 US trade representative Jamieson Greer said any trade deal with Canada will include tariffs. In related news: President Trump makes a new case for tariffs; Canada launches program to retool the forest sector; the US Lumber Coalition pans BC’s stumpage deferral program; and Quebec scraps its annual royalty charge for sawmills. Meanwhile: Ontario starts building first of its kind mass timber bridge; Steelworkers ratify BC forestry agreement; International Paper downsizes in South Carolina; and Boise Cascade and BlueLinx report Q4 earnings.
US trade representative Jamieson Greer said any trade deal with Canada will include tariffs. In related news: President Trump makes a new case for tariffs; Canada launches program to retool the forest sector; the US Lumber Coalition pans BC’s stumpage deferral program; and Quebec scraps its annual royalty charge for sawmills. Meanwhile: Ontario starts building first of its kind mass timber bridge; Steelworkers ratify BC forestry agreement; International Paper downsizes in South Carolina; and Boise Cascade and BlueLinx report Q4 earnings.
In Forestry news: the US Forest Service and Alaska sign forestry agreement; eight Western US states oppose Trump’s rollbacks; and BC Timber Sales include commercial thinning projects. Meanwhile: the Wood Pellet Association of Canada’s new safety plan; a CIF forestry event in Sault Ste. Marie; a Montreal conference on building with wood; and BC’s College of Applied Biologists’ 2026 conference keynote.
Finally, citing competitiveness and safety, BC business groups pan PST tax hike.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor
 US President Trump’s point man on trade talks says Canada needs to accept that tariffs will be a part of any deal with the administration, including renewal of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA). In interviews after Trump’s state of the union address, US trade representative Jamieson Greer suggested Canada can’t expect to land a trade agreement that is free of tariffs. …”If Canada wants to agree that we can have some level of higher tariff on them while they open up their markets to us on things like dairy and other things, then that’s a helpful conversation.” It’s the clearest signal yet from the Trump administration that it’s aiming for a fundamental rewrite of the free-trade deals that have existed since NAFTA took effect in 1994. …He also criticized Canada for failing to agree to US requests to back off from “practices that we think are unfair”.
US President Trump’s point man on trade talks says Canada needs to accept that tariffs will be a part of any deal with the administration, including renewal of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA). In interviews after Trump’s state of the union address, US trade representative Jamieson Greer suggested Canada can’t expect to land a trade agreement that is free of tariffs. …”If Canada wants to agree that we can have some level of higher tariff on them while they open up their markets to us on things like dairy and other things, then that’s a helpful conversation.” It’s the clearest signal yet from the Trump administration that it’s aiming for a fundamental rewrite of the free-trade deals that have existed since NAFTA took effect in 1994. …He also criticized Canada for failing to agree to US requests to back off from “practices that we think are unfair”.

 The Quebec government says it will hold a “mini-reform” of the province’s forest regime to provide relief for sawmills and other businesses pressured by cumulative U.S. tariffs. Jean-François Simard, Quebec’s minister of natural resources and forests, said that the changes aim to prevent plant closures and job losses which have surged in recent months. Simard said in a statement on Tuesday that 60,000 jobs are at risk. Quebec’s forestry and logging industry is the second largest in Canada in terms of employment, according to Statistics Canada. The forest regime dictates how Quebec’s forests are managed and harvested. The announcement comes days after a group of Indigenous land guardians and First Nations hereditary chiefs filed a lawsuit seeking formal recognition of their rights over a vast stretch of Quebec. Their legal challenge aims to curb industrial logging and ensure the protection of their traditional way of life.
The Quebec government says it will hold a “mini-reform” of the province’s forest regime to provide relief for sawmills and other businesses pressured by cumulative U.S. tariffs. Jean-François Simard, Quebec’s minister of natural resources and forests, said that the changes aim to prevent plant closures and job losses which have surged in recent months. Simard said in a statement on Tuesday that 60,000 jobs are at risk. Quebec’s forestry and logging industry is the second largest in Canada in terms of employment, according to Statistics Canada. The forest regime dictates how Quebec’s forests are managed and harvested. The announcement comes days after a group of Indigenous land guardians and First Nations hereditary chiefs filed a lawsuit seeking formal recognition of their rights over a vast stretch of Quebec. Their legal challenge aims to curb industrial logging and ensure the protection of their traditional way of life.

 The strong momentum and bull run of basic materials carried over into 2026 and appears poised to be the TSX’s top-performing sector for the second consecutive year. While mining heavyweights continue to lead the surge, lumber stocks are delivering market-beating returns. Stella-Jones, Canfor Corporation, and Doman Building Materials are worth watching right now. These companies offer operational leverage and have maintained resilience amid persistent price volatility and trade restrictions.
The strong momentum and bull run of basic materials carried over into 2026 and appears poised to be the TSX’s top-performing sector for the second consecutive year. While mining heavyweights continue to lead the surge, lumber stocks are delivering market-beating returns. Stella-Jones, Canfor Corporation, and Doman Building Materials are worth watching right now. These companies offer operational leverage and have maintained resilience amid persistent price volatility and trade restrictions.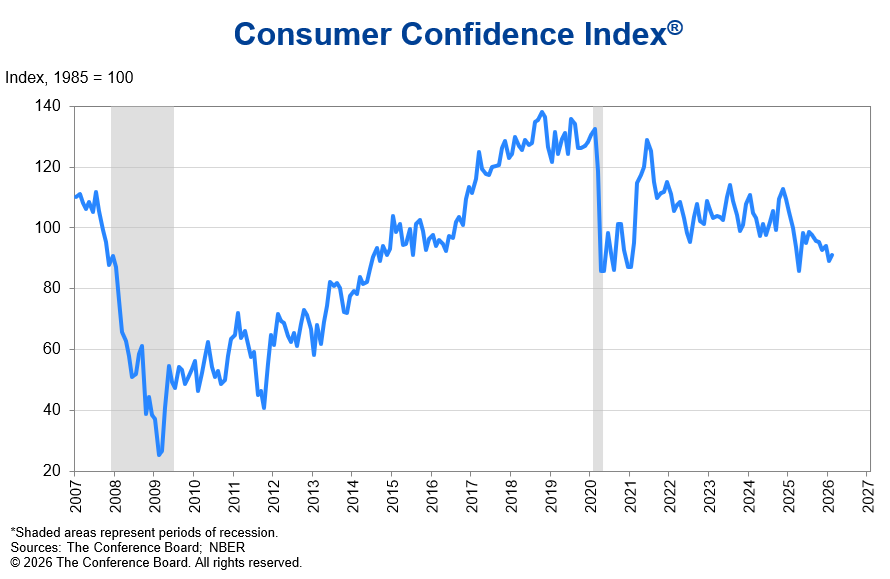

 MESA COUNTY, Colorado. – Mesa County commissioners have passed a wildfire resiliency code that will affect the construction of new houses and projects on current structures, including re-roofing. The code, required by state legislation, applies only to buildings in the Wildland Urban Interface — a designated area marking locations close to potential wildfires. It mandates that projects in those areas use more fire-resistant materials and regulates where new structures can be built. “It’s not going to keep houses from burning down…,” Davis said. “What it’s designed to do is to keep it from burning as quick and as violently so that people can get out and get to safety.” Davis said the new code could make building in affected areas slower and more expensive. “To make things fire resistant, it costs money. The cheapest siding out there is wood-based and more affordable, but it’s also going to be more flammable,” Davis said.
MESA COUNTY, Colorado. – Mesa County commissioners have passed a wildfire resiliency code that will affect the construction of new houses and projects on current structures, including re-roofing. The code, required by state legislation, applies only to buildings in the Wildland Urban Interface — a designated area marking locations close to potential wildfires. It mandates that projects in those areas use more fire-resistant materials and regulates where new structures can be built. “It’s not going to keep houses from burning down…,” Davis said. “What it’s designed to do is to keep it from burning as quick and as violently so that people can get out and get to safety.” Davis said the new code could make building in affected areas slower and more expensive. “To make things fire resistant, it costs money. The cheapest siding out there is wood-based and more affordable, but it’s also going to be more flammable,” Davis said.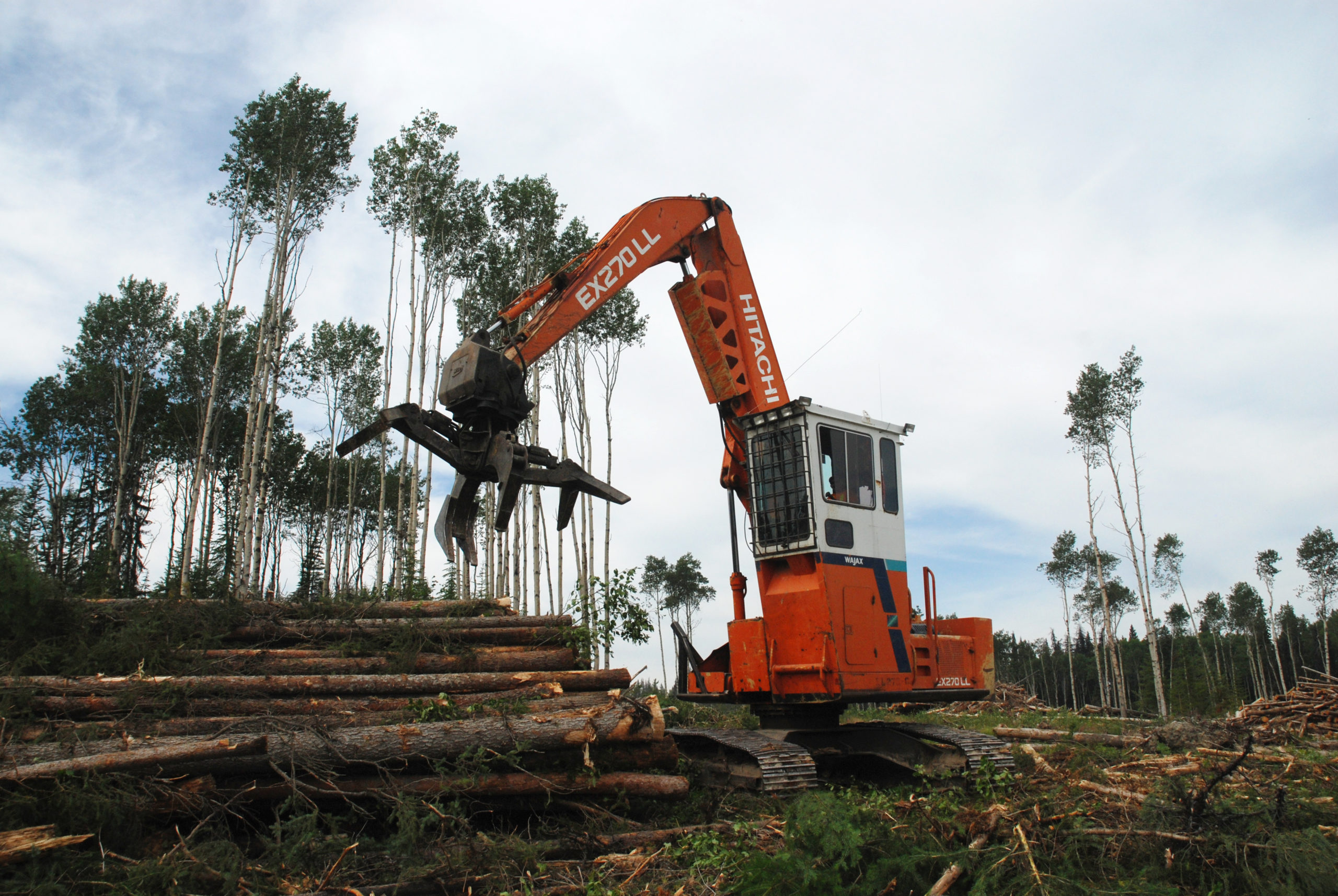 PRINCE GEORGE – British Columbia’s Forests Minister Ravi Parmar has announced that changes to BC Timber Sales are beginning to yield positive results, particularly in the Prince George area. The province aims to boost job creation, support local mills, and enhance forest health through this updated approach. Following a 2021 review of BC Timber Sales, several recommendations were made, and since then, the province has reported an increase in timber sales across British Columbia. This includes the recent auction of two new commercial thinning sales in the Prince George area, marking a significant achievement for the region.
PRINCE GEORGE – British Columbia’s Forests Minister Ravi Parmar has announced that changes to BC Timber Sales are beginning to yield positive results, particularly in the Prince George area. The province aims to boost job creation, support local mills, and enhance forest health through this updated approach. Following a 2021 review of BC Timber Sales, several recommendations were made, and since then, the province has reported an increase in timber sales across British Columbia. This includes the recent auction of two new commercial thinning sales in the Prince George area, marking a significant achievement for the region.

 More than 110 million acres of land across the U.S. are protected in 806 federally designated wilderness areas – together an area slightly larger than the state of California. For the most part, these places have been left alone for decades, in keeping with the 1964 Wilderness Act’s directive that they be “untrammeled by man.” But in a time when lands are experiencing the effects of climate change and people are renewing their understanding of Indigenous knowledge and stewardship practices, protecting these places may require action, not inaction. …First, the American ideal that wildlands flourish best in the absence of human management – conflicts with the growing understanding that many wilderness areas are part of the ancestral homelands of Indigenous peoples, who tended those lands for thousands of years. …And second, as climate change and ecological stressors affect wilderness, human intervention could help sustain the very ecological qualities that are protected.
More than 110 million acres of land across the U.S. are protected in 806 federally designated wilderness areas – together an area slightly larger than the state of California. For the most part, these places have been left alone for decades, in keeping with the 1964 Wilderness Act’s directive that they be “untrammeled by man.” But in a time when lands are experiencing the effects of climate change and people are renewing their understanding of Indigenous knowledge and stewardship practices, protecting these places may require action, not inaction. …First, the American ideal that wildlands flourish best in the absence of human management – conflicts with the growing understanding that many wilderness areas are part of the ancestral homelands of Indigenous peoples, who tended those lands for thousands of years. …And second, as climate change and ecological stressors affect wilderness, human intervention could help sustain the very ecological qualities that are protected. ARIZONA — The Forest Service budget to thin the forest is down. But hey, at least there’s a budget. That is the bad news/good news gist of a report on the 4-Forests Restoration Initiative (4-FRI) delivered last week at the Natural Resources Working Group meeting. Fortunately, the state Forestry Department is also continuing to fund thinning projects, including creating buffer zones around forested communities like Payson. However, time may be running out to restore the overgrown, drought-plagued forest. The meeting also featured a report documenting the worsening condition of the forest as thinning efforts falter. Jon Orona, with Arizona Department of Forestry and Fire Management, reported that 2025 was the fifth-driest year ever recorded – with average temperatures between 6 and 12 degrees above normal.
ARIZONA — The Forest Service budget to thin the forest is down. But hey, at least there’s a budget. That is the bad news/good news gist of a report on the 4-Forests Restoration Initiative (4-FRI) delivered last week at the Natural Resources Working Group meeting. Fortunately, the state Forestry Department is also continuing to fund thinning projects, including creating buffer zones around forested communities like Payson. However, time may be running out to restore the overgrown, drought-plagued forest. The meeting also featured a report documenting the worsening condition of the forest as thinning efforts falter. Jon Orona, with Arizona Department of Forestry and Fire Management, reported that 2025 was the fifth-driest year ever recorded – with average temperatures between 6 and 12 degrees above normal. Large, bipartisan majorities of voters across eight Western states remain concerned about the impacts of climate change and opposed to efforts by the Trump administration to weaken environmental rules and public lands protections. Eighty-four percent of Western voters say “rollbacks of laws that protect our land, water and wildlife” are a serious problem, up from 68% eight years ago, according to a poll released by Colorado College’s State of the Rockies project. The annual Conservation in the West poll has measured Western voters’ views of environmental and energy issues since 2011. The 2026 survey is based on interviews conducted in January with 3,419 voters in Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Wyoming. “After 16 years, it’s become a rare longitudinal data set that lets us track how public attitudes have shifted over time throughout the West,” said Ian Johnson, Colorado College’s director of strategic initiatives and sustainability.
Large, bipartisan majorities of voters across eight Western states remain concerned about the impacts of climate change and opposed to efforts by the Trump administration to weaken environmental rules and public lands protections. Eighty-four percent of Western voters say “rollbacks of laws that protect our land, water and wildlife” are a serious problem, up from 68% eight years ago, according to a poll released by Colorado College’s State of the Rockies project. The annual Conservation in the West poll has measured Western voters’ views of environmental and energy issues since 2011. The 2026 survey is based on interviews conducted in January with 3,419 voters in Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Wyoming. “After 16 years, it’s become a rare longitudinal data set that lets us track how public attitudes have shifted over time throughout the West,” said Ian Johnson, Colorado College’s director of strategic initiatives and sustainability.
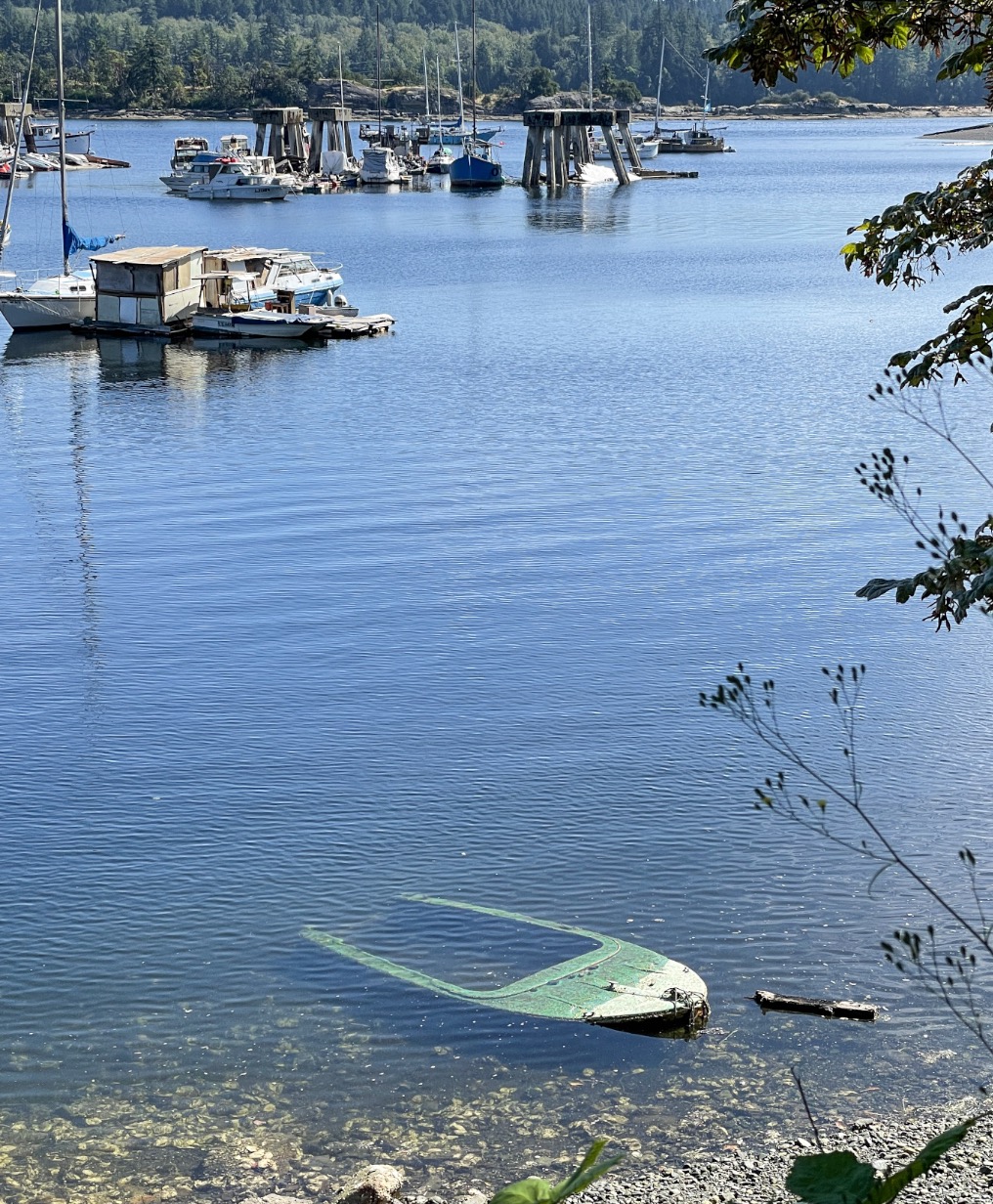
 COWICHAN BAY, BC — Simon Fraser University researchers have uncovered concerning fibreglass contamination in a key estuary on Vancouver Island, raising concerns about how an as-yet overlooked contaminant could affect aquatic birds, marine life and coastal communities that rely on shellfish and seafood. A
COWICHAN BAY, BC — Simon Fraser University researchers have uncovered concerning fibreglass contamination in a key estuary on Vancouver Island, raising concerns about how an as-yet overlooked contaminant could affect aquatic birds, marine life and coastal communities that rely on shellfish and seafood. A  Supporters of the “Make America Healthy Again” strategy have long railed against pesticides, making opposition to them a pillar of the movement. But an executive order issued by U.S. President Donald Trump last week collides with that long-held stance. The order states that glyphosate … is “central to American economic and national security” and calls for an adequate domestic supply. Glyphosate inhibits protein synthesis in plants and microorganisms, leading to their death. Scientists can genetically modify field crops — choosing which survive after glyphosate treatment. US Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a key figure in the MAHA movement, has long opposed glyphosate-based pesticides. …He reiterated last month on Katie Miller’s podcast that “I believe glyphosate causes cancer.” But Kennedy sounded a different tone. “Donald Trump’s executive order puts America first where it matters most — our defense readiness and our food supply,” said Kennedy.
Supporters of the “Make America Healthy Again” strategy have long railed against pesticides, making opposition to them a pillar of the movement. But an executive order issued by U.S. President Donald Trump last week collides with that long-held stance. The order states that glyphosate … is “central to American economic and national security” and calls for an adequate domestic supply. Glyphosate inhibits protein synthesis in plants and microorganisms, leading to their death. Scientists can genetically modify field crops — choosing which survive after glyphosate treatment. US Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a key figure in the MAHA movement, has long opposed glyphosate-based pesticides. …He reiterated last month on Katie Miller’s podcast that “I believe glyphosate causes cancer.” But Kennedy sounded a different tone. “Donald Trump’s executive order puts America first where it matters most — our defense readiness and our food supply,” said Kennedy.