TAPPI, the premier association for the global pulp, paper, tissue, packaging, and converting industries, announced the appointment of Lawton C. Roberts as its new President and CEO, effective November 3, 2025. Roberts will succeed Larry N. Montague, who is retiring at the end of 2025 after 19 years of leadership, according to Pulp & Paper Chronicle. “I’m confident Lawton is the right person to lead TAPPI into its next chapter”, as quoted by PaperAge. Roberts, currently TAPPI’s Chief Operating Officer, has been with TAPPI since 2017 and has worked alongside Montague since 2006 in various capacities. TAPPI is a non-profit, volunteer-led association that is built around “a community comprised of thousands of member engineers, managers, scientists, academics, suppliers and others from around the world”. TAPPI is headquartered right outside of Atlanta, Georgia.


 VANCOUVER, BC —
VANCOUVER, BC —
 Ikea is increasing the amount of products it makes in the US as the world’s largest home furnishings retailer comes under pressure from US President Donald Trump’s tariffs on furniture and kitchen cabinets. The flat-pack retailer, which made revenues of $5.5bn in the US last year, currently produces only about 15% of products that it sells in the US domestically. That compares with 75% local production in Europe and 80% in Asia. “We want to continue to expand in the US and Canada — how do we optimise a good supply set-up where we secure the right access to materials, to components, to production? That’s very long-term work that we’re doing,” Jon Abrahamsson Ring, chief executive of Inter Ikea. Trump imposed tariffs of between 10% and 50% on imports of foreign furniture and wood products. Ikea, which is responsible for about 1% of total industrial production, is set to take a significant hit.
Ikea is increasing the amount of products it makes in the US as the world’s largest home furnishings retailer comes under pressure from US President Donald Trump’s tariffs on furniture and kitchen cabinets. The flat-pack retailer, which made revenues of $5.5bn in the US last year, currently produces only about 15% of products that it sells in the US domestically. That compares with 75% local production in Europe and 80% in Asia. “We want to continue to expand in the US and Canada — how do we optimise a good supply set-up where we secure the right access to materials, to components, to production? That’s very long-term work that we’re doing,” Jon Abrahamsson Ring, chief executive of Inter Ikea. Trump imposed tariffs of between 10% and 50% on imports of foreign furniture and wood products. Ikea, which is responsible for about 1% of total industrial production, is set to take a significant hit. 


 Anthony Cabrera, who started working with a contractor in March to construct the three-bedroom house, was eager to get ahead of a fresh round of tariffs on key building materials and home items that took effect earlier this week. Mr Cabrera had already seen his initial budget of roughly $300,000 balloon to $450,000 as prices for a range of products. …A recent report from Goldman Sachs found that US consumers will shoulder as much as 55% of the cost. It takes time to raise prices on consumers, the economists noted, and US firms will increasingly pass on costs in the coming months. The new tariffs “will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market” Buddy Hughes, chairman for the NAHB, said. Affordable housing construction could be hit particularly hard, said Elena Patel, of the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center. …Matthew Walsh, at Moody’s Analytics, said that cost uncertainty will be the most immediate effect.
Anthony Cabrera, who started working with a contractor in March to construct the three-bedroom house, was eager to get ahead of a fresh round of tariffs on key building materials and home items that took effect earlier this week. Mr Cabrera had already seen his initial budget of roughly $300,000 balloon to $450,000 as prices for a range of products. …A recent report from Goldman Sachs found that US consumers will shoulder as much as 55% of the cost. It takes time to raise prices on consumers, the economists noted, and US firms will increasingly pass on costs in the coming months. The new tariffs “will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market” Buddy Hughes, chairman for the NAHB, said. Affordable housing construction could be hit particularly hard, said Elena Patel, of the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center. …Matthew Walsh, at Moody’s Analytics, said that cost uncertainty will be the most immediate effect. China’s pulp and paper industry continues to expand at an unprecedented pace, with new mill projects, advanced technologies, and state-backed financing driving record output. What began as a push to meet domestic demand has now evolved into an era of overcapacity and a structural imbalance that is reshaping trade dynamics, pricing strategies, and sustainability priorities worldwide. This expansion has far-reaching effects: global producers are contending with lower-priced exports, disrupted supply chains, and a shifting balance of power that challenges traditional market leaders in North America and Europe. …Industry observers expect consolidation in China’s pulp and paper sector, as smaller and less efficient mills struggle to survive. Strategic investments in transparency, benchmarking, and efficiency will be crucial for staying competitive in a tightening global market.
China’s pulp and paper industry continues to expand at an unprecedented pace, with new mill projects, advanced technologies, and state-backed financing driving record output. What began as a push to meet domestic demand has now evolved into an era of overcapacity and a structural imbalance that is reshaping trade dynamics, pricing strategies, and sustainability priorities worldwide. This expansion has far-reaching effects: global producers are contending with lower-priced exports, disrupted supply chains, and a shifting balance of power that challenges traditional market leaders in North America and Europe. …Industry observers expect consolidation in China’s pulp and paper sector, as smaller and less efficient mills struggle to survive. Strategic investments in transparency, benchmarking, and efficiency will be crucial for staying competitive in a tightening global market. Ireland must realise the “massive opportunity” that exists as timber construction is set to triple market value and deliver climate action, Forest Industries Ireland (FII) said. The director of FII, Mark McAuley has welcomed a
Ireland must realise the “massive opportunity” that exists as timber construction is set to triple market value and deliver climate action, Forest Industries Ireland (FII) said. The director of FII, Mark McAuley has welcomed a 
 More companies that provide rayon, lyocell and modal to fashion brands are sourcing less from ancient and endangered forests, according to the nonprofit Canopy. Although the vast majority of cellulosic fibers are still spun from virgin materials, some of the biggest producers have been quickly adopting forest-friendly and circular materials. 70% of companies making semi-synthetic, cellulose-based fibers now exhibit green practices that reduce pressures on forests. 54% of fiber producers that the group tracked have reached the nonprofit’s favorable green rating. …Canopy uses this annual report in part to help brands make informed sourcing decisions. The use of recycled materials for such fibers is still rare, although it grew to 1.1% in 2024. Such textiles represent only 6% of the global fiber market, according to Textile Exchange. It found that fibers approved by Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or other certification made up as much as 70 percent of cellulosic fiber market share.
More companies that provide rayon, lyocell and modal to fashion brands are sourcing less from ancient and endangered forests, according to the nonprofit Canopy. Although the vast majority of cellulosic fibers are still spun from virgin materials, some of the biggest producers have been quickly adopting forest-friendly and circular materials. 70% of companies making semi-synthetic, cellulose-based fibers now exhibit green practices that reduce pressures on forests. 54% of fiber producers that the group tracked have reached the nonprofit’s favorable green rating. …Canopy uses this annual report in part to help brands make informed sourcing decisions. The use of recycled materials for such fibers is still rare, although it grew to 1.1% in 2024. Such textiles represent only 6% of the global fiber market, according to Textile Exchange. It found that fibers approved by Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or other certification made up as much as 70 percent of cellulosic fiber market share.
 Several parliamentarians, key industry players and alternative materials start-ups in hemp, engineered bamboo and engineered timber attended an event designed to focus a spotlight on the new world of possibilities in building materials. The WWF and Forest Alliance NSW event was intended to showcase sustainable alternatives to timber products …with the protection of the proposed Great Koala National Park at the centre of conversations. The event was further by the Parliamentary Friends of Forests. Attending as exhibitors were House of Bamboo, Hemp Inside, Bamboo Society Australia, Australian Hemp Council, iHempNSW, BVN Architecture and betti & knutt. While XLAM … was originally on the list of presenters, an industry source says the pressure from forestry sources had forced the company to pull out. …Susie Russell was particularly inspired by House of Bamboo, realizing that similar products to timber can be made from bamboo, which only takes five years to grow.
Several parliamentarians, key industry players and alternative materials start-ups in hemp, engineered bamboo and engineered timber attended an event designed to focus a spotlight on the new world of possibilities in building materials. The WWF and Forest Alliance NSW event was intended to showcase sustainable alternatives to timber products …with the protection of the proposed Great Koala National Park at the centre of conversations. The event was further by the Parliamentary Friends of Forests. Attending as exhibitors were House of Bamboo, Hemp Inside, Bamboo Society Australia, Australian Hemp Council, iHempNSW, BVN Architecture and betti & knutt. While XLAM … was originally on the list of presenters, an industry source says the pressure from forestry sources had forced the company to pull out. …Susie Russell was particularly inspired by House of Bamboo, realizing that similar products to timber can be made from bamboo, which only takes five years to grow. The world’s largest green timber label will vote next week on whether to begin work on new traceability rules, amid renewed scrutiny and accusations over whether the body is doing enough to prevent fraud within its supply chains. The Bonn-based Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) bills itself as “the world’s most trusted mark for sustainable forestry.” …But forestry experts and whistleblowers have alleged for years that the FSC lacks a proper control system, allowing bad actors to fraudulently pass off timber that was illegally or unsustainably logged as FSC-certified. Phil Guillery, who was the FSC’s integrity director from 2011-21,
The world’s largest green timber label will vote next week on whether to begin work on new traceability rules, amid renewed scrutiny and accusations over whether the body is doing enough to prevent fraud within its supply chains. The Bonn-based Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) bills itself as “the world’s most trusted mark for sustainable forestry.” …But forestry experts and whistleblowers have alleged for years that the FSC lacks a proper control system, allowing bad actors to fraudulently pass off timber that was illegally or unsustainably logged as FSC-certified. Phil Guillery, who was the FSC’s integrity director from 2011-21, 
 Chopping down rainforests is daft. The social costs of clearing a typical patch of Brazilian Amazon are perhaps 30 times the benefits of rearing cows on it, by one estimate from 2023. The problem is, those costs, which include aggravating climate change, are spread across the entire world’s population, whereas the profits from cutting down the trees go to the men commanding the chainsaws. Somehow, the world has to find a way to make conservation pay. …Yet there is hope. Though Brazil lost more rainforest than any other country last year, due to to wildfires, it also shows how better policy can make a difference. …The pace of deforestation fell by 80% during Lula’s first terms (2003-11), and fell again when he returned in 2023, before the wildfires set things back. …Since preserving rainforests is a global public good, the world should help pay for it. [to access the full story an Economist subscription is required]
Chopping down rainforests is daft. The social costs of clearing a typical patch of Brazilian Amazon are perhaps 30 times the benefits of rearing cows on it, by one estimate from 2023. The problem is, those costs, which include aggravating climate change, are spread across the entire world’s population, whereas the profits from cutting down the trees go to the men commanding the chainsaws. Somehow, the world has to find a way to make conservation pay. …Yet there is hope. Though Brazil lost more rainforest than any other country last year, due to to wildfires, it also shows how better policy can make a difference. …The pace of deforestation fell by 80% during Lula’s first terms (2003-11), and fell again when he returned in 2023, before the wildfires set things back. …Since preserving rainforests is a global public good, the world should help pay for it. [to access the full story an Economist subscription is required]

 …The World Resources Institute calculates that forests are burning at twice the rate they were two decades ago. In Canada … the frequency and severity of forest fires have quadrupled over the last half century. …the global wildfire defence market is projecting annual growth rates that range from 8.4% to 12.6%, much of it driven by public funding. For example, the United States’ budget for wildland fire management was $1.9 billion in 2025, a 10% increase from the previous year. …On October 22, a consortium of national organizations in Canada published an open letter to the federal government asking for a five-year investment of $4.1 billion in wildfire defence. …Coupled with U.S. auto tariffs, the wildfires prompted South Korea’s government to quickly assemble a US$8.6-billion supplementary budget, of which nearly a billion was earmarked for wildfire recovery. …The bushfire crisis of 2019/2020 in Australia caused AUD$2.4 billion of insured loss. …in 2025, Brazil allocated the equivalent of USD$95 million for firefighting efforts.
…The World Resources Institute calculates that forests are burning at twice the rate they were two decades ago. In Canada … the frequency and severity of forest fires have quadrupled over the last half century. …the global wildfire defence market is projecting annual growth rates that range from 8.4% to 12.6%, much of it driven by public funding. For example, the United States’ budget for wildland fire management was $1.9 billion in 2025, a 10% increase from the previous year. …On October 22, a consortium of national organizations in Canada published an open letter to the federal government asking for a five-year investment of $4.1 billion in wildfire defence. …Coupled with U.S. auto tariffs, the wildfires prompted South Korea’s government to quickly assemble a US$8.6-billion supplementary budget, of which nearly a billion was earmarked for wildfire recovery. …The bushfire crisis of 2019/2020 in Australia caused AUD$2.4 billion of insured loss. …in 2025, Brazil allocated the equivalent of USD$95 million for firefighting efforts.




 SWEDEN — Ingka Investments, the investment arm of Ingka Group (the largest IKEA retailer), has agreed to acquire approximately 153,000 hectares of land in Latvia and Estonia, of which 89% are forestland, from Södra, Sweden’s largest forest owners’ association. Completion is subject to approval by the relevant regulatory authorities. “Our unique ownership structure allows us to invest with a long-term perspective rather than short-term quarterly thinking.” …As the world’s largest IKEA retailer, Ingka Group operates in 31 markets and represents 87% of global IKEA sales. …Niks Sauva, Country Manager, Ingka Investments Latvia, continued: “We’re committed to creating more value locally in the Baltics. Our goal is to increase the share of wood processed regionally to strengthen the Baltic forestry value chain.” …Completion is subject to approval by the relevant authorities in Latvia and Estonia.
SWEDEN — Ingka Investments, the investment arm of Ingka Group (the largest IKEA retailer), has agreed to acquire approximately 153,000 hectares of land in Latvia and Estonia, of which 89% are forestland, from Södra, Sweden’s largest forest owners’ association. Completion is subject to approval by the relevant regulatory authorities. “Our unique ownership structure allows us to invest with a long-term perspective rather than short-term quarterly thinking.” …As the world’s largest IKEA retailer, Ingka Group operates in 31 markets and represents 87% of global IKEA sales. …Niks Sauva, Country Manager, Ingka Investments Latvia, continued: “We’re committed to creating more value locally in the Baltics. Our goal is to increase the share of wood processed regionally to strengthen the Baltic forestry value chain.” …Completion is subject to approval by the relevant authorities in Latvia and Estonia.
 Europe’s sawn timber industry is grappling with growing strategic uncertainty and rising compliance costs while the EU prepares to delay implementation of its landmark anti-deforestation law for a second time. While the postponement of the regulation to December 2026 may offer temporary relief, it also threatens to erode market incentives for early adopters and undermine confidence in the bloc’s regulatory direction. Producers across the continent have already invested billions of euros to meet the regulation’s demanding traceability requirements—developing digital platforms, upgrading Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and restructuring supply chains to prove that every cubic meter of wood originates from deforestation-free sources. …In a strongly worded letter to the EC’s Environment Commissioner Jessika Roswall, a
Europe’s sawn timber industry is grappling with growing strategic uncertainty and rising compliance costs while the EU prepares to delay implementation of its landmark anti-deforestation law for a second time. While the postponement of the regulation to December 2026 may offer temporary relief, it also threatens to erode market incentives for early adopters and undermine confidence in the bloc’s regulatory direction. Producers across the continent have already invested billions of euros to meet the regulation’s demanding traceability requirements—developing digital platforms, upgrading Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and restructuring supply chains to prove that every cubic meter of wood originates from deforestation-free sources. …In a strongly worded letter to the EC’s Environment Commissioner Jessika Roswall, a 

 Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) rose faster in 2024 than in any year since records began. …Our new satellite analysis shows that the Amazon rainforest is struggling to keep up. And worryingly, the satellite that made this discovery could soon be switched off [due to proposed NASA budget cuts.]. Systematic measurements of CO₂ in the atmosphere began in the late 1950s. …Across six decades of measurements, CO₂ has gradually increased. …The largest change was over the Amazon, where much less CO₂ is being absorbed. Similar slowdowns also appeared over southern Africa and southeast Asia, parts of Australia, the eastern US, Alaska and western Russia. Conversely, we detected more carbon being absorbed over western Europe, the US and central Canada. …It’s not yet clear whether 2023-24 is a short-term blip or an early sign of a long-term shift. But evidence points to an increasingly fragile situation, as tropical forests are stressed by hot and dry conditions.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) rose faster in 2024 than in any year since records began. …Our new satellite analysis shows that the Amazon rainforest is struggling to keep up. And worryingly, the satellite that made this discovery could soon be switched off [due to proposed NASA budget cuts.]. Systematic measurements of CO₂ in the atmosphere began in the late 1950s. …Across six decades of measurements, CO₂ has gradually increased. …The largest change was over the Amazon, where much less CO₂ is being absorbed. Similar slowdowns also appeared over southern Africa and southeast Asia, parts of Australia, the eastern US, Alaska and western Russia. Conversely, we detected more carbon being absorbed over western Europe, the US and central Canada. …It’s not yet clear whether 2023-24 is a short-term blip or an early sign of a long-term shift. But evidence points to an increasingly fragile situation, as tropical forests are stressed by hot and dry conditions. Google has announced plans to address greenhouse gases beyond carbon dioxide by purchasing credits to support the emerging market for removing short-lived but highly potent “superpollutants.” The company will buy up to 25,000 tonnes of superpollutant-destruction credits by 2030 from two organisations, Recoolit and Cool Effect—equivalent to about one million tonnes of CO₂ removal over the long term. While carbon dioxide remains a key focus, Google said gases such as methane, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrous oxide have a much greater near-term warming impact. “It’s the right thing to do for the planet,” said Randy Spock, Google’s carbon credits and removals lead. “CO₂ is obviously very important… but if we think only about CO₂, then we’re just looking at one piece of the puzzle.” …Sam Abernethy, a climate scientist at Spark Climate Solutions, said: “Superpollutants only get a few percent of climate finance… that’s a misallocation given their importance.”
Google has announced plans to address greenhouse gases beyond carbon dioxide by purchasing credits to support the emerging market for removing short-lived but highly potent “superpollutants.” The company will buy up to 25,000 tonnes of superpollutant-destruction credits by 2030 from two organisations, Recoolit and Cool Effect—equivalent to about one million tonnes of CO₂ removal over the long term. While carbon dioxide remains a key focus, Google said gases such as methane, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrous oxide have a much greater near-term warming impact. “It’s the right thing to do for the planet,” said Randy Spock, Google’s carbon credits and removals lead. “CO₂ is obviously very important… but if we think only about CO₂, then we’re just looking at one piece of the puzzle.” …Sam Abernethy, a climate scientist at Spark Climate Solutions, said: “Superpollutants only get a few percent of climate finance… that’s a misallocation given their importance.”
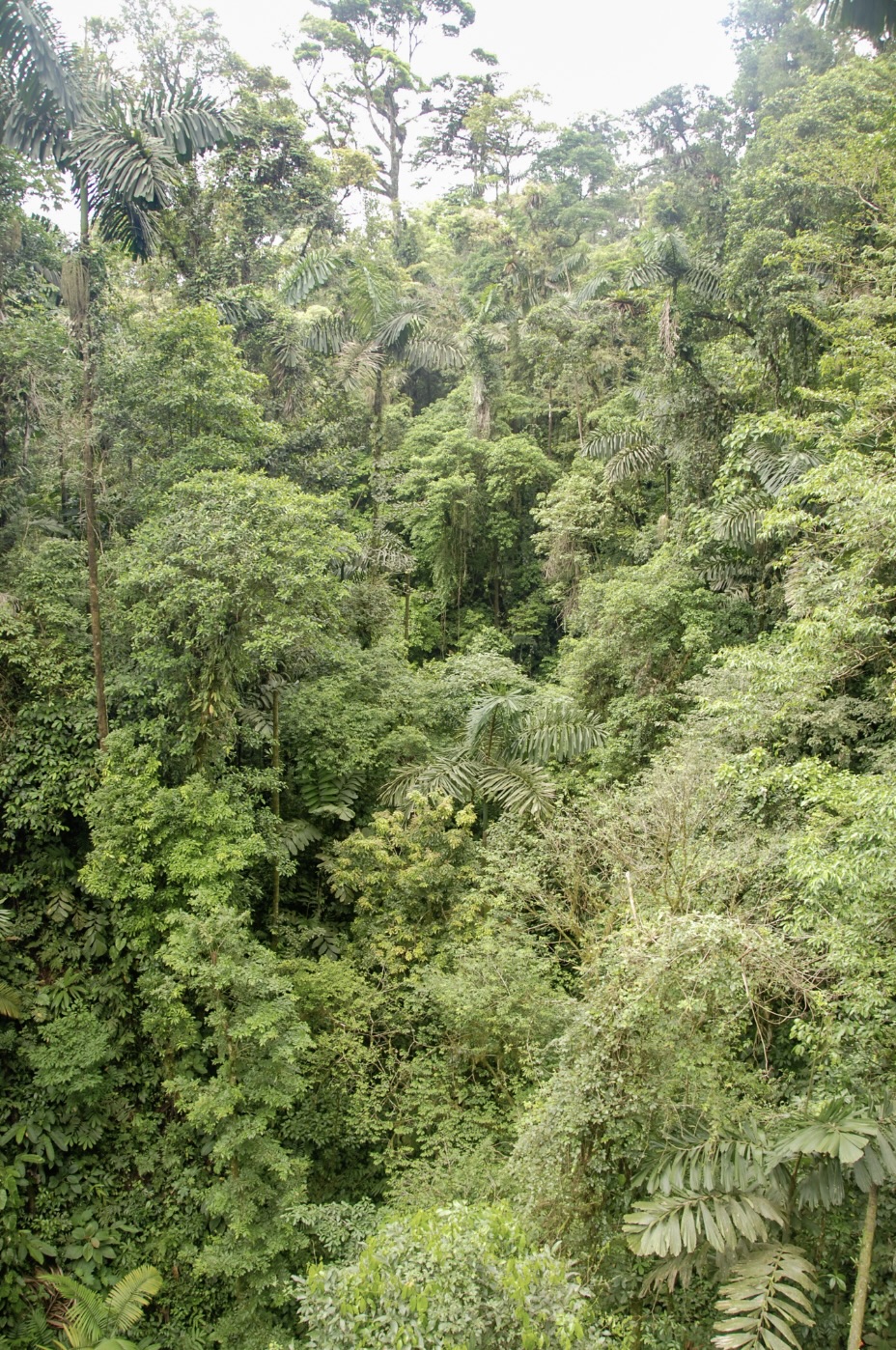 Woody trunks and branches of trees in the wet tropical rainforests of Queensland are losing their ability to absorb excess carbon dioxide. That’s according to an analysis of 49 years’ worth of data,
Woody trunks and branches of trees in the wet tropical rainforests of Queensland are losing their ability to absorb excess carbon dioxide. That’s according to an analysis of 49 years’ worth of data,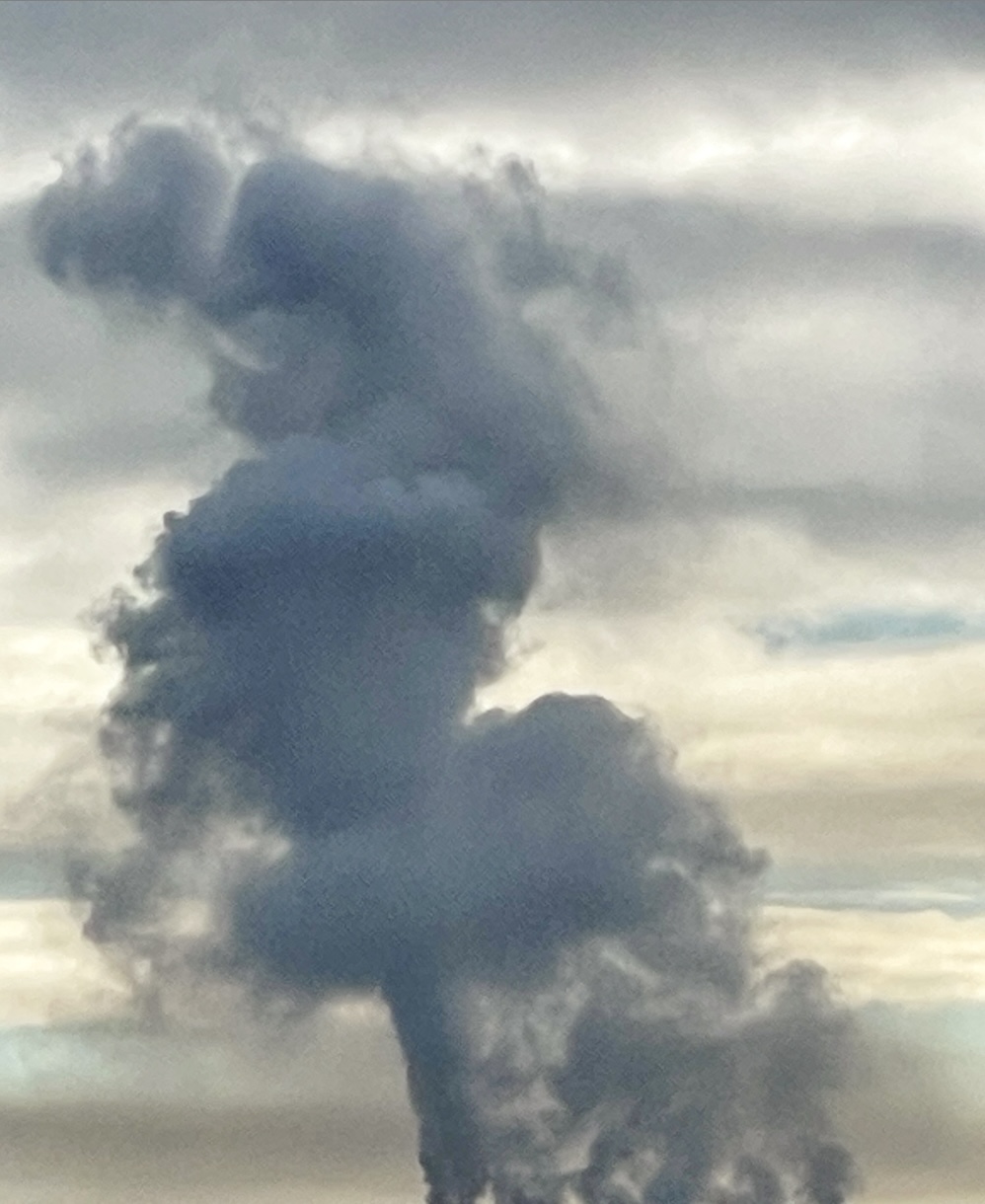  GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.
GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.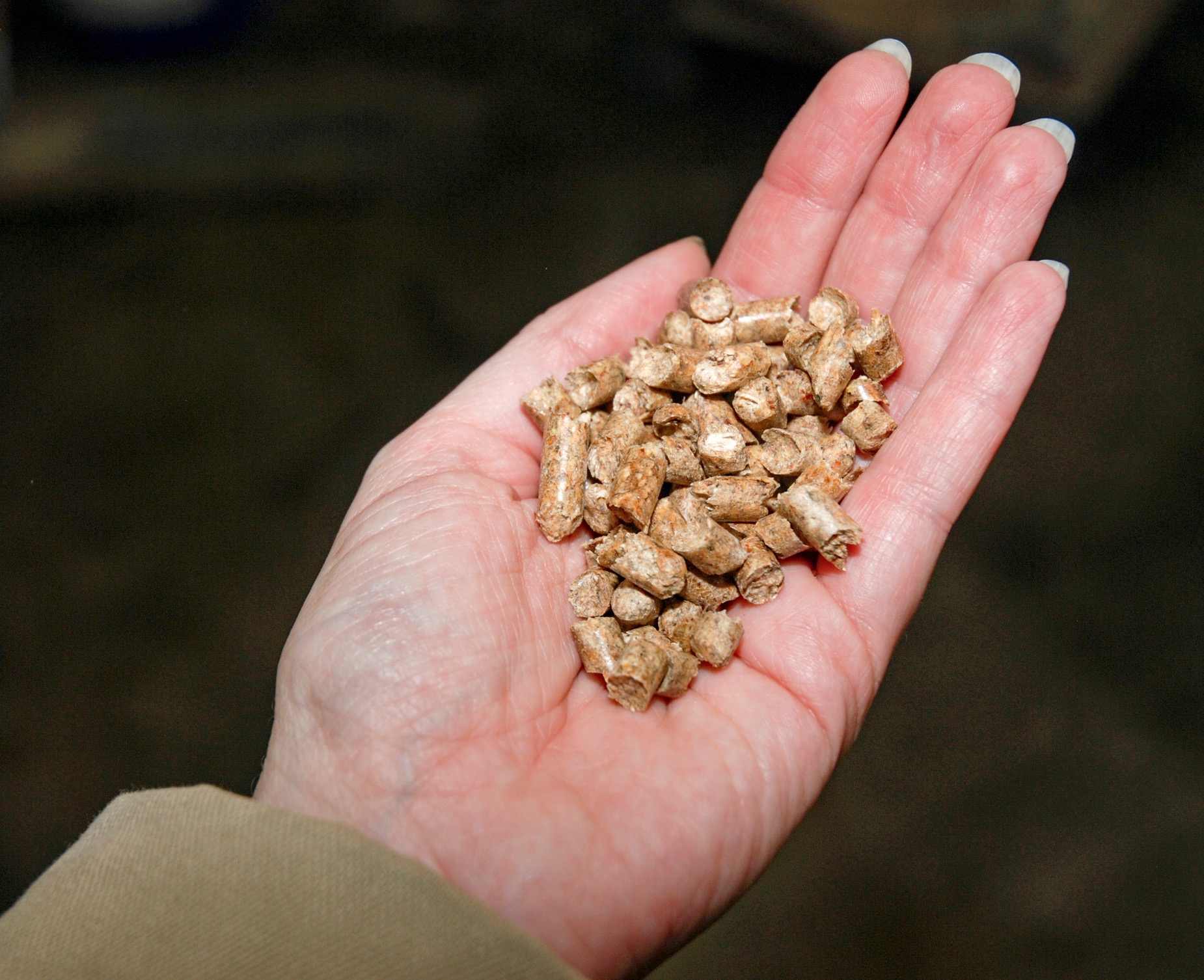 Ten lawsuits have been filed against Drax after diagnoses of asthma allegedly linked to its wood pellet fuel, it has been revealed. Current and former workers at the UK’s largest power station claim they have not been adequately protected against sustained exposure to wood dust, which can cause serious health problems including asthma, dermatitis and nasal cancer. Six compensation claims were settled out of court and four have trial dates in 2026, an investigation by Land and Climate Review found. A class action lawsuit was also filed against the company this month over health concerns in the US, representing 700 people who live near one of Drax’s wood pellet mills in Mississippi. The company is also being investigated by the UK Financial Conduct Authority over “historical statements” made about its wood pellet fuel.
Ten lawsuits have been filed against Drax after diagnoses of asthma allegedly linked to its wood pellet fuel, it has been revealed. Current and former workers at the UK’s largest power station claim they have not been adequately protected against sustained exposure to wood dust, which can cause serious health problems including asthma, dermatitis and nasal cancer. Six compensation claims were settled out of court and four have trial dates in 2026, an investigation by Land and Climate Review found. A class action lawsuit was also filed against the company this month over health concerns in the US, representing 700 people who live near one of Drax’s wood pellet mills in Mississippi. The company is also being investigated by the UK Financial Conduct Authority over “historical statements” made about its wood pellet fuel.