 Canada-US Trade Minister Dominic LeBlanc says he sees a path to renew the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) and anticipates more specifics from the U.S. administration soon. Gearing up to head back to Washington, DC next week to meet with US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer and “others” next week, LeBlanc said he’s “not pessimistic about renewing the trilateral framework.” “Renewing. It doesn’t expire, it expires in 2036. But the review is not a renegotiation,” LeBlanc said. LeBlanc said two of the key factors underpinning his optimism are that when US President Trump levied his latest global tariff, he maintained the CUSMA exemption, and because American political and business leaders are “speaking up more now.” …Amid speculation that Trump wants to scrap the trilateral trade pact and strike trade deals with Canada and Mexico independently, LeBlanc said the way he sees it, Trump may pursue separate bilateral deals, but that doesn’t necessarily mean the end of CUSMA.
Canada-US Trade Minister Dominic LeBlanc says he sees a path to renew the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) and anticipates more specifics from the U.S. administration soon. Gearing up to head back to Washington, DC next week to meet with US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer and “others” next week, LeBlanc said he’s “not pessimistic about renewing the trilateral framework.” “Renewing. It doesn’t expire, it expires in 2036. But the review is not a renegotiation,” LeBlanc said. LeBlanc said two of the key factors underpinning his optimism are that when US President Trump levied his latest global tariff, he maintained the CUSMA exemption, and because American political and business leaders are “speaking up more now.” …Amid speculation that Trump wants to scrap the trilateral trade pact and strike trade deals with Canada and Mexico independently, LeBlanc said the way he sees it, Trump may pursue separate bilateral deals, but that doesn’t necessarily mean the end of CUSMA.
 Trade negotiations used to be underpinned by an unspoken assumption: that trade barriers were lose-lose propositions. All sides could gain something if they mutually disarmed. …[They] were always about how much tariffs and other walls would go down, not how much they would go up. …United States Trade Representative Jamieson Greer sums up the Trump administration’s break with the postwar trade consensus, saying the administration is “focused on reshoring supply chains related to automotive, steel, aluminum … If Canada wants to come in and participate in this type of reshoring we’re trying to do, we’re happy to have those discussions.” …The U.S. wants higher tariffs at home, and lower tariffs abroad. The old give-and-take is now take-and-take. …”We want to have production here. We don’t necessarily want to be dependent on China, Canada or anybody else for things like cars.” [This article is only available to subscribers to the Globe and Mail]
Trade negotiations used to be underpinned by an unspoken assumption: that trade barriers were lose-lose propositions. All sides could gain something if they mutually disarmed. …[They] were always about how much tariffs and other walls would go down, not how much they would go up. …United States Trade Representative Jamieson Greer sums up the Trump administration’s break with the postwar trade consensus, saying the administration is “focused on reshoring supply chains related to automotive, steel, aluminum … If Canada wants to come in and participate in this type of reshoring we’re trying to do, we’re happy to have those discussions.” …The U.S. wants higher tariffs at home, and lower tariffs abroad. The old give-and-take is now take-and-take. …”We want to have production here. We don’t necessarily want to be dependent on China, Canada or anybody else for things like cars.” [This article is only available to subscribers to the Globe and Mail]
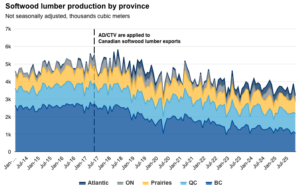 Anti-dumping and countervailing duties, and now additional tariffs on softwood lumber and derivative wood products add to a long history of trade measures applied to Canadian exports. …Recent trade data shows exports of targeted wood products to the US have declined by roughly 11% in 2025 from a year earlier with losses concentrated in Quebec and BC. Export gains elsewhere have only partially compensated for reduced US market access—in part reflecting the geographical constraints in shipping lumber and wood products. …Average industrial capacity utilization rate for wood product manufacturing has declined roughly 10 percentage points to 75% in 2025 Q3 from a decade earlier, while employment in sawmills and wood preservation fell roughly 20% between May 2017 and November 2025 with more pronounced declines in BC (-32%) and Quebec (-13%). …Reduced domestic supply could also put pressure on downstream industries such as pulp and paper mills and construction. The combination of weak demand and constrained supply raises the risk of further production curtailments and mill closures.
Anti-dumping and countervailing duties, and now additional tariffs on softwood lumber and derivative wood products add to a long history of trade measures applied to Canadian exports. …Recent trade data shows exports of targeted wood products to the US have declined by roughly 11% in 2025 from a year earlier with losses concentrated in Quebec and BC. Export gains elsewhere have only partially compensated for reduced US market access—in part reflecting the geographical constraints in shipping lumber and wood products. …Average industrial capacity utilization rate for wood product manufacturing has declined roughly 10 percentage points to 75% in 2025 Q3 from a decade earlier, while employment in sawmills and wood preservation fell roughly 20% between May 2017 and November 2025 with more pronounced declines in BC (-32%) and Quebec (-13%). …Reduced domestic supply could also put pressure on downstream industries such as pulp and paper mills and construction. The combination of weak demand and constrained supply raises the risk of further production curtailments and mill closures.

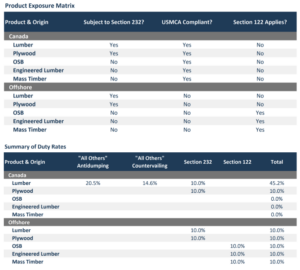 President Donald Trump announced a temporary import duty under Section 122 of the Trade Act of 1974, shortly after the US Supreme Court struck down his tariffs imposed under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act. The Section 122 surcharge is scheduled to take effect February 24 and remain in place for up to 150 days. Under the proclamation, Section 122 duties do not apply to goods that are subject to Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 or that are USMCA compliant. The implications for wood products are as follows:
President Donald Trump announced a temporary import duty under Section 122 of the Trade Act of 1974, shortly after the US Supreme Court struck down his tariffs imposed under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act. The Section 122 surcharge is scheduled to take effect February 24 and remain in place for up to 150 days. Under the proclamation, Section 122 duties do not apply to goods that are subject to Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 or that are USMCA compliant. The implications for wood products are as follows: Delaware – President Trump’s announcement of a 15% tariff following last week’s Supreme Court ruling has created uncertainty in financial markets. While some retailers and consumer companies may benefit from reduced trade barriers, domestic lumber and packaging firms face increased competition from cheaper imports. …On Monday, domestic lumber companies saw their stock prices drop amid concerns that cheaper foreign imports could undercut their pricing power. The court’s tariff decision threatens to erode the competitive advantage that domestic packaging and lumber businesses previously held against lower-cost foreign competitors, industry analysts warn. RBC analysts identified potential negative consequences for companies including Clearwater Paper, Rayonier, Sylvamo, and Smurfit WestRock. A recent industry survey revealed that most U.S. purchasers reported declining containerboard prices in February, as increased European imports expanded supply and created additional pricing pressures. Monday trading saw Smurfit and domestic competitor International Paper decline by 7% and 6%, respectively.
Delaware – President Trump’s announcement of a 15% tariff following last week’s Supreme Court ruling has created uncertainty in financial markets. While some retailers and consumer companies may benefit from reduced trade barriers, domestic lumber and packaging firms face increased competition from cheaper imports. …On Monday, domestic lumber companies saw their stock prices drop amid concerns that cheaper foreign imports could undercut their pricing power. The court’s tariff decision threatens to erode the competitive advantage that domestic packaging and lumber businesses previously held against lower-cost foreign competitors, industry analysts warn. RBC analysts identified potential negative consequences for companies including Clearwater Paper, Rayonier, Sylvamo, and Smurfit WestRock. A recent industry survey revealed that most U.S. purchasers reported declining containerboard prices in February, as increased European imports expanded supply and created additional pricing pressures. Monday trading saw Smurfit and domestic competitor International Paper decline by 7% and 6%, respectively. US President Donald Trump just lost his biggest emergency tariff weapon at the US Supreme Court – but for Canadian exporters and long‑term investors, the real story is that the pressure has shifted to narrower, more strategic sectors that matter for jobs, growth and returns. …Trump reacted by promising new tariffs through other statutes. …Section 232 now defines Canada’s real exposure. …Softwood timber and lumber: 10 percent tariffs imposed last October, alongside US countervailing and anti‑dumping duties on Canadian lumber that the Commerce Department increased from 14.5 percent to 35 percent earlier this year. …Upholstered wooden furniture, cabinets and vanities: 25 percent tariffs since last October; a planned increase in January was paused. …Dominic LeBlanc, Canada’s minister for US–Canadian trade relations, told CBC News that “what’s hurting the Canadian economy are the sectoral tariffs under a different American law,” and said this “reminds us again of the importance of diversifying our trading relationships.”
US President Donald Trump just lost his biggest emergency tariff weapon at the US Supreme Court – but for Canadian exporters and long‑term investors, the real story is that the pressure has shifted to narrower, more strategic sectors that matter for jobs, growth and returns. …Trump reacted by promising new tariffs through other statutes. …Section 232 now defines Canada’s real exposure. …Softwood timber and lumber: 10 percent tariffs imposed last October, alongside US countervailing and anti‑dumping duties on Canadian lumber that the Commerce Department increased from 14.5 percent to 35 percent earlier this year. …Upholstered wooden furniture, cabinets and vanities: 25 percent tariffs since last October; a planned increase in January was paused. …Dominic LeBlanc, Canada’s minister for US–Canadian trade relations, told CBC News that “what’s hurting the Canadian economy are the sectoral tariffs under a different American law,” and said this “reminds us again of the importance of diversifying our trading relationships.” 

 VANCOUVER, Washington — Canadian-owned Western Forest Products plans to expand its Fruit Valley manufacturing operation, according to pre-planning documents submitted to the city of Vancouver. Plans show the company expects to build up to three prefabricated steel buildings and an office building, as well as demolish its existing Fruit Valley lumber drying kilns and storage buildings. “We are supporting a modest expansion of our product and service portfolio,” Babita Khunkhun, the company’s senior director of communications, said. Khunkhun said planning for the expansion will continue throughout the year. The company intends to invest in new machinery at its Fruit Valley manufacturing site and make ready-to-install fabricated glulam beams, she said. The Fruit Valley operation is currently used for secondary lumber manufacturing. …A summer blaze left the company’s Columbia Vista sawmill beyond repair according to a state layoff notification from July. The company has decided to sell that site.
VANCOUVER, Washington — Canadian-owned Western Forest Products plans to expand its Fruit Valley manufacturing operation, according to pre-planning documents submitted to the city of Vancouver. Plans show the company expects to build up to three prefabricated steel buildings and an office building, as well as demolish its existing Fruit Valley lumber drying kilns and storage buildings. “We are supporting a modest expansion of our product and service portfolio,” Babita Khunkhun, the company’s senior director of communications, said. Khunkhun said planning for the expansion will continue throughout the year. The company intends to invest in new machinery at its Fruit Valley manufacturing site and make ready-to-install fabricated glulam beams, she said. The Fruit Valley operation is currently used for secondary lumber manufacturing. …A summer blaze left the company’s Columbia Vista sawmill beyond repair according to a state layoff notification from July. The company has decided to sell that site. An Oregon jury has awarded $305 million to 16 wildfire survivors harmed by the Santiam Canyon wildfire that burned across hundreds of thousands of acres in 2020. This is the largest jury verdict issued in relation to the James v. PacifiCorp class-action lawsuit, pushing PacifiCorp’s total liability past $1 billion. PacifiCorp — the parent company of Pacific Power, Oregon’s second-largest electric utility — kept its lines charged over the 2020 Labor Day weekend, despite fire officials’ warnings about hot, windy weather. Five people died in the Santiam Canyon fire, and more than 400,000 acres burned across four counties. In 2023, a jury found PacifiCorp was reckless and acted in “gross negligence” in relation to multiple wildfires, including the Santiam fire. In addition to the 17 plaintiffs who sued the company in that case, the jury found a broader class of thousands of people can bring additional claims against PacifiCorp for those wildfires.
An Oregon jury has awarded $305 million to 16 wildfire survivors harmed by the Santiam Canyon wildfire that burned across hundreds of thousands of acres in 2020. This is the largest jury verdict issued in relation to the James v. PacifiCorp class-action lawsuit, pushing PacifiCorp’s total liability past $1 billion. PacifiCorp — the parent company of Pacific Power, Oregon’s second-largest electric utility — kept its lines charged over the 2020 Labor Day weekend, despite fire officials’ warnings about hot, windy weather. Five people died in the Santiam Canyon fire, and more than 400,000 acres burned across four counties. In 2023, a jury found PacifiCorp was reckless and acted in “gross negligence” in relation to multiple wildfires, including the Santiam fire. In addition to the 17 plaintiffs who sued the company in that case, the jury found a broader class of thousands of people can bring additional claims against PacifiCorp for those wildfires.
 MOSINEE, Wisconsin — About 200 employees at the Mosinee paper mill were told before their shifts this week that their jobs are at risk as Ahlstrom moves forward with a phased shutdown of key operations at the plant. Several employees, speaking on condition of anonymity, told Wausau Pilot late Wednesday that management told workers Paper Machine No. 2 will shut down June 30, with Paper Machine No. 3 and the pulp mill slated to close Sept. 30. …In the letter to suppliers, Ahlstrom said it plans to permanently close the pulp mill and idle the M2 and M3 paper machines as part of a restructuring of operations at the Mosinee facility. The company cited rising costs and limited automation at those operations as reasons for the decision. …Ahlstrom said Paper Machines No. 1 and No. 4 will continue operating at the Mosinee mill. The company also said it plans to invest in modern technologies at those remaining machines.
MOSINEE, Wisconsin — About 200 employees at the Mosinee paper mill were told before their shifts this week that their jobs are at risk as Ahlstrom moves forward with a phased shutdown of key operations at the plant. Several employees, speaking on condition of anonymity, told Wausau Pilot late Wednesday that management told workers Paper Machine No. 2 will shut down June 30, with Paper Machine No. 3 and the pulp mill slated to close Sept. 30. …In the letter to suppliers, Ahlstrom said it plans to permanently close the pulp mill and idle the M2 and M3 paper machines as part of a restructuring of operations at the Mosinee facility. The company cited rising costs and limited automation at those operations as reasons for the decision. …Ahlstrom said Paper Machines No. 1 and No. 4 will continue operating at the Mosinee mill. The company also said it plans to invest in modern technologies at those remaining machines.
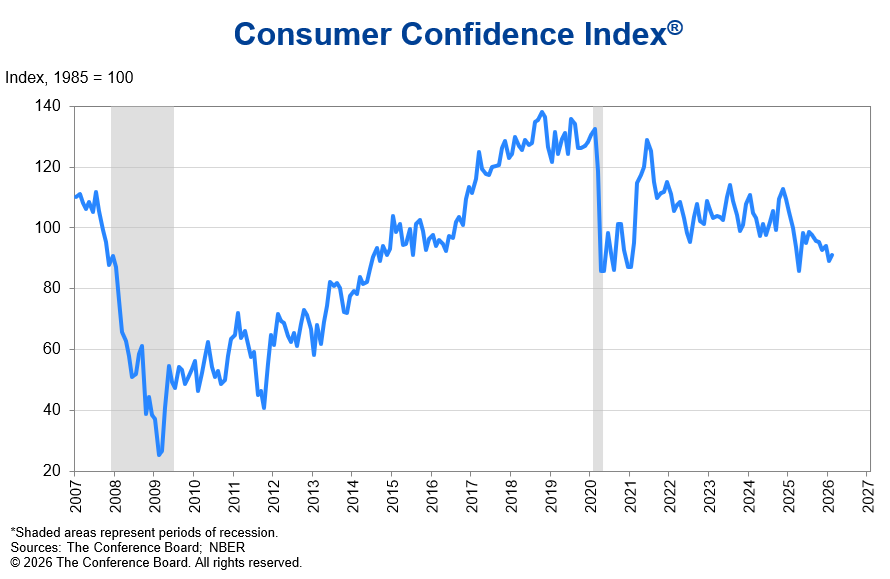
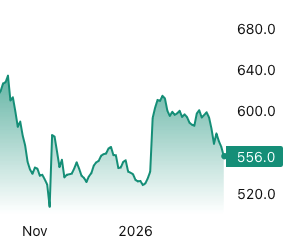 Lumber futures fell toward $550 per thousand board feet, marking a six-week low, as a stagnant North American housing sector failed to absorb heavy seasonal inventories. Demand weakened as January data showed a 7% year over year drop in single family starts and an 8.4% decline in units under construction. High 6.25% mortgage rates and a 5.8% slump in Canadian home sales during January 2026 further stalled new project starts. On the supply side, regional inventory remained bloated. While BC curtailments continued harsh winter storms in the US South halted jobsite activity more than mill output, creating a distributor logjam and forcing aggressive dealer discounting to clear yard space. Additionally, while Trump’s administration 45% softwood duties were meant to buoy prices they instead stifled demand by adding nearly $17,500 to average home costs. This eroded the builder confidence needed to clear current supply.
Lumber futures fell toward $550 per thousand board feet, marking a six-week low, as a stagnant North American housing sector failed to absorb heavy seasonal inventories. Demand weakened as January data showed a 7% year over year drop in single family starts and an 8.4% decline in units under construction. High 6.25% mortgage rates and a 5.8% slump in Canadian home sales during January 2026 further stalled new project starts. On the supply side, regional inventory remained bloated. While BC curtailments continued harsh winter storms in the US South halted jobsite activity more than mill output, creating a distributor logjam and forcing aggressive dealer discounting to clear yard space. Additionally, while Trump’s administration 45% softwood duties were meant to buoy prices they instead stifled demand by adding nearly $17,500 to average home costs. This eroded the builder confidence needed to clear current supply.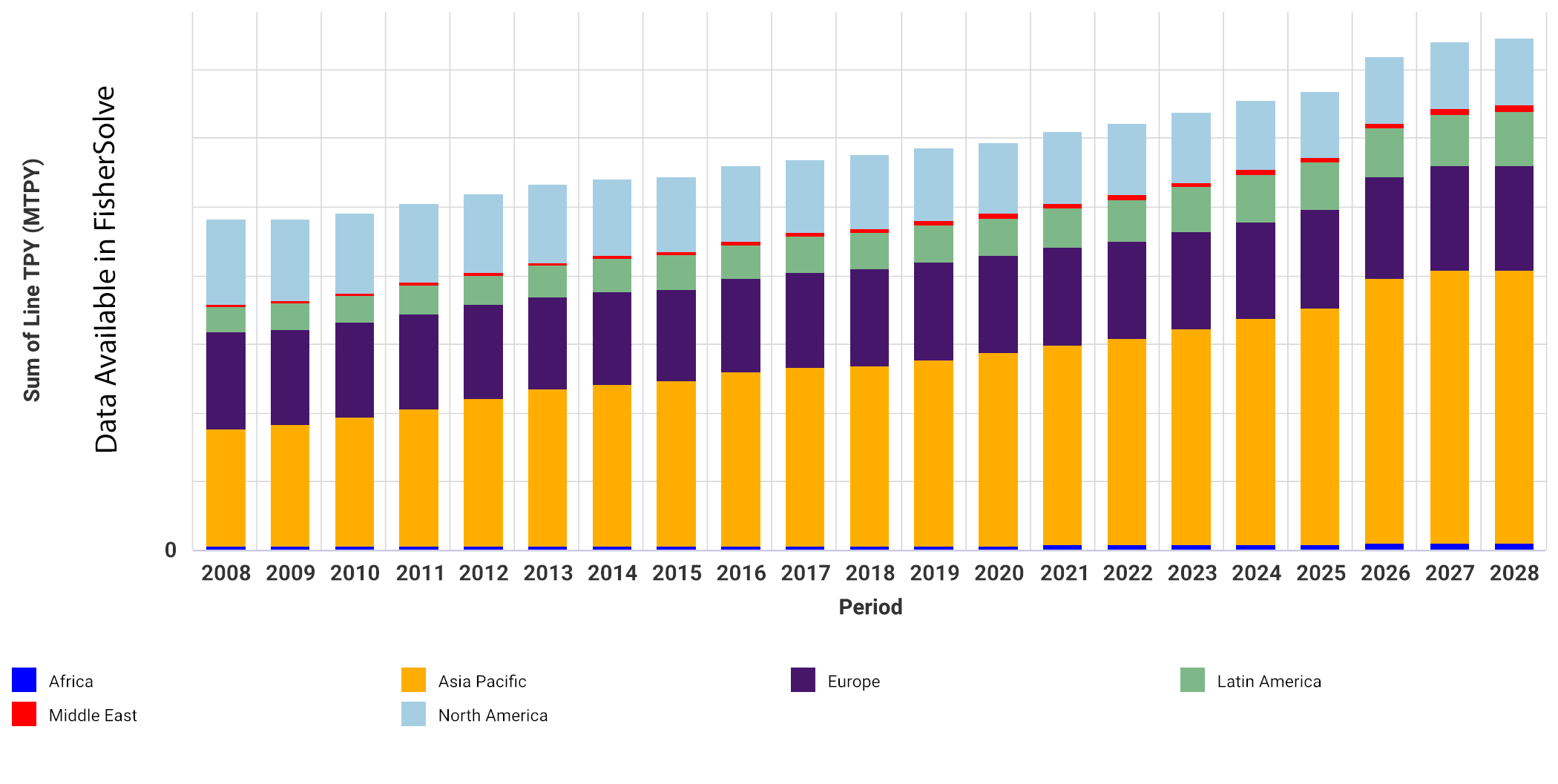
 US labor productivity in construction falls 30% from 1970 to 2024, while aggregate US labor productivity more than doubles over the same period, widening a long-running gap between construction and the wider economy. Since 1965, construction labor productivity falls by an average 0.6% per year, while economy-wide productivity grows about 1.6% per year, based on analysis by Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research. The analysis links part of the gap to limited innovation in construction equipment and processes after a period of faster adoption in the 1950s and 1960s. The share of industrial machines in total construction production costs rises from 4% in 1948 to 12% in 1968, then slips to 10% in the 1970s and stays near that level, while pre-fabrication’s share of new residential housing units falls from about one-third at its peak in 1960–1970 to 5%.
US labor productivity in construction falls 30% from 1970 to 2024, while aggregate US labor productivity more than doubles over the same period, widening a long-running gap between construction and the wider economy. Since 1965, construction labor productivity falls by an average 0.6% per year, while economy-wide productivity grows about 1.6% per year, based on analysis by Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research. The analysis links part of the gap to limited innovation in construction equipment and processes after a period of faster adoption in the 1950s and 1960s. The share of industrial machines in total construction production costs rises from 4% in 1948 to 12% in 1968, then slips to 10% in the 1970s and stays near that level, while pre-fabrication’s share of new residential housing units falls from about one-third at its peak in 1960–1970 to 5%.
 The Wood Innovations Funding Opportunity supports the growth and expansion of U.S. wood products and wood energy markets, advancing sustainable forest management and the long-term stewardship of National Forest System (NFS) lands and other forested areas. …The Wood Innovations Funding Opportunity provides a strategic platform for public, private, and non-profit entities to expand wood markets, promote sustainable forest management, and advance wood energy and mass timber technologies across the United States. By funding projects that create tangible economic and environmental impact, the program strengthens domestic wood product industries while supporting the responsible management of forest resources. Deadline is April 22, 2026
The Wood Innovations Funding Opportunity supports the growth and expansion of U.S. wood products and wood energy markets, advancing sustainable forest management and the long-term stewardship of National Forest System (NFS) lands and other forested areas. …The Wood Innovations Funding Opportunity provides a strategic platform for public, private, and non-profit entities to expand wood markets, promote sustainable forest management, and advance wood energy and mass timber technologies across the United States. By funding projects that create tangible economic and environmental impact, the program strengthens domestic wood product industries while supporting the responsible management of forest resources. Deadline is April 22, 2026 MESA COUNTY, Colorado. – Mesa County commissioners have passed a wildfire resiliency code that will affect the construction of new houses and projects on current structures, including re-roofing. The code, required by state legislation, applies only to buildings in the Wildland Urban Interface — a designated area marking locations close to potential wildfires. It mandates that projects in those areas use more fire-resistant materials and regulates where new structures can be built. “It’s not going to keep houses from burning down…,” Davis said. “What it’s designed to do is to keep it from burning as quick and as violently so that people can get out and get to safety.” Davis said the new code could make building in affected areas slower and more expensive. “To make things fire resistant, it costs money. The cheapest siding out there is wood-based and more affordable, but it’s also going to be more flammable,” Davis said.
MESA COUNTY, Colorado. – Mesa County commissioners have passed a wildfire resiliency code that will affect the construction of new houses and projects on current structures, including re-roofing. The code, required by state legislation, applies only to buildings in the Wildland Urban Interface — a designated area marking locations close to potential wildfires. It mandates that projects in those areas use more fire-resistant materials and regulates where new structures can be built. “It’s not going to keep houses from burning down…,” Davis said. “What it’s designed to do is to keep it from burning as quick and as violently so that people can get out and get to safety.” Davis said the new code could make building in affected areas slower and more expensive. “To make things fire resistant, it costs money. The cheapest siding out there is wood-based and more affordable, but it’s also going to be more flammable,” Davis said.
 Large, bipartisan majorities of voters across eight Western states remain concerned about the impacts of climate change and opposed to efforts by the Trump administration to weaken environmental rules and public lands protections. Eighty-four percent of Western voters say “rollbacks of laws that protect our land, water and wildlife” are a serious problem, up from 68% eight years ago, according to a poll released by Colorado College’s State of the Rockies project. The annual Conservation in the West poll has measured Western voters’ views of environmental and energy issues since 2011. The 2026 survey is based on interviews conducted in January with 3,419 voters in Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Wyoming. “After 16 years, it’s become a rare longitudinal data set that lets us track how public attitudes have shifted over time throughout the West,” said Ian Johnson, Colorado College’s director of strategic initiatives and sustainability.
Large, bipartisan majorities of voters across eight Western states remain concerned about the impacts of climate change and opposed to efforts by the Trump administration to weaken environmental rules and public lands protections. Eighty-four percent of Western voters say “rollbacks of laws that protect our land, water and wildlife” are a serious problem, up from 68% eight years ago, according to a poll released by Colorado College’s State of the Rockies project. The annual Conservation in the West poll has measured Western voters’ views of environmental and energy issues since 2011. The 2026 survey is based on interviews conducted in January with 3,419 voters in Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah and Wyoming. “After 16 years, it’s become a rare longitudinal data set that lets us track how public attitudes have shifted over time throughout the West,” said Ian Johnson, Colorado College’s director of strategic initiatives and sustainability. ARIZONA — The Forest Service budget to thin the forest is down. But hey, at least there’s a budget. That is the bad news/good news gist of a report on the 4-Forests Restoration Initiative (4-FRI) delivered last week at the Natural Resources Working Group meeting. Fortunately, the state Forestry Department is also continuing to fund thinning projects, including creating buffer zones around forested communities like Payson. However, time may be running out to restore the overgrown, drought-plagued forest. The meeting also featured a report documenting the worsening condition of the forest as thinning efforts falter. Jon Orona, with Arizona Department of Forestry and Fire Management, reported that 2025 was the fifth-driest year ever recorded – with average temperatures between 6 and 12 degrees above normal.
ARIZONA — The Forest Service budget to thin the forest is down. But hey, at least there’s a budget. That is the bad news/good news gist of a report on the 4-Forests Restoration Initiative (4-FRI) delivered last week at the Natural Resources Working Group meeting. Fortunately, the state Forestry Department is also continuing to fund thinning projects, including creating buffer zones around forested communities like Payson. However, time may be running out to restore the overgrown, drought-plagued forest. The meeting also featured a report documenting the worsening condition of the forest as thinning efforts falter. Jon Orona, with Arizona Department of Forestry and Fire Management, reported that 2025 was the fifth-driest year ever recorded – with average temperatures between 6 and 12 degrees above normal. More than 110 million acres of land across the U.S. are protected in 806 federally designated wilderness areas – together an area slightly larger than the state of California. For the most part, these places have been left alone for decades, in keeping with the 1964 Wilderness Act’s directive that they be “untrammeled by man.” But in a time when lands are experiencing the effects of climate change and people are renewing their understanding of Indigenous knowledge and stewardship practices, protecting these places may require action, not inaction. …First, the American ideal that wildlands flourish best in the absence of human management – conflicts with the growing understanding that many wilderness areas are part of the ancestral homelands of Indigenous peoples, who tended those lands for thousands of years. …And second, as climate change and ecological stressors affect wilderness, human intervention could help sustain the very ecological qualities that are protected.
More than 110 million acres of land across the U.S. are protected in 806 federally designated wilderness areas – together an area slightly larger than the state of California. For the most part, these places have been left alone for decades, in keeping with the 1964 Wilderness Act’s directive that they be “untrammeled by man.” But in a time when lands are experiencing the effects of climate change and people are renewing their understanding of Indigenous knowledge and stewardship practices, protecting these places may require action, not inaction. …First, the American ideal that wildlands flourish best in the absence of human management – conflicts with the growing understanding that many wilderness areas are part of the ancestral homelands of Indigenous peoples, who tended those lands for thousands of years. …And second, as climate change and ecological stressors affect wilderness, human intervention could help sustain the very ecological qualities that are protected. WILMINGTON, N.C. – The N.C. Forest Service (NCFS) is reminding the public to use best practices and common sense with outdoor fires ahead of the state’s spring wildfire season. NCFS officials say escaped yard debris burns are the leading cause of wildfires across the state, often due to carelessness. 99% of wildfires are caused by human activity, officials said, often when people work in their yards in spring and burn yard debris. Other causes of human-caused wildfires include machine and vehicle use, such as dragging tow chains, arson and escaped campfires. “With the recent rainfall combined with multiple winter storms earlier this year, some folks may not realize that most of North Carolina is still experiencing very dry conditions,” said Agriculture Commissioner Steve Troxler. “Our state’s gradual descent into drought and prolonged dry conditions are going to lead to wildfires igniting more easily, burning more intensely and spreading quicker.”
WILMINGTON, N.C. – The N.C. Forest Service (NCFS) is reminding the public to use best practices and common sense with outdoor fires ahead of the state’s spring wildfire season. NCFS officials say escaped yard debris burns are the leading cause of wildfires across the state, often due to carelessness. 99% of wildfires are caused by human activity, officials said, often when people work in their yards in spring and burn yard debris. Other causes of human-caused wildfires include machine and vehicle use, such as dragging tow chains, arson and escaped campfires. “With the recent rainfall combined with multiple winter storms earlier this year, some folks may not realize that most of North Carolina is still experiencing very dry conditions,” said Agriculture Commissioner Steve Troxler. “Our state’s gradual descent into drought and prolonged dry conditions are going to lead to wildfires igniting more easily, burning more intensely and spreading quicker.” LITTLE ROCK, Arkansas — The Arkansas Department of Agriculture announced some of its forestry personnel will go to Oklahoma and Tennessee to help with wildfire suppression and winter storm response. Governor Sarah Huckabee Sanders authorized state forestry personnel to support wildfire suppression in Oklahoma and urban tree recovery in Tennessee. …Six wildland firefighters will go to Oklahoma for around two weeks. These firefighters will focus on attacking and suppressing new wildfires to prevent further spread. The Department is also sending four bulldozers and two pick-up trucks to help. Three urban forestry personnel will go to Tennessee to join an Urban Forest Strike Team, a specialized group of certified arborists, foresters, and urban forestry experts. Arkansas forestry personnel will help the UFST with tree damage and risk assessments, hazard mitigation planning, and technical expertise and training.
LITTLE ROCK, Arkansas — The Arkansas Department of Agriculture announced some of its forestry personnel will go to Oklahoma and Tennessee to help with wildfire suppression and winter storm response. Governor Sarah Huckabee Sanders authorized state forestry personnel to support wildfire suppression in Oklahoma and urban tree recovery in Tennessee. …Six wildland firefighters will go to Oklahoma for around two weeks. These firefighters will focus on attacking and suppressing new wildfires to prevent further spread. The Department is also sending four bulldozers and two pick-up trucks to help. Three urban forestry personnel will go to Tennessee to join an Urban Forest Strike Team, a specialized group of certified arborists, foresters, and urban forestry experts. Arkansas forestry personnel will help the UFST with tree damage and risk assessments, hazard mitigation planning, and technical expertise and training. Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington.
Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington. Wildfires have increased in frequency and severity over the past few decades. More fires are burning at the wildland-urban interface (WUI), where homes and other buildings meet the natural landscape—but our understanding of emissions from structure fires is still growing. New research led by the University of Colorado Boulder’s Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences shows that common synthetic materials used in homes, like plastics and insulation, can release harmful compounds into the air when they burn. But synthetic materials make up only a small fraction of a home. Timber and wood panels make up the majority of the materials used, and the burning emissions from those are not so different from a vegetation fire. The work,
Wildfires have increased in frequency and severity over the past few decades. More fires are burning at the wildland-urban interface (WUI), where homes and other buildings meet the natural landscape—but our understanding of emissions from structure fires is still growing. New research led by the University of Colorado Boulder’s Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences shows that common synthetic materials used in homes, like plastics and insulation, can release harmful compounds into the air when they burn. But synthetic materials make up only a small fraction of a home. Timber and wood panels make up the majority of the materials used, and the burning emissions from those are not so different from a vegetation fire. The work,  Supporters of the “Make America Healthy Again” strategy have long railed against pesticides, making opposition to them a pillar of the movement. But an executive order issued by U.S. President Donald Trump last week collides with that long-held stance. The order states that glyphosate … is “central to American economic and national security” and calls for an adequate domestic supply. Glyphosate inhibits protein synthesis in plants and microorganisms, leading to their death. Scientists can genetically modify field crops — choosing which survive after glyphosate treatment. US Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a key figure in the MAHA movement, has long opposed glyphosate-based pesticides. …He reiterated last month on Katie Miller’s podcast that “I believe glyphosate causes cancer.” But Kennedy sounded a different tone. “Donald Trump’s executive order puts America first where it matters most — our defense readiness and our food supply,” said Kennedy.
Supporters of the “Make America Healthy Again” strategy have long railed against pesticides, making opposition to them a pillar of the movement. But an executive order issued by U.S. President Donald Trump last week collides with that long-held stance. The order states that glyphosate … is “central to American economic and national security” and calls for an adequate domestic supply. Glyphosate inhibits protein synthesis in plants and microorganisms, leading to their death. Scientists can genetically modify field crops — choosing which survive after glyphosate treatment. US Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a key figure in the MAHA movement, has long opposed glyphosate-based pesticides. …He reiterated last month on Katie Miller’s podcast that “I believe glyphosate causes cancer.” But Kennedy sounded a different tone. “Donald Trump’s executive order puts America first where it matters most — our defense readiness and our food supply,” said Kennedy.