 The US plans to revisit its climate change laws, and rollback some Environmental Protection Agency regulations. In related news: the US Supreme Court declines to hear red-state climate lawsuits; the US push for more logging is said to put climate at risk; and Sweden risks missing its carbon neutrality goals.
The US plans to revisit its climate change laws, and rollback some Environmental Protection Agency regulations. In related news: the US Supreme Court declines to hear red-state climate lawsuits; the US push for more logging is said to put climate at risk; and Sweden risks missing its carbon neutrality goals.
In US tariff news: the European Union responded ‘proportionately’ to Trump’s 25% tariff on steel and aluminum—Trump escalated with 200% on alcohol; Canadian officials are meeting with Commerce Secretary Lutnik today; and Vietnam wood exporters are tariff-wary. Meanwhile: US inflation eased in February; tariff uncertainty is slowing BC housing; and Conifex Timber reported a Q4, 2024 loss of $29.8 million.
In Wildfire news: Musk’s layoffs are said to undermine wildfire protection; what old trees can teach us about modern wildfires; a New Yorker feature on the Felling of the US Forest Service; and South Carolina forestry chief says the state needs to up its prevention efforts.
Finally, Canada’s Forest Owners—good neighbours in bad times.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor
 In the face of the unjustified economic attack by the leader of our U.S. neighbours, Canadian Forest Owners (CFO) stand fast as your good neighbours, who are committed to sustainable forest management for resilient, thriving communities coast to coast. Last week’s announced tariffs on Canada’s wood products by U.S. President Trump will harm not just forest landowners but local mills, workers and their families, communities, especially rural ones, and customers on both sides of the border. Together we stand firm with our colleagues in industry and the federal and provincial governments to strengthen the Canadian forest sector and work to bolster family woodlots and the economies of rural communities.
In the face of the unjustified economic attack by the leader of our U.S. neighbours, Canadian Forest Owners (CFO) stand fast as your good neighbours, who are committed to sustainable forest management for resilient, thriving communities coast to coast. Last week’s announced tariffs on Canada’s wood products by U.S. President Trump will harm not just forest landowners but local mills, workers and their families, communities, especially rural ones, and customers on both sides of the border. Together we stand firm with our colleagues in industry and the federal and provincial governments to strengthen the Canadian forest sector and work to bolster family woodlots and the economies of rural communities. WASHINGTON — Canadian officials are set to meet with the U.S. commerce secretary in Washington today — days after a dust-up with U.S. President Donald Trump that ended with Ontario pausing its surcharge on electricity exports to the United States. Finance Minister Dominic LeBlanc, Ambassador to the U.S. Kirsten Hillman and Ontario Premier Doug Ford are meeting with Howard Lutnick, and Ford says his goal for the meeting is to get a coherent sense of the Trump administration’s plans for tariffs. …Elsewhere in the American capital, Trump’s choice for the next U.S ambassador to Canada is set to take questions today as the relationship between the two countries is strained by tariffs and threats of annexation. Pete Hoekstra, a former Michigan congressman, is scheduled to appear before the Senate Foreign Relations Committee for a nomination hearing.
WASHINGTON — Canadian officials are set to meet with the U.S. commerce secretary in Washington today — days after a dust-up with U.S. President Donald Trump that ended with Ontario pausing its surcharge on electricity exports to the United States. Finance Minister Dominic LeBlanc, Ambassador to the U.S. Kirsten Hillman and Ontario Premier Doug Ford are meeting with Howard Lutnick, and Ford says his goal for the meeting is to get a coherent sense of the Trump administration’s plans for tariffs. …Elsewhere in the American capital, Trump’s choice for the next U.S ambassador to Canada is set to take questions today as the relationship between the two countries is strained by tariffs and threats of annexation. Pete Hoekstra, a former Michigan congressman, is scheduled to appear before the Senate Foreign Relations Committee for a nomination hearing.



 VANCOUVER — Conifex Timber reported results for the fourth quarter and year ended December 31, 2024. EBITDA from continuing operations was negative $2.1 million for the quarter and negative $13.6 million for the year, compared to EBITDA of negative $3.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2023 and negative $25.8 million for the year. Net loss was $29.8 million for the quarter while it was $11.8 million for the full year. …While there are signs that the macro-environment for the lumber industry is starting to improve, Conifex continues to review its options to improve liquidity. …Since January 6, 2025, we have been operating our sawmill complex on a two-shift basis and capturing the dual benefits of higher shipments and lower unit costs that a two-shift operation provides over a single-shift configuration.
VANCOUVER — Conifex Timber reported results for the fourth quarter and year ended December 31, 2024. EBITDA from continuing operations was negative $2.1 million for the quarter and negative $13.6 million for the year, compared to EBITDA of negative $3.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2023 and negative $25.8 million for the year. Net loss was $29.8 million for the quarter while it was $11.8 million for the full year. …While there are signs that the macro-environment for the lumber industry is starting to improve, Conifex continues to review its options to improve liquidity. …Since January 6, 2025, we have been operating our sawmill complex on a two-shift basis and capturing the dual benefits of higher shipments and lower unit costs that a two-shift operation provides over a single-shift configuration. 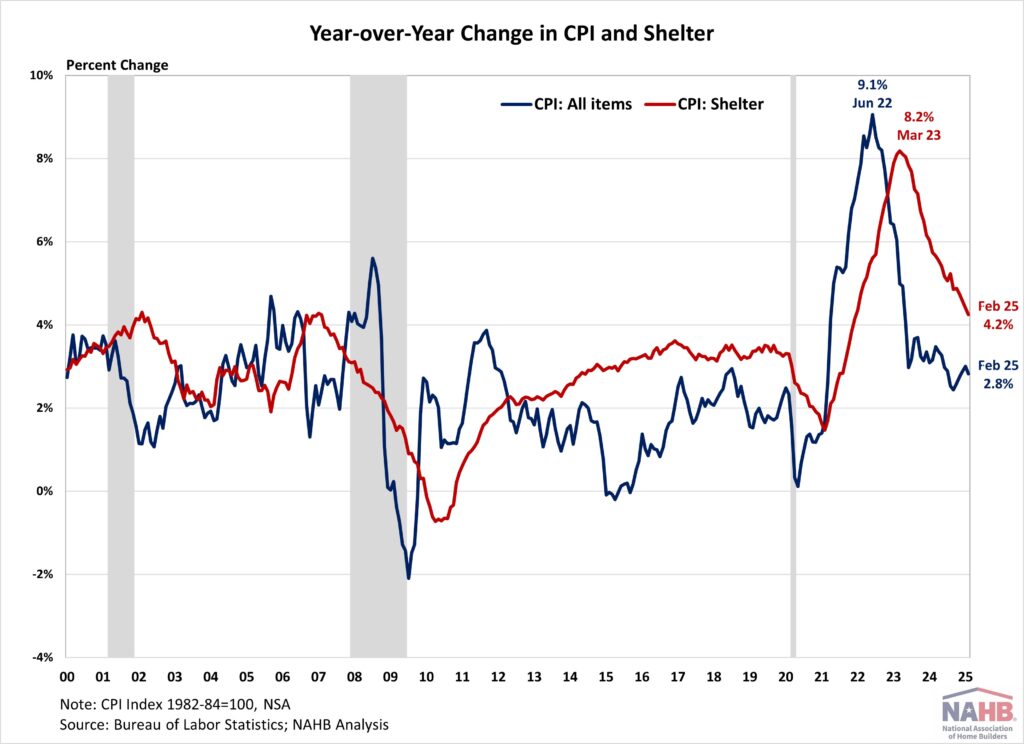
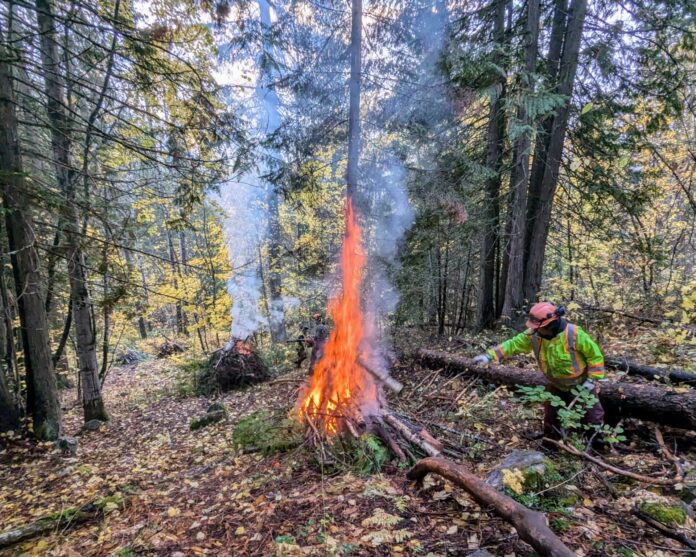
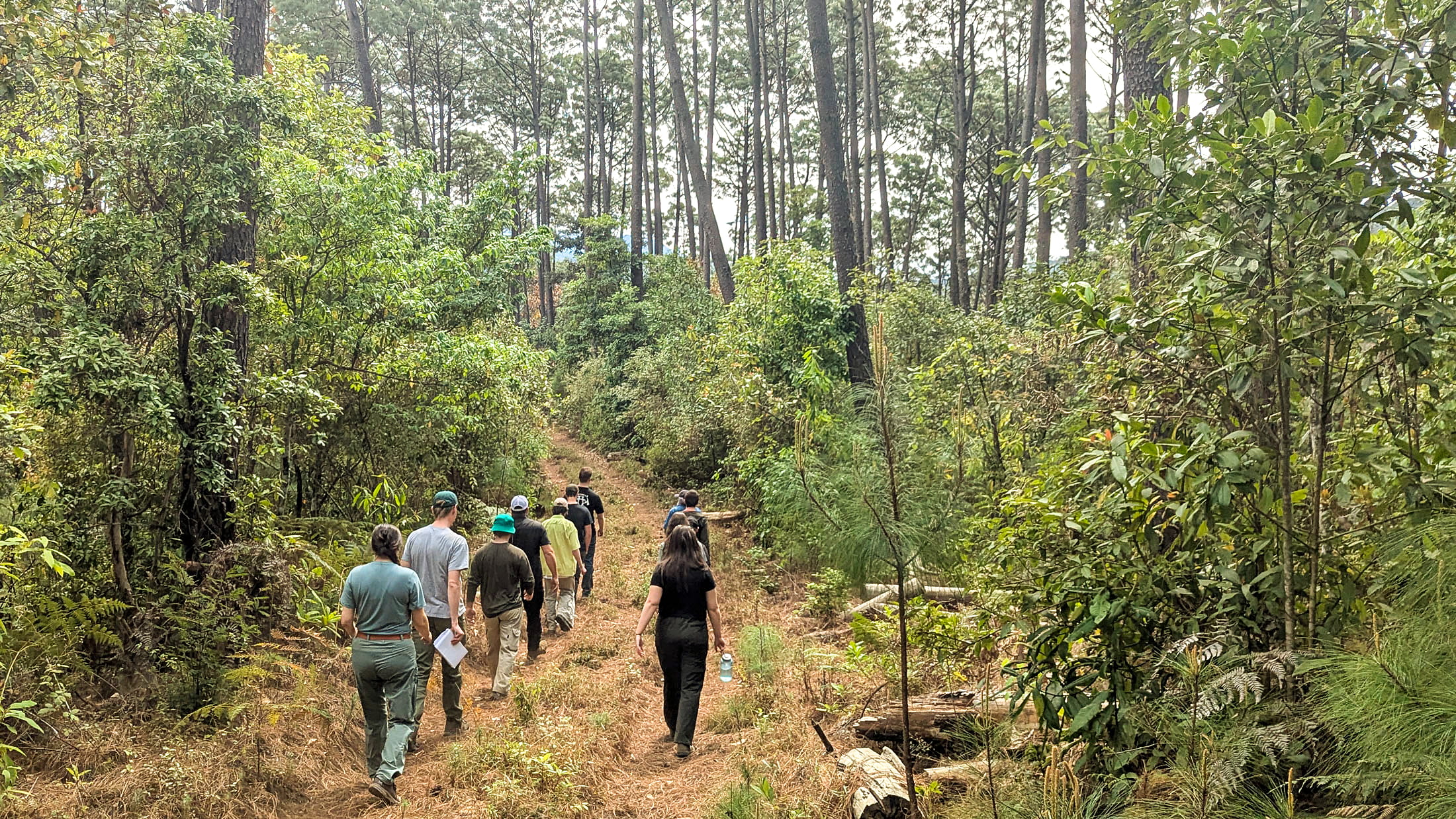





 As forestry practices evolve, the intersection of conservation, Indigenous consultation, third-party certification, and workforce development is central to the future of the industry. The “Breaking New Ground” panel at the 2025 COFI Convention will explore how innovative partnerships and collaborative approaches can balance ecological stewardship with economic opportunity. Panelists will share insights on advancing reconciliation through meaningful consultation, supporting the next generation of forestry professionals, and ensuring sustainable practices through conservation financing and certification. Panelists: Lennard Joe, CEO, BC First Nations Forestry Council; Michael Reid, BC Program Director, Nature United; Kathy Abusow, President & CEO, Sustainable Forestry Initiative; and Aspen Dudzic, Director of Communications, Alberta Forest Products Association & “Forestry Together” Initiative. Moderator: Jason Fisher, Executive Director, Forest Enhancement Society of BC (FESBC). Join us for a forward-looking discussion that brings together diverse perspectives on how BC’s working forests can thrive while meeting environmental and social responsibilities.
As forestry practices evolve, the intersection of conservation, Indigenous consultation, third-party certification, and workforce development is central to the future of the industry. The “Breaking New Ground” panel at the 2025 COFI Convention will explore how innovative partnerships and collaborative approaches can balance ecological stewardship with economic opportunity. Panelists will share insights on advancing reconciliation through meaningful consultation, supporting the next generation of forestry professionals, and ensuring sustainable practices through conservation financing and certification. Panelists: Lennard Joe, CEO, BC First Nations Forestry Council; Michael Reid, BC Program Director, Nature United; Kathy Abusow, President & CEO, Sustainable Forestry Initiative; and Aspen Dudzic, Director of Communications, Alberta Forest Products Association & “Forestry Together” Initiative. Moderator: Jason Fisher, Executive Director, Forest Enhancement Society of BC (FESBC). Join us for a forward-looking discussion that brings together diverse perspectives on how BC’s working forests can thrive while meeting environmental and social responsibilities. Simcoe County forests are growing — and not just up. Councillors got a brief update Tuesday on the county’s forest management activities last year, as well as finding out what the future holds as the county moves into its 103rd year operating the local forest system… The fact the county has been managing these forests for more than a century is “quite exceptional,” Graeme Davis, who works as a forester for the county, said during Tuesday’s committee of the whole meeting… Of particular note is that the county forests are very active and working forests, Davis added. While harvesting does play an important role, Davis said it’s also important to note that they are about much more than forest harvesting — they also provide “incredible” recreational uses.
Simcoe County forests are growing — and not just up. Councillors got a brief update Tuesday on the county’s forest management activities last year, as well as finding out what the future holds as the county moves into its 103rd year operating the local forest system… The fact the county has been managing these forests for more than a century is “quite exceptional,” Graeme Davis, who works as a forester for the county, said during Tuesday’s committee of the whole meeting… Of particular note is that the county forests are very active and working forests, Davis added. While harvesting does play an important role, Davis said it’s also important to note that they are about much more than forest harvesting — they also provide “incredible” recreational uses. …When the Terrace Bay pulp mill opened, an effluent canal was built to connect with Blackbird Creek — a convenient way to send its liquid waste into Lake Superior. It wasn’t until the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement was signed in 1972 that researchers started to focus on the impact industry was having on the Great Lakes. Following that agreement, in 1987 Jackfish Bay and 42 other sites across the Great Lakes in Canada and the U.S. were officially listed as areas of concern. New guidelines were created for discharging effluent into the Great Lakes and their tributaries, and remedial action plans were proposed. But the use of Blackbird Creek as an effluent canal was grandfathered into the Terrace Bay mill’s operations. When it first opened, the mill owner was entitled to choose where to monitor the receiving environment for its effluent. They chose Moberly Bay, the smaller bay at the mouth of Blackbird Creek, on Jackfish Bay.
…When the Terrace Bay pulp mill opened, an effluent canal was built to connect with Blackbird Creek — a convenient way to send its liquid waste into Lake Superior. It wasn’t until the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement was signed in 1972 that researchers started to focus on the impact industry was having on the Great Lakes. Following that agreement, in 1987 Jackfish Bay and 42 other sites across the Great Lakes in Canada and the U.S. were officially listed as areas of concern. New guidelines were created for discharging effluent into the Great Lakes and their tributaries, and remedial action plans were proposed. But the use of Blackbird Creek as an effluent canal was grandfathered into the Terrace Bay mill’s operations. When it first opened, the mill owner was entitled to choose where to monitor the receiving environment for its effluent. They chose Moberly Bay, the smaller bay at the mouth of Blackbird Creek, on Jackfish Bay.  What are Musk, Trump and the congressional right really after? Anyone who works in land management knows these agencies have long gone underfunded and unsupported by Republicans, rendering them less and less effective as the demands on them grow ever more pressing. Now this bloodletting is accelerating, and soon it will be time to go for the throat. As these agencies flounder, turning their lands over to private administration — to timber, mineral and oil extraction or to private ownership and development — will begin to seem logical and even appealing. While sustainable logging can be a valuable forest management tool, research shows that when lands are managed primarily for resource extraction, they become less resilient to wildfire. This is a shortsighted, profit-driven turn toward a land-use model that is ultimately unsustainable. What will the public be left with? Will we still have places to hike, fish, hunt, dirt-bike and ski? Or will a new landlord be setting new rates?
What are Musk, Trump and the congressional right really after? Anyone who works in land management knows these agencies have long gone underfunded and unsupported by Republicans, rendering them less and less effective as the demands on them grow ever more pressing. Now this bloodletting is accelerating, and soon it will be time to go for the throat. As these agencies flounder, turning their lands over to private administration — to timber, mineral and oil extraction or to private ownership and development — will begin to seem logical and even appealing. While sustainable logging can be a valuable forest management tool, research shows that when lands are managed primarily for resource extraction, they become less resilient to wildfire. This is a shortsighted, profit-driven turn toward a land-use model that is ultimately unsustainable. What will the public be left with? Will we still have places to hike, fish, hunt, dirt-bike and ski? Or will a new landlord be setting new rates? With $2.6 billion in hurricane-recovery money on its way to the national forests of North Carolina, Jenifer Bunty, a US Forest Service disaster-recovery specialist, spent much of the week of February 10th working on a plan to start spending the money. Four months after Hurricane Helene, this meant deciding which bridges urgently needed to be rebuilt, which road repairs prioritized. …“The days of rule by unelected bureaucrats are over,” Donald Trump declared in his speech to Congress last week. For the White House, the firing of tens of thousands of federal workers like Bunty is evidence of “promises made, promises kept.” But for the Forest Service the loss of at least two thousand workers will make it harder to fight ever-worsening wildfires and storms across the country. …After the Trump cuts, a spokesperson for the USDA said that they didn’t include “operational firefighters,” a term Bunty had never heard.
With $2.6 billion in hurricane-recovery money on its way to the national forests of North Carolina, Jenifer Bunty, a US Forest Service disaster-recovery specialist, spent much of the week of February 10th working on a plan to start spending the money. Four months after Hurricane Helene, this meant deciding which bridges urgently needed to be rebuilt, which road repairs prioritized. …“The days of rule by unelected bureaucrats are over,” Donald Trump declared in his speech to Congress last week. For the White House, the firing of tens of thousands of federal workers like Bunty is evidence of “promises made, promises kept.” But for the Forest Service the loss of at least two thousand workers will make it harder to fight ever-worsening wildfires and storms across the country. …After the Trump cuts, a spokesperson for the USDA said that they didn’t include “operational firefighters,” a term Bunty had never heard. 
 Businesses, communities, and wildlife across a vast portion of western Washington, western Oregon, and northwestern California rely on healthy national forests. Since 1994, the Northwest Forest Plan (NWFP) has guided conservation, recreation, timber production, and other uses of these 19.2 million acres of species-rich and economically important lands and rivers, and now, as it does periodically, the U.S. Forest Service is updating the NWFP… The scientists and land managers who authored the original NWFP recognized the importance of drawing on the best available science. They also had the foresight to incorporate ways to monitor the forests and adjust management if their assumptions—for example, about the plan’s impact on nature and communities—proved wrong… The Forest Service is
Businesses, communities, and wildlife across a vast portion of western Washington, western Oregon, and northwestern California rely on healthy national forests. Since 1994, the Northwest Forest Plan (NWFP) has guided conservation, recreation, timber production, and other uses of these 19.2 million acres of species-rich and economically important lands and rivers, and now, as it does periodically, the U.S. Forest Service is updating the NWFP… The scientists and land managers who authored the original NWFP recognized the importance of drawing on the best available science. They also had the foresight to incorporate ways to monitor the forests and adjust management if their assumptions—for example, about the plan’s impact on nature and communities—proved wrong… The Forest Service is 
 HORRY COUNTY, S.C. — The
HORRY COUNTY, S.C. — The 
 Large, undisturbed forests are better for harboring biodiversity than fragmented landscapes, according to University of Michigan research. Ecologists agree that habitat loss and the fragmentation of forests reduces biodiversity in the remaining fragments. But ecologists don’t agree whether it’s better to focus on preserving many smaller, fragmented tracts of land or larger, continuous landscapes. The
Large, undisturbed forests are better for harboring biodiversity than fragmented landscapes, according to University of Michigan research. Ecologists agree that habitat loss and the fragmentation of forests reduces biodiversity in the remaining fragments. But ecologists don’t agree whether it’s better to focus on preserving many smaller, fragmented tracts of land or larger, continuous landscapes. The  In wild Tasmania there are trees whose direct ancestors lived with dinosaurs. Many of those alive today are thousands of years old, and some have been growing for ten millennia or more. They are mostly hard to reach, hidden in forest valleys or on remote mountains, survivors of human greed and fire.
In wild Tasmania there are trees whose direct ancestors lived with dinosaurs. Many of those alive today are thousands of years old, and some have been growing for ten millennia or more. They are mostly hard to reach, hidden in forest valleys or on remote mountains, survivors of human greed and fire. If forest fires burn organic matter, and biochar is created by burning of organic matter shouldn’t forest soils be full of biochar? Not exactly. There is a difference between the burnt product of wildfire and biochar. Forest fires do produce charcoal, but while both charcoal and biochar are types of pyrogenic carbon, they’re not quite the same thing… Forests in Alberta have been affected by the mountain pine beetle, leaving behind dead trees that act as easy fuel for fires. These dead, dry trees are extremely flammable. The Canadian government has looked into using these dead trees as biofuels and some companies do use them to create biochar. Another source of organic matter for biochar is the material removed from forests as part of fuel management… Both of these methods help manage wildfire and could potentially increase the carbon sequestration of forests if the resulting biochar was added back into the forest’s soil.
If forest fires burn organic matter, and biochar is created by burning of organic matter shouldn’t forest soils be full of biochar? Not exactly. There is a difference between the burnt product of wildfire and biochar. Forest fires do produce charcoal, but while both charcoal and biochar are types of pyrogenic carbon, they’re not quite the same thing… Forests in Alberta have been affected by the mountain pine beetle, leaving behind dead trees that act as easy fuel for fires. These dead, dry trees are extremely flammable. The Canadian government has looked into using these dead trees as biofuels and some companies do use them to create biochar. Another source of organic matter for biochar is the material removed from forests as part of fuel management… Both of these methods help manage wildfire and could potentially increase the carbon sequestration of forests if the resulting biochar was added back into the forest’s soil. Donald Trump’s administration is to reconsider the official finding that greenhouse gases are harmful to public health, a move that threatens to rip apart the foundation of the US’s climate laws, amid a stunning barrage of actions to weaken or repeal a host of pollution limits upon power plants, cars and waterways. Trump’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued an extraordinary cavalcade of pollution rule rollbacks on Wednesday, led by the announcement it would potentially scrap a landmark 2009 finding by the US government that planet-heating gases, such carbon dioxide, pose a threat to human health. The so-called endangerment finding, which followed a supreme court ruling that the EPA could regulate greenhouse gases, provides the underpinning for all rules aimed at cutting the pollution that scientists have unequivocally found is worsening the climate crisis.
Donald Trump’s administration is to reconsider the official finding that greenhouse gases are harmful to public health, a move that threatens to rip apart the foundation of the US’s climate laws, amid a stunning barrage of actions to weaken or repeal a host of pollution limits upon power plants, cars and waterways. Trump’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued an extraordinary cavalcade of pollution rule rollbacks on Wednesday, led by the announcement it would potentially scrap a landmark 2009 finding by the US government that planet-heating gases, such carbon dioxide, pose a threat to human health. The so-called endangerment finding, which followed a supreme court ruling that the EPA could regulate greenhouse gases, provides the underpinning for all rules aimed at cutting the pollution that scientists have unequivocally found is worsening the climate crisis. President Trump is pushing federal agencies to expand timber harvests… The U.S. Forest Service is already set to increase the number of trees it harvests to one of the highest levels since 2019, a result of Biden-era policies. But advocates argue that we need trees now more than ever and that this increase in timber harvest doesn’t make sense. The Forest Service is facing a lawsuit
President Trump is pushing federal agencies to expand timber harvests… The U.S. Forest Service is already set to increase the number of trees it harvests to one of the highest levels since 2019, a result of Biden-era policies. But advocates argue that we need trees now more than ever and that this increase in timber harvest doesn’t make sense. The Forest Service is facing a lawsuit  WASHINGTON — The Supreme Court on Monday rejected a lawsuit from Republican attorneys general in 19 states aimed at blocking climate change suits against the oil and gas industry from Democratic-led states. The justices acted on an unusual Republican effort to file suit in the Supreme Court over the Democratic states’ use of their own state courts to sue fossil fuel companies for deceiving the public about the risks of their products contributing to climate change. The Supreme Court typically hears only appeals, but the Constitution gives the court authority to hear original lawsuits states file against each other. Justices Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito said they would have allowed the lawsuit to proceed for now. The justices don’t have the discretion to reject the complaint at this stage, Thomas wrote in a dissent that did not deal with the merits of the claim.
WASHINGTON — The Supreme Court on Monday rejected a lawsuit from Republican attorneys general in 19 states aimed at blocking climate change suits against the oil and gas industry from Democratic-led states. The justices acted on an unusual Republican effort to file suit in the Supreme Court over the Democratic states’ use of their own state courts to sue fossil fuel companies for deceiving the public about the risks of their products contributing to climate change. The Supreme Court typically hears only appeals, but the Constitution gives the court authority to hear original lawsuits states file against each other. Justices Clarence Thomas and Samuel Alito said they would have allowed the lawsuit to proceed for now. The justices don’t have the discretion to reject the complaint at this stage, Thomas wrote in a dissent that did not deal with the merits of the claim. Denmark has long been praised for its transition to renewable energy, with renewable energy use rising from 6% in 1990 to 42.8% in 2022. However, behind this achievement lies an overdependence on woody biomass, which now accounts for up to 68% of its total renewable energy use. This growth has been sustained through direct and indirect subsidies, often exceeding those allocated to wind and solar energy. Denmark’s dependence on woody biomass is largely fuelled by imports from Estonia and Latvia. The country ranks among the largest, if not the largest, importer of woody biomass from the Baltic region, with 52% of its wood chips and pellets coming from these two nations. …Intensive logging is also devastating Estonian and Latvian bird populations.
Denmark has long been praised for its transition to renewable energy, with renewable energy use rising from 6% in 1990 to 42.8% in 2022. However, behind this achievement lies an overdependence on woody biomass, which now accounts for up to 68% of its total renewable energy use. This growth has been sustained through direct and indirect subsidies, often exceeding those allocated to wind and solar energy. Denmark’s dependence on woody biomass is largely fuelled by imports from Estonia and Latvia. The country ranks among the largest, if not the largest, importer of woody biomass from the Baltic region, with 52% of its wood chips and pellets coming from these two nations. …Intensive logging is also devastating Estonian and Latvian bird populations.  Sweden might fail to meet its and the EU’s carbon neutrality targets after recent environmental policy shifts, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) warned in a report published Wednesday. Long considered a champion in environmental protection and the fight against climate change, the Scandinavian country has set a goal of net zero emissions by 2045, five years ahead of the European Union’s target. But Sweden might not be able meet either of those goals, according to a review conducted by the OECD, a 38-member group of mostly developed nations. “Over the last decade, the country has cut its greenhouse gas emissions faster than the EU average,” the report said. “However, recent policy shifts, particularly in the transport sector, have put into question Sweden’s ability to meet EU and domestic climate targets.” …In January, the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) criticised Sweden for not adequately protecting primary and old-growth forests from logging.
Sweden might fail to meet its and the EU’s carbon neutrality targets after recent environmental policy shifts, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) warned in a report published Wednesday. Long considered a champion in environmental protection and the fight against climate change, the Scandinavian country has set a goal of net zero emissions by 2045, five years ahead of the European Union’s target. But Sweden might not be able meet either of those goals, according to a review conducted by the OECD, a 38-member group of mostly developed nations. “Over the last decade, the country has cut its greenhouse gas emissions faster than the EU average,” the report said. “However, recent policy shifts, particularly in the transport sector, have put into question Sweden’s ability to meet EU and domestic climate targets.” …In January, the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) criticised Sweden for not adequately protecting primary and old-growth forests from logging.