Nova Scotia government officials will know if they’re the successful bidder for the Northern Pulp timberlands following an auction Friday, but it will be a few weeks before the result is publicly known. “This is a very confidential process,” Natural Resources Minister Kim Masland said. …The auction is part of the creditor protection process Northern Pulp has been moving through. Nova Scotia is bidding on the company’s 162,000 hectares of timberlands and a nursery and seed orchard in Debert. “This has economic benefit and certainly we want to add that to our Crown land,” said Masland. …Premier Tim Houston said he has no issue with Macer but it “wasn’t the assessment of the province” that Macer’s initial bid “should win the day.” …Masland said her government is committed to supporting the forestry industry, and trying to buy the Northern Pulp timberlands is one way to do that.



 Pierre Poilievre says he’d succeed where Prime Minister Mark Carney has failed, and that New Brunswick’s softwood lumber sector would quickly get a “tariff-free” deal with the US if he was in charge. …Ottawa responded by releasing a financial aid package for the industry that includes up to $700 million in federal loans, “$500 million to supercharge product and market diversification. …Poilievre said that “one of my top priorities as prime minister will be to go down to Washington, get a deal on lumber, make the pitch that they will get more affordable homes if we can get tariff-free access to their market.” …MP Dominic LeBlanc sent a statement…. “In the coming weeks, we will take further urgent action, building on the significant support for the sector announced on August 5, 2025. In addition, Build Canada Homes, a new federal agency that will build affordable housing at scale, will prioritize the use of Canadian-made materials. [Access may require a Telegraph-Journal subscription]
Pierre Poilievre says he’d succeed where Prime Minister Mark Carney has failed, and that New Brunswick’s softwood lumber sector would quickly get a “tariff-free” deal with the US if he was in charge. …Ottawa responded by releasing a financial aid package for the industry that includes up to $700 million in federal loans, “$500 million to supercharge product and market diversification. …Poilievre said that “one of my top priorities as prime minister will be to go down to Washington, get a deal on lumber, make the pitch that they will get more affordable homes if we can get tariff-free access to their market.” …MP Dominic LeBlanc sent a statement…. “In the coming weeks, we will take further urgent action, building on the significant support for the sector announced on August 5, 2025. In addition, Build Canada Homes, a new federal agency that will build affordable housing at scale, will prioritize the use of Canadian-made materials. [Access may require a Telegraph-Journal subscription]
 The Nova Scotia Forestry Innovation Transition Trust is investing $1.8 million to assist private landowners and forest contractors in finding new markets for underutilized wood fibre and to support sustainable forestry management. According to a
The Nova Scotia Forestry Innovation Transition Trust is investing $1.8 million to assist private landowners and forest contractors in finding new markets for underutilized wood fibre and to support sustainable forestry management. According to a 
 EAR FALLS, Ontario — Northerners know what it means to put in an honest day’s work. …But in Ear Falls, that northern way of life is under threat. In October, Interfor announced the indefinite closure of the Ear Falls sawmill. Over 160 jobs have vanished, and the community is left waiting—hoping that leaders in Ottawa and Toronto will step up, restore these jobs, and fight for the future of Ear Falls. But Ear Falls did not just stand by, they united. Workers, families, municipal leaders, Unifor, and MPP Sol Mamakwa stood shoulder to shoulder to demand action. …But the response from Premier Ford and Prime Minster Carney? Deafening silence. The indefinite closure of Ear Falls’ sawmill, and the silence from Conservative and Liberal governments lay bare the legacy of under-development, under-investment, and under-representation that holds Northerners back.
EAR FALLS, Ontario — Northerners know what it means to put in an honest day’s work. …But in Ear Falls, that northern way of life is under threat. In October, Interfor announced the indefinite closure of the Ear Falls sawmill. Over 160 jobs have vanished, and the community is left waiting—hoping that leaders in Ottawa and Toronto will step up, restore these jobs, and fight for the future of Ear Falls. But Ear Falls did not just stand by, they united. Workers, families, municipal leaders, Unifor, and MPP Sol Mamakwa stood shoulder to shoulder to demand action. …But the response from Premier Ford and Prime Minster Carney? Deafening silence. The indefinite closure of Ear Falls’ sawmill, and the silence from Conservative and Liberal governments lay bare the legacy of under-development, under-investment, and under-representation that holds Northerners back.
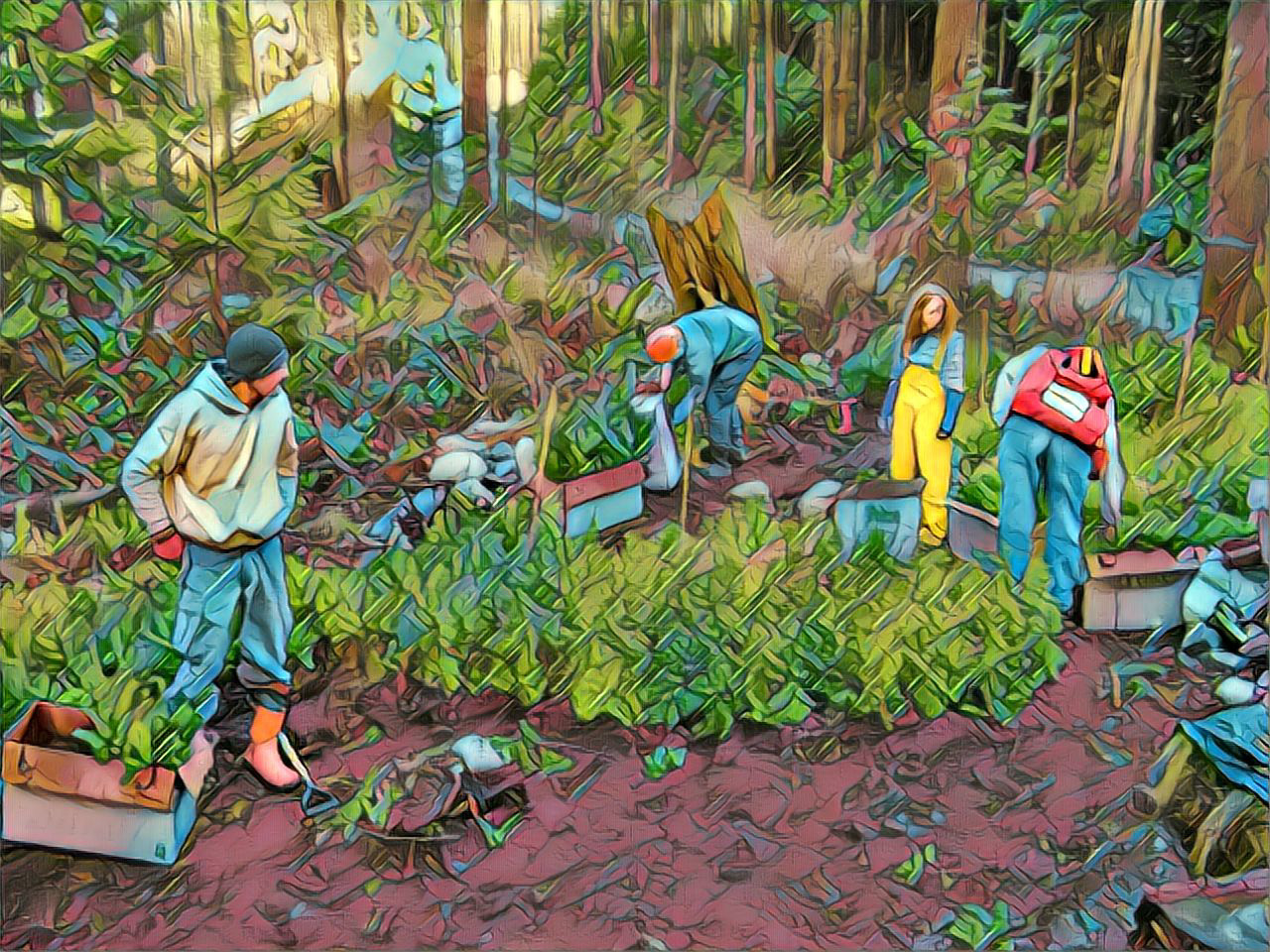 A decision to cut a tree-planting in the federal budget was met with disappointment by seedling producers. The Canadian Tree Nursery Association represents more than 95 per cent of Canada’s forest restoration seedling producers. The federal government decided to cut short the Two Billion Trees (2BT) Program, saving an estimated $200 million over four years. CTNA executive director Rob Keen said the decision would threaten the long-term environmental recovery of Canada’s forests and jeopardize the forest restoration sector. “I think the whole program was just starting to get some good momentum,” Keen said. …Keen said about 600 million trees are planted each year by the forestry industry. “So, really there was a very significant increase in overall tree planting in Canada,” he said. “And then, I guess in the budget … the government decided, ‘OK, we’re done.’ ”
A decision to cut a tree-planting in the federal budget was met with disappointment by seedling producers. The Canadian Tree Nursery Association represents more than 95 per cent of Canada’s forest restoration seedling producers. The federal government decided to cut short the Two Billion Trees (2BT) Program, saving an estimated $200 million over four years. CTNA executive director Rob Keen said the decision would threaten the long-term environmental recovery of Canada’s forests and jeopardize the forest restoration sector. “I think the whole program was just starting to get some good momentum,” Keen said. …Keen said about 600 million trees are planted each year by the forestry industry. “So, really there was a very significant increase in overall tree planting in Canada,” he said. “And then, I guess in the budget … the government decided, ‘OK, we’re done.’ ”









 MONTREAL, Quebec – Stella-Jones announced financial results for its third quarter ended September 30, 2025. Highlights include: Sales of $958 million, up 5% from Q3 2024; Operating income of $135 million, up 4% from Q3 2024; EBITDA of $171 million, or 17.8% margin, up 6% from Q3 2024; and Net Income of $88 million, up 10% from Q3, 2024. …“Stella-Jones achieved another solid performance in the third quarter, supported by volume improvements, robust margins, improved cash flow and a strong balance sheet,” said Eric Vachon, CEO. …The increase in pressure-treated wood sales resulted from an increase in utility poles and industrial products volumes and higher pricing for railway ties and residential lumber. This was partially offset by lower pricing for utility poles. Logs and lumber sales decreased by $14 million or 47%, mainly driven by lower logs activity.
MONTREAL, Quebec – Stella-Jones announced financial results for its third quarter ended September 30, 2025. Highlights include: Sales of $958 million, up 5% from Q3 2024; Operating income of $135 million, up 4% from Q3 2024; EBITDA of $171 million, or 17.8% margin, up 6% from Q3 2024; and Net Income of $88 million, up 10% from Q3, 2024. …“Stella-Jones achieved another solid performance in the third quarter, supported by volume improvements, robust margins, improved cash flow and a strong balance sheet,” said Eric Vachon, CEO. …The increase in pressure-treated wood sales resulted from an increase in utility poles and industrial products volumes and higher pricing for railway ties and residential lumber. This was partially offset by lower pricing for utility poles. Logs and lumber sales decreased by $14 million or 47%, mainly driven by lower logs activity.

%20(6).jpg)
 OTTAWA — The Carney government will still pay to help plant a previously announced 52 million trees in New Brunswick, even though hardly any of them are in the ground and the program’s funding has been cancelled. The recent federal budget scrapped a program to plant two billion trees across the country by 2031 in order to find hundreds of millions of dollars in savings. It was a climate change initiative first announced by former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the 2019 election campaign with $3.2 billion over 10 years earmarked to carry it out. New Brunswick was one of the last provinces to reach an agreement for its cut of that money. It didn’t sign on until March 2024. A few months after that, the feds and the New Brunswick government announced $71.6 million to plant more than 52 million trees on Crown lands across the province over the next eight years. [A Telegraph-Journal subscription is required for full access]
OTTAWA — The Carney government will still pay to help plant a previously announced 52 million trees in New Brunswick, even though hardly any of them are in the ground and the program’s funding has been cancelled. The recent federal budget scrapped a program to plant two billion trees across the country by 2031 in order to find hundreds of millions of dollars in savings. It was a climate change initiative first announced by former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau during the 2019 election campaign with $3.2 billion over 10 years earmarked to carry it out. New Brunswick was one of the last provinces to reach an agreement for its cut of that money. It didn’t sign on until March 2024. A few months after that, the feds and the New Brunswick government announced $71.6 million to plant more than 52 million trees on Crown lands across the province over the next eight years. [A Telegraph-Journal subscription is required for full access]
 BANFF, Alberta – Because of this importance of whitebark pine, Parks Canada is working across the mountain national parks of Banff, Yoho, Kootenay, Jasper, Revelstoke-Glacier and Waterton Lakes to try to give endangered whitebark pine a fighting chance. The higher elevation trees, which can live to be 1,000 years old, are dying off at an alarming rate. Climate change, more than a century of wildfire suppression and mountain pine beetle are all playing a role, but the biggest threat comes from white pine blister rust. …One clear sign of infection is orange blisters on the bark. McLellan said less than one per cent of whitebark pine are naturally resistant to the rust. …Charlie McLellan said last summer about 6,500 rust-resistant saplings were planted in the Banff National Park field unit and in Kootenay National Park – made up of whitebark pine and limber pine, another species recommended to be listed as endangered.
BANFF, Alberta – Because of this importance of whitebark pine, Parks Canada is working across the mountain national parks of Banff, Yoho, Kootenay, Jasper, Revelstoke-Glacier and Waterton Lakes to try to give endangered whitebark pine a fighting chance. The higher elevation trees, which can live to be 1,000 years old, are dying off at an alarming rate. Climate change, more than a century of wildfire suppression and mountain pine beetle are all playing a role, but the biggest threat comes from white pine blister rust. …One clear sign of infection is orange blisters on the bark. McLellan said less than one per cent of whitebark pine are naturally resistant to the rust. …Charlie McLellan said last summer about 6,500 rust-resistant saplings were planted in the Banff National Park field unit and in Kootenay National Park – made up of whitebark pine and limber pine, another species recommended to be listed as endangered. The best time to plant a tree is 10 years ago. Or 20. That’s what I was told by the two retired foresters who put 2,000 one-year-old seedlings in the ground on my farm back in 2017. I had signed on with what was then called the 50 Million Tree program run by Forests Ontario, which subsidized plantings for private landowners. …the Forests Ontario program made tree planting easy. At 40 cents a stem, those trees cost me $800. While 2,000 trees seems like a lot, they cover just under one hectare. We got the seedlings in the ground a couple years before Doug Ford nixed the initiative in 2019. But then, Justin Trudeau created the
The best time to plant a tree is 10 years ago. Or 20. That’s what I was told by the two retired foresters who put 2,000 one-year-old seedlings in the ground on my farm back in 2017. I had signed on with what was then called the 50 Million Tree program run by Forests Ontario, which subsidized plantings for private landowners. …the Forests Ontario program made tree planting easy. At 40 cents a stem, those trees cost me $800. While 2,000 trees seems like a lot, they cover just under one hectare. We got the seedlings in the ground a couple years before Doug Ford nixed the initiative in 2019. But then, Justin Trudeau created the 
 The provincial government has awarded a pair of contracts to build firebreaks in areas of the Avalon Peninsula ravaged by this summer’s historic wildfire season — fires that forced hundreds of people from their homes and destroyed more than 200 structures. A firebreak is an intentionally created gap where burnable material, like vegetation and trees, are cleared in an effort to stop a fire from spreading further by removing flammable materials that could feed it. It was employed as a firefighting tactic against the Kingston, Martin Lake and Paddy’s Pond fires. According to a list of recently disclosed provincial government procurement contracts, Conception Bay South-based Platinum Construction Company Limited was awarded a $51,600 contract. Another contract, valued at $419,983.35, was awarded to Jerseyside-based Tier 1 Capital Corporation to build firebreaks in Burnt Point and Salmon Cove. Both contracts were awarded shortly after the PC party won a majority government on Oct. 14.
The provincial government has awarded a pair of contracts to build firebreaks in areas of the Avalon Peninsula ravaged by this summer’s historic wildfire season — fires that forced hundreds of people from their homes and destroyed more than 200 structures. A firebreak is an intentionally created gap where burnable material, like vegetation and trees, are cleared in an effort to stop a fire from spreading further by removing flammable materials that could feed it. It was employed as a firefighting tactic against the Kingston, Martin Lake and Paddy’s Pond fires. According to a list of recently disclosed provincial government procurement contracts, Conception Bay South-based Platinum Construction Company Limited was awarded a $51,600 contract. Another contract, valued at $419,983.35, was awarded to Jerseyside-based Tier 1 Capital Corporation to build firebreaks in Burnt Point and Salmon Cove. Both contracts were awarded shortly after the PC party won a majority government on Oct. 14.
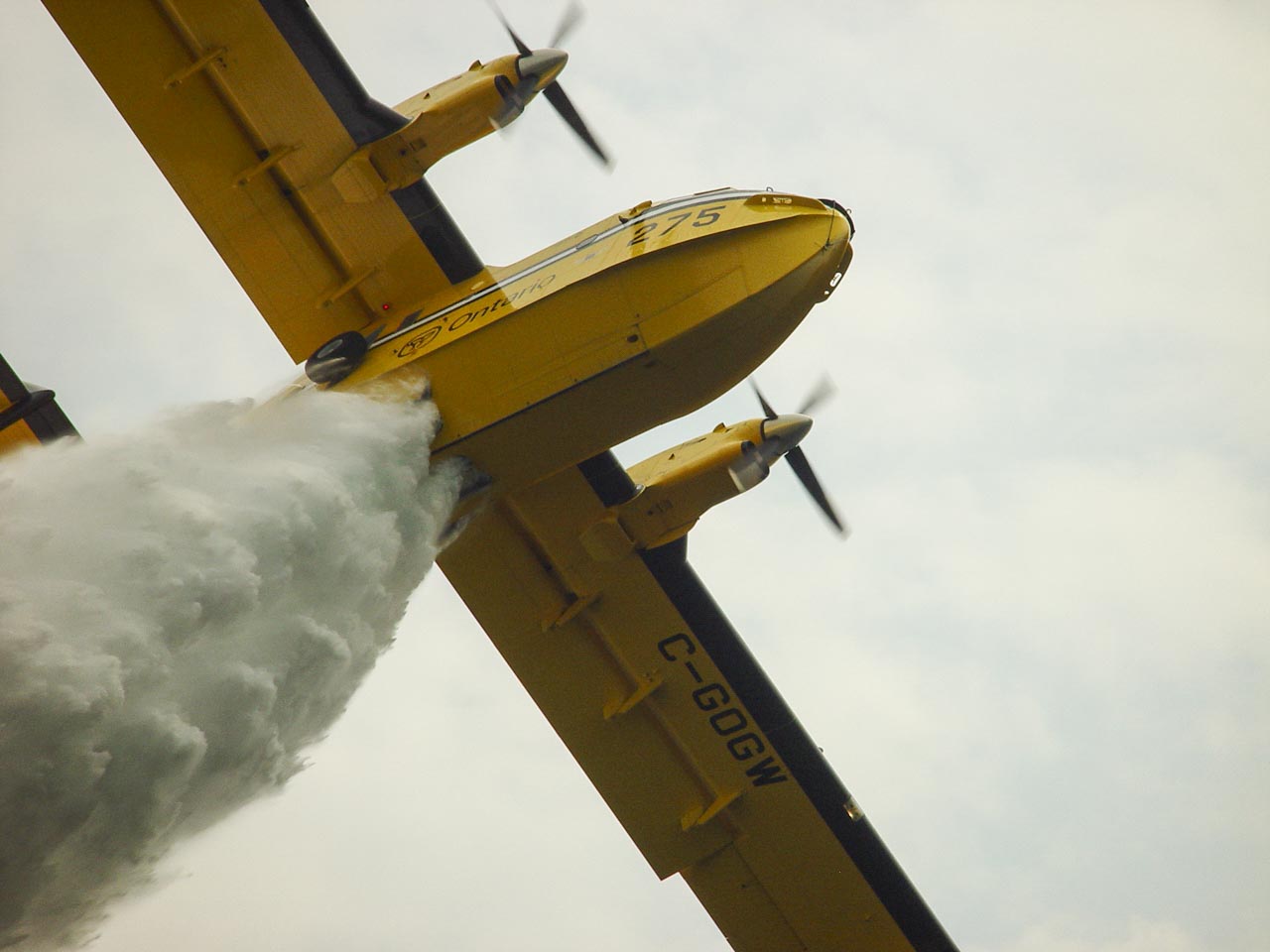
 The Ministry of Natural Resources says nearly 6,000 square kilometres burned in Ontario this wildfire season, much more than last year and well above the province’s 10-year average. The ministry says 643 wildfires were recorded between April and October, with 597,654 hectares — or just over 5,976 square kilometres — burned. The province says 480 fires burned nearly 900 square kilometres in 2024, and the 10-year average for Ontario is 712 fires and about 2,100 square kilometres burned. Figures released by the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre in August showed that Canada’s 2025 wildfire season was the second-worst on record. Those figures suggested the fires tore through 72,000 square kilometres, an area roughly the size of New Brunswick. Scientists say that climate change, driven by the burning of fossil fuels, has made Canada’s fire seasons longer and more intense.
The Ministry of Natural Resources says nearly 6,000 square kilometres burned in Ontario this wildfire season, much more than last year and well above the province’s 10-year average. The ministry says 643 wildfires were recorded between April and October, with 597,654 hectares — or just over 5,976 square kilometres — burned. The province says 480 fires burned nearly 900 square kilometres in 2024, and the 10-year average for Ontario is 712 fires and about 2,100 square kilometres burned. Figures released by the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre in August showed that Canada’s 2025 wildfire season was the second-worst on record. Those figures suggested the fires tore through 72,000 square kilometres, an area roughly the size of New Brunswick. Scientists say that climate change, driven by the burning of fossil fuels, has made Canada’s fire seasons longer and more intense. TORONTO — As the 2025 fire season ends, Ontario’s fire crews, aviation services and support staff responded to 643 fires between April and October with 597,654 hectares burned. While the 2025 fire season began with an early active start, the coordinated efforts of frontline staff, municipalities, Indigenous communities and firefighting crews ensured a rapid response to protect people and communities from wildland fires. …With the rest of Canada also experiencing a demanding fire season, Ontario extended support to our partners, with over 400 fire personnel and six aircraft supporting firefighting in British Columbia, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and Labrador, New Brunswick, as well as south of the border in Minnesota. As this year’s fire season ends, Ontario is now turning its focus to ensuring provincial fire crews are ready to respond next fire season. …The 2026 fire season will begin on April 1, 2026.
TORONTO — As the 2025 fire season ends, Ontario’s fire crews, aviation services and support staff responded to 643 fires between April and October with 597,654 hectares burned. While the 2025 fire season began with an early active start, the coordinated efforts of frontline staff, municipalities, Indigenous communities and firefighting crews ensured a rapid response to protect people and communities from wildland fires. …With the rest of Canada also experiencing a demanding fire season, Ontario extended support to our partners, with over 400 fire personnel and six aircraft supporting firefighting in British Columbia, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and Labrador, New Brunswick, as well as south of the border in Minnesota. As this year’s fire season ends, Ontario is now turning its focus to ensuring provincial fire crews are ready to respond next fire season. …The 2026 fire season will begin on April 1, 2026.


 A new law, Bill 27, could allow for large-scale geologic carbon storage to reduce the emissions from industrial processes like natural gas power generation, cement and steel-making, but critics say it’s not a silver bullet. …Ontario’s associate minister Sam Oosterhoff is impressed by Suncor Energy. The company… “cares deeply about reducing emissions.” And Oosterhoff believes they should do it through a process known as carbon capture and storage. That’s why Ontario should pass new legislation that would enable this process for high-emitting industries like cement and steel. …Bruce Hart, an adjunct professor in earth sciences at Western University, said he’s optimistic about Ontario’s carbon storage plans, given the types of rock available in the southwestern part of the province. …Aly Hyder Ali, at Environmental Defence, characterizes it as a tactic that allows emitters to expand fossil fuel production, not a meaningful solution to climate change.
A new law, Bill 27, could allow for large-scale geologic carbon storage to reduce the emissions from industrial processes like natural gas power generation, cement and steel-making, but critics say it’s not a silver bullet. …Ontario’s associate minister Sam Oosterhoff is impressed by Suncor Energy. The company… “cares deeply about reducing emissions.” And Oosterhoff believes they should do it through a process known as carbon capture and storage. That’s why Ontario should pass new legislation that would enable this process for high-emitting industries like cement and steel. …Bruce Hart, an adjunct professor in earth sciences at Western University, said he’s optimistic about Ontario’s carbon storage plans, given the types of rock available in the southwestern part of the province. …Aly Hyder Ali, at Environmental Defence, characterizes it as a tactic that allows emitters to expand fossil fuel production, not a meaningful solution to climate change.