 Some of Canada’s major labour organizations are urging Ottawa to put workers at the centre of any renegotiation of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement as preparations begin for the pact’s mandatory 2026 review. Leaders met with Dominic LeBlanc, the federal minister responsible for Canada–US trade, for what they described as a high-level roundtable on the future of CUSMA amid rising trade tensions and renewed threats of U.S. tariffs. Canadian Labour Congress president Bea Bruske said unions delivered a “clear and urgent message” that Canada should not accept a revised trade deal that weakens domestic industry or costs Canadian jobs. …Bruske was joined by leaders from several large manufacturing and building trades unions representing sectors heavily exposed to trade policy decisions, including auto manufacturing, construction and resource-based industries. Bruske said the upcoming CUSMA review should strengthen Canadian industries and working-class communities, not “hollow them out” in the rush to renew the agreement.
Some of Canada’s major labour organizations are urging Ottawa to put workers at the centre of any renegotiation of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement as preparations begin for the pact’s mandatory 2026 review. Leaders met with Dominic LeBlanc, the federal minister responsible for Canada–US trade, for what they described as a high-level roundtable on the future of CUSMA amid rising trade tensions and renewed threats of U.S. tariffs. Canadian Labour Congress president Bea Bruske said unions delivered a “clear and urgent message” that Canada should not accept a revised trade deal that weakens domestic industry or costs Canadian jobs. …Bruske was joined by leaders from several large manufacturing and building trades unions representing sectors heavily exposed to trade policy decisions, including auto manufacturing, construction and resource-based industries. Bruske said the upcoming CUSMA review should strengthen Canadian industries and working-class communities, not “hollow them out” in the rush to renew the agreement.
 PORTLAND, Ore. – Layoffs are expected at the beginning of April for Roseburg Forest Products Co.’s Riddle Plywood facility, according to a WARN notice filed this week. The notice, filed Feb. 4, says the company expects to permanently lay off 146 team members at the Riddle By-Pass Road location, though the facility will remain open. These layoffs are expected to take place after a 60-day WARN period. The company said April 5 “will be the last day of work for a majority of the affected team members before the layoff and that the remaining affected team members, if any, will be within 14 days of that date.” Impacted positions span a number of job titles, though the majority consist of Layup WAT Operators, Finish End WAT Operators, and Common Laborers.
PORTLAND, Ore. – Layoffs are expected at the beginning of April for Roseburg Forest Products Co.’s Riddle Plywood facility, according to a WARN notice filed this week. The notice, filed Feb. 4, says the company expects to permanently lay off 146 team members at the Riddle By-Pass Road location, though the facility will remain open. These layoffs are expected to take place after a 60-day WARN period. The company said April 5 “will be the last day of work for a majority of the affected team members before the layoff and that the remaining affected team members, if any, will be within 14 days of that date.” Impacted positions span a number of job titles, though the majority consist of Layup WAT Operators, Finish End WAT Operators, and Common Laborers.
 Duties on Canadian imports are driving up domestic sales at some Maine lumber companies. …Protection from historically lower Canadian lumber prices has given Pleasant River Lumber the confidence to add an additional manufacturing shift in Enfield, according to co-owner Jason Brochu. Photo by Katherine Emery. …Historically Canadian companies have both outbid them for timber harvested in Maine and undercut American lumber prices when they export the finished lumber product back across the border. …An industry analyst and two other mill leaders said that inflation and a sputtering housing market make it unclear whether the tariffs will have a positive or negative effect on business in the long run. The effects of the tariffs will also vary based on the different products sawmills make. …Sawmills rely on certainty, said Alden Robbins, of Robbins Lumber, and neither the markets nor foreign trade relationships have been stable recently.
Duties on Canadian imports are driving up domestic sales at some Maine lumber companies. …Protection from historically lower Canadian lumber prices has given Pleasant River Lumber the confidence to add an additional manufacturing shift in Enfield, according to co-owner Jason Brochu. Photo by Katherine Emery. …Historically Canadian companies have both outbid them for timber harvested in Maine and undercut American lumber prices when they export the finished lumber product back across the border. …An industry analyst and two other mill leaders said that inflation and a sputtering housing market make it unclear whether the tariffs will have a positive or negative effect on business in the long run. The effects of the tariffs will also vary based on the different products sawmills make. …Sawmills rely on certainty, said Alden Robbins, of Robbins Lumber, and neither the markets nor foreign trade relationships have been stable recently.
 The Bank of Canada’s latest survey of financial-market participants pointed to a modestly brighter growth outlook than the central bank’s own projections, even as trade tensions with the US remain the dominant threat hanging over Canada’s economy and housing market. In the fourth‑quarter Market Participants Survey, 93% of respondents cited an “increase in trade tensions” as the top downside risk to Canadian growth, well ahead of tighter global financial conditions and weaker consumer spending. Participants still assign a 20% probability to a recession over the next six months, but their median forecast calls for real GDP growth of 1.6% by the end of 2026 and 1.9% by late 2027, slightly stronger than the Bank’s own projections of 1.1% and 1.5%. While the survey suggests some stabilization in expectations, it underscores that tariff policy remains the key macroeconomic swing factor. …PwC Canada’s latest survey among 133 CEOs showed that only 27% expect the domestic economy to improve over the next 12 months.
The Bank of Canada’s latest survey of financial-market participants pointed to a modestly brighter growth outlook than the central bank’s own projections, even as trade tensions with the US remain the dominant threat hanging over Canada’s economy and housing market. In the fourth‑quarter Market Participants Survey, 93% of respondents cited an “increase in trade tensions” as the top downside risk to Canadian growth, well ahead of tighter global financial conditions and weaker consumer spending. Participants still assign a 20% probability to a recession over the next six months, but their median forecast calls for real GDP growth of 1.6% by the end of 2026 and 1.9% by late 2027, slightly stronger than the Bank’s own projections of 1.1% and 1.5%. While the survey suggests some stabilization in expectations, it underscores that tariff policy remains the key macroeconomic swing factor. …PwC Canada’s latest survey among 133 CEOs showed that only 27% expect the domestic economy to improve over the next 12 months.
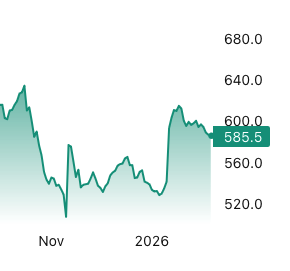 Lumber futures slipped below $590 per thousand board feet, the lowest level in nearly four weeks, as housing demand weakened and earlier restocking momentum faded. Demand softened as financing costs edged higher and housing activity cooled, with US pending home sales plunging 9.3% month on month in December 2025, removing a key source of construction and renovation related wood consumption ahead of the spring building season. At the same time, mills continued running to rebuild inventories after the winter squeeze, increasing physical availability while distributors reported quieter order books. The combination of softer demand and rising availability encouraged position unwinds after January’s rally, with falling volumes and open interest amplifying the price decline. [END]
Lumber futures slipped below $590 per thousand board feet, the lowest level in nearly four weeks, as housing demand weakened and earlier restocking momentum faded. Demand softened as financing costs edged higher and housing activity cooled, with US pending home sales plunging 9.3% month on month in December 2025, removing a key source of construction and renovation related wood consumption ahead of the spring building season. At the same time, mills continued running to rebuild inventories after the winter squeeze, increasing physical availability while distributors reported quieter order books. The combination of softer demand and rising availability encouraged position unwinds after January’s rally, with falling volumes and open interest amplifying the price decline. [END]

 Long-term mortgage rates continued to decline in January. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.10% last month, 9 basis points (bps) lower than December. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 4 bps to 5.44%. Compared to a year ago, the 30-year rate is lower by 86 bps. The 15-year rate is also lower by 72 bps. The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term borrowing, averaged 4.20% in January – an increase of 8 bps from the previous month, but remained considerably lower than last year by 43 bps. While mortgage rates typically move in tandem with the treasury yields, the spread between the two narrowed during the month. Reports that the Trump administration encouraged Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to expand purchases of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) boosted demand for MBS, pushing mortgage rates lower. However, treasury yields rose sharply in the final week of January from global and fiscal pressures.
Long-term mortgage rates continued to decline in January. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.10% last month, 9 basis points (bps) lower than December. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 4 bps to 5.44%. Compared to a year ago, the 30-year rate is lower by 86 bps. The 15-year rate is also lower by 72 bps. The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term borrowing, averaged 4.20% in January – an increase of 8 bps from the previous month, but remained considerably lower than last year by 43 bps. While mortgage rates typically move in tandem with the treasury yields, the spread between the two narrowed during the month. Reports that the Trump administration encouraged Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to expand purchases of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) boosted demand for MBS, pushing mortgage rates lower. However, treasury yields rose sharply in the final week of January from global and fiscal pressures.  As mass timber continues to grow in popularity in the US, manufacturers are evolving the scale and sourcing of wood production to meet rising demand.
As mass timber continues to grow in popularity in the US, manufacturers are evolving the scale and sourcing of wood production to meet rising demand.  Walk through any design-forward neighbourhood… and you’ll notice something the catalogues haven’t caught up with yet. The windows are changing. After decades dominated by vinyl, aluminium, and composite frames, timber is making a decisive return to high-end residential architecture. And the architects driving this shift aren’t motivated by nostalgia. They’re choosing wood because, for the homes they’re designing, nothing else performs quite the same way. The broader design world has been moving in this direction for several years. Mass timber construction, reclaimed wood interiors, rammed earth walls, natural stone — the 2025–2026 architectural conversation is dominated by what designers call “material honesty.” The idea is straightforward: use materials that are what they appear to be. No laminate pretending to be oak. …The knock against timber windows has always been practical: they need maintenance, they warp, they cost more. Two decades ago, much of that was fair. Modern engineered timber has changed the equation.
Walk through any design-forward neighbourhood… and you’ll notice something the catalogues haven’t caught up with yet. The windows are changing. After decades dominated by vinyl, aluminium, and composite frames, timber is making a decisive return to high-end residential architecture. And the architects driving this shift aren’t motivated by nostalgia. They’re choosing wood because, for the homes they’re designing, nothing else performs quite the same way. The broader design world has been moving in this direction for several years. Mass timber construction, reclaimed wood interiors, rammed earth walls, natural stone — the 2025–2026 architectural conversation is dominated by what designers call “material honesty.” The idea is straightforward: use materials that are what they appear to be. No laminate pretending to be oak. …The knock against timber windows has always been practical: they need maintenance, they warp, they cost more. Two decades ago, much of that was fair. Modern engineered timber has changed the equation. 
 California’s wildfire insurance crisis intensified this week as major insurers faced renewed scrutiny over denied or delayed payouts, while regulators and lawmakers moved to address mounting consumer complaints. The
California’s wildfire insurance crisis intensified this week as major insurers faced renewed scrutiny over denied or delayed payouts, while regulators and lawmakers moved to address mounting consumer complaints. The LANSING, Michigan – A state program to aid mass timber projects in Michigan has been extended for the Upper Peninsula after the region submitted no applications for funding in 2026. …A supplemental call for proposals makes available $50,000 through March 2. Those awards will be announced March 16. The awardees are:
LANSING, Michigan – A state program to aid mass timber projects in Michigan has been extended for the Upper Peninsula after the region submitted no applications for funding in 2026. …A supplemental call for proposals makes available $50,000 through March 2. Those awards will be announced March 16. The awardees are:
 For the first time, researchers have been able to confirm that our planet’s boreal forests are on the move. Using nearly a quarter million Landsat satellite images spanning 36 years, scientists have confirmed for the first time that Earth’s boreal forest—the planet’s largest forested biome—is shifting northward, revealing unprecedented changes in this critical ecosystem that stores more than a third of the world’s forests and helps regulate our global climate. [5 min. video]
For the first time, researchers have been able to confirm that our planet’s boreal forests are on the move. Using nearly a quarter million Landsat satellite images spanning 36 years, scientists have confirmed for the first time that Earth’s boreal forest—the planet’s largest forested biome—is shifting northward, revealing unprecedented changes in this critical ecosystem that stores more than a third of the world’s forests and helps regulate our global climate. [5 min. video] The Interior Department is blazing ahead with a reorganization plan that will bring all of its wildland firefighting operations into a single agency. Starting next week, all the department’s wildland fire employees and programs will be moved into a new Wildland Fire Service. Congress did not approve funds for this consolidation of federal firefighting programs into one agency. The Wildland Fire Service also stops short of merging wildland fire personnel or programs from the USDA’s Forest Service with those same resources at the Interior Department. An internal memo sent to staff on Monday states the Wildland Fire Service “will unify wildland fire management within DOI only.” According to the memo, obtained by Federal News Network, the Wildland Fire Service will “align operations” with USDA through shared procurement, predictive services, research, and policy reforms.
The Interior Department is blazing ahead with a reorganization plan that will bring all of its wildland firefighting operations into a single agency. Starting next week, all the department’s wildland fire employees and programs will be moved into a new Wildland Fire Service. Congress did not approve funds for this consolidation of federal firefighting programs into one agency. The Wildland Fire Service also stops short of merging wildland fire personnel or programs from the USDA’s Forest Service with those same resources at the Interior Department. An internal memo sent to staff on Monday states the Wildland Fire Service “will unify wildland fire management within DOI only.” According to the memo, obtained by Federal News Network, the Wildland Fire Service will “align operations” with USDA through shared procurement, predictive services, research, and policy reforms.
 COLORADO — The U.S. Forest Service is proposing logging southwest of Glenwood Springs, involving about 2,600 acres in what’s known as the Fourmile area along the borders of Pitkin, Mesa and Garfield counties. The White River National Forest’s proposal includes acreage in all three counties. It involves selective thinning and vegetation clearing in two treatment areas and along several roads to improve forest health, reduce wildfire risk and provide timber, the Forest Service said in a news release. “The timber treatments would improve the forest’s ability to withstand and recover from drought and insect outbreaks by creating more diversity in the size and ages of trees. Additionally, work along roads will strengthen predetermined areas where firefighters could more effectively engage wildfires,” the Forest Service said in its release. …“Active forest management is an important tool for maintaining healthy forests,” Acting Aspen-Sopris District Ranger Jennifer Schuller said in the release.
COLORADO — The U.S. Forest Service is proposing logging southwest of Glenwood Springs, involving about 2,600 acres in what’s known as the Fourmile area along the borders of Pitkin, Mesa and Garfield counties. The White River National Forest’s proposal includes acreage in all three counties. It involves selective thinning and vegetation clearing in two treatment areas and along several roads to improve forest health, reduce wildfire risk and provide timber, the Forest Service said in a news release. “The timber treatments would improve the forest’s ability to withstand and recover from drought and insect outbreaks by creating more diversity in the size and ages of trees. Additionally, work along roads will strengthen predetermined areas where firefighters could more effectively engage wildfires,” the Forest Service said in its release. …“Active forest management is an important tool for maintaining healthy forests,” Acting Aspen-Sopris District Ranger Jennifer Schuller said in the release.  MISSOULA, Montana — Forester Sean Steinebach felt stunned when US District Court Judge Donald Molloy in Missoula vacated a federal magistrate judge’s favorable recommendations about the proposed South Plateau timber project. “Judge Molloy is a thorn in my side,” said Steinebach, outreach forester for Sun Mountain Lumber, based in Deer Lodge. …Molloy’s ruling was filed Dec. 11, vacating March 31 recommendations by Magistrate Judge Kathleen DeSoto that had allowed the project to proceed. Sun Mountain Lumber operates a sawmill in Deer Lodge and one in Livingston. …Steinebach said incessant lawsuits by environmental groups like the Alliance for the Wild Rockies, the Center for Biological Diversity and the Council on Wildlife and Fish sabotage timber projects, threaten sawmill communities, loggers and others. …One key issue for Judge Molloy was secure habitat for grizzly bears, but Canada lynx habitat was also a concern. Both are considered threatened species under the Endangered Species Act.
MISSOULA, Montana — Forester Sean Steinebach felt stunned when US District Court Judge Donald Molloy in Missoula vacated a federal magistrate judge’s favorable recommendations about the proposed South Plateau timber project. “Judge Molloy is a thorn in my side,” said Steinebach, outreach forester for Sun Mountain Lumber, based in Deer Lodge. …Molloy’s ruling was filed Dec. 11, vacating March 31 recommendations by Magistrate Judge Kathleen DeSoto that had allowed the project to proceed. Sun Mountain Lumber operates a sawmill in Deer Lodge and one in Livingston. …Steinebach said incessant lawsuits by environmental groups like the Alliance for the Wild Rockies, the Center for Biological Diversity and the Council on Wildlife and Fish sabotage timber projects, threaten sawmill communities, loggers and others. …One key issue for Judge Molloy was secure habitat for grizzly bears, but Canada lynx habitat was also a concern. Both are considered threatened species under the Endangered Species Act.


 University of Oregon Assistant Research Professor James Johnston said he was taught that when a large fire burned a moist, Western Cascade forest to the ground, and the area didn’t burn for hundreds of years afterward, that’s what created a complex, old-growth landscape. Instead, his study found that ancient tree stumps in the Mount Hood and Willamette National Forests had burn scars from multiple fires over their long lives. It’s the first time tree-ring scars have been used to document fire records in the region. Johnston said forests are complex because of—not in spite of—lower-severity wildfires which don’t kill many of the trees. …Johnston said to figure out the best ways to foster healthy forests, relatively recent upheavals also need to be considered. Those include clearcuts, human infrastructure at the margins of forests, and hotter and drier weather patterns.
University of Oregon Assistant Research Professor James Johnston said he was taught that when a large fire burned a moist, Western Cascade forest to the ground, and the area didn’t burn for hundreds of years afterward, that’s what created a complex, old-growth landscape. Instead, his study found that ancient tree stumps in the Mount Hood and Willamette National Forests had burn scars from multiple fires over their long lives. It’s the first time tree-ring scars have been used to document fire records in the region. Johnston said forests are complex because of—not in spite of—lower-severity wildfires which don’t kill many of the trees. …Johnston said to figure out the best ways to foster healthy forests, relatively recent upheavals also need to be considered. Those include clearcuts, human infrastructure at the margins of forests, and hotter and drier weather patterns. OLYMPIA, WA – Two Washington tribal leaders could soon sit on the state’s Board of Natural Resources, which guides logging sales and other management decisions on public land. Sen. Claudia Kauffman, a Democrat and first Native American woman to serve in the state Senate, proposed Senate Bill 5838. On Monday, it was voted out of the Senate Committee on Agriculture and Natural Resources. The bill originally called for only one tribal representative, but it was changed to two members as it moved through the committee process. The proposal is backed by Public Lands Commissioner Dave Upthegrove, who chairs the board and leads the Department of Natural Resources. The department requested the legislation. If enacted, the governor would appoint a tribal representative from each side of the Cascades… Eligible tribal members must hold an elected position in a federally recognized tribe whose reservation or treaty-ceded lands are in Washington.
OLYMPIA, WA – Two Washington tribal leaders could soon sit on the state’s Board of Natural Resources, which guides logging sales and other management decisions on public land. Sen. Claudia Kauffman, a Democrat and first Native American woman to serve in the state Senate, proposed Senate Bill 5838. On Monday, it was voted out of the Senate Committee on Agriculture and Natural Resources. The bill originally called for only one tribal representative, but it was changed to two members as it moved through the committee process. The proposal is backed by Public Lands Commissioner Dave Upthegrove, who chairs the board and leads the Department of Natural Resources. The department requested the legislation. If enacted, the governor would appoint a tribal representative from each side of the Cascades… Eligible tribal members must hold an elected position in a federally recognized tribe whose reservation or treaty-ceded lands are in Washington.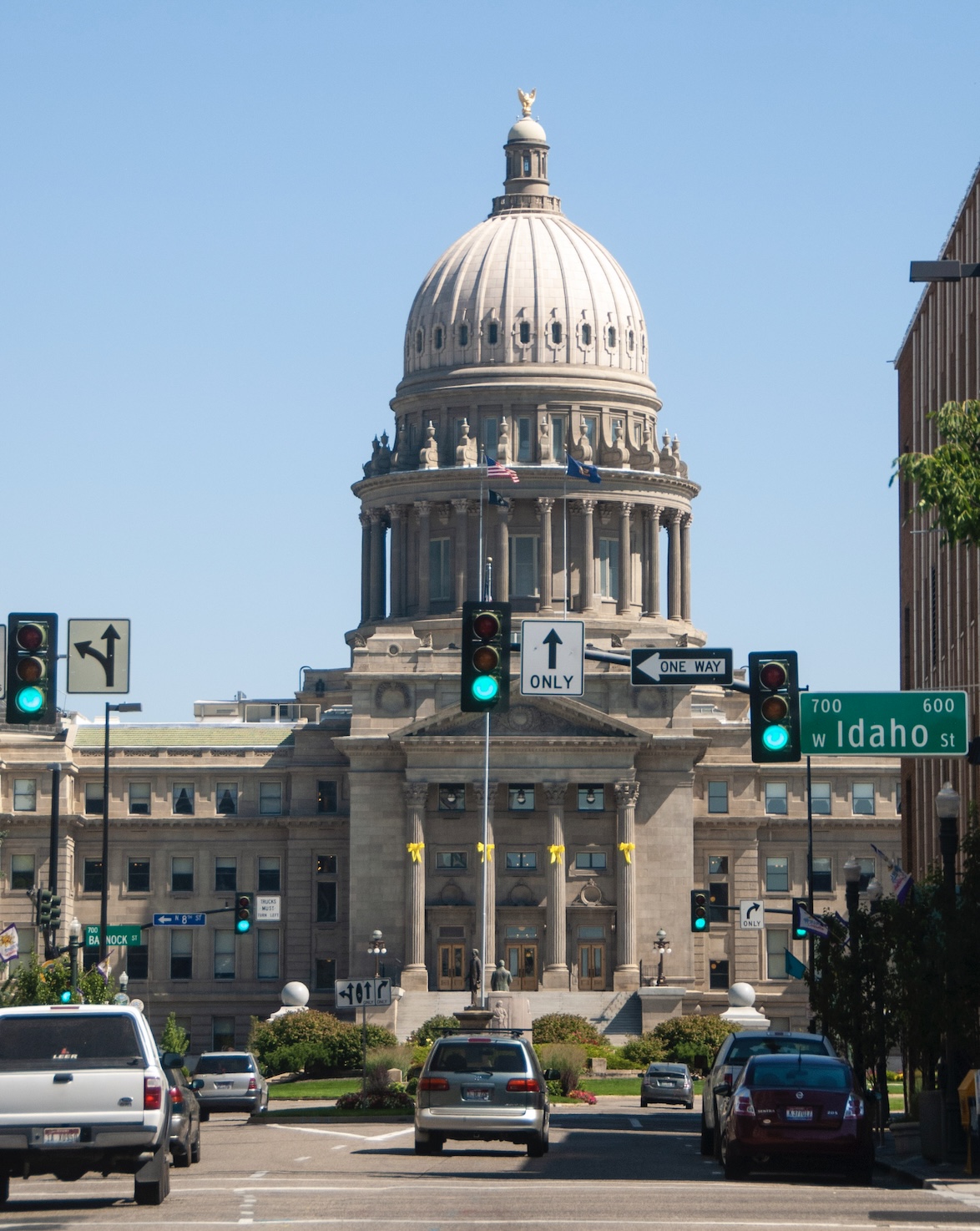 Anytime someone talks about shifting management of federal lands to Idaho, know that they have a bigger goal in mind. In a recent interview on The Ranch Podcast, Rep. Jordan Redman, R-Coeur d’Alene, was frank about his goals for public lands in Idaho. He said his father, former Rep. Eric Redman, dreamed of Idaho taking ownership of federal lands, and his goal is the same. The first step is for Idaho to manage public lands for a bit, then the state takes ownership of them. “How do we get that federal land back in ownership for the state?” Rep. Jordan Redman said. Back? It should be said that Idaho has never owned federal land. Redman should try reading the Constitution he swore to uphold: “… the people of the state of Idaho do agree and declare that we forever disclaim all right and title to the unappropriated public lands lying within the boundaries thereof … .” You can’t get back what you never owned; you can only take it. In service of the goal of taking federal land, Redman made a familiar argument.
Anytime someone talks about shifting management of federal lands to Idaho, know that they have a bigger goal in mind. In a recent interview on The Ranch Podcast, Rep. Jordan Redman, R-Coeur d’Alene, was frank about his goals for public lands in Idaho. He said his father, former Rep. Eric Redman, dreamed of Idaho taking ownership of federal lands, and his goal is the same. The first step is for Idaho to manage public lands for a bit, then the state takes ownership of them. “How do we get that federal land back in ownership for the state?” Rep. Jordan Redman said. Back? It should be said that Idaho has never owned federal land. Redman should try reading the Constitution he swore to uphold: “… the people of the state of Idaho do agree and declare that we forever disclaim all right and title to the unappropriated public lands lying within the boundaries thereof … .” You can’t get back what you never owned; you can only take it. In service of the goal of taking federal land, Redman made a familiar argument. Baker City, Oregon — Baker County Commissioner Christina Witham lauded the Wallowa-Whitman National Forest for cutting and piling trees southwest of Baker City, the start of a project that will continue for several years with a goal of reducing the risk of a wildfire in the city’s watershed. “It’s looking really nice,” Witham said during commissioners’ meeting Wednesday morning, Feb. 4. Witham, whose focus areas as a commissioner include natural resources, said she recently toured some of the work areas with Forest Service officials. …According to the Wallowa-Whitman, the project, which totals about 23,000 acres, is designed not only to reduce the fire risk within the watershed, but also to curb the threat of a fire spreading into the watershed, particularly from the south, a path that summer lightning storms often follow.
Baker City, Oregon — Baker County Commissioner Christina Witham lauded the Wallowa-Whitman National Forest for cutting and piling trees southwest of Baker City, the start of a project that will continue for several years with a goal of reducing the risk of a wildfire in the city’s watershed. “It’s looking really nice,” Witham said during commissioners’ meeting Wednesday morning, Feb. 4. Witham, whose focus areas as a commissioner include natural resources, said she recently toured some of the work areas with Forest Service officials. …According to the Wallowa-Whitman, the project, which totals about 23,000 acres, is designed not only to reduce the fire risk within the watershed, but also to curb the threat of a fire spreading into the watershed, particularly from the south, a path that summer lightning storms often follow. WASHINGTON — The Trump administration on Thursday will revoke a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the White House announced. The Environmental Protection Agency will issue a final rule rescinding a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding. That Obama-era policy determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. …White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt said… the action “will save $1.3 trillion in crushing regulations,” she said. …The endangerment finding is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. It is used to justify regulations, such as auto emissions standards, intended to protect against threats made increasingly severe by climate change — deadly floods, extreme heat waves, catastrophic wildfires and other natural disasters.
WASHINGTON — The Trump administration on Thursday will revoke a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the White House announced. The Environmental Protection Agency will issue a final rule rescinding a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding. That Obama-era policy determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. …White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt said… the action “will save $1.3 trillion in crushing regulations,” she said. …The endangerment finding is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. It is used to justify regulations, such as auto emissions standards, intended to protect against threats made increasingly severe by climate change — deadly floods, extreme heat waves, catastrophic wildfires and other natural disasters.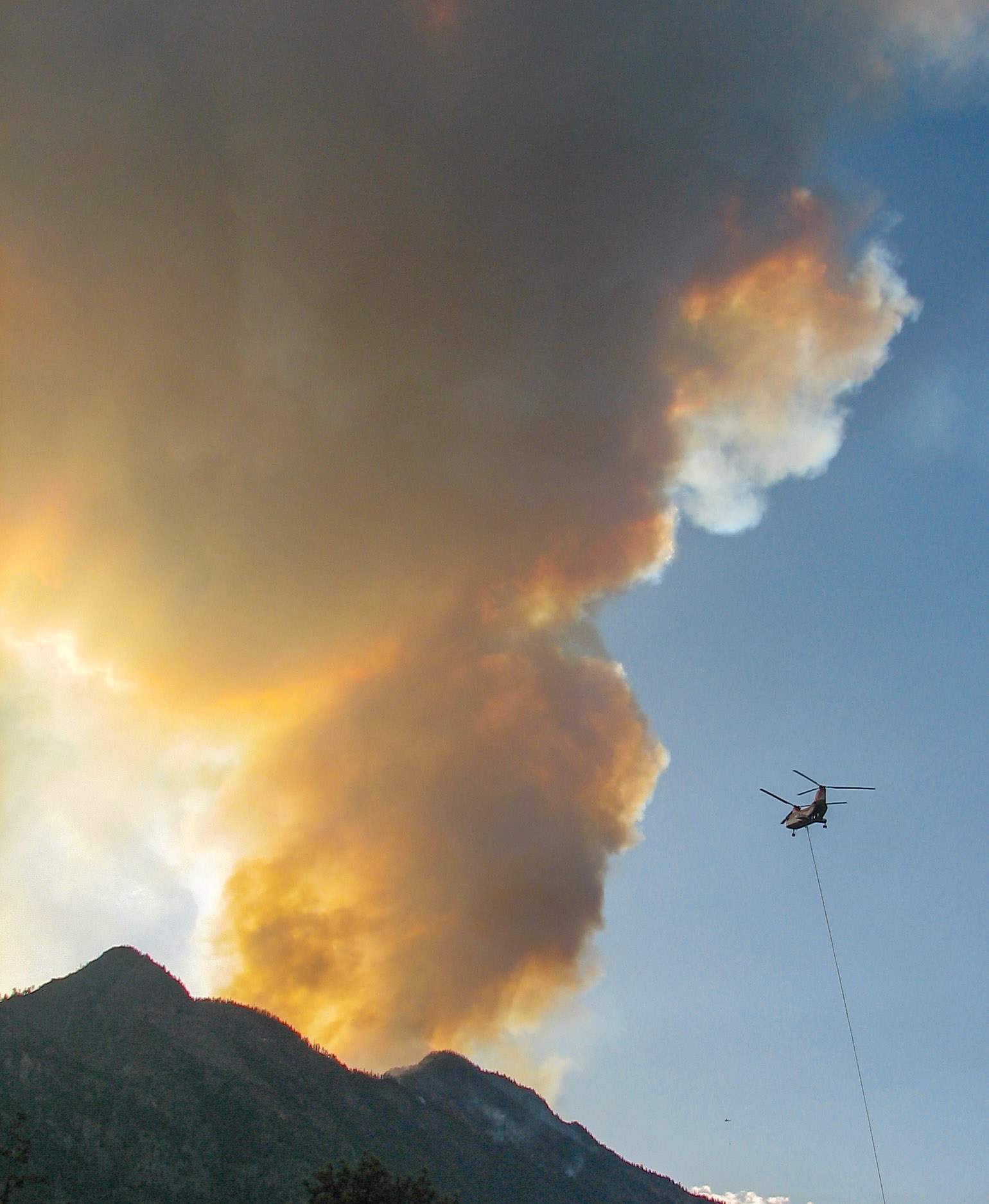 Chronic exposure to pollution from wildfires has been linked to tens of thousands of deaths annually in the United States, according to a new study. The paper found that from 2006 to 2020, long-term exposure to tiny particulates from wildfire smoke contributed to an average of 24,100 deaths a year in the lower 48 states. “Our message is: Wildfire smoke is very dangerous. It is an increasing threat to human health,” said Yaguang Wei, a study author and assistant professor in the department of environmental medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. …“It’s only if we’re doing multiple studies with many different designs that we gain scientific confidence of our outcomes,” said Michael Jerrett, professor of environmental health science at the University of California, Los Angeles. The paper’s researchers focused on deaths linked to chronic exposure to fine particulate matter, or PM2.5 — the main concern from wildfire smoke.
Chronic exposure to pollution from wildfires has been linked to tens of thousands of deaths annually in the United States, according to a new study. The paper found that from 2006 to 2020, long-term exposure to tiny particulates from wildfire smoke contributed to an average of 24,100 deaths a year in the lower 48 states. “Our message is: Wildfire smoke is very dangerous. It is an increasing threat to human health,” said Yaguang Wei, a study author and assistant professor in the department of environmental medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. …“It’s only if we’re doing multiple studies with many different designs that we gain scientific confidence of our outcomes,” said Michael Jerrett, professor of environmental health science at the University of California, Los Angeles. The paper’s researchers focused on deaths linked to chronic exposure to fine particulate matter, or PM2.5 — the main concern from wildfire smoke.
 Construction in New York City is one of the most dynamic and demanding industries in the country — but it’s also one of the most dangerous. …That’s why innovation in building materials and methods can have a real impact not only on efficiency and sustainability but also on safety. One such innovation, mass timber, is gaining traction. …Mass timber components are prefabricated in controlled factory settings. This approach greatly reduces the need for tasks like cutting, welding, or mixing concrete on-site — tasks that are commonly associated with jobsite injuries. …Additionally, since large panels arrive ready to install, crews spend less time working at height, which directly reduces the risk of falls — the leading cause of construction fatalities in the U.S., according to OSHA’s fall protection guidelines. …It also means a reduced need for powered hand tools and high-decibel equipment, lowering the risk of accidents related to hand injuries or communication breakdowns.
Construction in New York City is one of the most dynamic and demanding industries in the country — but it’s also one of the most dangerous. …That’s why innovation in building materials and methods can have a real impact not only on efficiency and sustainability but also on safety. One such innovation, mass timber, is gaining traction. …Mass timber components are prefabricated in controlled factory settings. This approach greatly reduces the need for tasks like cutting, welding, or mixing concrete on-site — tasks that are commonly associated with jobsite injuries. …Additionally, since large panels arrive ready to install, crews spend less time working at height, which directly reduces the risk of falls — the leading cause of construction fatalities in the U.S., according to OSHA’s fall protection guidelines. …It also means a reduced need for powered hand tools and high-decibel equipment, lowering the risk of accidents related to hand injuries or communication breakdowns.