 Almost three years after declaring bankruptcy, and more than two years under new owners, legal proceedings for Penticton’s Structurlam are continuing through the courts as it fights with the company that sent it into bankruptcy in the first place. In January, the case returned to the BC Supreme Court in Vancouver to order two Canadian engineering firms to produce documents and reports for the proceedings as Structurlam faces $80 million US in claims from Walmart, according to a decision published on Feb. 11. In 2023, Structurlam began bankruptcy proceedings after Walmart ended its contract to build the company’s new home office campus in Arkansas. …In July, Walmart filed a claim for over $80 million US for allegedly defective, nonconforming, rejected, nondelivered, or returned goods that it had paid for and alleged costs to replace said goods. The January 2026 B.C. Supreme Court decision orders two engineering firms to provide their documentation.
Almost three years after declaring bankruptcy, and more than two years under new owners, legal proceedings for Penticton’s Structurlam are continuing through the courts as it fights with the company that sent it into bankruptcy in the first place. In January, the case returned to the BC Supreme Court in Vancouver to order two Canadian engineering firms to produce documents and reports for the proceedings as Structurlam faces $80 million US in claims from Walmart, according to a decision published on Feb. 11. In 2023, Structurlam began bankruptcy proceedings after Walmart ended its contract to build the company’s new home office campus in Arkansas. …In July, Walmart filed a claim for over $80 million US for allegedly defective, nonconforming, rejected, nondelivered, or returned goods that it had paid for and alleged costs to replace said goods. The January 2026 B.C. Supreme Court decision orders two engineering firms to provide their documentation.
 WINDSOR, Ontario — For months, trade negotiations between Canada and the United States have been stalled. This week that all changed when US President Trump announced negotiations were back on. During his social media tirade about Windsor, Ontario’s Gordie Howe Bridge, and a list of other perceived transgressions, Trump wrote… we will start negotiations, IMMEDIATELY.” While Trump’s political speed bump threatens to derail the planned opening of the commercial corridor, some industry leaders see an opening to accelerate negotiations. “Trade conversations have now restarted, a few weeks ago conversations weren’t happening. I see this as a positive,” says Canadian Association of Moldmakers Nicole Vlanich. …With Trump restarting trade negotiations that he once brought to a screeching halt, business leaders in Windsor hope this will be an important first step towards paving a clearer picture for economic growth for both the Canadian and US economies.
WINDSOR, Ontario — For months, trade negotiations between Canada and the United States have been stalled. This week that all changed when US President Trump announced negotiations were back on. During his social media tirade about Windsor, Ontario’s Gordie Howe Bridge, and a list of other perceived transgressions, Trump wrote… we will start negotiations, IMMEDIATELY.” While Trump’s political speed bump threatens to derail the planned opening of the commercial corridor, some industry leaders see an opening to accelerate negotiations. “Trade conversations have now restarted, a few weeks ago conversations weren’t happening. I see this as a positive,” says Canadian Association of Moldmakers Nicole Vlanich. …With Trump restarting trade negotiations that he once brought to a screeching halt, business leaders in Windsor hope this will be an important first step towards paving a clearer picture for economic growth for both the Canadian and US economies. WASHINGTON, DC — In a vote that GOP leaders fought hard to avoid, a half dozen Republicans sent a blunt message to President Trump that they do not support the tariff regime that he has made the centerpiece of his second term. Six Republicans joined with Democrats in the vote to effectively repeal the president’s tariffs on Canada, the culmination of months of consternation in the GOP over the president’s trade war that has quietly rattled even some of his staunchest loyalists in Congress. …The Senate has already passed a similar measure to cancel Trump’s tariffs on Canada, which — unlike most measures — can be passed with a simple majority rather than 60 votes. But even if the Senate does agree to this same House measure, Trump would still have the power to veto it. The House did not secure enough votes to protect a veto override.
WASHINGTON, DC — In a vote that GOP leaders fought hard to avoid, a half dozen Republicans sent a blunt message to President Trump that they do not support the tariff regime that he has made the centerpiece of his second term. Six Republicans joined with Democrats in the vote to effectively repeal the president’s tariffs on Canada, the culmination of months of consternation in the GOP over the president’s trade war that has quietly rattled even some of his staunchest loyalists in Congress. …The Senate has already passed a similar measure to cancel Trump’s tariffs on Canada, which — unlike most measures — can be passed with a simple majority rather than 60 votes. But even if the Senate does agree to this same House measure, Trump would still have the power to veto it. The House did not secure enough votes to protect a veto override. Some of Canada’s major labour organizations are urging Ottawa to put workers at the centre of any renegotiation of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement as preparations begin for the pact’s mandatory 2026 review. Leaders met with Dominic LeBlanc, the federal minister responsible for Canada–US trade, for what they described as a high-level roundtable on the future of CUSMA amid rising trade tensions and renewed threats of U.S. tariffs. Canadian Labour Congress president Bea Bruske said unions delivered a “clear and urgent message” that Canada should not accept a revised trade deal that weakens domestic industry or costs Canadian jobs. …Bruske was joined by leaders from several large manufacturing and building trades unions representing sectors heavily exposed to trade policy decisions, including auto manufacturing, construction and resource-based industries. Bruske said the upcoming CUSMA review should strengthen Canadian industries and working-class communities, not “hollow them out” in the rush to renew the agreement.
Some of Canada’s major labour organizations are urging Ottawa to put workers at the centre of any renegotiation of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement as preparations begin for the pact’s mandatory 2026 review. Leaders met with Dominic LeBlanc, the federal minister responsible for Canada–US trade, for what they described as a high-level roundtable on the future of CUSMA amid rising trade tensions and renewed threats of U.S. tariffs. Canadian Labour Congress president Bea Bruske said unions delivered a “clear and urgent message” that Canada should not accept a revised trade deal that weakens domestic industry or costs Canadian jobs. …Bruske was joined by leaders from several large manufacturing and building trades unions representing sectors heavily exposed to trade policy decisions, including auto manufacturing, construction and resource-based industries. Bruske said the upcoming CUSMA review should strengthen Canadian industries and working-class communities, not “hollow them out” in the rush to renew the agreement.





 BURNABY, BC — Interfor recorded a net loss in Q4, 2025 of $104.6 million, compared to a net loss of $215.8 million in Q3’25 and a net loss of $49.9 million in Q4’24. Adjusted EBITDA was a loss of $29.2 million on sales of $600.6 million in Q4’25 versus an Adjusted EBITDA loss of $183.8 million on sales of $689.3 million in Q3’25 and Adjusted EBITDA of $80.4 million on sales of $746.5 million in Q4’24. …During and subsequent to Q4’25, Interfor completed a series of financing transactions. Taken together, these transactions significantly enhance Interfor’s financial flexibility, bolster liquidity and provide meaningful additional runway as the Company continues to navigate volatile lumber market conditions. …Lumber production of 753 million board feet was down 159 million board feet versus the preceding quarter. …Interfor’s strategy of maintaining a diversified portfolio of operations in multiple regions allows the Company to both reduce risk and maximize returns on capital over the business cycle.
BURNABY, BC — Interfor recorded a net loss in Q4, 2025 of $104.6 million, compared to a net loss of $215.8 million in Q3’25 and a net loss of $49.9 million in Q4’24. Adjusted EBITDA was a loss of $29.2 million on sales of $600.6 million in Q4’25 versus an Adjusted EBITDA loss of $183.8 million on sales of $689.3 million in Q3’25 and Adjusted EBITDA of $80.4 million on sales of $746.5 million in Q4’24. …During and subsequent to Q4’25, Interfor completed a series of financing transactions. Taken together, these transactions significantly enhance Interfor’s financial flexibility, bolster liquidity and provide meaningful additional runway as the Company continues to navigate volatile lumber market conditions. …Lumber production of 753 million board feet was down 159 million board feet versus the preceding quarter. …Interfor’s strategy of maintaining a diversified portfolio of operations in multiple regions allows the Company to both reduce risk and maximize returns on capital over the business cycle. NEW YORK, New York — Mercer International reported fourth quarter 2025 Operating EBITDA of negative $20.1 million compared to positive $99.2 million in the same quarter of 2024 and negative $28.1 million in the third quarter of 2025. In the fourth quarter of 2025, net loss was $308.7 million compared to net income of $16.7 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and a net loss of $80.8 million in the third quarter of 2025. The net loss in the fourth quarter of 2025 included total non-cash impairments of $238.7 million. This included non-cash impairments of $203.5 million recognized against long-lived assets at our Peace River mill due to the continued down-cycle environment of hardwood pulp markets, $12.2 million against certain obsolete equipment and $23.0 million against pulp inventory due to low prices and high fiber costs. …Mr. Juan Carlos Bueno, CEO: “We continue to prioritize improving liquidity and working capital, committing to rebalancing our asset portfolio and maintaining operating discipline.”
NEW YORK, New York — Mercer International reported fourth quarter 2025 Operating EBITDA of negative $20.1 million compared to positive $99.2 million in the same quarter of 2024 and negative $28.1 million in the third quarter of 2025. In the fourth quarter of 2025, net loss was $308.7 million compared to net income of $16.7 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and a net loss of $80.8 million in the third quarter of 2025. The net loss in the fourth quarter of 2025 included total non-cash impairments of $238.7 million. This included non-cash impairments of $203.5 million recognized against long-lived assets at our Peace River mill due to the continued down-cycle environment of hardwood pulp markets, $12.2 million against certain obsolete equipment and $23.0 million against pulp inventory due to low prices and high fiber costs. …Mr. Juan Carlos Bueno, CEO: “We continue to prioritize improving liquidity and working capital, committing to rebalancing our asset portfolio and maintaining operating discipline.” VANCOUVER, BC
VANCOUVER, BC The Bank of Canada’s latest survey of financial-market participants pointed to a modestly brighter growth outlook than the central bank’s own projections, even as trade tensions with the US remain the dominant threat hanging over Canada’s economy and housing market. In the fourth‑quarter Market Participants Survey, 93% of respondents cited an “increase in trade tensions” as the top downside risk to Canadian growth, well ahead of tighter global financial conditions and weaker consumer spending. Participants still assign a 20% probability to a recession over the next six months, but their median forecast calls for real GDP growth of 1.6% by the end of 2026 and 1.9% by late 2027, slightly stronger than the Bank’s own projections of 1.1% and 1.5%. While the survey suggests some stabilization in expectations, it underscores that tariff policy remains the key macroeconomic swing factor. …PwC Canada’s latest survey among 133 CEOs showed that only 27% expect the domestic economy to improve over the next 12 months.
The Bank of Canada’s latest survey of financial-market participants pointed to a modestly brighter growth outlook than the central bank’s own projections, even as trade tensions with the US remain the dominant threat hanging over Canada’s economy and housing market. In the fourth‑quarter Market Participants Survey, 93% of respondents cited an “increase in trade tensions” as the top downside risk to Canadian growth, well ahead of tighter global financial conditions and weaker consumer spending. Participants still assign a 20% probability to a recession over the next six months, but their median forecast calls for real GDP growth of 1.6% by the end of 2026 and 1.9% by late 2027, slightly stronger than the Bank’s own projections of 1.1% and 1.5%. While the survey suggests some stabilization in expectations, it underscores that tariff policy remains the key macroeconomic swing factor. …PwC Canada’s latest survey among 133 CEOs showed that only 27% expect the domestic economy to improve over the next 12 months. Reality-television stars are rarely consulted on matters of public policy. But in April, Realtor.com asked Tarek El Moussa to comment on the White House’s “Liberation Day” tariffs. The Southern California entrepreneur, who rose to fame on the popularity of HGTV’s Flip or Fop franchise, warned that higher import taxes would harm “new-home builders” and “first-time buyers” the most — after all, “luxury buyers” could absorb greater costs. Aspiring homeowners, he averred, are “usually strapped for cash,” and “doing everything they can just to buy a house.” Now that the second Trump administration has passed its one-year anniversary, all evidence indicates that El Moussa understands his industry well. There is little doubt that his trade war erects a sizable obstacle before those looking to find a place of their own. …The types of wood available in the US are not always the same as what’s available from Canadian imports.
Reality-television stars are rarely consulted on matters of public policy. But in April, Realtor.com asked Tarek El Moussa to comment on the White House’s “Liberation Day” tariffs. The Southern California entrepreneur, who rose to fame on the popularity of HGTV’s Flip or Fop franchise, warned that higher import taxes would harm “new-home builders” and “first-time buyers” the most — after all, “luxury buyers” could absorb greater costs. Aspiring homeowners, he averred, are “usually strapped for cash,” and “doing everything they can just to buy a house.” Now that the second Trump administration has passed its one-year anniversary, all evidence indicates that El Moussa understands his industry well. There is little doubt that his trade war erects a sizable obstacle before those looking to find a place of their own. …The types of wood available in the US are not always the same as what’s available from Canadian imports.

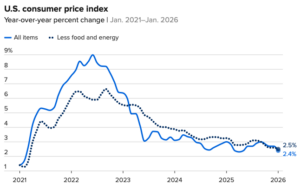 The cost of goods and services rose at a slower annual rate than expected in January, providing hope that the nagging U.S. inflation problem could be starting to ease. The consumer price index for January accelerated 2.4% from the same time a year ago, down 0.3 percentage point from the prior month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Friday. That pulled the inflation rate down to where it was the month after President Donald Trump in April 2025 announced aggressive tariffs on U.S. imports. Excluding food and energy, the core CPI was up 2.5%. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for an annual rate of 2.5% for both readings. On a monthly basis, the all-items index was up a seasonally adjusted 0.2% while core gained 0.3%. …Though the category accounted for much of the CPI gain, shelter costs rose just 0.2% for the month, bringing the annual increase down to 3%.
The cost of goods and services rose at a slower annual rate than expected in January, providing hope that the nagging U.S. inflation problem could be starting to ease. The consumer price index for January accelerated 2.4% from the same time a year ago, down 0.3 percentage point from the prior month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Friday. That pulled the inflation rate down to where it was the month after President Donald Trump in April 2025 announced aggressive tariffs on U.S. imports. Excluding food and energy, the core CPI was up 2.5%. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for an annual rate of 2.5% for both readings. On a monthly basis, the all-items index was up a seasonally adjusted 0.2% while core gained 0.3%. …Though the category accounted for much of the CPI gain, shelter costs rose just 0.2% for the month, bringing the annual increase down to 3%. 


 Building homes inside a factory has long been seen as a way to revolutionize the American housing industry, ushering in a new era of higher quality homes at lower price. That dream has never quite panned out. Can California finally make it happen? …For decades engineers, architects, futurists, industrialists, investors and politicians have been pining for a better, faster and cheaper way to build homes. Now, amid a national housing shortage, the question felt as pressing as ever: What if construction could harness the speed, efficiency, quality control and cost-savings of the assembly line? …What if the United States could mass-produce its way out of a housing crisis? …This year, state legislators in California believe the turning-point might actually be here. With a little state assistance, they want to make 2026 the Year of the Housing Factory. At long last.
Building homes inside a factory has long been seen as a way to revolutionize the American housing industry, ushering in a new era of higher quality homes at lower price. That dream has never quite panned out. Can California finally make it happen? …For decades engineers, architects, futurists, industrialists, investors and politicians have been pining for a better, faster and cheaper way to build homes. Now, amid a national housing shortage, the question felt as pressing as ever: What if construction could harness the speed, efficiency, quality control and cost-savings of the assembly line? …What if the United States could mass-produce its way out of a housing crisis? …This year, state legislators in California believe the turning-point might actually be here. With a little state assistance, they want to make 2026 the Year of the Housing Factory. At long last.  The Berkeley Wood Lab’s research on mass timber production has the potential to improve California’s sustainability by sourcing from local forests. The lab is collaborating with Northern Californian lumber company Mad River Mass Timber, or MRMT. The company will use Californian trees that otherwise would have either been turned into woodchips or burned in a forest fire to build panels that can be used in new housing and commercial buildings. This is the first time these types of panels will be produced locally in California instead of being shipped in from other countries. The technology to create dowel-laminated timber, or DLT, has existed for decades, but the Berkeley Wood Lab adapted it for use in Californian forests. Through the process of making DLT, glue is not required, which enables the timber to be recycled in the future and turned into new material.
The Berkeley Wood Lab’s research on mass timber production has the potential to improve California’s sustainability by sourcing from local forests. The lab is collaborating with Northern Californian lumber company Mad River Mass Timber, or MRMT. The company will use Californian trees that otherwise would have either been turned into woodchips or burned in a forest fire to build panels that can be used in new housing and commercial buildings. This is the first time these types of panels will be produced locally in California instead of being shipped in from other countries. The technology to create dowel-laminated timber, or DLT, has existed for decades, but the Berkeley Wood Lab adapted it for use in Californian forests. Through the process of making DLT, glue is not required, which enables the timber to be recycled in the future and turned into new material.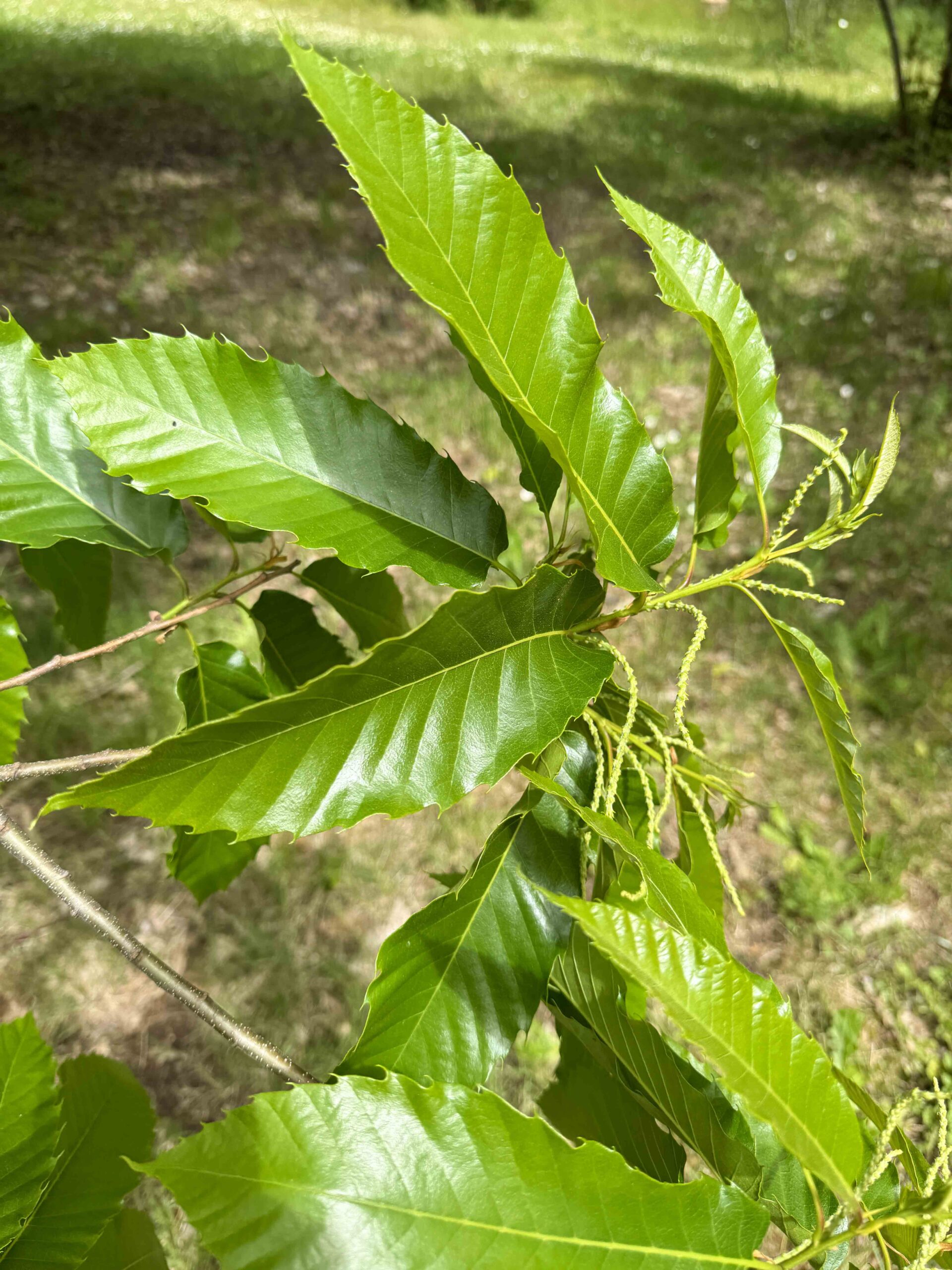 WASHINGTON — Billions of American chestnut trees once covered the eastern United States. …But by the 1950s, this venerable tree went functionally extinct, culled by a deadly airborne fungal blight and lethal root rot. A new study provides hope for its revitalization, finding that the genetic testing of individual trees can reveal which are most likely to resist disease and grow tall, thus shortening how long it takes to plant the next, more robust, generation. …The American chestnut … had little defense against foreign-introduced blight and root rot. Another type of chestnut, however, had evolved alongside those diseases. The Chinese chestnut had been introduced for its valuable nuts and it could resist diseases. …So, the authors want a tree with the characteristics of the American chestnut and the disease resistance of the Chinese chestnut. …Breed for disease resistance alone and the trees get shorter, less competitive.
WASHINGTON — Billions of American chestnut trees once covered the eastern United States. …But by the 1950s, this venerable tree went functionally extinct, culled by a deadly airborne fungal blight and lethal root rot. A new study provides hope for its revitalization, finding that the genetic testing of individual trees can reveal which are most likely to resist disease and grow tall, thus shortening how long it takes to plant the next, more robust, generation. …The American chestnut … had little defense against foreign-introduced blight and root rot. Another type of chestnut, however, had evolved alongside those diseases. The Chinese chestnut had been introduced for its valuable nuts and it could resist diseases. …So, the authors want a tree with the characteristics of the American chestnut and the disease resistance of the Chinese chestnut. …Breed for disease resistance alone and the trees get shorter, less competitive. COLORADO — Forest experts are warning that Boulder’s foothills could look markedly different this year as a mountain pine beetle outbreak intensifies, with potentially far-reaching impacts on recreation and fire risk. Landowners are urged to watch for signs of beetle infestation. The state has taken action: Gov. Jared Polis announced a task force in December aimed at protecting Front Range forests from mountain pine beetle over the next decade. Boulder County has seen increased beetle activity in several areas, including upper Lefthand Canyon and Jamestown. Years of drought, warmer temperatures and overcrowded forests have weakened trees, creating ideal conditions for beetles to spread rapidly and overwhelm remaining healthy stands. …The brood of beetles already in trees and poised to spread this summer is substantial, according to Colorado State Forest Service entomologist Dan West. “It’s kind of this cake that’s already being baked,” West told Boulder Reporting Lab.
COLORADO — Forest experts are warning that Boulder’s foothills could look markedly different this year as a mountain pine beetle outbreak intensifies, with potentially far-reaching impacts on recreation and fire risk. Landowners are urged to watch for signs of beetle infestation. The state has taken action: Gov. Jared Polis announced a task force in December aimed at protecting Front Range forests from mountain pine beetle over the next decade. Boulder County has seen increased beetle activity in several areas, including upper Lefthand Canyon and Jamestown. Years of drought, warmer temperatures and overcrowded forests have weakened trees, creating ideal conditions for beetles to spread rapidly and overwhelm remaining healthy stands. …The brood of beetles already in trees and poised to spread this summer is substantial, according to Colorado State Forest Service entomologist Dan West. “It’s kind of this cake that’s already being baked,” West told Boulder Reporting Lab.
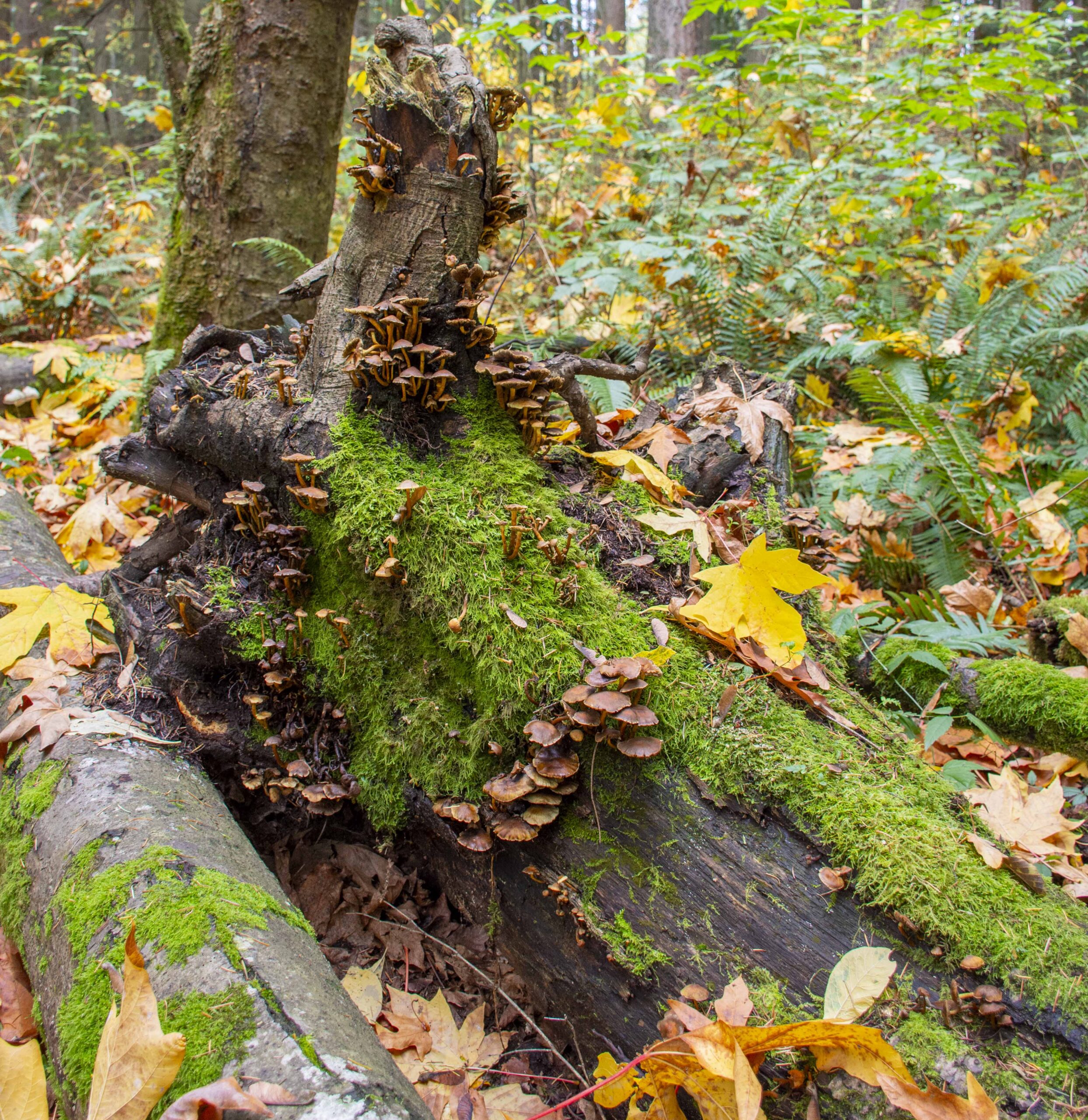 Biological legacies (i.e., materials that persist following disturbance; “legacies”) shape ecosystem functioning and feedbacks to future disturbances, yet how legacies are driven by pre-disturbance ecosystem state and disturbance severity is poorly understood—especially in ecosystems influenced by infrequent and severe disturbances. Focusing on wet temperate forests as an archetype of these ecosystems, we characterized live and dead aboveground biomass 2–5 years post-fire in western Washington and northwestern Oregon, USA, to ask: How do pre-fire stand age and burn severity drive variability in initial post-fire legacies, specifically aboveground biomass carbon and fuel profiles? …Our findings demonstrate the importance of pre-disturbance ecosystem state in dictating many aspects of initial post-disturbance structure and function, with important implications for managing post-fire recovery trajectories in some of Earth’s most productive and high-biomass forests.
Biological legacies (i.e., materials that persist following disturbance; “legacies”) shape ecosystem functioning and feedbacks to future disturbances, yet how legacies are driven by pre-disturbance ecosystem state and disturbance severity is poorly understood—especially in ecosystems influenced by infrequent and severe disturbances. Focusing on wet temperate forests as an archetype of these ecosystems, we characterized live and dead aboveground biomass 2–5 years post-fire in western Washington and northwestern Oregon, USA, to ask: How do pre-fire stand age and burn severity drive variability in initial post-fire legacies, specifically aboveground biomass carbon and fuel profiles? …Our findings demonstrate the importance of pre-disturbance ecosystem state in dictating many aspects of initial post-disturbance structure and function, with important implications for managing post-fire recovery trajectories in some of Earth’s most productive and high-biomass forests. COLORADO — The U.S. Forest Service is proposing logging southwest of Glenwood Springs, involving about 2,600 acres in what’s known as the Fourmile area along the borders of Pitkin, Mesa and Garfield counties. The White River National Forest’s proposal includes acreage in all three counties. It involves selective thinning and vegetation clearing in two treatment areas and along several roads to improve forest health, reduce wildfire risk and provide timber, the Forest Service said in a news release. “The timber treatments would improve the forest’s ability to withstand and recover from drought and insect outbreaks by creating more diversity in the size and ages of trees. Additionally, work along roads will strengthen predetermined areas where firefighters could more effectively engage wildfires,” the Forest Service said in its release. …“Active forest management is an important tool for maintaining healthy forests,” Acting Aspen-Sopris District Ranger Jennifer Schuller said in the release.
COLORADO — The U.S. Forest Service is proposing logging southwest of Glenwood Springs, involving about 2,600 acres in what’s known as the Fourmile area along the borders of Pitkin, Mesa and Garfield counties. The White River National Forest’s proposal includes acreage in all three counties. It involves selective thinning and vegetation clearing in two treatment areas and along several roads to improve forest health, reduce wildfire risk and provide timber, the Forest Service said in a news release. “The timber treatments would improve the forest’s ability to withstand and recover from drought and insect outbreaks by creating more diversity in the size and ages of trees. Additionally, work along roads will strengthen predetermined areas where firefighters could more effectively engage wildfires,” the Forest Service said in its release. …“Active forest management is an important tool for maintaining healthy forests,” Acting Aspen-Sopris District Ranger Jennifer Schuller said in the release. 
 NEW YORK — BTG Pactual Timberland Investment Group has acquired approximately 107,000 acres of sustainably managed timberlands in Central Virginia from the Weyerhaeuser Company. The acquisition represents one of the largest recent timberland transactions in Virginia, significantly expanding BTG Pactual TIG’s footprint in the region and bringing the firm’s total US portfolio to approximately 1.6 million acres under management. The property is Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certified, consisting primarily of loblolly pine, and will be well-integrated with BTG Pactual TIG’s existing regional operations. …The acquisition also enables BTG Pactual TIG to further expand conservation efforts in the region through its long-term collaboration with NatureVest, The Nature Conservancy’s (TNC’s) in-house impact investing and nature finance team. A preliminary assessment of the asset conducted by TNC found that 25% of the property falls within areas of high ecological and biodiversity value.
NEW YORK — BTG Pactual Timberland Investment Group has acquired approximately 107,000 acres of sustainably managed timberlands in Central Virginia from the Weyerhaeuser Company. The acquisition represents one of the largest recent timberland transactions in Virginia, significantly expanding BTG Pactual TIG’s footprint in the region and bringing the firm’s total US portfolio to approximately 1.6 million acres under management. The property is Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certified, consisting primarily of loblolly pine, and will be well-integrated with BTG Pactual TIG’s existing regional operations. …The acquisition also enables BTG Pactual TIG to further expand conservation efforts in the region through its long-term collaboration with NatureVest, The Nature Conservancy’s (TNC’s) in-house impact investing and nature finance team. A preliminary assessment of the asset conducted by TNC found that 25% of the property falls within areas of high ecological and biodiversity value. The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say.
The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say. CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet at increased risk of a “hothouse” trajectory driven by feedback loops that can amplify the consequences of global warming. “The risk of a hothouse Earth
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet at increased risk of a “hothouse” trajectory driven by feedback loops that can amplify the consequences of global warming. “The risk of a hothouse Earth  FREMONT, Nebraska — Fremont wood processor Horizon Biofuels will be fined up to $147,500 by the Occupational Health and Safety Administration for “willful and serious safety violations after a deadly explosion at the company’s Fremont facility in July 2025,” the US Department of Labor announced. Horizon has until Feb. 19 to decide whether it wants to appeal the citation, according to a spokesperson with the Kansas City OSHA office. …The explosion killed 32-year-old employee Dylan Danielson and his two daughters, both under the age of 12. The violations include “combustible dust buildup, failure to ensure equipment within the facility was protected from creating an ignition source and lack of fall protection for employees working at heights greater than four feet,” the Department of Labor said. …The Nebraska State Fire Marshal’s office also has a pending investigation.
FREMONT, Nebraska — Fremont wood processor Horizon Biofuels will be fined up to $147,500 by the Occupational Health and Safety Administration for “willful and serious safety violations after a deadly explosion at the company’s Fremont facility in July 2025,” the US Department of Labor announced. Horizon has until Feb. 19 to decide whether it wants to appeal the citation, according to a spokesperson with the Kansas City OSHA office. …The explosion killed 32-year-old employee Dylan Danielson and his two daughters, both under the age of 12. The violations include “combustible dust buildup, failure to ensure equipment within the facility was protected from creating an ignition source and lack of fall protection for employees working at heights greater than four feet,” the Department of Labor said. …The Nebraska State Fire Marshal’s office also has a pending investigation. 