
Kevin Mason
The US tariff regime is far from over despite a US Supreme Court ruling striking down last year’s tariffs authorized by President Trump under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA). Although the court noted in its ruling that the president overstepped his authority in applying reciprocal tariffs on virtually all trading partners, it did leave the door open for other means of tariff application—and the US Administration has wasted no time in charging through that door, turning to Section 122 of the Trade Act of 1974 to impose new global tariffs of 10% (likely moving to 15%). Tariffs under Section 122 expire after 150 days without congressional approval, but we assume other options will be put in place before expiry (Section 232, 301 or some other creative mechanism).
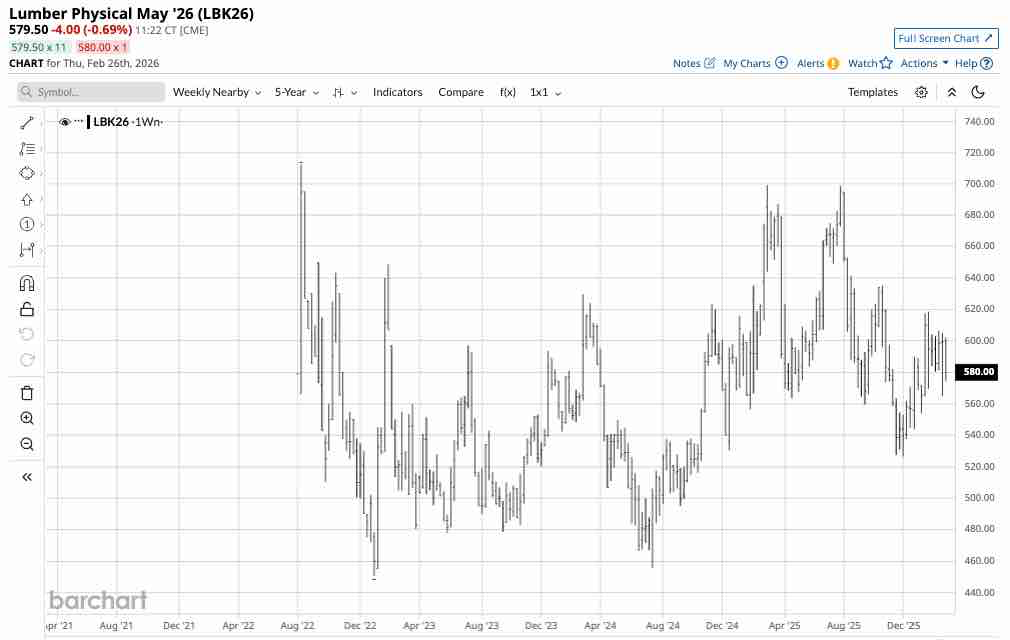
With respect to the forest products industry, cessation of IEEPA tariffs and application of these new Section 122 tariffs have no impact on existing lumber duties (35% remains intact), nor for any existing tariffs under Section 232 (at 10%) or goods currently compliant under USMCA (such goods remain tariff-free under Section 122). Although USMCA-compliant goods are safe from tariffs for now, with that trade deal being reviewed this summer the tariff-free flow of goods among the US, Mexico and Canada could be upended. Since almost all newsprint supply comes from Canada (see page 19), that fear is ostensibly already causing U.S. buyers to accelerate purchases. Our table details what we know at the moment about the new tariff regime (Section 122 at 10% but probably moving to 15%). Brazil and China appear to be winners in these latest moves, but, with other mechanisms available to Trump, we don’t think these recent tariff reductions are going to lead to any dramatic increase in imports from these countries (uncertainty seems to be part of the goal under Trump’s methods).

 The Musqueam First Nation’s agreement with Ottawa to advance the nation’s rights and title over an area that spans the western half of Greater Vancouver will force Canada to grapple with overlapping Indigenous claims, the boundaries of civic governance, and the principles of co-operative federalism. The deal acknowledges the existence of constitutionally protected Aboriginal title and creates a framework to implement Musqueam’s rights and title in their traditional territory. It is accompanied by two other agreements that create a framework for shared decision-making over fisheries, marine stewardship and land use. Just where that title will be recognized, and what rights will be affirmed, are yet to be negotiated. The Musqueam’s traditional territory has overlapping and shared territories with its First Nation neighbours. …Ottawa’s deal with Musqueam First Nation raises alarm about property rights in Vancouver area. …Cowichan decision leads to another claim on private lands in BC. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
The Musqueam First Nation’s agreement with Ottawa to advance the nation’s rights and title over an area that spans the western half of Greater Vancouver will force Canada to grapple with overlapping Indigenous claims, the boundaries of civic governance, and the principles of co-operative federalism. The deal acknowledges the existence of constitutionally protected Aboriginal title and creates a framework to implement Musqueam’s rights and title in their traditional territory. It is accompanied by two other agreements that create a framework for shared decision-making over fisheries, marine stewardship and land use. Just where that title will be recognized, and what rights will be affirmed, are yet to be negotiated. The Musqueam’s traditional territory has overlapping and shared territories with its First Nation neighbours. …Ottawa’s deal with Musqueam First Nation raises alarm about property rights in Vancouver area. …Cowichan decision leads to another claim on private lands in BC. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
 March 19, 2026 | 6:30-9 PM | UBC Robson Square Theatre — Experts from the Allard School of Law (Ljiljana Biuković), Vancouver School of Economics (Torsten Jaccard), Faculty of Forestry & Environmental Stewardship (Harry Nelson), and Political Science (Stewart Prest) will explore the evolving Canada–U.S. economic relationship and what it means for Canada’s future. As the 2026 joint review of the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) approaches, Canada faces significant shifts in its most important trading relationship. From tariffs on steel to ongoing tensions in British Columbia’s forestry sector, long-standing trade dynamics are being tested and the era of predictable trade and stable multilateral rules may be coming to an end. Policymakers, industry leaders, and people interested in understanding the structural changes shaping Canada’s economic future are encouraged to attend. Panelists will examine emerging geopolitical realities and their implications for Canada, highlighting BC forestry as a case study on how international trade pressures are affecting local industries, workers, and communities.
March 19, 2026 | 6:30-9 PM | UBC Robson Square Theatre — Experts from the Allard School of Law (Ljiljana Biuković), Vancouver School of Economics (Torsten Jaccard), Faculty of Forestry & Environmental Stewardship (Harry Nelson), and Political Science (Stewart Prest) will explore the evolving Canada–U.S. economic relationship and what it means for Canada’s future. As the 2026 joint review of the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) approaches, Canada faces significant shifts in its most important trading relationship. From tariffs on steel to ongoing tensions in British Columbia’s forestry sector, long-standing trade dynamics are being tested and the era of predictable trade and stable multilateral rules may be coming to an end. Policymakers, industry leaders, and people interested in understanding the structural changes shaping Canada’s economic future are encouraged to attend. Panelists will examine emerging geopolitical realities and their implications for Canada, highlighting BC forestry as a case study on how international trade pressures are affecting local industries, workers, and communities.
 The head of B.C.’s Declaration Act Secretariat has left government on the eve of Premier David Eby’s move to change the landmark law to address court rulings that threaten private property rights. Jessica Wood, the province’s first Indigenous deputy minister, announced late last week she was departing the secretariat. “The Declaration Act was the first legislation in Canada to require consideration and alignment of provincial law with the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in consultation and cooperation with Indigenous Peoples,” Wood said in a post on
The head of B.C.’s Declaration Act Secretariat has left government on the eve of Premier David Eby’s move to change the landmark law to address court rulings that threaten private property rights. Jessica Wood, the province’s first Indigenous deputy minister, announced late last week she was departing the secretariat. “The Declaration Act was the first legislation in Canada to require consideration and alignment of provincial law with the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in consultation and cooperation with Indigenous Peoples,” Wood said in a post on  Twenty years after spinning out Canfor Pulp Products as a separate entity, Canfor Corp. plans to bring it back into the fold to prevent the subsidiary from sinking. …Since December, its stock has plunged to about $0.50 per share. A March 6 shareholder vote on a plan of arrangement is just one of the vital signs indicating how bad 2025 was for the forestry sector in general, and BC forestry companies in particular. …But B.C. has been particularly hard hit with sawmill and pulp mill closures due to its fibre constraints and higher operating costs. The most recent high-profile mill closure in BC was the Domtar pulp mill in Crofton at the end of December. BC pulp mills rely on wood chips from sawmills to produce pulp. But so many sawmills have permanently shuttered in B.C. in the last few years that pulp mills now struggle to find enough fibre to run their mills.
Twenty years after spinning out Canfor Pulp Products as a separate entity, Canfor Corp. plans to bring it back into the fold to prevent the subsidiary from sinking. …Since December, its stock has plunged to about $0.50 per share. A March 6 shareholder vote on a plan of arrangement is just one of the vital signs indicating how bad 2025 was for the forestry sector in general, and BC forestry companies in particular. …But B.C. has been particularly hard hit with sawmill and pulp mill closures due to its fibre constraints and higher operating costs. The most recent high-profile mill closure in BC was the Domtar pulp mill in Crofton at the end of December. BC pulp mills rely on wood chips from sawmills to produce pulp. But so many sawmills have permanently shuttered in B.C. in the last few years that pulp mills now struggle to find enough fibre to run their mills.

 On Dec. 2, 2025, Domtar announced it would permanently close Crofton’s nearly 70-year-old mill citing a lack of affordable fibre in BC and rising cost of materials. In response, the Municipality of North Cowichan created a Community Transition Table to coordinate union leadership, worker support and discussions on the future of the mill site. …The Discourse has compiled a timeline of major events at the Crofton mill to help understand the historical context of the latest mill closure. …1957: The mill opens and BC Forest Products (BCFP) told the citizens of Crofton it would employ 300 people and have an annual payroll of $1.5 million. Crofton was chosen as the location for the mill after an “extensive” three year survey by BCFP found the Cowichan River had adequate water supply for the mill. 1963: BCFP announced an $18.5 million expansion of the Crofton mill to expand the capacity to produce paper for its second newsprint machine.
On Dec. 2, 2025, Domtar announced it would permanently close Crofton’s nearly 70-year-old mill citing a lack of affordable fibre in BC and rising cost of materials. In response, the Municipality of North Cowichan created a Community Transition Table to coordinate union leadership, worker support and discussions on the future of the mill site. …The Discourse has compiled a timeline of major events at the Crofton mill to help understand the historical context of the latest mill closure. …1957: The mill opens and BC Forest Products (BCFP) told the citizens of Crofton it would employ 300 people and have an annual payroll of $1.5 million. Crofton was chosen as the location for the mill after an “extensive” three year survey by BCFP found the Cowichan River had adequate water supply for the mill. 1963: BCFP announced an $18.5 million expansion of the Crofton mill to expand the capacity to produce paper for its second newsprint machine. The mayors of Squamish and 100 Mile House, B.C., want to see the railway linking their two communities preserved. CN Rail is responsible for the maintenance and upkeep of a portion of B.C.’s rail network between Squamish and Exeter, just northwest of 100 Mile House. In July 2025, the national rail operator said it provided notice of its intent to discontinue those operations. 100 Mile House Mayor Maureen Pinkney says her town is working with several other municipalities to make a business case for the railway, and have hired a consultant to research the details. The rail line goes through an industrial park in 100 Mile House, explained Pinkney, connecting industries like forestry. The town’s oriented strand board plant shut down in 2019 and West Fraser closed its lumber mill at the end of last year, but Pinkney said there’s still fibre that can be utilized for other wood products.
The mayors of Squamish and 100 Mile House, B.C., want to see the railway linking their two communities preserved. CN Rail is responsible for the maintenance and upkeep of a portion of B.C.’s rail network between Squamish and Exeter, just northwest of 100 Mile House. In July 2025, the national rail operator said it provided notice of its intent to discontinue those operations. 100 Mile House Mayor Maureen Pinkney says her town is working with several other municipalities to make a business case for the railway, and have hired a consultant to research the details. The rail line goes through an industrial park in 100 Mile House, explained Pinkney, connecting industries like forestry. The town’s oriented strand board plant shut down in 2019 and West Fraser closed its lumber mill at the end of last year, but Pinkney said there’s still fibre that can be utilized for other wood products. EAR FALLS, Ontario — No news is not good news when it comes to the future of the sawmill in Ear Falls. Mayor of the community Kevin Kahoot says he’s supposed to talk with Interfor, the owner of the mill, this week. “We have regular conversations in the last few months…every couple of weeks,” says Kahoot. “It’s been kind of status quo recently. They keep pushing markets and tariffs and those kinds of things. But I don’t see a lot of movement maybe until springtime.” The sawmill shut down indefinitely back in October throwing 150 people out of work. [END]
EAR FALLS, Ontario — No news is not good news when it comes to the future of the sawmill in Ear Falls. Mayor of the community Kevin Kahoot says he’s supposed to talk with Interfor, the owner of the mill, this week. “We have regular conversations in the last few months…every couple of weeks,” says Kahoot. “It’s been kind of status quo recently. They keep pushing markets and tariffs and those kinds of things. But I don’t see a lot of movement maybe until springtime.” The sawmill shut down indefinitely back in October throwing 150 people out of work. [END] New Brunswick royalty revenues have plummeted by $45 million. It’s a figure that has forestry royalties on track to come in at an historic low in the current fiscal year. And it was a decision to significantly cut royalty rates made quietly by the Holt government last July that’s behind it. That’s as the government suggests it’s a move that’s successfully sheltered the industry from curtailments and closures that are being felt across the country. …The province moved to overhaul timber royalty rates in 2022 after acknowledging its former policy of charging forestry companies a flat rate for wood cut in public forests had failed to take advantage of a two-year explosion in international lumber prices. A new system created under the former Higgs government allowed for rates to rise and fall with the prices of various wood-based commodities. “As forest product markets improve in the future, royalty rates will index upwards,” Herron said.
New Brunswick royalty revenues have plummeted by $45 million. It’s a figure that has forestry royalties on track to come in at an historic low in the current fiscal year. And it was a decision to significantly cut royalty rates made quietly by the Holt government last July that’s behind it. That’s as the government suggests it’s a move that’s successfully sheltered the industry from curtailments and closures that are being felt across the country. …The province moved to overhaul timber royalty rates in 2022 after acknowledging its former policy of charging forestry companies a flat rate for wood cut in public forests had failed to take advantage of a two-year explosion in international lumber prices. A new system created under the former Higgs government allowed for rates to rise and fall with the prices of various wood-based commodities. “As forest product markets improve in the future, royalty rates will index upwards,” Herron said.

 Visit Canada Wood’s Market News for these stories and more:
Visit Canada Wood’s Market News for these stories and more: VANCOUVER — UBC’s newest building, Gateway Health, is opening as a hub for student health, interdisciplinary teaching and collaborative research. The 270,550-square-foot building gives a purpose-built home to the school of nursing, consolidates kinesiology programs from eight campus locations, and centralizes student health and wellbeing services for the first time. …
VANCOUVER — UBC’s newest building, Gateway Health, is opening as a hub for student health, interdisciplinary teaching and collaborative research. The 270,550-square-foot building gives a purpose-built home to the school of nursing, consolidates kinesiology programs from eight campus locations, and centralizes student health and wellbeing services for the first time. …




 Canada’s drinking water can remain at risk long after wildfires burn out, according to a
Canada’s drinking water can remain at risk long after wildfires burn out, according to a  PRINCE GEORGE – Recent shifts in the global wood pellet industry have started a debate in BC about forestry, climate impacts, and local jobs. Drax, a UK-based energy company, plans to stop using wood pellets from BC at its power plant in England. Environmental groups believe this move will not affect BC much, but the province’s Forest Minister disagrees. Ravi Parmar, BC’s forests minister, says critics are spreading fear and insists the industry uses byproducts from forestry, not old-growth trees. Michelle Connolly from Conservation North says that although Drax stopping shipments to the UK seems important, the situation in BC is actually much more complex. …Forest Minister Ravi Parmar says BC uses some of the world’s strongest sustainable harvesting practices. He adds that pellet plants use leftover byproducts from logging, not valuable logs from primary forests.
PRINCE GEORGE – Recent shifts in the global wood pellet industry have started a debate in BC about forestry, climate impacts, and local jobs. Drax, a UK-based energy company, plans to stop using wood pellets from BC at its power plant in England. Environmental groups believe this move will not affect BC much, but the province’s Forest Minister disagrees. Ravi Parmar, BC’s forests minister, says critics are spreading fear and insists the industry uses byproducts from forestry, not old-growth trees. Michelle Connolly from Conservation North says that although Drax stopping shipments to the UK seems important, the situation in BC is actually much more complex. …Forest Minister Ravi Parmar says BC uses some of the world’s strongest sustainable harvesting practices. He adds that pellet plants use leftover byproducts from logging, not valuable logs from primary forests. 


 BC Wildfire Service (BCWS) staff have returned to B.C. after supporting Forest Fire Management Victoria in Australia for the past month with wildfire-fighting efforts. “Our world-class BC Wildfire Service has once again stepped up on the global stage,” said Ravi Parmar, Minister of Forests. “As we prepare for the 2026 wildfire season, our BCWS crews consistently demonstrate exceptional skills, courage and professionalism wherever they’re called to serve.” On Jan. 25, 2026, BCWS deployed 37 people to the state of Victoria to help respond to the Walwa River Road fire and provide support in the Tallangatta Incident Control Centre. The team consisted of a 15-person incident management team, a 20-person fire crew and two agency representatives. …Ahead of this year’s wildfire season, B.C. continues work to keep people and communities safe by focusing on all four pillars of emergency management: prevention, preparedness, response and recovery.
BC Wildfire Service (BCWS) staff have returned to B.C. after supporting Forest Fire Management Victoria in Australia for the past month with wildfire-fighting efforts. “Our world-class BC Wildfire Service has once again stepped up on the global stage,” said Ravi Parmar, Minister of Forests. “As we prepare for the 2026 wildfire season, our BCWS crews consistently demonstrate exceptional skills, courage and professionalism wherever they’re called to serve.” On Jan. 25, 2026, BCWS deployed 37 people to the state of Victoria to help respond to the Walwa River Road fire and provide support in the Tallangatta Incident Control Centre. The team consisted of a 15-person incident management team, a 20-person fire crew and two agency representatives. …Ahead of this year’s wildfire season, B.C. continues work to keep people and communities safe by focusing on all four pillars of emergency management: prevention, preparedness, response and recovery.
 The February 2026 FGC eNewsletter highlights several key developments in forest genetics across British Columbia and beyond. It introduces Dan Nadir, RPF, as the new Executive Secretariat for FGC, succeeding Brian Barber, and outlines his forestry background and experience. The newsletter promotes an upcoming BC Seed Orchard Association webinar on March 12, featuring presentations on seed extraction and orchard management from Quebec and New Brunswick. Recent events where forest genetics featured prominently are covered, including presentations on seed planning in a changing climate at the Western Forestry Contractors’ Association conference and FGC’s participation at the Forest Professionals BC conference. The update also highlights a new national report identifying challenges and solutions for improving Canada’s tree seed supply chain. Finally, it lists upcoming meetings and conferences in 2026, such as tree improvement workshops and international seed orchard conferences, encouraging engagement and continued professional development.
The February 2026 FGC eNewsletter highlights several key developments in forest genetics across British Columbia and beyond. It introduces Dan Nadir, RPF, as the new Executive Secretariat for FGC, succeeding Brian Barber, and outlines his forestry background and experience. The newsletter promotes an upcoming BC Seed Orchard Association webinar on March 12, featuring presentations on seed extraction and orchard management from Quebec and New Brunswick. Recent events where forest genetics featured prominently are covered, including presentations on seed planning in a changing climate at the Western Forestry Contractors’ Association conference and FGC’s participation at the Forest Professionals BC conference. The update also highlights a new national report identifying challenges and solutions for improving Canada’s tree seed supply chain. Finally, it lists upcoming meetings and conferences in 2026, such as tree improvement workshops and international seed orchard conferences, encouraging engagement and continued professional development. In this newsletter you will find:
In this newsletter you will find: How the hell did we end up in this situation? It’s a question that everyone involved in BC’s wood products business has asked themselves during the last few years. The question doesn’t have a simple answer. Instead, there are several contributing factors that have steered the forest industry into its current mess. But two problems are of critical importance now: securing reliable fibre access and dealing calmly with the international uncertainty triggered by US President Donald Trump’s lust for world trade dominance and military supremacy. But the BC forest industry has deep roots and some of the issues which began long ago have now come home to roost. All at the same time. They’ve created a confluence of concerns. That’s evident in the silent sawmills, the scattering of a skilled workforce—and communities in crisis throughout the BC interior.
How the hell did we end up in this situation? It’s a question that everyone involved in BC’s wood products business has asked themselves during the last few years. The question doesn’t have a simple answer. Instead, there are several contributing factors that have steered the forest industry into its current mess. But two problems are of critical importance now: securing reliable fibre access and dealing calmly with the international uncertainty triggered by US President Donald Trump’s lust for world trade dominance and military supremacy. But the BC forest industry has deep roots and some of the issues which began long ago have now come home to roost. All at the same time. They’ve created a confluence of concerns. That’s evident in the silent sawmills, the scattering of a skilled workforce—and communities in crisis throughout the BC interior.

 Transport truck drivers have the most injury claims for work-related crashes of any occupation in BC over the last 10 years. And driver fatigue is a contributing factor in many crashes. Developing a strategy for reducing driver fatigue is smart business. It can help save lives and reduce the risk of injuries. It can also help you meet your legal responsibilities. Use Road Safety at Work’s no-cost resources to create or enhance your fatigue management strategy. Transport truck drivers account for nearly one-quarter of all injury claims from work-related vehicle crashes in our province, according to WorkSafeBC. …A successful fatigue management strategy depends on an effective safety culture and employee engagement. Encourage drivers to report fatigue and to pull over for a short rest when they feel it. Discuss it at safety meetings. Make fatigue part of your fit for duty assessments. Emphasize the importance of adequate sleep.
Transport truck drivers have the most injury claims for work-related crashes of any occupation in BC over the last 10 years. And driver fatigue is a contributing factor in many crashes. Developing a strategy for reducing driver fatigue is smart business. It can help save lives and reduce the risk of injuries. It can also help you meet your legal responsibilities. Use Road Safety at Work’s no-cost resources to create or enhance your fatigue management strategy. Transport truck drivers account for nearly one-quarter of all injury claims from work-related vehicle crashes in our province, according to WorkSafeBC. …A successful fatigue management strategy depends on an effective safety culture and employee engagement. Encourage drivers to report fatigue and to pull over for a short rest when they feel it. Discuss it at safety meetings. Make fatigue part of your fit for duty assessments. Emphasize the importance of adequate sleep.