Across the Los Angeles River from downtown Los Angeles is an unexpected sight, in the nation’s second-biggest city: a working lumber mill. The dusty, noisy mill is processing logs from the city itself. Angel City Lumber’s “whole purpose is to connect Angelenos to their community trees,” said founder Jeff Perry, by turning fallen local trees into wood products like tabletops, benches and flooring. The city of Los Angeles is home to over 10 million trees … an average of 2,000 trees are removed each year when they die and other reasons. …Angel City Lumber now works with municipal crews during tree removal, arriving in time to scoop up the trunks and bring them back to its mill to be processed into lumber. …Part of Perry’s vision involves rethinking the perception of street trees, chosen for ornamental or shade benefits, as the “perfectly good lumber” that most of those trees could become after their death.


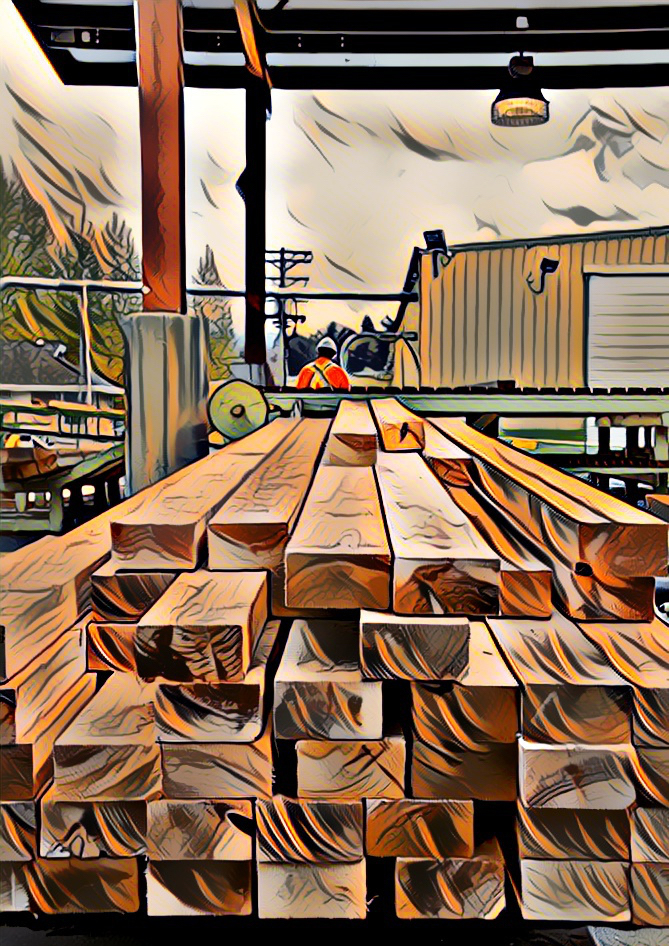
 VANCOUVER, British Columbia – Western Forest Products announced today that the sawmill at its Columbia Vista Division, located in Vancouver, Washington, sustained extensive damage in a fire, rendering the mill inoperable. “On behalf of Western, I want to extend my sincere gratitude to the firefighters and first responders who attended the fire at our site,” said Steven Hofer, Western’s President and CEO. “While we are shocked by the damage to the mill, we feel incredibly fortunate that no employees or emergency personnel were injured. We are focused on supporting our team members and completing an incident investigation and assessment.” The Columbia Vista Division produced approximately 53 million board feet of lumber in 2024, with production focused on Douglas Fir specialty products for Japan and U.S. markets.
VANCOUVER, British Columbia – Western Forest Products announced today that the sawmill at its Columbia Vista Division, located in Vancouver, Washington, sustained extensive damage in a fire, rendering the mill inoperable. “On behalf of Western, I want to extend my sincere gratitude to the firefighters and first responders who attended the fire at our site,” said Steven Hofer, Western’s President and CEO. “While we are shocked by the damage to the mill, we feel incredibly fortunate that no employees or emergency personnel were injured. We are focused on supporting our team members and completing an incident investigation and assessment.” The Columbia Vista Division produced approximately 53 million board feet of lumber in 2024, with production focused on Douglas Fir specialty products for Japan and U.S. markets.
 …In August 2024, a lumber mill owned by K & D Products and nestled in Panguitch, Garfield County’s largest city, went up in flames. Reports stated that, while the blaze didn’t get to the timber, the site’s machinery was severely damaged. The destruction landed a heavy blow to the community and the Frandsen family, who have owned and operated the mill for generations. …Between the area’s lumber heritage and the need to balance out tourism’s seasonal employment waves, Fiala gained enthusiastic support from state and local governments to build another sawmill. With his business partner, Barco — a logging company — Fiala acquired 25 acres north of Panguitch and began clearing space and bringing in power, water and gas. When the K & D Products sawmill burned during Fiala’s development, he spoke to the Frandsens and together they worked out a way for Fiala to take over what was left of the old mill and utilize it for his new business.
…In August 2024, a lumber mill owned by K & D Products and nestled in Panguitch, Garfield County’s largest city, went up in flames. Reports stated that, while the blaze didn’t get to the timber, the site’s machinery was severely damaged. The destruction landed a heavy blow to the community and the Frandsen family, who have owned and operated the mill for generations. …Between the area’s lumber heritage and the need to balance out tourism’s seasonal employment waves, Fiala gained enthusiastic support from state and local governments to build another sawmill. With his business partner, Barco — a logging company — Fiala acquired 25 acres north of Panguitch and began clearing space and bringing in power, water and gas. When the K & D Products sawmill burned during Fiala’s development, he spoke to the Frandsens and together they worked out a way for Fiala to take over what was left of the old mill and utilize it for his new business. The U.S. Senate unanimously passed a bill to reauthorize a program that has provided billions to schools, roads and other services in rural Oregon and Idaho. The U.S. Forest Service’s “Secure Rural Schools and Self-Determination Program,” was initially crafted in 2000 to help offset the loss of timber revenue in rural counties. The program expired at the end of 2023, but the recently passed “Secure Rural Schools Reauthorization Act of 2025” would reauthorize the funding for more than 4,000 school districts and 700 counties across the country through the 2026 fiscal year. The bill’s lead sponsors include U.S. Sens. Ron Wyden and Jeff Merkley, both Oregon Democrats, and U.S. Sens. Jim Risch and Mike Crapo, both Idaho Republicans. …This year, bill sponsors are urging the U.S. House to reauthorize the program. Without its passage in the House, rural counties in Oregon, Idaho and across the country will fall short of funds that support local services.
The U.S. Senate unanimously passed a bill to reauthorize a program that has provided billions to schools, roads and other services in rural Oregon and Idaho. The U.S. Forest Service’s “Secure Rural Schools and Self-Determination Program,” was initially crafted in 2000 to help offset the loss of timber revenue in rural counties. The program expired at the end of 2023, but the recently passed “Secure Rural Schools Reauthorization Act of 2025” would reauthorize the funding for more than 4,000 school districts and 700 counties across the country through the 2026 fiscal year. The bill’s lead sponsors include U.S. Sens. Ron Wyden and Jeff Merkley, both Oregon Democrats, and U.S. Sens. Jim Risch and Mike Crapo, both Idaho Republicans. …This year, bill sponsors are urging the U.S. House to reauthorize the program. Without its passage in the House, rural counties in Oregon, Idaho and across the country will fall short of funds that support local services.
 Congressional Republicans have passed their domestic policy bill that makes sweeping changes to entitlement programs like Medicaid and SNAP, significantly increases funding for immigration enforcement efforts and cuts funding for a number of environmental programs. …In Oregon, the impacts of the legislation will be significant. An analysis …found the state would be disproportionately hit by the cuts to Medicaid. The Senate’s version of the bill would also cut funds to the state’s timber counties, and could reshape Oregonian college tuition and student loans. …Oregon will see more logging, less timber money going to local communities and less support for private forest owners. …However much more is logged, Oregon counties will not get a cut. That’s a change from current practice. Many counties in rural areas rely on a cut of revenues from timber sales on federal public lands to pay for schools, law enforcement and public infrastructure.
Congressional Republicans have passed their domestic policy bill that makes sweeping changes to entitlement programs like Medicaid and SNAP, significantly increases funding for immigration enforcement efforts and cuts funding for a number of environmental programs. …In Oregon, the impacts of the legislation will be significant. An analysis …found the state would be disproportionately hit by the cuts to Medicaid. The Senate’s version of the bill would also cut funds to the state’s timber counties, and could reshape Oregonian college tuition and student loans. …Oregon will see more logging, less timber money going to local communities and less support for private forest owners. …However much more is logged, Oregon counties will not get a cut. That’s a change from current practice. Many counties in rural areas rely on a cut of revenues from timber sales on federal public lands to pay for schools, law enforcement and public infrastructure. University of Oregon researchers hope to make wood — often overlooked in health care facilities — more commonplace in those settings. Exposed wood, they’ve found, can resist microbial growth after a brief wetting. During the study, wood samples tested lower for levels of bacterial abundance than an empty plastic enclosure used as a control. “People generally think of wood as unhygienic in a medical setting,” said assistant professor Mark Fretz, co-director of the UO’s Institute for Health in the Built Environment and principal investigator for the study. “But wood actually transfers microbes at a lower rate than other less porous materials such as stainless steel.” Numerous studies support those properties of wood. A UO-led research team including scientists from the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego and Portland State University wanted to explore what happens when wood gets wet and then dries.
University of Oregon researchers hope to make wood — often overlooked in health care facilities — more commonplace in those settings. Exposed wood, they’ve found, can resist microbial growth after a brief wetting. During the study, wood samples tested lower for levels of bacterial abundance than an empty plastic enclosure used as a control. “People generally think of wood as unhygienic in a medical setting,” said assistant professor Mark Fretz, co-director of the UO’s Institute for Health in the Built Environment and principal investigator for the study. “But wood actually transfers microbes at a lower rate than other less porous materials such as stainless steel.” Numerous studies support those properties of wood. A UO-led research team including scientists from the Salk Institute for Biological Studies in San Diego and Portland State University wanted to explore what happens when wood gets wet and then dries.  Picture a hospital and you might imagine concrete, stainless steel or plastic. But University of Oregon researchers hope to make wood—often overlooked in health care facilities—more commonplace in those settings. Exposed wood, they’ve found, can resist microbial growth after it briefly gets wet. During their study, wood samples tested lower for levels of bacterial abundance than an empty plastic enclosure used as a control. “People generally think of wood as unhygienic in a medical setting,” said assistant professor Mark Fretz, co-director of the UO’s Institute for Health in the Built Environment and principal investigator for the study. “But wood actually transfers microbes at a lower rate than other less porous materials such as stainless steel.” In a
Picture a hospital and you might imagine concrete, stainless steel or plastic. But University of Oregon researchers hope to make wood—often overlooked in health care facilities—more commonplace in those settings. Exposed wood, they’ve found, can resist microbial growth after it briefly gets wet. During their study, wood samples tested lower for levels of bacterial abundance than an empty plastic enclosure used as a control. “People generally think of wood as unhygienic in a medical setting,” said assistant professor Mark Fretz, co-director of the UO’s Institute for Health in the Built Environment and principal investigator for the study. “But wood actually transfers microbes at a lower rate than other less porous materials such as stainless steel.” In a  A decade-spanning political battle between housing developers and defenders of California’s preeminent environmental law likely came to an end this afternoon with only a smattering of “no” votes. The forces of housing won. With the passage of a state budget-related housing bill, the California Environmental Quality Act will be a non-issue for a decisive swath of urban residential development in California. In practice, that means most new apartment buildings will no longer face the open threat of environmental litigation. It also means most urban developers will no longer have to study, predict and mitigate the ways that new housing might affect local traffic, air pollution, flora and fauna, noise levels, groundwater quality and objects of historic or archeological significance. And it means that when housing advocates argue that the state isn’t doing enough to build more homes amid crippling rents and stratospheric prices, they won’t — with a few exceptions — have CEQA to blame anymore.
A decade-spanning political battle between housing developers and defenders of California’s preeminent environmental law likely came to an end this afternoon with only a smattering of “no” votes. The forces of housing won. With the passage of a state budget-related housing bill, the California Environmental Quality Act will be a non-issue for a decisive swath of urban residential development in California. In practice, that means most new apartment buildings will no longer face the open threat of environmental litigation. It also means most urban developers will no longer have to study, predict and mitigate the ways that new housing might affect local traffic, air pollution, flora and fauna, noise levels, groundwater quality and objects of historic or archeological significance. And it means that when housing advocates argue that the state isn’t doing enough to build more homes amid crippling rents and stratospheric prices, they won’t — with a few exceptions — have CEQA to blame anymore.

 Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks (FWP) completed its review of a proposal to permanently protect 53,000 acres of private timberland in Flathead and Lincoln counties, recommending the state purchase a conservation easement that would keep the working forest in timber production while guaranteeing year-round public access and preserving wildlife habitat. The Montana Fish and Wildlife Commission is scheduled to vote on the proposal on Aug. 21 in Helena. …In total, the project would encompass 85,752 acres of private timberland owned by Green Diamond Resource Company. The first phase of the project… received final approval in December. The new easement would encompass forestlands in the Cabinet Mountains between Kalispell and Libby. …If approved, Green Diamond would maintain ownership of the land under an easement owned by FWP [allowing them to] sustainably harvest wood, preclude development, protect important wildlife habitat and associated key landscape connectivity, and provide permanent free public access to the easement lands.
Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks (FWP) completed its review of a proposal to permanently protect 53,000 acres of private timberland in Flathead and Lincoln counties, recommending the state purchase a conservation easement that would keep the working forest in timber production while guaranteeing year-round public access and preserving wildlife habitat. The Montana Fish and Wildlife Commission is scheduled to vote on the proposal on Aug. 21 in Helena. …In total, the project would encompass 85,752 acres of private timberland owned by Green Diamond Resource Company. The first phase of the project… received final approval in December. The new easement would encompass forestlands in the Cabinet Mountains between Kalispell and Libby. …If approved, Green Diamond would maintain ownership of the land under an easement owned by FWP [allowing them to] sustainably harvest wood, preclude development, protect important wildlife habitat and associated key landscape connectivity, and provide permanent free public access to the easement lands. Our many stunning hiking and walking trails in the Columbia-Pacific region offer locals and visitors alike wondrous views of forests of many different stages of succession, from recent clearcuts attempting to come back to life, to ancient old growth stands that somehow avoided the ax and the saw. The beauty of our area is one of its most valuable assets — so it may seem odd to some people that these forests include significant numbers of dead trees. Some call them ugly, while others refer to them as beautiful, but they do in fact have formal names. A standing dead tree is known as a snag, but once it falls to the ground it is a nurse log, so named because its rotting wood nurses young plants and fungi in their first years of life. One could also refer to a decaying stump covered in mosses, lichens, and other green growing things as a nurse stump.
Our many stunning hiking and walking trails in the Columbia-Pacific region offer locals and visitors alike wondrous views of forests of many different stages of succession, from recent clearcuts attempting to come back to life, to ancient old growth stands that somehow avoided the ax and the saw. The beauty of our area is one of its most valuable assets — so it may seem odd to some people that these forests include significant numbers of dead trees. Some call them ugly, while others refer to them as beautiful, but they do in fact have formal names. A standing dead tree is known as a snag, but once it falls to the ground it is a nurse log, so named because its rotting wood nurses young plants and fungi in their first years of life. One could also refer to a decaying stump covered in mosses, lichens, and other green growing things as a nurse stump. Streams that wind through Western Washington’s forests are essential habitat for frogs, bugs, and lots of other tiny critters. These streams are also a critical source of clean, cool water downstream. This means these streams are an important part of large watershed ecosystems. For the past 26 years, the timber industry, Tribes, environmental organizations, and Washington State agencies have worked together to address pollution and meet water quality standards through the “Forests and Fish Agreement.” The agreement aims to address pollution that can come from forestry activities like logging and forest road construction and maintenance, while maintaining both a viable timber industry and water quality. This coordination primarily happens through the Forest Practices Board, an independent state agency chaired by the elected Commissioner of Public Lands. Rules adopted by the Board are implemented and enforced by Washington’s Department of Natural Resources.
Streams that wind through Western Washington’s forests are essential habitat for frogs, bugs, and lots of other tiny critters. These streams are also a critical source of clean, cool water downstream. This means these streams are an important part of large watershed ecosystems. For the past 26 years, the timber industry, Tribes, environmental organizations, and Washington State agencies have worked together to address pollution and meet water quality standards through the “Forests and Fish Agreement.” The agreement aims to address pollution that can come from forestry activities like logging and forest road construction and maintenance, while maintaining both a viable timber industry and water quality. This coordination primarily happens through the Forest Practices Board, an independent state agency chaired by the elected Commissioner of Public Lands. Rules adopted by the Board are implemented and enforced by Washington’s Department of Natural Resources. In the face of a backlash, Utah Republican Sen. Mike Lee has revamped his public land sell-off measure to target only Bureau of Land Management holdings while also declaring, “we’re just getting started.” A reconciliation budget proposal revised by Lee’s Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee targets BLM land within five miles of undefined “population centers.” It puts checkerboard BLM holdings back on a priority list for his “mandatory disposal” measure and takes lands under permit for grazing off the auction block. The revision would shift 15% of revenue to local governments and conservation. The bill would appropriate $5 million to carry out the mandatory sales, which are designed to be offered within 60 days of passage and regularly thereafter. …But opposition to Lee’s measure comes from “all walks of life,” said Land Tawney, former president and CEO of Backcountry Hunters and Anglers. That includes “Democrats, Independents, Republicans, hunters, anglers, bird watchers, kayakers, ranchers [and] loggers,” he said.
In the face of a backlash, Utah Republican Sen. Mike Lee has revamped his public land sell-off measure to target only Bureau of Land Management holdings while also declaring, “we’re just getting started.” A reconciliation budget proposal revised by Lee’s Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee targets BLM land within five miles of undefined “population centers.” It puts checkerboard BLM holdings back on a priority list for his “mandatory disposal” measure and takes lands under permit for grazing off the auction block. The revision would shift 15% of revenue to local governments and conservation. The bill would appropriate $5 million to carry out the mandatory sales, which are designed to be offered within 60 days of passage and regularly thereafter. …But opposition to Lee’s measure comes from “all walks of life,” said Land Tawney, former president and CEO of Backcountry Hunters and Anglers. That includes “Democrats, Independents, Republicans, hunters, anglers, bird watchers, kayakers, ranchers [and] loggers,” he said. Don Hardin’s hillside was largely cleared of trees killed by the mountain pine beetle. Some of the trees have died in just a few weeks with Ips beetles munching their tops and mountain pine beetles coming through their bark in large visible holes. …Across Colorado, mountain pine beetles also are on the rise in Douglas, Jefferson and Gilpin counties, among other areas, said Dan West, forest entomologist with the State Forest Service. The agency’s annual aerial survey shows the number of infected acres increasing from less than 2,000 acres in 2021 to nearly 6,000 acres last year. …To combat the beetle, the State Forest Service is putting small packets on trees to send the message to mountain pine beetles to seek a home elsewhere, West said. The message will be sent through a synthetic replication of beetle pheromones that sends a “no-vacancy signal” to adult pine beetles looking for a healthy tree to infest.
Don Hardin’s hillside was largely cleared of trees killed by the mountain pine beetle. Some of the trees have died in just a few weeks with Ips beetles munching their tops and mountain pine beetles coming through their bark in large visible holes. …Across Colorado, mountain pine beetles also are on the rise in Douglas, Jefferson and Gilpin counties, among other areas, said Dan West, forest entomologist with the State Forest Service. The agency’s annual aerial survey shows the number of infected acres increasing from less than 2,000 acres in 2021 to nearly 6,000 acres last year. …To combat the beetle, the State Forest Service is putting small packets on trees to send the message to mountain pine beetles to seek a home elsewhere, West said. The message will be sent through a synthetic replication of beetle pheromones that sends a “no-vacancy signal” to adult pine beetles looking for a healthy tree to infest. In the parched summer of 1988, wildfires ripped through more than one-third of Yellowstone National Park during the most severe fire year in park history. Approximately 1.2 million acres scorched by September. …While new forests sprouted in most of Yellowstone’s charred woodlands, recent research has identified that 16 percent of the forests consumed by the fires still have few trees. A recent study found that much of this land has transformed into green meadows full of grasses and wildflowers. Of the roughly 965 square miles of forest killed by the fires, 158 remain unforested, largely due to a lack of available seeds to start the next generation of trees. Seventy square miles of the previously forested land is now open meadow… The forests that [recovered quickly] were full of lodgepole pines with serotinous cones. …Alternatively, the areas that remain unforested were mainly above 8,200 feet in elevation and dominated by subalpine fir, Engelmenn spruce and non-serotinous lodgepole pines.
In the parched summer of 1988, wildfires ripped through more than one-third of Yellowstone National Park during the most severe fire year in park history. Approximately 1.2 million acres scorched by September. …While new forests sprouted in most of Yellowstone’s charred woodlands, recent research has identified that 16 percent of the forests consumed by the fires still have few trees. A recent study found that much of this land has transformed into green meadows full of grasses and wildflowers. Of the roughly 965 square miles of forest killed by the fires, 158 remain unforested, largely due to a lack of available seeds to start the next generation of trees. Seventy square miles of the previously forested land is now open meadow… The forests that [recovered quickly] were full of lodgepole pines with serotinous cones. …Alternatively, the areas that remain unforested were mainly above 8,200 feet in elevation and dominated by subalpine fir, Engelmenn spruce and non-serotinous lodgepole pines. More than half a million acres of trees spread across Washington were sick, struggling, or dead last year, according to the results of an aerial survey of forests by the state’s Department of Natural Resources. Surveyors identified about 545,000 acres with some level of tree mortality, defoliation, or disease, the department said this week. That’s less than 1% of the total forestland surveyed. The amount of forest with problems is up nearly 30,000 acres from 2023 and more than the 10-year average of 519,000 acres, but well below the acres mapped with diseased or dead trees in 2022, according to the Department of Natural Resources. The Department of Natural Resources and the U.S. Forest Service partnered to conduct an aerial survey of 22 million forested acres in Washington state to observe recently killed and damaged trees. They carried out the survey between June and September last year.
More than half a million acres of trees spread across Washington were sick, struggling, or dead last year, according to the results of an aerial survey of forests by the state’s Department of Natural Resources. Surveyors identified about 545,000 acres with some level of tree mortality, defoliation, or disease, the department said this week. That’s less than 1% of the total forestland surveyed. The amount of forest with problems is up nearly 30,000 acres from 2023 and more than the 10-year average of 519,000 acres, but well below the acres mapped with diseased or dead trees in 2022, according to the Department of Natural Resources. The Department of Natural Resources and the U.S. Forest Service partnered to conduct an aerial survey of 22 million forested acres in Washington state to observe recently killed and damaged trees. They carried out the survey between June and September last year. HELENA, Montana — US Secretary of Agriculture Brooke L. Rollins announced US Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Montana Governor Greg Gianforte signed a historic Shared Stewardship Memorandum of Understanding, establishing a new framework between the US Forest Service (USFS) and the State of Montana to advance forest restoration and reduce wildfire risk across the state. Montana’s Shared Stewardship Agreement expands collaborative efforts to accelerate active forest management, safeguard communities, and support sustainable timber production. …“By cutting burdensome, unnecessary red tape and empowering Montana to lead, we’re proving that through real partnership, conservation and economic growth can go hand-in-hand. …The Forest Service and Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) will jointly identify and execute large-scale forest management projects, initially focusing on approximately 200,000 acres in northwest Montana.
HELENA, Montana — US Secretary of Agriculture Brooke L. Rollins announced US Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Montana Governor Greg Gianforte signed a historic Shared Stewardship Memorandum of Understanding, establishing a new framework between the US Forest Service (USFS) and the State of Montana to advance forest restoration and reduce wildfire risk across the state. Montana’s Shared Stewardship Agreement expands collaborative efforts to accelerate active forest management, safeguard communities, and support sustainable timber production. …“By cutting burdensome, unnecessary red tape and empowering Montana to lead, we’re proving that through real partnership, conservation and economic growth can go hand-in-hand. …The Forest Service and Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) will jointly identify and execute large-scale forest management projects, initially focusing on approximately 200,000 acres in northwest Montana.

 WHITE SULPHUR SPRINGS, Montana — The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest has released a final decision for the Bonanza Project, located in the Castle Mountains just east of White Sulphur Springs. Primary management activities planned include timber harvest and prescribed fire. “The project area is highly impacted by the mountain pine beetle and some areas have experienced 90% tree mortality,” said District Ranger Jason Oltrogge. “The timber generated from this project will provide wood products to local companies and prescribed fire will restore forests and reduce wildfire severity.” The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest partnered with the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation to plan this project, and the joint effort made this project a reality. …The project includes commercial timber harvest on 1,980 acres and prescribed burning on 918 acres. Project implementation is anticipated to start later this summer.
WHITE SULPHUR SPRINGS, Montana — The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest has released a final decision for the Bonanza Project, located in the Castle Mountains just east of White Sulphur Springs. Primary management activities planned include timber harvest and prescribed fire. “The project area is highly impacted by the mountain pine beetle and some areas have experienced 90% tree mortality,” said District Ranger Jason Oltrogge. “The timber generated from this project will provide wood products to local companies and prescribed fire will restore forests and reduce wildfire severity.” The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest partnered with the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation to plan this project, and the joint effort made this project a reality. …The project includes commercial timber harvest on 1,980 acres and prescribed burning on 918 acres. Project implementation is anticipated to start later this summer.

 When U.S. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins announced on Monday that her department would be opening up more US Forest Service land to development, she did so with the caveat that just two states — Colorado and Idaho — would not be impacted. Rollins, who serves in President Donald Trump’s cabinet, unveiled the plans during a meeting of Western state governors in Santa Fe, where she told reporters that the Agriculture Department would be rescinding the 2001 “roadless rule” established under former President Bill Clinton. The rule, hailed by conservationists as a landmark preservation effort, protects roughly 58.5 million acres of backcountry Forest Service land from road construction, logging and other development. “For too long, Western states, especially those with large swaths of land administered by our incredible Forest Service, have been inhibited from innovating because of burdensome regulations imposed by the federal government,” Rollins said.
When U.S. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins announced on Monday that her department would be opening up more US Forest Service land to development, she did so with the caveat that just two states — Colorado and Idaho — would not be impacted. Rollins, who serves in President Donald Trump’s cabinet, unveiled the plans during a meeting of Western state governors in Santa Fe, where she told reporters that the Agriculture Department would be rescinding the 2001 “roadless rule” established under former President Bill Clinton. The rule, hailed by conservationists as a landmark preservation effort, protects roughly 58.5 million acres of backcountry Forest Service land from road construction, logging and other development. “For too long, Western states, especially those with large swaths of land administered by our incredible Forest Service, have been inhibited from innovating because of burdensome regulations imposed by the federal government,” Rollins said.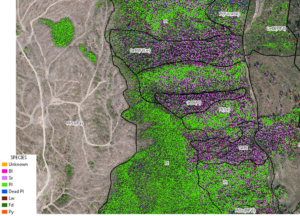 After a longer wait than expected, the a bill that would eliminate the unpopular Oregon Wildfire Hazard Map passed the Oregon House on June 24. Senate Bill 83 repeals a map meant to identify parts of Oregon at high risk of catastrophic wildfires but has become a lightning rod for anger from rural residents who say it places an unfair burden on them. The bill, which passed the Senate in April, now heads to the desk of Gov. Tina Kotek. The map, which was released earlier in 2025 and identifies areas at high wildfire risk, requires stricter building codes and creation of defensible space for roughly 100,000 properties in the name of wildfire prevention. The map was roundly condemned by impacted residents who said it was inaccurate, decreased property values and imposed burdensome regulations.
After a longer wait than expected, the a bill that would eliminate the unpopular Oregon Wildfire Hazard Map passed the Oregon House on June 24. Senate Bill 83 repeals a map meant to identify parts of Oregon at high risk of catastrophic wildfires but has become a lightning rod for anger from rural residents who say it places an unfair burden on them. The bill, which passed the Senate in April, now heads to the desk of Gov. Tina Kotek. The map, which was released earlier in 2025 and identifies areas at high wildfire risk, requires stricter building codes and creation of defensible space for roughly 100,000 properties in the name of wildfire prevention. The map was roundly condemned by impacted residents who said it was inaccurate, decreased property values and imposed burdensome regulations. The Idaho roadless rule is not included in the effort by the Trump administration to rescind the national rule. A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Agriculture said, “the Idaho state-specific roadless rule was part of the Administrative Procedures Act petitions and will not be affected by rescinding the 2001 Roadless Rule.” The rule, a collaboratively written offshoot of the national rule, was spearheaded by then-Gov. Jim Risch in 2006. It is more flexible than the national rule and allows limited logging and road building in some of the state’s roadless forests that are not otherwise protected as wilderness areas. But it also offers more stringent protections to the most remote areas. …Risch’s Idaho-specific roadless rule, implemented in 2008, overrides the national rule and forbids logging and roads on 3.2 million acres of the state’s 9 million acres of inventoried roadless areas. Some logging and roads are allowed, under limited circumstances, on the remaining 6 million acres.
The Idaho roadless rule is not included in the effort by the Trump administration to rescind the national rule. A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Agriculture said, “the Idaho state-specific roadless rule was part of the Administrative Procedures Act petitions and will not be affected by rescinding the 2001 Roadless Rule.” The rule, a collaboratively written offshoot of the national rule, was spearheaded by then-Gov. Jim Risch in 2006. It is more flexible than the national rule and allows limited logging and road building in some of the state’s roadless forests that are not otherwise protected as wilderness areas. But it also offers more stringent protections to the most remote areas. …Risch’s Idaho-specific roadless rule, implemented in 2008, overrides the national rule and forbids logging and roads on 3.2 million acres of the state’s 9 million acres of inventoried roadless areas. Some logging and roads are allowed, under limited circumstances, on the remaining 6 million acres.

 A California nonprofit organization has decided to revise its controversial plan to build two wood pellet processing plants that would turn excess biomass in the state’s forests into pellets to be shipped overseas for use in renewable energy generation. Golden State Natural Resources said Wednesday it will develop a reduced-scale project focused on domestic, rather than international, use of sourced wood, producing wood chips instead of pellets. The project will target emerging demand in California and nearby regions for sustainable energy and alternative wood products. The organization’s proposed Forest Resiliency Project has drawn the ire of environmentalists who say California needs to rethink “falling for the biomass delusion.” Golden State Natural Resources was formed by rural counties to reduce massive wildfires fueled by overgrown, undermanaged forests. The project aims to use low-value forest material like ladder fuels and dead trees to lower wildfire risk and improve forest health.
A California nonprofit organization has decided to revise its controversial plan to build two wood pellet processing plants that would turn excess biomass in the state’s forests into pellets to be shipped overseas for use in renewable energy generation. Golden State Natural Resources said Wednesday it will develop a reduced-scale project focused on domestic, rather than international, use of sourced wood, producing wood chips instead of pellets. The project will target emerging demand in California and nearby regions for sustainable energy and alternative wood products. The organization’s proposed Forest Resiliency Project has drawn the ire of environmentalists who say California needs to rethink “falling for the biomass delusion.” Golden State Natural Resources was formed by rural counties to reduce massive wildfires fueled by overgrown, undermanaged forests. The project aims to use low-value forest material like ladder fuels and dead trees to lower wildfire risk and improve forest health. 

 PANGUITCH, Utah — The France Canyon fire has increased to 23,353 acres and is currently at 10% containment, according to the latest information posted by the U.S. Forest Service – Dixie National Forest. Officials say fire activity increased at around 2 p.m. on Sunday, June 22, pushing eastward into the Kings Creek Campground area. Firefighters had to conduct a tactical firing operation to protect the campground. A total of 749 personnel are battling the fire and working on securing structures within Wilson Peak, the Hillsdale and Johnson Canyons. Firefighters are also working to keep the fire west of East Fork Road. Efforts are also underway to protect the Bryce Woodland community on the southwest side of the wildfire perimeter.
PANGUITCH, Utah — The France Canyon fire has increased to 23,353 acres and is currently at 10% containment, according to the latest information posted by the U.S. Forest Service – Dixie National Forest. Officials say fire activity increased at around 2 p.m. on Sunday, June 22, pushing eastward into the Kings Creek Campground area. Firefighters had to conduct a tactical firing operation to protect the campground. A total of 749 personnel are battling the fire and working on securing structures within Wilson Peak, the Hillsdale and Johnson Canyons. Firefighters are also working to keep the fire west of East Fork Road. Efforts are also underway to protect the Bryce Woodland community on the southwest side of the wildfire perimeter. Forest fires have broken out in parts of New Mexico that state forecasters had already warned would see an elevated wildfire risk this summer due to high temperatures, low snowpack and ongoing drought. At least 25 New Mexico jurisdictions imposed some level of fire restriction this spring. State Forester Laura McCarthy said the peak of fire season is still a week away, beginning June 26. …On Tuesday, New Mexico Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham declared a state of emergency in response to the Trout Fire, which is burning in the Gila National Forest, forcing residents to evacuate. The Buck Fire also has burned more than 57,000 acres in the same area of Southwest New Mexico. The governor has urged localities to ban fireworks and restrict water usage. …”If you look at every single big fire we’ve had, there was either a lightning strike or a person behind it,” she added.
Forest fires have broken out in parts of New Mexico that state forecasters had already warned would see an elevated wildfire risk this summer due to high temperatures, low snowpack and ongoing drought. At least 25 New Mexico jurisdictions imposed some level of fire restriction this spring. State Forester Laura McCarthy said the peak of fire season is still a week away, beginning June 26. …On Tuesday, New Mexico Governor Michelle Lujan Grisham declared a state of emergency in response to the Trout Fire, which is burning in the Gila National Forest, forcing residents to evacuate. The Buck Fire also has burned more than 57,000 acres in the same area of Southwest New Mexico. The governor has urged localities to ban fireworks and restrict water usage. …”If you look at every single big fire we’ve had, there was either a lightning strike or a person behind it,” she added.