and future. National Forest Week, happening September 21–27, 2025, reminds us to balance economic opportunities with sustainability. Indigenous-led forest ventures already exemplify this. Indigenous communities have managed forests responsibly for thousands of years, and their involvement has increased significantly, with more land and resources under their control, including forest tenures. …The future of sustainable forestry depends on increasing Indigenous participation. This includes stronger industry-Indigenous partnerships, expanded forest tenures, fair forest sector procurement policies, better Indigenous recruitment and retention within the forestry world, and greater integration of Indigenous knowledge into policy frameworks. Let’s celebrate National Forest Week by honouring Canada’s original forest managers and their lasting legacy in sustainable forest management.

 … Fires in Canada’s Wildland Urban Interface (WUI) are becoming more common as cities continue to sprawl, increasing the risk to structures. Regions across the country are grappling with the competing pressures of building housing and expanding industry, while climate change… continues to create hot, dry conditions that make wildfires more intense and frequent. A
… Fires in Canada’s Wildland Urban Interface (WUI) are becoming more common as cities continue to sprawl, increasing the risk to structures. Regions across the country are grappling with the competing pressures of building housing and expanding industry, while climate change… continues to create hot, dry conditions that make wildfires more intense and frequent. A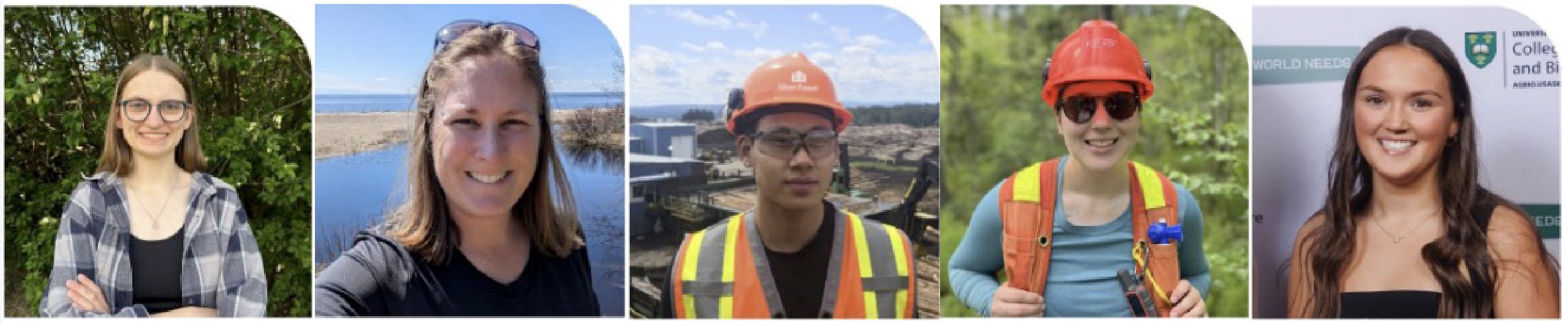  This summer, five exceptional students from across Canada were selected for the Forest Products Association of Canada’s (FPAC) 2025 Green Dream Internship Program, an initiative that continues to spotlight the next generation of forestry professionals. Now in its twelfth year, the Green Dream Internship offers students a unique opportunity to explore the forest sector from the inside out. Over six weeks, interns shared their experiences through creative storytelling—capturing everyday moments in forest operations, conducting interviews, and reflecting on their career journeys. Each intern received a $1,000 scholarship to support their studies. “As these students return to their studies and continue building their expertise, they now carry with them an even deeper understanding of the sector’s challenges, innovations, and opportunities,” said Derek Nighbor, FPAC’s President and CEO.
This summer, five exceptional students from across Canada were selected for the Forest Products Association of Canada’s (FPAC) 2025 Green Dream Internship Program, an initiative that continues to spotlight the next generation of forestry professionals. Now in its twelfth year, the Green Dream Internship offers students a unique opportunity to explore the forest sector from the inside out. Over six weeks, interns shared their experiences through creative storytelling—capturing everyday moments in forest operations, conducting interviews, and reflecting on their career journeys. Each intern received a $1,000 scholarship to support their studies. “As these students return to their studies and continue building their expertise, they now carry with them an even deeper understanding of the sector’s challenges, innovations, and opportunities,” said Derek Nighbor, FPAC’s President and CEO.  People should continue to use caution and take steps to be prepared by staying up to date on current conditions, following fire prohibitions and being Firesmart, as the risk of wildfire is expected to continue into fall. The BC Wildfire Service’s fall seasonal outlook forecasts ongoing wildfire risk for much of the province, especially in the Cariboo and southwestern Interior. Convective thunderstorms typically decrease as fall approaches; however, despite a lower likelihood of wildfires due to lightning, human-caused wildfires remain a risk. Until the southern coast shifts to a stormier fall-like pattern and the Prince George and Kamloops fire centres receive substantial rainfall, the wildfire danger ratings will continue to be elevated. As a result of the late summer’s record-breaking heat wave, combined with ongoing drought, people in B.C. are encouraged to be prepared for the risk of wildfire this fall.
People should continue to use caution and take steps to be prepared by staying up to date on current conditions, following fire prohibitions and being Firesmart, as the risk of wildfire is expected to continue into fall. The BC Wildfire Service’s fall seasonal outlook forecasts ongoing wildfire risk for much of the province, especially in the Cariboo and southwestern Interior. Convective thunderstorms typically decrease as fall approaches; however, despite a lower likelihood of wildfires due to lightning, human-caused wildfires remain a risk. Until the southern coast shifts to a stormier fall-like pattern and the Prince George and Kamloops fire centres receive substantial rainfall, the wildfire danger ratings will continue to be elevated. As a result of the late summer’s record-breaking heat wave, combined with ongoing drought, people in B.C. are encouraged to be prepared for the risk of wildfire this fall.
 The District of 100 Mile House is refusing a proposed project that could see solar and wind farms built in the South Cariboo. During the Sept. 9 District of 100 Mile House Council meeting, around 50 people showed up to council to hear them deliberate about the Cariboo Wind and Solar Projects, which are a collection of wind and solar projects that are being proposed by MK Ince and Associates Ltd. …In a letter to the district, Tyrell Law, who is the current manager of the 100 Mile Community Forest, said that the project significantly overlaps with the Community Forest areas. The 100 Mile Community Forest is around 18,000 hectares in size and is managed by the 100 Mile Development Corporation. The proposal comprises around 730 hectares of the community forest. Law said that while Ince is partially correct to say that the area had been recently harvested and was in a plantation, it is more complicated than that.
The District of 100 Mile House is refusing a proposed project that could see solar and wind farms built in the South Cariboo. During the Sept. 9 District of 100 Mile House Council meeting, around 50 people showed up to council to hear them deliberate about the Cariboo Wind and Solar Projects, which are a collection of wind and solar projects that are being proposed by MK Ince and Associates Ltd. …In a letter to the district, Tyrell Law, who is the current manager of the 100 Mile Community Forest, said that the project significantly overlaps with the Community Forest areas. The 100 Mile Community Forest is around 18,000 hectares in size and is managed by the 100 Mile Development Corporation. The proposal comprises around 730 hectares of the community forest. Law said that while Ince is partially correct to say that the area had been recently harvested and was in a plantation, it is more complicated than that.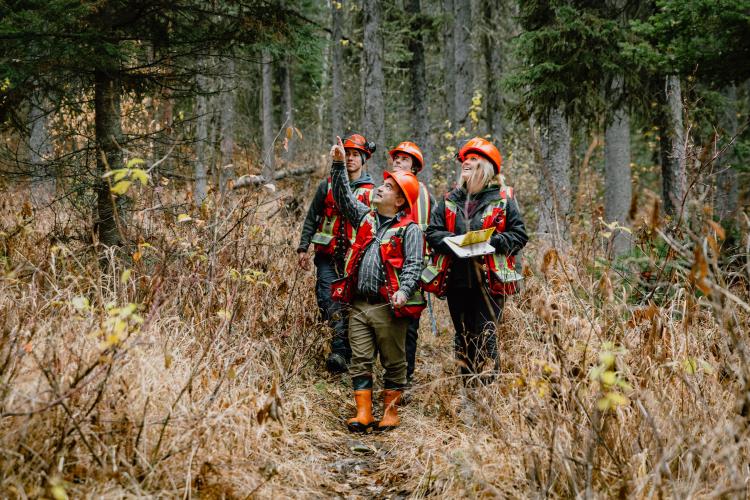 
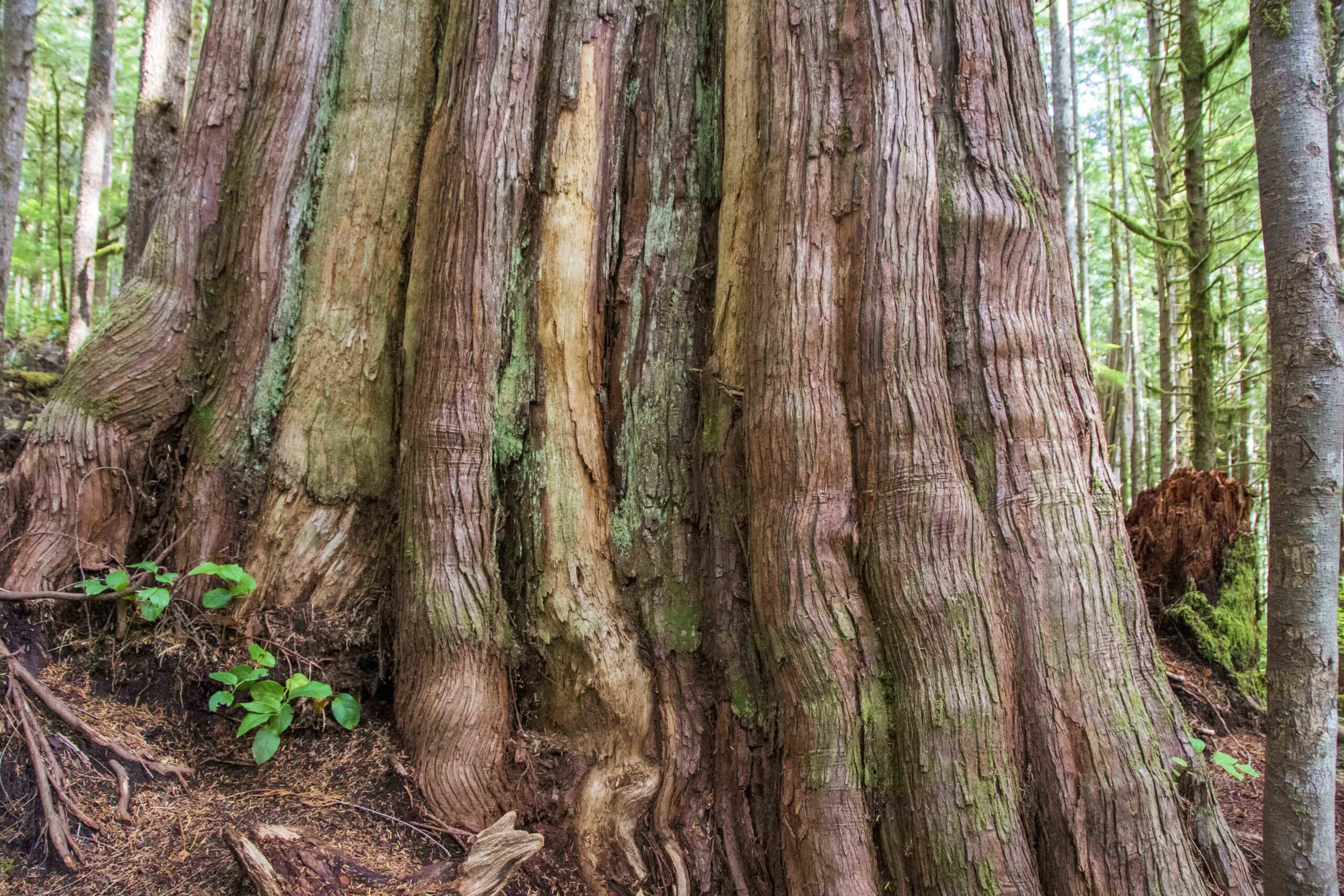 A shaggy, cool-green lichen hangs from the trunk of a tree in a forest on northeastern Vancouver Island. Lichenologist Trevor Goward has named it oldgrowth specklebelly. …Old-growth advocate Joshua Wright photographed oldgrowth specklebelly this summer in a forest about 400 kilometres northwest of Victoria. …Wright and Goward prize the forest in the Tsitika River watershed for its age and biodiversity, and a provincially appointed panel recommended that it be set aside from logging in 2021. But if a plan by the provincial logging agency, BC Timber Sales, goes ahead, the site will be auctioned for clearcut logging by the end of September. The area was stewarded by several Indigenous nations. …The plan to log it reveals differing opinions among Kwakwaka’wakw leaders on how to protect old-growth forests, while raising questions about which Aboriginal rights holders the BC government chooses to listen to, and why.
A shaggy, cool-green lichen hangs from the trunk of a tree in a forest on northeastern Vancouver Island. Lichenologist Trevor Goward has named it oldgrowth specklebelly. …Old-growth advocate Joshua Wright photographed oldgrowth specklebelly this summer in a forest about 400 kilometres northwest of Victoria. …Wright and Goward prize the forest in the Tsitika River watershed for its age and biodiversity, and a provincially appointed panel recommended that it be set aside from logging in 2021. But if a plan by the provincial logging agency, BC Timber Sales, goes ahead, the site will be auctioned for clearcut logging by the end of September. The area was stewarded by several Indigenous nations. …The plan to log it reveals differing opinions among Kwakwaka’wakw leaders on how to protect old-growth forests, while raising questions about which Aboriginal rights holders the BC government chooses to listen to, and why.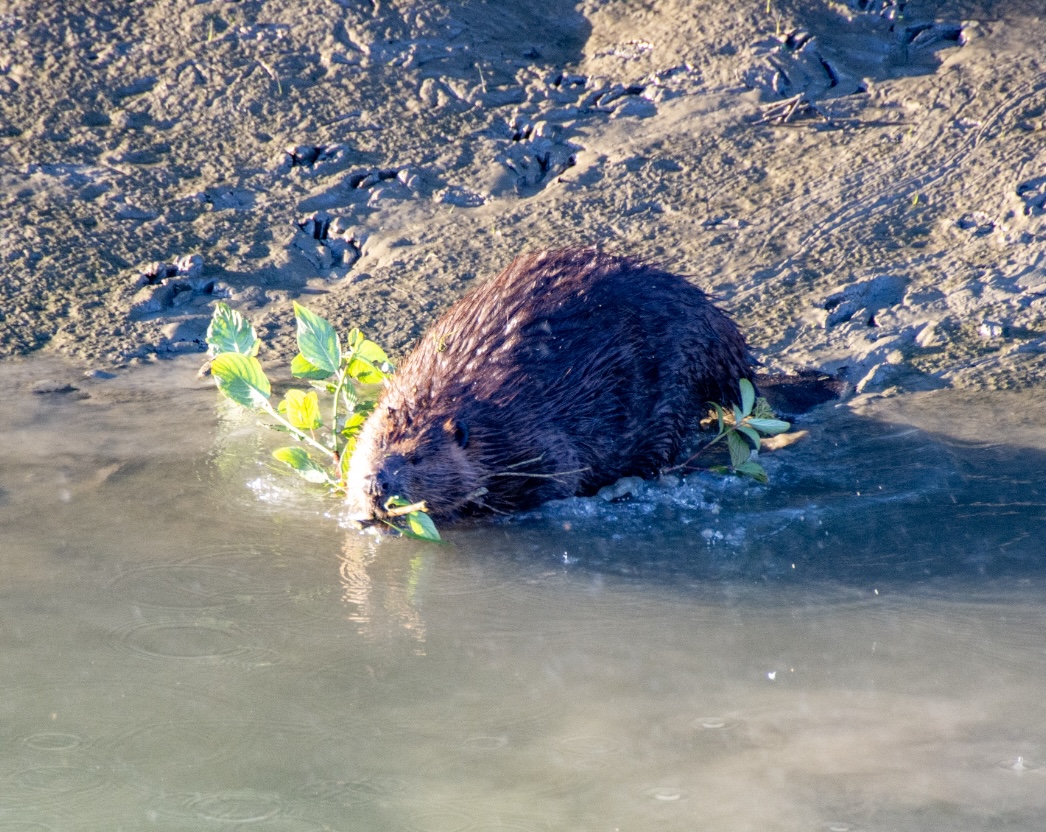 Drought and wildfire have become the rule rather than the exception and that is bad news for wildlife, for fish, and for British Columbians who rely on healthy watersheds. …over the past couple of decades we drained wetlands, straightened streams, logged forests, built highways, and ripped millions of beavers from the landscape. The result is dry forests, destructive fire seasons, and choking smoke … every summer. Dry riverbeds are unable to support salmon populations, or any wildlife for that matter. A dewatered landscape is a towering forest of matchsticks waiting to burn. … So, how do we get from here to there? Fortunately, some of the answers are simple, natural, and inexpensive. …Prescribed and cultural burning helps restore native grassland and shrub-steppe ecosystems providing improved forage for large mammals. …BCWF’s 10,000 Wetlands Project has recently installed more than 100 beaver dam analogues and dozens of post-assisted log structures…
Drought and wildfire have become the rule rather than the exception and that is bad news for wildlife, for fish, and for British Columbians who rely on healthy watersheds. …over the past couple of decades we drained wetlands, straightened streams, logged forests, built highways, and ripped millions of beavers from the landscape. The result is dry forests, destructive fire seasons, and choking smoke … every summer. Dry riverbeds are unable to support salmon populations, or any wildlife for that matter. A dewatered landscape is a towering forest of matchsticks waiting to burn. … So, how do we get from here to there? Fortunately, some of the answers are simple, natural, and inexpensive. …Prescribed and cultural burning helps restore native grassland and shrub-steppe ecosystems providing improved forage for large mammals. …BCWF’s 10,000 Wetlands Project has recently installed more than 100 beaver dam analogues and dozens of post-assisted log structures… The Osoyoos Indian Band is kicking off its first commercial thinning silviculture treatment via Siya Forestry. In the project 28 kilometres northeast of Oliver, select trees will be harvested while the strongest will remain left to grow in the OIB First Nations woodland licence area. …Siya Forestry, the OIB-owned new company, said it aims to care for the land through stewardship, balance, and responsibility. “This is a great pilot project and hopefully it will lead to a bigger program within the Osoyoos Indian Band’s traditional territory,” said Luke Robertson, Siya Forestry, operations supervisor, in the press release.
The Osoyoos Indian Band is kicking off its first commercial thinning silviculture treatment via Siya Forestry. In the project 28 kilometres northeast of Oliver, select trees will be harvested while the strongest will remain left to grow in the OIB First Nations woodland licence area. …Siya Forestry, the OIB-owned new company, said it aims to care for the land through stewardship, balance, and responsibility. “This is a great pilot project and hopefully it will lead to a bigger program within the Osoyoos Indian Band’s traditional territory,” said Luke Robertson, Siya Forestry, operations supervisor, in the press release.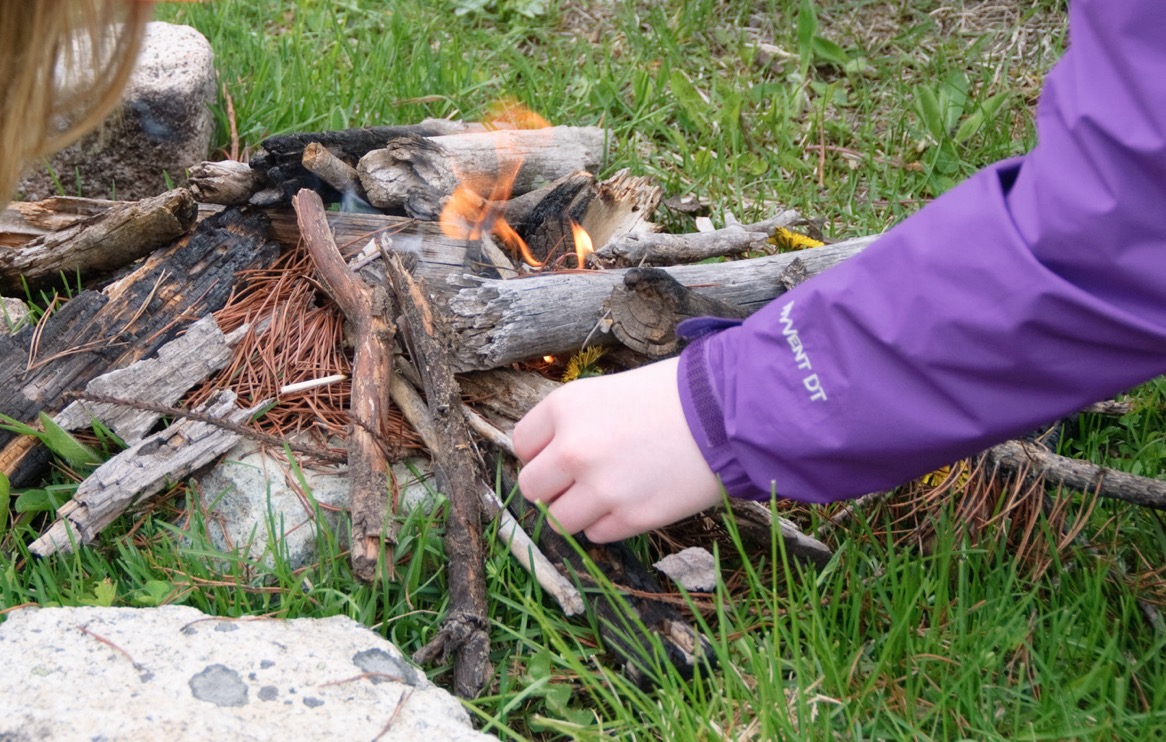 The Coastal Fire Centre is lifting the campfire ban for the Campbell River, North Island and Sunshine Coast forest districts as of Sept. 17 at noon. Due to declining fire danger ratings on the northern part of Vancouver Island, the Province has chosen to re-allow campfires and other small fires in the area. Campfires will remain prohibited for the rest of the Coastal Fire Centre, with the exception of the Haida Gwaii Forest District. The activities that will be allowed also include the use of sky lanterns, wood-fired hot tubs, pizza ovens and other devices that are not vented through a flue or are incorporated into buildings. Category 2 and 3 open fires remain prohibited throughout the Coastal Fire Centre, which includes backyard burning, industrial burning, fireworks, burn barrels and burn cages. These restrictions will remain in place until 12:00 (noon), PDT, on Friday October 31, 2025, or until the order is rescinded.
The Coastal Fire Centre is lifting the campfire ban for the Campbell River, North Island and Sunshine Coast forest districts as of Sept. 17 at noon. Due to declining fire danger ratings on the northern part of Vancouver Island, the Province has chosen to re-allow campfires and other small fires in the area. Campfires will remain prohibited for the rest of the Coastal Fire Centre, with the exception of the Haida Gwaii Forest District. The activities that will be allowed also include the use of sky lanterns, wood-fired hot tubs, pizza ovens and other devices that are not vented through a flue or are incorporated into buildings. Category 2 and 3 open fires remain prohibited throughout the Coastal Fire Centre, which includes backyard burning, industrial burning, fireworks, burn barrels and burn cages. These restrictions will remain in place until 12:00 (noon), PDT, on Friday October 31, 2025, or until the order is rescinded.
 First Nations in the North Cowichan region on Vancouver Island say a motion by the municipality is undermining collaborative efforts on the future of logging in the region’s forest reserve. …Cindy Daniels, chief of Cowichan Tribes, said the move by the council “undermines the collaborative nature” of work to date on a joint plan for the forest. …The North Cowichan council has been in discussions for a collaborative framework with Quw’utsun Nation since 2021 and announced a commitment to establish a co-management strategy for the forest reserve in April 2024. …Gary Merkel, director of the Centre for Indigenous Land Stewardship at UBC…. “It’s a little bit ahead of itself that motion, but not too far. I mean, they haven’t said ‘we’re just going to go and log,’ they’ve allowed the possibility”. …”We are going to get a staff report outlining some of the implications and next steps,” North Cowichan Mayor Rob Douglas said.
First Nations in the North Cowichan region on Vancouver Island say a motion by the municipality is undermining collaborative efforts on the future of logging in the region’s forest reserve. …Cindy Daniels, chief of Cowichan Tribes, said the move by the council “undermines the collaborative nature” of work to date on a joint plan for the forest. …The North Cowichan council has been in discussions for a collaborative framework with Quw’utsun Nation since 2021 and announced a commitment to establish a co-management strategy for the forest reserve in April 2024. …Gary Merkel, director of the Centre for Indigenous Land Stewardship at UBC…. “It’s a little bit ahead of itself that motion, but not too far. I mean, they haven’t said ‘we’re just going to go and log,’ they’ve allowed the possibility”. …”We are going to get a staff report outlining some of the implications and next steps,” North Cowichan Mayor Rob Douglas said.
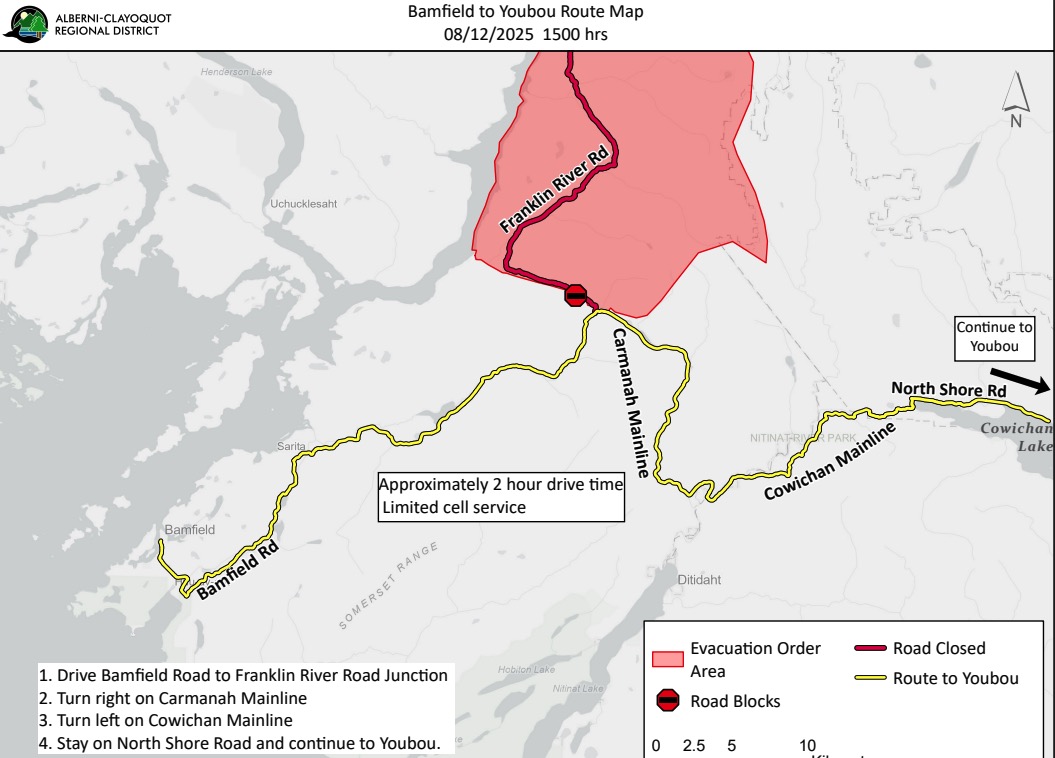 The fire-ravaged Bamfield Main Road, which connects Bamfield and several First Nation communities to Port Alberni, will reopen by the end of October, the Transportation Ministry announced. The ministry said temporary closures could still occur, however, during periods of heavy rain and strong winds. It said a geotechnical assessment to identify hazards, and assessments of the stability of trees are ongoing. Based on those findings, thresholds are being established for wind and rain events that will trigger increased patrols of Bamfield Main and potentially closures. A weather station and closure gates will be installed in the coming weeks, according to the ministry, which is leading efforts to reopen the road with Mosaic Forest Management, the company that oversees the affected stretch. …Ditidaht Nation Chief Judi Thomas said she suspects the Alberni-Clayoquot Regional District, Huu-ay-aht First Nation and Mosaic and Bamfield would be more than happy to support a provincial paved alternate route.
The fire-ravaged Bamfield Main Road, which connects Bamfield and several First Nation communities to Port Alberni, will reopen by the end of October, the Transportation Ministry announced. The ministry said temporary closures could still occur, however, during periods of heavy rain and strong winds. It said a geotechnical assessment to identify hazards, and assessments of the stability of trees are ongoing. Based on those findings, thresholds are being established for wind and rain events that will trigger increased patrols of Bamfield Main and potentially closures. A weather station and closure gates will be installed in the coming weeks, according to the ministry, which is leading efforts to reopen the road with Mosaic Forest Management, the company that oversees the affected stretch. …Ditidaht Nation Chief Judi Thomas said she suspects the Alberni-Clayoquot Regional District, Huu-ay-aht First Nation and Mosaic and Bamfield would be more than happy to support a provincial paved alternate route.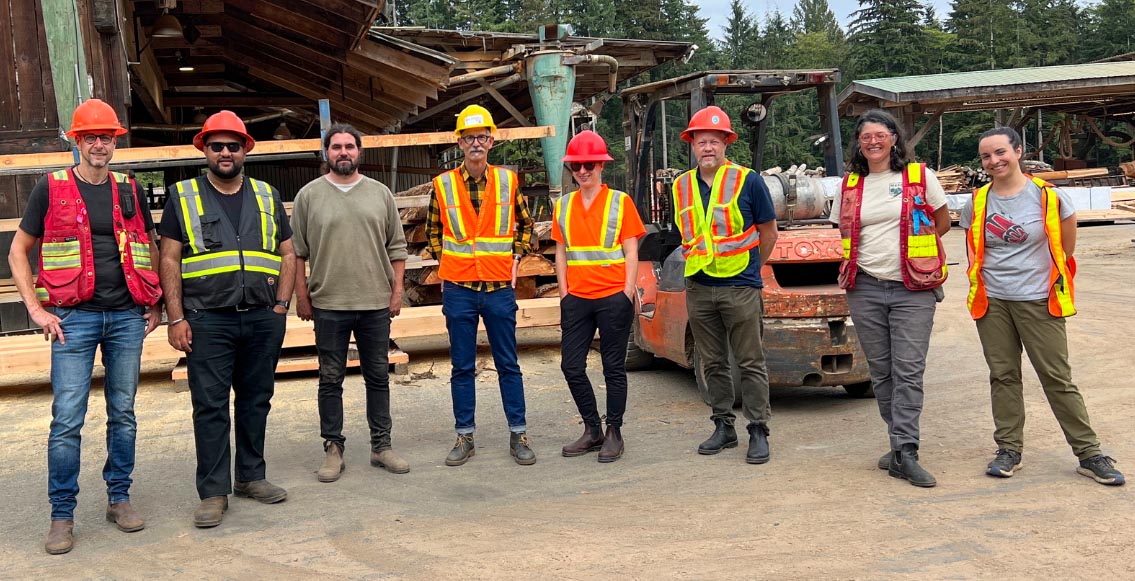 On September 11, 2025, UBC’s Faculty of Forestry welcomed British Columbia’s Minister of Forests, Ravi Parmar, to the Malcolm Knapp Research Forest (MKRF) to witness the critical work being done to advance sustainable forest management and educate the next generation of foresters. The tour, led by Dr. Dominik Roeser, Associate Dean of Research Forests and Community Outreach, and joined by Dr. Robert Kozak, Professor and Dean of the Faculty of Forestry and Hélène Marcoux, Malcolm Knapp Research Forest Manager, provided an important opportunity to showcase MKRF’s role in bridging scientific research, education and practical forest management. Minister Parmar’s visit included important conversations focused on forest stewardship and the role research plays, not just in understanding forests, but also in driving innovation, education, and creating future opportunities. Minister Parmar was able to see firsthand the vital research taking place to support both industry and government, and the advancement of sustainable forest management practices in British Columbia.
On September 11, 2025, UBC’s Faculty of Forestry welcomed British Columbia’s Minister of Forests, Ravi Parmar, to the Malcolm Knapp Research Forest (MKRF) to witness the critical work being done to advance sustainable forest management and educate the next generation of foresters. The tour, led by Dr. Dominik Roeser, Associate Dean of Research Forests and Community Outreach, and joined by Dr. Robert Kozak, Professor and Dean of the Faculty of Forestry and Hélène Marcoux, Malcolm Knapp Research Forest Manager, provided an important opportunity to showcase MKRF’s role in bridging scientific research, education and practical forest management. Minister Parmar’s visit included important conversations focused on forest stewardship and the role research plays, not just in understanding forests, but also in driving innovation, education, and creating future opportunities. Minister Parmar was able to see firsthand the vital research taking place to support both industry and government, and the advancement of sustainable forest management practices in British Columbia. The ancient forests near Fairy Creek, where the largest act of civil disobedience in Canadian history took place in 2021, have been fairly silent for nearly four years. But as logging in Vancouver Island’s old-growth forests picks up, protesters have returned to protect these ancient trees. On Friday, BC Supreme Court judge Amy Francis approved an injunction requested by Tsawak-qin Forestry Inc.—co-owned by Western Forest Products and the Huu-ay-aht First Nations—after two days of hearings. Those named in the injunction—including Elder Bill Jones…are banned from blocking the logging company’s access to old-growth forests in the Tree Farm License 44 area. …The removal of the sculpture and the people protesting could happen at any time. Today, blockaders at Cougar Camp—named for the sculpture blocking the logging road—said they were ready and waiting to be arrested while protecting Upper Walbran.
The ancient forests near Fairy Creek, where the largest act of civil disobedience in Canadian history took place in 2021, have been fairly silent for nearly four years. But as logging in Vancouver Island’s old-growth forests picks up, protesters have returned to protect these ancient trees. On Friday, BC Supreme Court judge Amy Francis approved an injunction requested by Tsawak-qin Forestry Inc.—co-owned by Western Forest Products and the Huu-ay-aht First Nations—after two days of hearings. Those named in the injunction—including Elder Bill Jones…are banned from blocking the logging company’s access to old-growth forests in the Tree Farm License 44 area. …The removal of the sculpture and the people protesting could happen at any time. Today, blockaders at Cougar Camp—named for the sculpture blocking the logging road—said they were ready and waiting to be arrested while protecting Upper Walbran.  Zoom Presentation
Zoom Presentation 


 A B.C. Supreme Court justice has ordered a group of people blocking a logging road in the Walbran Valley on southern Vancouver Island to stop. The decision to grant an injunction to Tsawak-qin Forestry Limited Partnership, a joint partnership between the Huu-ay-aht First Nations and Western Forest Products, alongside an enforcement order is expected to set the stage for the RCMP to remove people from the area. This fight over British Columbia’s old-growth forests comes four years after the start of the historic Fairy Creek protests, where more than 1,100 people were arrested. The Walbran Valley blockade began in late August and has prevented a logging company from working and accessing tools, equipment and vehicles on the other side of the blockade. Pacheedaht Elder Bill Jones, who was at the forefront of the Fairy Creek protests, is one of the parties named in the court filing, and the only person to respond to the application.
A B.C. Supreme Court justice has ordered a group of people blocking a logging road in the Walbran Valley on southern Vancouver Island to stop. The decision to grant an injunction to Tsawak-qin Forestry Limited Partnership, a joint partnership between the Huu-ay-aht First Nations and Western Forest Products, alongside an enforcement order is expected to set the stage for the RCMP to remove people from the area. This fight over British Columbia’s old-growth forests comes four years after the start of the historic Fairy Creek protests, where more than 1,100 people were arrested. The Walbran Valley blockade began in late August and has prevented a logging company from working and accessing tools, equipment and vehicles on the other side of the blockade. Pacheedaht Elder Bill Jones, who was at the forefront of the Fairy Creek protests, is one of the parties named in the court filing, and the only person to respond to the application.  Researchers from Trent University are immersing themselves in forests and streams in northwestern Ontario to understand how forestry practices and climate change affect brook trout populations and freshwater ecosystems. The team is working in the Walkinshaw and Wolf watersheds, northeast of Thunder Bay. They are focusing on headwater streams, which are small rivers that feed larger waterways across the Great Lakes. “Northern freshwater ecosystems are currently experiencing major disturbances, two of which are forest harvest and climate change. One of the effects of climate change is an increase in water temperatures. And the consequences of these predicted increased temperatures on the stream ecosystem are still unclear,” said PhD student Celeste Milli, who is leading the fieldwork. …Milli said the research could help inform science-based policy decisions in Canada’s northern forests, ensuring that both forest ecosystems and freshwater resources remain resilient in a changing climate.
Researchers from Trent University are immersing themselves in forests and streams in northwestern Ontario to understand how forestry practices and climate change affect brook trout populations and freshwater ecosystems. The team is working in the Walkinshaw and Wolf watersheds, northeast of Thunder Bay. They are focusing on headwater streams, which are small rivers that feed larger waterways across the Great Lakes. “Northern freshwater ecosystems are currently experiencing major disturbances, two of which are forest harvest and climate change. One of the effects of climate change is an increase in water temperatures. And the consequences of these predicted increased temperatures on the stream ecosystem are still unclear,” said PhD student Celeste Milli, who is leading the fieldwork. …Milli said the research could help inform science-based policy decisions in Canada’s northern forests, ensuring that both forest ecosystems and freshwater resources remain resilient in a changing climate.
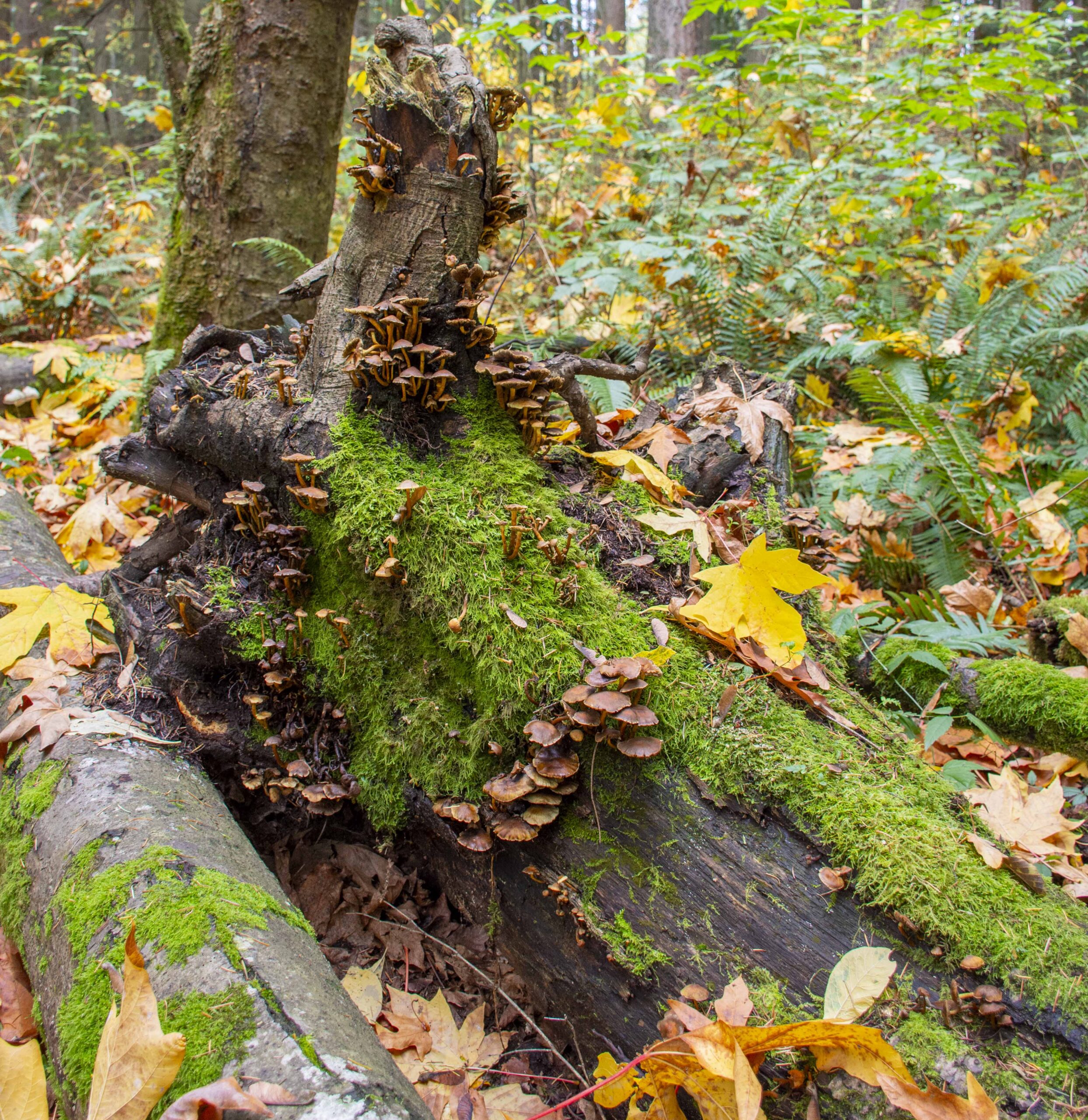 One of the great challenges of ecology is to understand the factors that maintain, or undermine, diversity in ecosystems, researchers write in a
One of the great challenges of ecology is to understand the factors that maintain, or undermine, diversity in ecosystems, researchers write in a 

 US Secretary of Agriculture Rollins issued a
US Secretary of Agriculture Rollins issued a 
 The U.S. Department of Agriculture announced this summer it was moving to rescind the Roadless Rule, a 2001 law that protects large swaths of National Forest land from development. That includes more than half of the Tongass National Forest, where Juneau is located. On Saturday, more than 100 people gathered in the state capital to protest the move. …Alaska’s Congressional delegation unanimously supports the rollback of the Roadless Rule. U.S. Sen. Lisa Murkowski has said that most of the Tongass would still be protected without it — the parts of the forest that are already designated as wilderness. …But protesters say Alaskans have more to lose in risks to the land and waterways than what they have to gain through further development. Lingít elders and fishing and tourism industry experts took the mic Saturday to deliver a message: the Roadless Rule should be left alone.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture announced this summer it was moving to rescind the Roadless Rule, a 2001 law that protects large swaths of National Forest land from development. That includes more than half of the Tongass National Forest, where Juneau is located. On Saturday, more than 100 people gathered in the state capital to protest the move. …Alaska’s Congressional delegation unanimously supports the rollback of the Roadless Rule. U.S. Sen. Lisa Murkowski has said that most of the Tongass would still be protected without it — the parts of the forest that are already designated as wilderness. …But protesters say Alaskans have more to lose in risks to the land and waterways than what they have to gain through further development. Lingít elders and fishing and tourism industry experts took the mic Saturday to deliver a message: the Roadless Rule should be left alone.
 The Trump administration is looking to finalize a repeal of a longstanding Roadless Rule with a public comment period that
The Trump administration is looking to finalize a repeal of a longstanding Roadless Rule with a public comment period that 

 The European Commission has announced dates for virtual training sessions on the EUDR Information System, open to all interested parties. These sessions provide guidance on submitting due diligence statements under the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). While these sessions are available to all, WPAC anticipates that most of our members will meet their EUDR obligations through the Sustainable Biomass Program (SBP) system, which we helped to develop. EUDR establishes robust requirements for traceability, due diligence, and risk mitigation. SBP has developed a voluntary EUDR module integrated into its Data Transfer System (DTS), helping Certificate Holders prepare now for compliance ahead of the December 2025 implementation deadline. …Learn more about
The European Commission has announced dates for virtual training sessions on the EUDR Information System, open to all interested parties. These sessions provide guidance on submitting due diligence statements under the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR). While these sessions are available to all, WPAC anticipates that most of our members will meet their EUDR obligations through the Sustainable Biomass Program (SBP) system, which we helped to develop. EUDR establishes robust requirements for traceability, due diligence, and risk mitigation. SBP has developed a voluntary EUDR module integrated into its Data Transfer System (DTS), helping Certificate Holders prepare now for compliance ahead of the December 2025 implementation deadline. …Learn more about  Austria’s softwood sector may face a production decline of up to 10% if the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) takes effect in its current form at the end of the year. The regulation requires full traceability of wood products across the entire supply chain, which industry representatives say is unworkable according to Markus Schmölzer of the Austrian Sawmill Association. Although the sector expects a 2% production increase in 2025, the EUDR poses a direct threat to the entire wood value chain. A decline in softwood production would affect manufacturers of building components, furniture, panel boards, paper, and pellet products, especially during winter months. …The Austrian industry urges the EU to either suspend the regulation entirely or revise it through an “Omnibus” legislative package aimed at reducing bureaucracy. …While supporting the goal of halting global deforestation, the sector proposes targeted monitoring for high-risk regions and exemptions for low-risk countries such as Austria.
Austria’s softwood sector may face a production decline of up to 10% if the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) takes effect in its current form at the end of the year. The regulation requires full traceability of wood products across the entire supply chain, which industry representatives say is unworkable according to Markus Schmölzer of the Austrian Sawmill Association. Although the sector expects a 2% production increase in 2025, the EUDR poses a direct threat to the entire wood value chain. A decline in softwood production would affect manufacturers of building components, furniture, panel boards, paper, and pellet products, especially during winter months. …The Austrian industry urges the EU to either suspend the regulation entirely or revise it through an “Omnibus” legislative package aimed at reducing bureaucracy. …While supporting the goal of halting global deforestation, the sector proposes targeted monitoring for high-risk regions and exemptions for low-risk countries such as Austria. The European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), one of the world’s most comprehensive legislations to curb tropical deforestation, will take effect at the end of December 2025. Since its adoption in 2023, debates over its implementation and effectiveness have been loud and persistent. Some claim the requirements are unclear or impossible to meet, especially for smallholders, while others fear the regulation will disrupt trade or place heavy burdens on businesses. …Despite the challenges, governments, companies and smallholders worldwide are showing that EUDR compliance is not only possible — it is already underway. Building on our previous analysis of why the EUDR is a necessary regulation to tackle deforestation linked to commodity supply chains, this article focuses on the practicality of compliance and highlights concrete steps being taken to prepare. …Guidance from EU national enforcement authorities, such as the Netherlands’ report, show that compliance with the EUDR is not rocket science.
The European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), one of the world’s most comprehensive legislations to curb tropical deforestation, will take effect at the end of December 2025. Since its adoption in 2023, debates over its implementation and effectiveness have been loud and persistent. Some claim the requirements are unclear or impossible to meet, especially for smallholders, while others fear the regulation will disrupt trade or place heavy burdens on businesses. …Despite the challenges, governments, companies and smallholders worldwide are showing that EUDR compliance is not only possible — it is already underway. Building on our previous analysis of why the EUDR is a necessary regulation to tackle deforestation linked to commodity supply chains, this article focuses on the practicality of compliance and highlights concrete steps being taken to prepare. …Guidance from EU national enforcement authorities, such as the Netherlands’ report, show that compliance with the EUDR is not rocket science.