 The Canadian and American economies are woven together tightly. So when Donald Trump slapped 25% tariffs on Canadian imports last year, many economists—myself included saw a disaster looming. …The most exposed sectors were those most dependent on US demand: steel, aluminum, autos, energy and lumber. …In our worst-case scenario, we expected it would shrink Canada’s GDP by 2.6 per cent, leading to a moderate recession and shaving nearly $2,000 a year off income for every Canadian. So far, however, that doomsday scenario hasn’t materialized. This was possible because of the Canada-US-Mexico trade agreement. …Avoiding the worst of the tariffs doesn’t mean we’ve won or even survived the trade war. Communities across the country are still hurting. …Regions in Quebec and British Columbia are under strain, with key industrial sectors—steel, aluminum, copper, lumber—are facing additional tariffs under Section 232 authority.
The Canadian and American economies are woven together tightly. So when Donald Trump slapped 25% tariffs on Canadian imports last year, many economists—myself included saw a disaster looming. …The most exposed sectors were those most dependent on US demand: steel, aluminum, autos, energy and lumber. …In our worst-case scenario, we expected it would shrink Canada’s GDP by 2.6 per cent, leading to a moderate recession and shaving nearly $2,000 a year off income for every Canadian. So far, however, that doomsday scenario hasn’t materialized. This was possible because of the Canada-US-Mexico trade agreement. …Avoiding the worst of the tariffs doesn’t mean we’ve won or even survived the trade war. Communities across the country are still hurting. …Regions in Quebec and British Columbia are under strain, with key industrial sectors—steel, aluminum, copper, lumber—are facing additional tariffs under Section 232 authority.

 MONTREAL, Quebec – Domtar announced a curtailment in its lumber production. Due to challenging market conditions, US tariffs, and ongoing economic uncertainty, the company will temporarily reduce its lumber production by 150 million board feet for the first quarter of 2026 across its facilities in Quebec, Ontario and the United States. “The demand for lumber in North America remains weak, requiring us to adjust our production levels in line with market conditions,” said Luc Thériault, CEO, Wood Products, and President – Canada, for Domtar. “While this decision is necessary, we are fully aware of the impact it will have on our employees, contractors, suppliers and the communities in which we operate.” Domtar will continue to monitor market conditions and adjust its production plans accordingly. Domtar has a workforce of nearly 14,000 employees in more than 60 locations across North America.
MONTREAL, Quebec – Domtar announced a curtailment in its lumber production. Due to challenging market conditions, US tariffs, and ongoing economic uncertainty, the company will temporarily reduce its lumber production by 150 million board feet for the first quarter of 2026 across its facilities in Quebec, Ontario and the United States. “The demand for lumber in North America remains weak, requiring us to adjust our production levels in line with market conditions,” said Luc Thériault, CEO, Wood Products, and President – Canada, for Domtar. “While this decision is necessary, we are fully aware of the impact it will have on our employees, contractors, suppliers and the communities in which we operate.” Domtar will continue to monitor market conditions and adjust its production plans accordingly. Domtar has a workforce of nearly 14,000 employees in more than 60 locations across North America.
 The National Lumber & Building Material Dealers Association (NLBMDA) released its
The National Lumber & Building Material Dealers Association (NLBMDA) released its  WASHINGTON — U.S. President Donald Trump said Tuesday the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement on trade is “irrelevant” to him and Americans don’t need Canadian products. “It expires very shortly and we could have it or not,” Trump said while touring a Ford plant in Michigan. “It wouldn’t matter to me. I think they want it. I don’t really care about it.” Trump statements have rattled Canada and Mexico ahead of a mandatory review this year of the future of the continental trade pact, known as CUSMA. The president told reporters that “Canada wants it” but the United States doesn’t need anything from its northern neighbour. The three countries have started domestic consultations on the review and Dominic LeBlanc, the minister in charge of Canada-U.S. relations, is set to meet with U.S. counterparts in mid-January to launch formal CUSMA talks. The trade pact has shielded Canada and Mexico from the worst impacts of Trump’s tariffs.
WASHINGTON — U.S. President Donald Trump said Tuesday the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement on trade is “irrelevant” to him and Americans don’t need Canadian products. “It expires very shortly and we could have it or not,” Trump said while touring a Ford plant in Michigan. “It wouldn’t matter to me. I think they want it. I don’t really care about it.” Trump statements have rattled Canada and Mexico ahead of a mandatory review this year of the future of the continental trade pact, known as CUSMA. The president told reporters that “Canada wants it” but the United States doesn’t need anything from its northern neighbour. The three countries have started domestic consultations on the review and Dominic LeBlanc, the minister in charge of Canada-U.S. relations, is set to meet with U.S. counterparts in mid-January to launch formal CUSMA talks. The trade pact has shielded Canada and Mexico from the worst impacts of Trump’s tariffs. The U.S. Endowment for Forestry and Communities has announced a new collaboration with the Georgia Institute of Technology to address the far-reaching social, economic and environmental impacts of pulp and paper mill closures across the United States, particularly in the rural South, where these mills have long served as economic anchors. The Endowment and Georgia Tech are developing an integrated decision-making dashboard to help policymakers, community leaders and industry stakeholders quantify the effects of mill closures and identify data-driven pathways to offset them through the sustainable use of forestry residues… Over the past decade, nearly 50 paper mills have shut down nationwide … resulting in the loss of thousands of jobs and disrupted local supply chains that once connected family forest owners, loggers, sawmills and manufacturers… As markets for timber and forestry byproducts contract, landowners face reduced incentives for active management – conditions that can increase the risk of wildfire, invasive species and forest conversion to other uses.
The U.S. Endowment for Forestry and Communities has announced a new collaboration with the Georgia Institute of Technology to address the far-reaching social, economic and environmental impacts of pulp and paper mill closures across the United States, particularly in the rural South, where these mills have long served as economic anchors. The Endowment and Georgia Tech are developing an integrated decision-making dashboard to help policymakers, community leaders and industry stakeholders quantify the effects of mill closures and identify data-driven pathways to offset them through the sustainable use of forestry residues… Over the past decade, nearly 50 paper mills have shut down nationwide … resulting in the loss of thousands of jobs and disrupted local supply chains that once connected family forest owners, loggers, sawmills and manufacturers… As markets for timber and forestry byproducts contract, landowners face reduced incentives for active management – conditions that can increase the risk of wildfire, invasive species and forest conversion to other uses.

 There are solid reasons to expect near-term strength in the US and Canadian construction markets. In the US, rapid technological progress and supportive federal policies are driving major investments in semiconductor fabrication, AI-related data centers, and energy infrastructure, with growing momentum toward nuclear power. In Canada, federal and provincial governments are promoting “nation-building” projects that emphasize LNG export capacity, port expansions, and new mines for critical minerals required by the digital economy. Both nations recognize that housing supply must rise substantially to meet population needs, signaling a long-term boost in residential construction. Yet, 2025 proved disappointing for overall construction performance, especially in employment. …Housing activity revealed a sharper divide between the two nations. U.S. housing starts in November 2025 dropped to an annualized 1.246 million units, the lowest since the pandemic. Most analysts believe the country needs at least 1.5 million starts per year to meet demand.
There are solid reasons to expect near-term strength in the US and Canadian construction markets. In the US, rapid technological progress and supportive federal policies are driving major investments in semiconductor fabrication, AI-related data centers, and energy infrastructure, with growing momentum toward nuclear power. In Canada, federal and provincial governments are promoting “nation-building” projects that emphasize LNG export capacity, port expansions, and new mines for critical minerals required by the digital economy. Both nations recognize that housing supply must rise substantially to meet population needs, signaling a long-term boost in residential construction. Yet, 2025 proved disappointing for overall construction performance, especially in employment. …Housing activity revealed a sharper divide between the two nations. U.S. housing starts in November 2025 dropped to an annualized 1.246 million units, the lowest since the pandemic. Most analysts believe the country needs at least 1.5 million starts per year to meet demand. 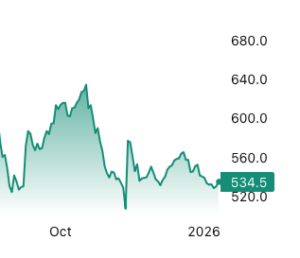 Lumber futures rose toward $535 per thousand board feet, rebounding from the September low of $528 reached on January 7th after a low liquidity holiday sell off unwound, improving seasonal demand expectations and longer term supply tightening. Renewed engagement from market participants, signaled that forced selling and the thin trading conditions that pushed prices to multi month lows have faded. Seasonal demand expectations have strengthened as builders begin positioning ahead of the spring construction period, when consumption typically improves following year end destocking. Industry forecasts point to a modest pickup in US housing starts and repair and remodel activity in 2026 as interest rates ease and trade uncertainty recedes, supporting demand after a weak finish to 2025. At the same time, longer term supply growth remains constrained by ongoing tariffs on Canadian softwood and slower capacity expansion across North American sawmills, limiting surplus.
Lumber futures rose toward $535 per thousand board feet, rebounding from the September low of $528 reached on January 7th after a low liquidity holiday sell off unwound, improving seasonal demand expectations and longer term supply tightening. Renewed engagement from market participants, signaled that forced selling and the thin trading conditions that pushed prices to multi month lows have faded. Seasonal demand expectations have strengthened as builders begin positioning ahead of the spring construction period, when consumption typically improves following year end destocking. Industry forecasts point to a modest pickup in US housing starts and repair and remodel activity in 2026 as interest rates ease and trade uncertainty recedes, supporting demand after a weak finish to 2025. At the same time, longer term supply growth remains constrained by ongoing tariffs on Canadian softwood and slower capacity expansion across North American sawmills, limiting surplus.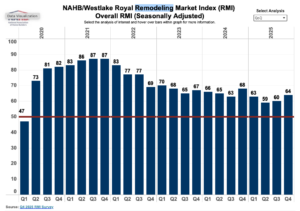 In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB remodeling index (RMI) posted a reading of 64, increasing four points compared to the previous quarter. Most remodelers are finding reasonably strong market conditions, even with the normal seasonal slowdown during the holidays. The major headwinds the industry is experiencing continue to be rising costs and potential customers hesitating due to policy and economic uncertainty. Demand for remodeling is being supported by an aging housing stock, strong homeowner equity and increasing need for aging-in-place improvements. …In the fourth quarter of 2025, the Current Conditions Index averaged 71, increasing three points from the previous quarter. …The Future Indicators Index averaged 56, up four points from the previous quarter.
In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB remodeling index (RMI) posted a reading of 64, increasing four points compared to the previous quarter. Most remodelers are finding reasonably strong market conditions, even with the normal seasonal slowdown during the holidays. The major headwinds the industry is experiencing continue to be rising costs and potential customers hesitating due to policy and economic uncertainty. Demand for remodeling is being supported by an aging housing stock, strong homeowner equity and increasing need for aging-in-place improvements. …In the fourth quarter of 2025, the Current Conditions Index averaged 71, increasing three points from the previous quarter. …The Future Indicators Index averaged 56, up four points from the previous quarter. 






 A recent federal court ruling tossing out a streamlined environmental review for three Oregon timber projects will point the way for conservation groups to challenge the Trump administration’s nationwide logging agenda, natural resources attorneys say. Judge Michael McShane of the US District Court for the District of Oregon in his Jan. 13 ruling set aside a categorical exclusion under the National Environmental Policy Act called “CE-6.” The 1992 exclusion allowed for quick approval of logging projects designed to thin forests to reduce wildfire hazards. Fast-tracking an expansion of logging on federal land is among President Donald Trump’s top priorities in order to cut lumber imports and grow domestic timber industry jobs. The administration is loosening public notice and environmental review requirements for logging and other projects under NEPA, and it’s rolling back protections for roadless areas in national forests in order to open them to possible logging projects.
A recent federal court ruling tossing out a streamlined environmental review for three Oregon timber projects will point the way for conservation groups to challenge the Trump administration’s nationwide logging agenda, natural resources attorneys say. Judge Michael McShane of the US District Court for the District of Oregon in his Jan. 13 ruling set aside a categorical exclusion under the National Environmental Policy Act called “CE-6.” The 1992 exclusion allowed for quick approval of logging projects designed to thin forests to reduce wildfire hazards. Fast-tracking an expansion of logging on federal land is among President Donald Trump’s top priorities in order to cut lumber imports and grow domestic timber industry jobs. The administration is loosening public notice and environmental review requirements for logging and other projects under NEPA, and it’s rolling back protections for roadless areas in national forests in order to open them to possible logging projects.
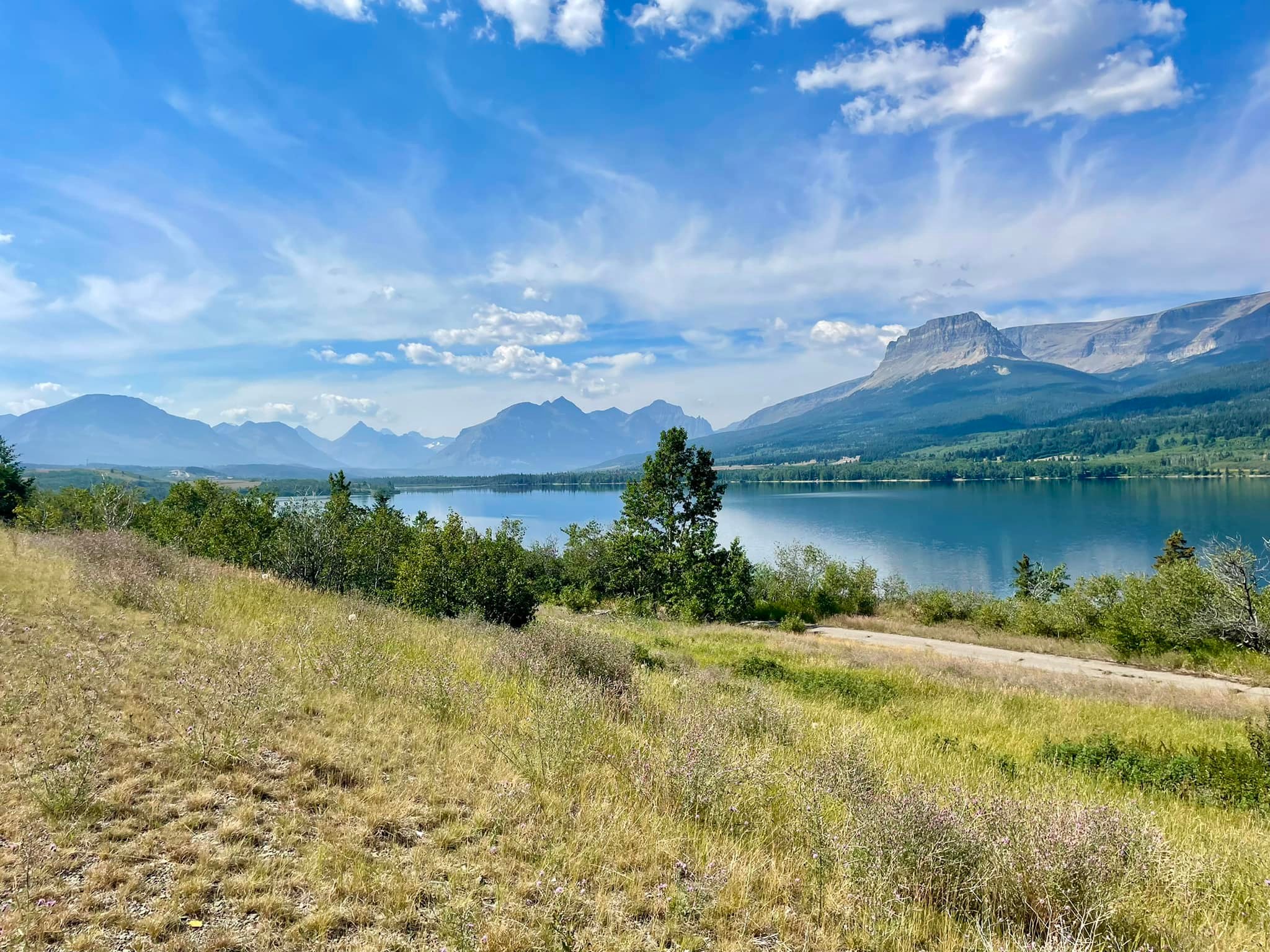 A major logging project has been proposed on the southern border of Glacier National Park, prompting concern from conservationists… “This is the heart of some of our wildest, most intact landscapes left in the U.S., anywhere south of Alaska,” said Peter Metcalf, the executive director of the Glacier-Two Medicine Alliance, a conservation organization in East Glacier Park, Montana. “We are really concerned that this kind of logging proposal would be slated for this landscape.” U.S. Forest Service district ranger Robert Davies said he plans to use the emergency authority authorized by an April 2025 executive order to expedite the project. The order calls for increasing timber production and reducing wildfire risk in areas of national forest considered to have very high or high wildfire risk. Roughly half the proposed project qualifies, but the entire project is subject to the streamlined timeline, which cuts out the majority of opportunities for public participation.
A major logging project has been proposed on the southern border of Glacier National Park, prompting concern from conservationists… “This is the heart of some of our wildest, most intact landscapes left in the U.S., anywhere south of Alaska,” said Peter Metcalf, the executive director of the Glacier-Two Medicine Alliance, a conservation organization in East Glacier Park, Montana. “We are really concerned that this kind of logging proposal would be slated for this landscape.” U.S. Forest Service district ranger Robert Davies said he plans to use the emergency authority authorized by an April 2025 executive order to expedite the project. The order calls for increasing timber production and reducing wildfire risk in areas of national forest considered to have very high or high wildfire risk. Roughly half the proposed project qualifies, but the entire project is subject to the streamlined timeline, which cuts out the majority of opportunities for public participation. In 1980, Washington State’s Mount St Helens erupted…causing an ecological nightmare as the volcano spewed lava, ash, and debris over the surrounding landscape that was followed by mudflows and pyroclastic flows, leaving the vegetation covered in mud and detritus as far as 27 kilometers from the volcano. …But one team of scientists had an unconventional idea to help jumpstart the process: send a few gophers on a one-day mission to the mountain. “Gophers are known as ‘hole diggers’,” says a 2024 paper assessing the long-term effects of the rodents at Mount St Helens, adding, “a single gopher can move 227 kg [500 pounds] of soil per month”. Digging is a useful quality in restoring an area devastated by volcanic eruption. Plant life was struggling to return… But while the top layers of soil were destroyed by the eruption and lava flows, the soil underneath could still have been rich in bacteria and fungi.
In 1980, Washington State’s Mount St Helens erupted…causing an ecological nightmare as the volcano spewed lava, ash, and debris over the surrounding landscape that was followed by mudflows and pyroclastic flows, leaving the vegetation covered in mud and detritus as far as 27 kilometers from the volcano. …But one team of scientists had an unconventional idea to help jumpstart the process: send a few gophers on a one-day mission to the mountain. “Gophers are known as ‘hole diggers’,” says a 2024 paper assessing the long-term effects of the rodents at Mount St Helens, adding, “a single gopher can move 227 kg [500 pounds] of soil per month”. Digging is a useful quality in restoring an area devastated by volcanic eruption. Plant life was struggling to return… But while the top layers of soil were destroyed by the eruption and lava flows, the soil underneath could still have been rich in bacteria and fungi. PORTLAND, Ore. — In a win for conservation groups, a federal judge
PORTLAND, Ore. — In a win for conservation groups, a federal judge  Western Washington forests are vital to the identity, economy, and quality of life vital to the region. From the Puget Sound to the Olympic Peninsula and Columbia Gorge, healthy forests provide clean air and water, sustain fish and wildlife habitat, store carbon, and support local jobs in forestry, recreation, and tourism. …The Western Washington Forest Health Strategic Plan is the result of an holistic and collaborative effort by the Washington State Department of Natural Resources to bring partners representing all lands and stakeholder groups together to identify priorities and strategies for how to steward and manage western Washington forests at a landscape scale. This plan builds on lessons learned from the development and implementation of the
Western Washington forests are vital to the identity, economy, and quality of life vital to the region. From the Puget Sound to the Olympic Peninsula and Columbia Gorge, healthy forests provide clean air and water, sustain fish and wildlife habitat, store carbon, and support local jobs in forestry, recreation, and tourism. …The Western Washington Forest Health Strategic Plan is the result of an holistic and collaborative effort by the Washington State Department of Natural Resources to bring partners representing all lands and stakeholder groups together to identify priorities and strategies for how to steward and manage western Washington forests at a landscape scale. This plan builds on lessons learned from the development and implementation of the  PUEBLO, Colo. — The Pike-San Isabel National Forests & Cimarron and Comanche National Grasslands began a 10-year partnership and $7.3 million investment to implement forest health treatments as part of the War Department’s Readiness and Environmental Protection Integration (REPI) program. The partners will use $3 million in REPI funds, along with $4.3 million in partner contributions, to treat 2,000 acres of National Forest System land and nonfederal lands near the U.S. Air Force Academy and Cheyenne Mountain Space Force Station. The REPI program preserves military missions by avoiding land use conflicts near military installations, addressing environmental restrictions that limit military activities and increasing military installation resilience.
PUEBLO, Colo. — The Pike-San Isabel National Forests & Cimarron and Comanche National Grasslands began a 10-year partnership and $7.3 million investment to implement forest health treatments as part of the War Department’s Readiness and Environmental Protection Integration (REPI) program. The partners will use $3 million in REPI funds, along with $4.3 million in partner contributions, to treat 2,000 acres of National Forest System land and nonfederal lands near the U.S. Air Force Academy and Cheyenne Mountain Space Force Station. The REPI program preserves military missions by avoiding land use conflicts near military installations, addressing environmental restrictions that limit military activities and increasing military installation resilience.  As climate change drives more frequent and severe wildfires across boreal forests in Alaska and northwestern Canada, scientists are asking a critical question: Will these ecosystems continue to store carbon or become a growing source of carbon emissions? New research published shows that when forests shift from coniferous—consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches—to deciduous—consisting mostly of birches and aspens—they could release substantially less carbon when they burn. The study, led by researchers from the Center for Ecosystem Science and Society (ECOSS) at Northern Arizona University and published in Nature Climate Change, found that boreal forests dominated by deciduous species lose less than half as much carbon per unit area burned compared to historically dominant black spruce forests. Even under severe fire weather conditions, carbon losses in deciduous stands were consistently lower than those in conifer forests.
As climate change drives more frequent and severe wildfires across boreal forests in Alaska and northwestern Canada, scientists are asking a critical question: Will these ecosystems continue to store carbon or become a growing source of carbon emissions? New research published shows that when forests shift from coniferous—consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches—to deciduous—consisting mostly of birches and aspens—they could release substantially less carbon when they burn. The study, led by researchers from the Center for Ecosystem Science and Society (ECOSS) at Northern Arizona University and published in Nature Climate Change, found that boreal forests dominated by deciduous species lose less than half as much carbon per unit area burned compared to historically dominant black spruce forests. Even under severe fire weather conditions, carbon losses in deciduous stands were consistently lower than those in conifer forests.
 SEATTLE — Twenty-five years ago, I stood in a snowy National Arboretum in Washington, DC, shaking hands with President Bill Clinton at the signing ceremony for the most important forest conservation mandate in our country’s history. But now that landmark law, which went into effect on Jan. 12, 2001, is hanging by a thread, marked for repeal by the Trump administration — even though 99% of citizen input opposes the idea. The “Roadless Rule” was adopted to curtail harmful logging and industrial roadbuilding across 58 million undeveloped acres of our national forests. More than 2 million acres of those wild lands are in Washington, helping keep this the Evergreen State. …Trump officials claim that opening these areas to bulldozers and chain saws will protect communities from wildfire. But that’s a story that just doesn’t wash. [to access the full story a Seattle Times subscription is required]
SEATTLE — Twenty-five years ago, I stood in a snowy National Arboretum in Washington, DC, shaking hands with President Bill Clinton at the signing ceremony for the most important forest conservation mandate in our country’s history. But now that landmark law, which went into effect on Jan. 12, 2001, is hanging by a thread, marked for repeal by the Trump administration — even though 99% of citizen input opposes the idea. The “Roadless Rule” was adopted to curtail harmful logging and industrial roadbuilding across 58 million undeveloped acres of our national forests. More than 2 million acres of those wild lands are in Washington, helping keep this the Evergreen State. …Trump officials claim that opening these areas to bulldozers and chain saws will protect communities from wildfire. But that’s a story that just doesn’t wash. [to access the full story a Seattle Times subscription is required]
 VALLEJO, Calif. — The USDA Forest Service Pacific Southwest Region and CAL FIRE have renewed their commitment to battling wildfires across California. This renewal extends the California Fire Master Agreement for another five years. The agreement, signed by Pacific Southwest interim Regional Forester Jacque Buchanan and CAL FIRE Chief Joe Tyler on Dec. 12, allows for a cooperative approach to wildfire response. According to the USDA Forest Service, this collaboration enables firefighters to share resources and respond across jurisdictional lines during emergencies. “This complex operating environment within California and the challenges we face year-round require this collaborative approach,” Jaime Gamboa, fire director for the Forest Service’s Pacific Southwest Region, said. The agreement emphasizes a united front in wildfire emergencies, prioritizing the closest available resources to protect lives and property. It also covers hazardous fuels reduction and streamlines training and equipment sharing.
VALLEJO, Calif. — The USDA Forest Service Pacific Southwest Region and CAL FIRE have renewed their commitment to battling wildfires across California. This renewal extends the California Fire Master Agreement for another five years. The agreement, signed by Pacific Southwest interim Regional Forester Jacque Buchanan and CAL FIRE Chief Joe Tyler on Dec. 12, allows for a cooperative approach to wildfire response. According to the USDA Forest Service, this collaboration enables firefighters to share resources and respond across jurisdictional lines during emergencies. “This complex operating environment within California and the challenges we face year-round require this collaborative approach,” Jaime Gamboa, fire director for the Forest Service’s Pacific Southwest Region, said. The agreement emphasizes a united front in wildfire emergencies, prioritizing the closest available resources to protect lives and property. It also covers hazardous fuels reduction and streamlines training and equipment sharing.
 President Donald Trump’s administration has set in motion efforts to repeal the Roadless Rule, a 2001 administrative mandate that put 45 million acres of the least developed forest land under protection from logging and construction of roads. As the nation observes the rule’s 25th anniversary, Virginia’s federal lawmakers and advocates are calling for its preservation and say hundreds of thousands of acres of forests could be at stake if it is axed. The federal government has framed the proposed repeal as necessary for forest management against wildfires. …Environmental advocates have said since last summer that repealing the rule will lead to land degradation, sediment pollution, and create risks to clean water sources. It would also open up large swaths of the 400,000 acres of the protected forestland in Virginia to logging and potential new roads.
President Donald Trump’s administration has set in motion efforts to repeal the Roadless Rule, a 2001 administrative mandate that put 45 million acres of the least developed forest land under protection from logging and construction of roads. As the nation observes the rule’s 25th anniversary, Virginia’s federal lawmakers and advocates are calling for its preservation and say hundreds of thousands of acres of forests could be at stake if it is axed. The federal government has framed the proposed repeal as necessary for forest management against wildfires. …Environmental advocates have said since last summer that repealing the rule will lead to land degradation, sediment pollution, and create risks to clean water sources. It would also open up large swaths of the 400,000 acres of the protected forestland in Virginia to logging and potential new roads.
 New Hampshire and its counties may soon be barred from enrolling publicly owned lands in carbon sequestration programs. “We don’t see sequestration as a traditional use,” said Rep. Mike Ouellet, a Colebrook Republican, at a hearing before the House Committee on Municipal and County Government on Tuesday. The committee later voted, 13-1, to recommend passage of House Bill 1205, which would prohibit “carbon sequestration projects” on state- and county-owned lands. …No county- or state-owned land is currently listed on the registry of New Hampshire carbon sequestration projects. But the long duration of forest carbon contracts and the possibility they would impose restrictions on land use were two reasons bill proponents cited for preventing them on public lands in the future. …Others said timber harvest could be an important source of revenue for counties and the state, and worried the contracts would have a negative impact on the timber industry.
New Hampshire and its counties may soon be barred from enrolling publicly owned lands in carbon sequestration programs. “We don’t see sequestration as a traditional use,” said Rep. Mike Ouellet, a Colebrook Republican, at a hearing before the House Committee on Municipal and County Government on Tuesday. The committee later voted, 13-1, to recommend passage of House Bill 1205, which would prohibit “carbon sequestration projects” on state- and county-owned lands. …No county- or state-owned land is currently listed on the registry of New Hampshire carbon sequestration projects. But the long duration of forest carbon contracts and the possibility they would impose restrictions on land use were two reasons bill proponents cited for preventing them on public lands in the future. …Others said timber harvest could be an important source of revenue for counties and the state, and worried the contracts would have a negative impact on the timber industry.