WASHINGTON, DC – New Brunswick Premier Holt announced on Monday that yet another subsidy package is coming from the Canadian federal government to prop up Canada’s massive excess lumber production capacity. “By pouring on yet more subsidies, Canada is making it perfectly clear that they are looking to circumvent U.S. trade measures, and neutralize President Trump’s Section 232 measures, imposed specifically to address Canada’s unfair trade in lumber. This cat and mouse game has to stop now,” stated Zoltan van Heyningen, Executive Director. “We urge President Trump to increase tariff measures on unfairly traded Canadian lumber until Canada gets the message that subsidies for its industry to the detriment of our industry are not tolerated,” added van Heyningen. “This is an issue of survival, prosperity, and growth of U.S. manufacturing, in local communities, and state economies nationwide.”
WASHINGTON, DC – New Brunswick Premier Holt announced on Monday that yet another subsidy package is coming from the Canadian federal government to prop up Canada’s massive excess lumber production capacity. “By pouring on yet more subsidies, Canada is making it perfectly clear that they are looking to circumvent U.S. trade measures, and neutralize President Trump’s Section 232 measures, imposed specifically to address Canada’s unfair trade in lumber. This cat and mouse game has to stop now,” stated Zoltan van Heyningen, Executive Director. “We urge President Trump to increase tariff measures on unfairly traded Canadian lumber until Canada gets the message that subsidies for its industry to the detriment of our industry are not tolerated,” added van Heyningen. “This is an issue of survival, prosperity, and growth of U.S. manufacturing, in local communities, and state economies nationwide.”
 Canada’s forestry industry plans to divert a significant share of its wood exports from the US to new international markets. …The aim to send some 1bn board feet to alternative markets underscores how Trump’s tariffs are starting to reshape some global supply chains, although tensions between the US and Canada over wood exports have simmered for more than half a century. …“The US simply needs to fact-check better before they end up with a large shortage of lumber that may cause further housing shortages,” said Rick Doman, chair of FII BC. …Zoltan van Heyningen for the US Lumber Coalition said the American timber industry could replace 1bn board feet of Canadian imports “without batting an eyelid”. …The NAHB says at just 64% of capacity it “will take years” for US domestic lumber production to expand to meet industry demands. …Mike McDonald, a UK-based consultant, acknowledged it would take time to establish confidence among European consumers. [to access the full story a FT subscription is required]
Canada’s forestry industry plans to divert a significant share of its wood exports from the US to new international markets. …The aim to send some 1bn board feet to alternative markets underscores how Trump’s tariffs are starting to reshape some global supply chains, although tensions between the US and Canada over wood exports have simmered for more than half a century. …“The US simply needs to fact-check better before they end up with a large shortage of lumber that may cause further housing shortages,” said Rick Doman, chair of FII BC. …Zoltan van Heyningen for the US Lumber Coalition said the American timber industry could replace 1bn board feet of Canadian imports “without batting an eyelid”. …The NAHB says at just 64% of capacity it “will take years” for US domestic lumber production to expand to meet industry demands. …Mike McDonald, a UK-based consultant, acknowledged it would take time to establish confidence among European consumers. [to access the full story a FT subscription is required] KINGSPORT, Tennessee — About 300 gallons of waste leaked from Domtar’s mill site to Domtar Park, according to Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation documents. Of the 300 gallons of waste, which included liquids and solids, about 150 gallons were recovered. The mill’s 25-acre lagoon was lowered four to six inches as a precautionary measure in response to the leak, Domtar told the Times News. In its letter to TDEC, Domtar said no detrimental effects were observed to the property or the environment due to the “organic nature” of the lagoon’s contents. Domtar also said it believed the waste found at Domtar Park was “partially” treated through its wastewater treatment process. “The leak did not reach waters of the state and Domtar representatives indicated mitigation was taking place. No further action was taken by the department,” said TDEC spokesperson Jennifer Donnals in a statement to Six Rivers Media.
KINGSPORT, Tennessee — About 300 gallons of waste leaked from Domtar’s mill site to Domtar Park, according to Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation documents. Of the 300 gallons of waste, which included liquids and solids, about 150 gallons were recovered. The mill’s 25-acre lagoon was lowered four to six inches as a precautionary measure in response to the leak, Domtar told the Times News. In its letter to TDEC, Domtar said no detrimental effects were observed to the property or the environment due to the “organic nature” of the lagoon’s contents. Domtar also said it believed the waste found at Domtar Park was “partially” treated through its wastewater treatment process. “The leak did not reach waters of the state and Domtar representatives indicated mitigation was taking place. No further action was taken by the department,” said TDEC spokesperson Jennifer Donnals in a statement to Six Rivers Media.




 STEVENS POINT, Wisconsin – USDA Rural Development Wisconsin State Director Andrew Iverson announced the Timber Professionals Cooperative Enterprises (TPCE) will use a Rural Development loan of $800,000 to re-open and expand the former Hoffman Wood Fiber sawmill in Shawano County. This investment is through the Timber Production Expansion Guaranteed Loan Program (TPEP). TPCE will use guaranteed loan funds to purchase over 49 acres of real estate and equipment. The equipment will allow TCPE to improve the efficiency of manufacturing wood chips. The project also includes plans to expand capabilities of the site to manufacture new, higher-value products from the same raw materials. The project will create six jobs. …TPCE plans to implement a detailed process to improve productivity involving processes in the wood yard and chip mill. Installation of an automatic log feed deck will help increase production from 2,500 to 4,000 tons per month.
STEVENS POINT, Wisconsin – USDA Rural Development Wisconsin State Director Andrew Iverson announced the Timber Professionals Cooperative Enterprises (TPCE) will use a Rural Development loan of $800,000 to re-open and expand the former Hoffman Wood Fiber sawmill in Shawano County. This investment is through the Timber Production Expansion Guaranteed Loan Program (TPEP). TPCE will use guaranteed loan funds to purchase over 49 acres of real estate and equipment. The equipment will allow TCPE to improve the efficiency of manufacturing wood chips. The project also includes plans to expand capabilities of the site to manufacture new, higher-value products from the same raw materials. The project will create six jobs. …TPCE plans to implement a detailed process to improve productivity involving processes in the wood yard and chip mill. Installation of an automatic log feed deck will help increase production from 2,500 to 4,000 tons per month.


 After four major paper and pulp mills closed in Georgia this fall, the phone at the South Georgia Sawmill began ringing nonstop. …woodsmen from Georgia were begging owner Adam Williams to buy at least some of their logs… Williams had to say no. The scene here in Georgia is being replicated in other timber markets, raising larger questions about what measures the United States could take to become more self-reliant and preserve its foundational industries. While most of the U.S. wood supply has historically been homegrown, imports have surged, particularly from Canada. … Republican Gov. Brian Kemp has assembled a task force to suss out new opportunities for Georgia wood. Georgia Tech University, for one, is at the forefront of technology that might one day refine new types of aviation fuel from trees. The state is also pioneering the use of so-called “mass timber” – cross-laminated panels of two-by-sixes that replace concrete and steel.
After four major paper and pulp mills closed in Georgia this fall, the phone at the South Georgia Sawmill began ringing nonstop. …woodsmen from Georgia were begging owner Adam Williams to buy at least some of their logs… Williams had to say no. The scene here in Georgia is being replicated in other timber markets, raising larger questions about what measures the United States could take to become more self-reliant and preserve its foundational industries. While most of the U.S. wood supply has historically been homegrown, imports have surged, particularly from Canada. … Republican Gov. Brian Kemp has assembled a task force to suss out new opportunities for Georgia wood. Georgia Tech University, for one, is at the forefront of technology that might one day refine new types of aviation fuel from trees. The state is also pioneering the use of so-called “mass timber” – cross-laminated panels of two-by-sixes that replace concrete and steel.  Nearly 40 Tennessee hardwood companies are among hundreds of U.S. hardwood industry operators calling for federal relief from tariff-induced economic hardship. Tennessee’s forestry products industry supports an estimated 85,000 jobs, according to the
Nearly 40 Tennessee hardwood companies are among hundreds of U.S. hardwood industry operators calling for federal relief from tariff-induced economic hardship. Tennessee’s forestry products industry supports an estimated 85,000 jobs, according to the 
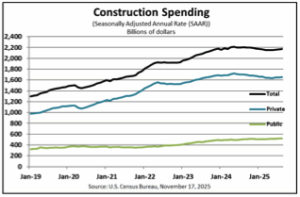 The US Census Bureau announced the following value put in place construction statistics. …Construction spending during August 2025 was estimated at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $2,169.5 billion, 0.2 percent (±0.7 percent) above the revised July estimate of $2,165.0 billion. The August figure is 1.6 percent (±1.5 percent) below the August 2024 estimate of $2,205.3 billion. During the first eight months of this year, construction spending amounted to $1,438.0 billion, 1.8 percent (±1.0 percent) below the $1,463.7 billion for the same period in 2024. …Spending on private construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $1,652.1 billion, 0.3 percent (±0.5 percent) above the revised July estimate of $1,647.5 billion. …In August, the estimated seasonally adjusted annual rate of public construction spending was $517.3 billion, virtually unchanged from (±1.2 percent) the revised July estimate of $517.5 billion.
The US Census Bureau announced the following value put in place construction statistics. …Construction spending during August 2025 was estimated at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $2,169.5 billion, 0.2 percent (±0.7 percent) above the revised July estimate of $2,165.0 billion. The August figure is 1.6 percent (±1.5 percent) below the August 2024 estimate of $2,205.3 billion. During the first eight months of this year, construction spending amounted to $1,438.0 billion, 1.8 percent (±1.0 percent) below the $1,463.7 billion for the same period in 2024. …Spending on private construction was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $1,652.1 billion, 0.3 percent (±0.5 percent) above the revised July estimate of $1,647.5 billion. …In August, the estimated seasonally adjusted annual rate of public construction spending was $517.3 billion, virtually unchanged from (±1.2 percent) the revised July estimate of $517.5 billion.  The Supreme Court could decide on the legality of many of the Trump administration’s tariffs within months, but the ruling won’t impact many of the administration’s levies on imported construction materials such as lumber, steel, aluminum and copper. …Many construction materials imported into the US will remain subject to hefty tariffs regardless of how the Supreme Court rules. Some homebuilding leaders warn that home prices could increase by thousands of dollars beginning next year. …Cristian deRitis, at Moody’s Analytics, said “While importers of other building materials might experience some relief, this could be temporary. The administration may choose to expand the Section 232 tariffs as a fallback strategy if the reciprocal tariffs are invalidated,” deRitis said. …There hasn’t yet been an increase in lumber prices, but NAHB Chairman Buddy Hughes forecasted that the lumber tariffs “will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market by further raising construction and renovation costs.”
The Supreme Court could decide on the legality of many of the Trump administration’s tariffs within months, but the ruling won’t impact many of the administration’s levies on imported construction materials such as lumber, steel, aluminum and copper. …Many construction materials imported into the US will remain subject to hefty tariffs regardless of how the Supreme Court rules. Some homebuilding leaders warn that home prices could increase by thousands of dollars beginning next year. …Cristian deRitis, at Moody’s Analytics, said “While importers of other building materials might experience some relief, this could be temporary. The administration may choose to expand the Section 232 tariffs as a fallback strategy if the reciprocal tariffs are invalidated,” deRitis said. …There hasn’t yet been an increase in lumber prices, but NAHB Chairman Buddy Hughes forecasted that the lumber tariffs “will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market by further raising construction and renovation costs.”

 SALT LAKE CITY — Homeowners in high wildfire risk areas should soon expect home assessments and a new fee. HB48 Wildland Urban Interface Modifications requires the Utah Division of Forestry, Fire and State Lands to draw a high wildfire risk boundary across the state. The division will inspect homes within the boundary for fire risk, and property owners will pay a fee based on their risk and square footage, which will cover the cost of the program and lot assessments. State Wildfire Risk Reductions Programs Manager Joseph Anderson said the assessments will focus on the vegetation surrounding the home and the materials used in the structure. “The goal is to remove any vegetation or anything that could catch an ember and allow that ember to burn and catch the structure on fire,” Anderson said. The bill comes after catastrophic wildfires across the West, like the California Eaton Fire from January 2025.
SALT LAKE CITY — Homeowners in high wildfire risk areas should soon expect home assessments and a new fee. HB48 Wildland Urban Interface Modifications requires the Utah Division of Forestry, Fire and State Lands to draw a high wildfire risk boundary across the state. The division will inspect homes within the boundary for fire risk, and property owners will pay a fee based on their risk and square footage, which will cover the cost of the program and lot assessments. State Wildfire Risk Reductions Programs Manager Joseph Anderson said the assessments will focus on the vegetation surrounding the home and the materials used in the structure. “The goal is to remove any vegetation or anything that could catch an ember and allow that ember to burn and catch the structure on fire,” Anderson said. The bill comes after catastrophic wildfires across the West, like the California Eaton Fire from January 2025. 
 The timber industry built around the Tongass National Forest in Alaska got a boost from the Trump administration’s latest trade deal with China. In settling part of its trade battles, China agreed to accept imports of US sawlogs for the first time since banning them in March due to worries about insect pests. The resumption of exports — effective Nov. 12 — would help companies like Alcan Forest Products in Ketchikan, which for years has sold unprocessed logs to China. The latest agreement lasts one year, said Tessa Axelson, executive director of the Alaska Forest Association. A 10% tariff on products from both countries would still apply. …Southeast Alaska’s timber industry relies heavily on the nearly 17-million-acre Tongass, although most of the forest is off-limits to logging. Federal law allows the export of unprocessed logs, a practice long banned elsewhere to protect the domestic lumber processing industry. [to access the full story an E&ENews subscription is required]
The timber industry built around the Tongass National Forest in Alaska got a boost from the Trump administration’s latest trade deal with China. In settling part of its trade battles, China agreed to accept imports of US sawlogs for the first time since banning them in March due to worries about insect pests. The resumption of exports — effective Nov. 12 — would help companies like Alcan Forest Products in Ketchikan, which for years has sold unprocessed logs to China. The latest agreement lasts one year, said Tessa Axelson, executive director of the Alaska Forest Association. A 10% tariff on products from both countries would still apply. …Southeast Alaska’s timber industry relies heavily on the nearly 17-million-acre Tongass, although most of the forest is off-limits to logging. Federal law allows the export of unprocessed logs, a practice long banned elsewhere to protect the domestic lumber processing industry. [to access the full story an E&ENews subscription is required]

 Oregon — Deschutes County is preparing to deploy $3.4 million for wildfire mitigation projects to reduce the likelihood of catastrophic wildfire in La Pine. The money comes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and is part of a $200 million funding package to assist fire-prone areas across the country. Work is expected to begin in the spring on a variety of projects ranging from fuels reduction to community education, according to Lauren Street, a natural resources specialist with Deschutes County. The project is expected to continue for five years. La Pine was one of 58 recipients nationwide to benefit from community wildfire defense grants. The grants are funded by the Biden-era bipartisan infrastructure law of 2021. Elsewhere in Oregon, the Sweet Home Fire and Ambulance District is set to receive $8.7 million, the largest grant for any project in the state.
Oregon — Deschutes County is preparing to deploy $3.4 million for wildfire mitigation projects to reduce the likelihood of catastrophic wildfire in La Pine. The money comes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and is part of a $200 million funding package to assist fire-prone areas across the country. Work is expected to begin in the spring on a variety of projects ranging from fuels reduction to community education, according to Lauren Street, a natural resources specialist with Deschutes County. The project is expected to continue for five years. La Pine was one of 58 recipients nationwide to benefit from community wildfire defense grants. The grants are funded by the Biden-era bipartisan infrastructure law of 2021. Elsewhere in Oregon, the Sweet Home Fire and Ambulance District is set to receive $8.7 million, the largest grant for any project in the state.

 OLYMPIA — The Washington Forest Practices Board took 200,000 acres of timberland out of production, voting 7-5 to require loggers to stay farther back from streams without fish. The close vote Nov. 12 capped a contentious debate over the environmental and economic consequences of widening and lengthening riparian buffers to shade streams. Forest landowners will lose $2.8 billion in harvestable timber because of the new buffers, according to a University of Washington analysis. Ten state representatives, five Democrats and five Republicans, questioned whether the board had thoroughly examined the social costs. And the Environmental Protection Agency said the bigger buffers are not needed to meet the Clean Water Act. But the Department of Ecology championed wider and longer buffers. The buffers will keep timber harvests from warming water temperatures in most cases, according to Ecology. “Not taking action is not an option,” said Ecology Director Casey Sixkiller, a member of the forest board.
OLYMPIA — The Washington Forest Practices Board took 200,000 acres of timberland out of production, voting 7-5 to require loggers to stay farther back from streams without fish. The close vote Nov. 12 capped a contentious debate over the environmental and economic consequences of widening and lengthening riparian buffers to shade streams. Forest landowners will lose $2.8 billion in harvestable timber because of the new buffers, according to a University of Washington analysis. Ten state representatives, five Democrats and five Republicans, questioned whether the board had thoroughly examined the social costs. And the Environmental Protection Agency said the bigger buffers are not needed to meet the Clean Water Act. But the Department of Ecology championed wider and longer buffers. The buffers will keep timber harvests from warming water temperatures in most cases, according to Ecology. “Not taking action is not an option,” said Ecology Director Casey Sixkiller, a member of the forest board.