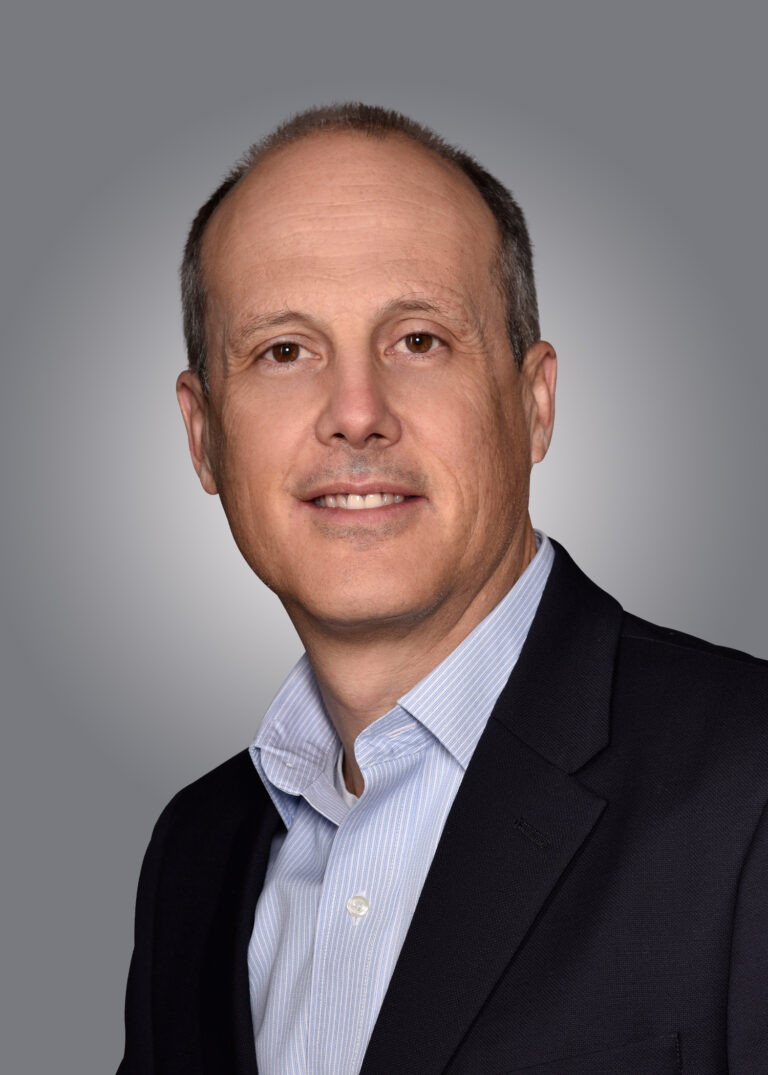
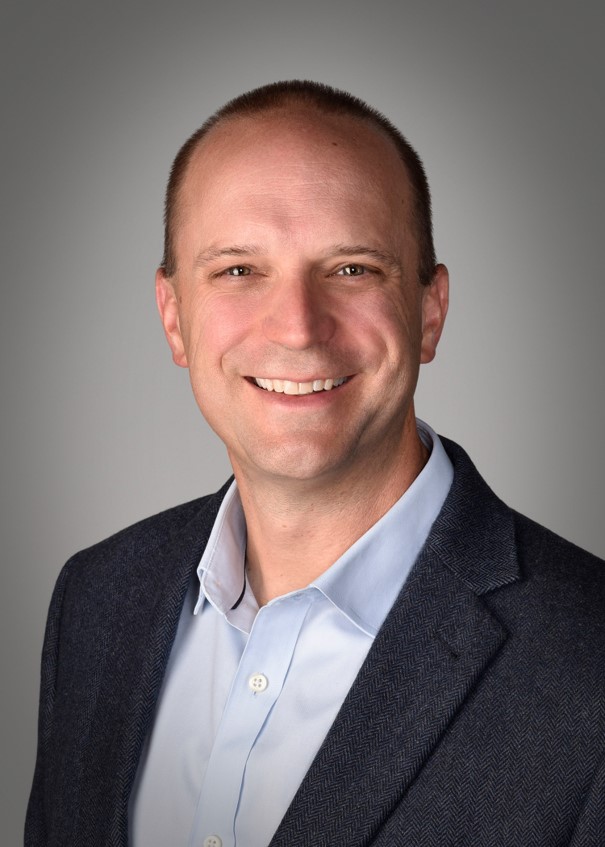
BOISE, IDAHO – Boise Cascade announced two executive leadership promotions. Dennis Fringuelli was named Vice President of Sales and Marketing for the Company’s Building Materials Distribution (BMD) division. Jeff Dracup was named Vice President of Sales and Marketing for Engineered Wood Products (EWP). Both promotions are effective January 19, 2026. Dennis joined Boise Cascade in 1999 as national account manager when the Company acquired his previous employer, Furman Lumber. …Before this promotion, Dennis was the director of BMD sales and marketing. …Jeff joined Boise Cascade in 2004. His began his career in sales and product management roles at the Company’s BMD facility in Phoenix, Arizona. …Before this promotion, Jeff was the director of EWP sales and marketing. Jeff earned a bachelor’s degree in psychology with a minor in business administration from the University of Arizona.



 On this episode of This is Oregon Podcast, we’re joined by Judith Sheine, Professor of Architecture and Director of Design of the TallWood Design Institute at the University of Oregon. She shares her work with helping mass timber become more accessible and discusses it potential to create affordable, sustainable housing. Sheine also discusses the challenges and opportunities in advancing mass timber development and what its future could look like for the Pacific Northwest and homeowners. This is part two of our conversation with Judith Sheine. Part one is titled:
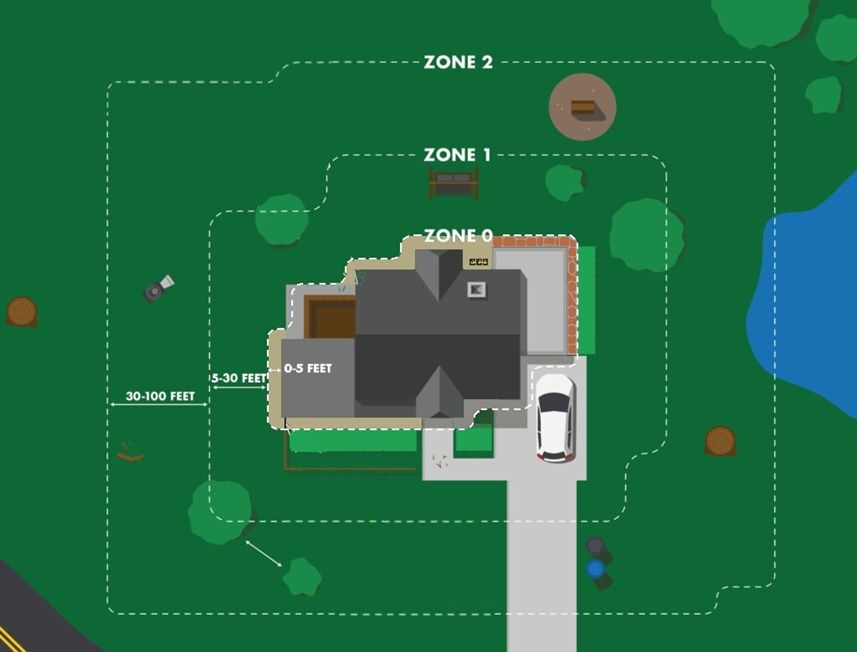
On this episode of This is Oregon Podcast, we’re joined by Judith Sheine, Professor of Architecture and Director of Design of the TallWood Design Institute at the University of Oregon. She shares her work with helping mass timber become more accessible and discusses it potential to create affordable, sustainable housing. Sheine also discusses the challenges and opportunities in advancing mass timber development and what its future could look like for the Pacific Northwest and homeowners. This is part two of our conversation with Judith Sheine. Part one is titled:  One year after wildfires tore through neighborhoods in Los Angeles County, killing at least 31 people and destroying more than 10,000 buildings, architects and developers are rethinking what home looks like in LA, and how resilient residential architecture evolves. …So far, hundreds of new homes have been submitted for permitting, but it’s a process shaping out to be an uneven one, based on damage, insurance and wealth. Affected homeowners are grappling with the details of fire-resilient construction and landscaping techniques, along with some more fundamental questions about what their communities should look like. …These 10 projects — all in various stages of completion — showcase several of the design concepts, construction techniques and development proposals in play as LA’s post-fire rebuilding process begins. …Many forthcoming home projects emphasize the latest in wildfire-resilience features: Think noncombustible sheathing and roof materials, triple-glazed windows that can resist high heat, and defensible outdoor space.
One year after wildfires tore through neighborhoods in Los Angeles County, killing at least 31 people and destroying more than 10,000 buildings, architects and developers are rethinking what home looks like in LA, and how resilient residential architecture evolves. …So far, hundreds of new homes have been submitted for permitting, but it’s a process shaping out to be an uneven one, based on damage, insurance and wealth. Affected homeowners are grappling with the details of fire-resilient construction and landscaping techniques, along with some more fundamental questions about what their communities should look like. …These 10 projects — all in various stages of completion — showcase several of the design concepts, construction techniques and development proposals in play as LA’s post-fire rebuilding process begins. …Many forthcoming home projects emphasize the latest in wildfire-resilience features: Think noncombustible sheathing and roof materials, triple-glazed windows that can resist high heat, and defensible outdoor space.
 Schools built with mass timber have recently opened to positive community response in the Seattle, Renton and Highline school districts, and another is under construction in West Seattle. … Throughout the United States and Canada, about 150 educational projects have already been built with mass timber. Mass timber products such as Glulam and Cross-Laminated Timber are made from lumber stacked in layers to create large components — columns, beams and panels that become the structures of buildings of all types. These large building components drive efficiency in construction while reducing the carbon footprint. In Washington, mass timber can now be used in buildings up to 18 stories, a renewable, resilient alternative to steel and concrete. The Pacific Northwest is well-positioned to be a leader in this industry. …structures made from mass timber, where the wood remains exposed, have
Schools built with mass timber have recently opened to positive community response in the Seattle, Renton and Highline school districts, and another is under construction in West Seattle. … Throughout the United States and Canada, about 150 educational projects have already been built with mass timber. Mass timber products such as Glulam and Cross-Laminated Timber are made from lumber stacked in layers to create large components — columns, beams and panels that become the structures of buildings of all types. These large building components drive efficiency in construction while reducing the carbon footprint. In Washington, mass timber can now be used in buildings up to 18 stories, a renewable, resilient alternative to steel and concrete. The Pacific Northwest is well-positioned to be a leader in this industry. …structures made from mass timber, where the wood remains exposed, have  A 34-year-old rule exempting some commercial logging projects on federal lands from environmental review is unlawful, a federal judge recently ruled. Judge Michael McShane in the U.S. District Court in Medford earlier this month struck down the exemption, and with it, reversed recent approvals for three commercial logging projects covering tens of thousands of acres in Fremont-Winema National Forest in southern Oregon. The decision is the result of a 2022 lawsuit brought against the U.S. Forest Service by regional conservation groups Oregon Wild, WildEarth Guardians and GO Alliance. Since 1992, the U.S. Forest Service has been able to bypass environmental reviews required by federal law for logging projects on federal land, if the logging is meant to “improve forest stand conditions,” habitat or prevent wildfires, without “significant effect” on the human environment.
A 34-year-old rule exempting some commercial logging projects on federal lands from environmental review is unlawful, a federal judge recently ruled. Judge Michael McShane in the U.S. District Court in Medford earlier this month struck down the exemption, and with it, reversed recent approvals for three commercial logging projects covering tens of thousands of acres in Fremont-Winema National Forest in southern Oregon. The decision is the result of a 2022 lawsuit brought against the U.S. Forest Service by regional conservation groups Oregon Wild, WildEarth Guardians and GO Alliance. Since 1992, the U.S. Forest Service has been able to bypass environmental reviews required by federal law for logging projects on federal land, if the logging is meant to “improve forest stand conditions,” habitat or prevent wildfires, without “significant effect” on the human environment.



 New Mexico’s Forestry Division is concerned after thousands of trees died last year due to warm temperatures, drought conditions, and native insects. Victor Lucero, the forest health program coordinator, said in 2024, about 67,000 acres of trees died. Last year, that jumped to about 209,000 acres. Most of the damage is south of I-40, including parts of the Lincoln National Forest near Ruidoso and areas west of Socorro in the Gila National Forest. The main culprit is native bark beetles. Lucero explained that when it’s warm and dry, trees get stressed and weakened, giving off chemicals that attract the beetles. Once the beetles get under the bark, they tunnel in, cut off the tree’s ability to move water and nutrients, and bring in fungi, leading to the tree’s death over time.
New Mexico’s Forestry Division is concerned after thousands of trees died last year due to warm temperatures, drought conditions, and native insects. Victor Lucero, the forest health program coordinator, said in 2024, about 67,000 acres of trees died. Last year, that jumped to about 209,000 acres. Most of the damage is south of I-40, including parts of the Lincoln National Forest near Ruidoso and areas west of Socorro in the Gila National Forest. The main culprit is native bark beetles. Lucero explained that when it’s warm and dry, trees get stressed and weakened, giving off chemicals that attract the beetles. Once the beetles get under the bark, they tunnel in, cut off the tree’s ability to move water and nutrients, and bring in fungi, leading to the tree’s death over time.
 MONTANA — A proposal to use thinning and prescribed burning to remove vegetation across portions of the Flathead National Forest bordering the Middle Fork Flathead River has gained wide attention for its inclusion of sensitive management areas in the project’s 67,536-acre footprint, which provides wildlife with critical habitat and is one of the region’s most popular havens of outdoor recreation. But even as conservation groups push for additional layers of environmental review, proponents of the project, including industry leaders, recreation advocates and residents, say it’s needed to reduce the risk of wildfire in a corridor brimming with untreated fuels that threaten infrastructure and communities on US Highway 2, as well as to support local timber mills and improve forest health. If approved, portions of the project would occur in recommended wilderness areas, although the scope of that work would be confined to whitebark pine restoration and tree planting with hand tools.
MONTANA — A proposal to use thinning and prescribed burning to remove vegetation across portions of the Flathead National Forest bordering the Middle Fork Flathead River has gained wide attention for its inclusion of sensitive management areas in the project’s 67,536-acre footprint, which provides wildlife with critical habitat and is one of the region’s most popular havens of outdoor recreation. But even as conservation groups push for additional layers of environmental review, proponents of the project, including industry leaders, recreation advocates and residents, say it’s needed to reduce the risk of wildfire in a corridor brimming with untreated fuels that threaten infrastructure and communities on US Highway 2, as well as to support local timber mills and improve forest health. If approved, portions of the project would occur in recommended wilderness areas, although the scope of that work would be confined to whitebark pine restoration and tree planting with hand tools. 
 A major logging project has been proposed on the southern border of Glacier National Park, prompting concern from conservationists… “This is the heart of some of our wildest, most intact landscapes left in the U.S., anywhere south of Alaska,” said Peter Metcalf, the executive director of the Glacier-Two Medicine Alliance, a conservation organization in East Glacier Park, Montana. “We are really concerned that this kind of logging proposal would be slated for this landscape.” U.S. Forest Service district ranger Robert Davies said he plans to use the emergency authority authorized by an April 2025 executive order to expedite the project. The order calls for increasing timber production and reducing wildfire risk in areas of national forest considered to have very high or high wildfire risk. Roughly half the proposed project qualifies, but the entire project is subject to the streamlined timeline, which cuts out the majority of opportunities for public participation.
A major logging project has been proposed on the southern border of Glacier National Park, prompting concern from conservationists… “This is the heart of some of our wildest, most intact landscapes left in the U.S., anywhere south of Alaska,” said Peter Metcalf, the executive director of the Glacier-Two Medicine Alliance, a conservation organization in East Glacier Park, Montana. “We are really concerned that this kind of logging proposal would be slated for this landscape.” U.S. Forest Service district ranger Robert Davies said he plans to use the emergency authority authorized by an April 2025 executive order to expedite the project. The order calls for increasing timber production and reducing wildfire risk in areas of national forest considered to have very high or high wildfire risk. Roughly half the proposed project qualifies, but the entire project is subject to the streamlined timeline, which cuts out the majority of opportunities for public participation. In 1980, Washington State’s Mount St Helens erupted…causing an ecological nightmare as the volcano spewed lava, ash, and debris over the surrounding landscape that was followed by mudflows and pyroclastic flows, leaving the vegetation covered in mud and detritus as far as 27 kilometers from the volcano. …But one team of scientists had an unconventional idea to help jumpstart the process: send a few gophers on a one-day mission to the mountain. “Gophers are known as ‘hole diggers’,” says a 2024 paper assessing the long-term effects of the rodents at Mount St Helens, adding, “a single gopher can move 227 kg [500 pounds] of soil per month”. Digging is a useful quality in restoring an area devastated by volcanic eruption. Plant life was struggling to return… But while the top layers of soil were destroyed by the eruption and lava flows, the soil underneath could still have been rich in bacteria and fungi.
In 1980, Washington State’s Mount St Helens erupted…causing an ecological nightmare as the volcano spewed lava, ash, and debris over the surrounding landscape that was followed by mudflows and pyroclastic flows, leaving the vegetation covered in mud and detritus as far as 27 kilometers from the volcano. …But one team of scientists had an unconventional idea to help jumpstart the process: send a few gophers on a one-day mission to the mountain. “Gophers are known as ‘hole diggers’,” says a 2024 paper assessing the long-term effects of the rodents at Mount St Helens, adding, “a single gopher can move 227 kg [500 pounds] of soil per month”. Digging is a useful quality in restoring an area devastated by volcanic eruption. Plant life was struggling to return… But while the top layers of soil were destroyed by the eruption and lava flows, the soil underneath could still have been rich in bacteria and fungi. PORTLAND, Ore. — In a win for conservation groups, a federal judge
PORTLAND, Ore. — In a win for conservation groups, a federal judge  Western Washington forests are vital to the identity, economy, and quality of life vital to the region. From the Puget Sound to the Olympic Peninsula and Columbia Gorge, healthy forests provide clean air and water, sustain fish and wildlife habitat, store carbon, and support local jobs in forestry, recreation, and tourism. …The Western Washington Forest Health Strategic Plan is the result of an holistic and collaborative effort by the Washington State Department of Natural Resources to bring partners representing all lands and stakeholder groups together to identify priorities and strategies for how to steward and manage western Washington forests at a landscape scale. This plan builds on lessons learned from the development and implementation of the
Western Washington forests are vital to the identity, economy, and quality of life vital to the region. From the Puget Sound to the Olympic Peninsula and Columbia Gorge, healthy forests provide clean air and water, sustain fish and wildlife habitat, store carbon, and support local jobs in forestry, recreation, and tourism. …The Western Washington Forest Health Strategic Plan is the result of an holistic and collaborative effort by the Washington State Department of Natural Resources to bring partners representing all lands and stakeholder groups together to identify priorities and strategies for how to steward and manage western Washington forests at a landscape scale. This plan builds on lessons learned from the development and implementation of the  PUEBLO, Colo. — The Pike-San Isabel National Forests & Cimarron and Comanche National Grasslands began a 10-year partnership and $7.3 million investment to implement forest health treatments as part of the War Department’s Readiness and Environmental Protection Integration (REPI) program. The partners will use $3 million in REPI funds, along with $4.3 million in partner contributions, to treat 2,000 acres of National Forest System land and nonfederal lands near the U.S. Air Force Academy and Cheyenne Mountain Space Force Station. The REPI program preserves military missions by avoiding land use conflicts near military installations, addressing environmental restrictions that limit military activities and increasing military installation resilience.
PUEBLO, Colo. — The Pike-San Isabel National Forests & Cimarron and Comanche National Grasslands began a 10-year partnership and $7.3 million investment to implement forest health treatments as part of the War Department’s Readiness and Environmental Protection Integration (REPI) program. The partners will use $3 million in REPI funds, along with $4.3 million in partner contributions, to treat 2,000 acres of National Forest System land and nonfederal lands near the U.S. Air Force Academy and Cheyenne Mountain Space Force Station. The REPI program preserves military missions by avoiding land use conflicts near military installations, addressing environmental restrictions that limit military activities and increasing military installation resilience.  As climate change drives more frequent and severe wildfires across boreal forests in Alaska and northwestern Canada, scientists are asking a critical question: Will these ecosystems continue to store carbon or become a growing source of carbon emissions? New research published shows that when forests shift from coniferous—consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches—to deciduous—consisting mostly of birches and aspens—they could release substantially less carbon when they burn. The study, led by researchers from the Center for Ecosystem Science and Society (ECOSS) at Northern Arizona University and published in Nature Climate Change, found that boreal forests dominated by deciduous species lose less than half as much carbon per unit area burned compared to historically dominant black spruce forests. Even under severe fire weather conditions, carbon losses in deciduous stands were consistently lower than those in conifer forests.
As climate change drives more frequent and severe wildfires across boreal forests in Alaska and northwestern Canada, scientists are asking a critical question: Will these ecosystems continue to store carbon or become a growing source of carbon emissions? New research published shows that when forests shift from coniferous—consisting mostly of pines, spruces and larches—to deciduous—consisting mostly of birches and aspens—they could release substantially less carbon when they burn. The study, led by researchers from the Center for Ecosystem Science and Society (ECOSS) at Northern Arizona University and published in Nature Climate Change, found that boreal forests dominated by deciduous species lose less than half as much carbon per unit area burned compared to historically dominant black spruce forests. Even under severe fire weather conditions, carbon losses in deciduous stands were consistently lower than those in conifer forests.
 SEATTLE — Twenty-five years ago, I stood in a snowy National Arboretum in Washington, DC, shaking hands with President Bill Clinton at the signing ceremony for the most important forest conservation mandate in our country’s history. But now that landmark law, which went into effect on Jan. 12, 2001, is hanging by a thread, marked for repeal by the Trump administration — even though 99% of citizen input opposes the idea. The “Roadless Rule” was adopted to curtail harmful logging and industrial roadbuilding across 58 million undeveloped acres of our national forests. More than 2 million acres of those wild lands are in Washington, helping keep this the Evergreen State. …Trump officials claim that opening these areas to bulldozers and chain saws will protect communities from wildfire. But that’s a story that just doesn’t wash. [to access the full story a Seattle Times subscription is required]
SEATTLE — Twenty-five years ago, I stood in a snowy National Arboretum in Washington, DC, shaking hands with President Bill Clinton at the signing ceremony for the most important forest conservation mandate in our country’s history. But now that landmark law, which went into effect on Jan. 12, 2001, is hanging by a thread, marked for repeal by the Trump administration — even though 99% of citizen input opposes the idea. The “Roadless Rule” was adopted to curtail harmful logging and industrial roadbuilding across 58 million undeveloped acres of our national forests. More than 2 million acres of those wild lands are in Washington, helping keep this the Evergreen State. …Trump officials claim that opening these areas to bulldozers and chain saws will protect communities from wildfire. But that’s a story that just doesn’t wash. [to access the full story a Seattle Times subscription is required]
 VALLEJO, Calif. — The USDA Forest Service Pacific Southwest Region and CAL FIRE have renewed their commitment to battling wildfires across California. This renewal extends the California Fire Master Agreement for another five years. The agreement, signed by Pacific Southwest interim Regional Forester Jacque Buchanan and CAL FIRE Chief Joe Tyler on Dec. 12, allows for a cooperative approach to wildfire response. According to the USDA Forest Service, this collaboration enables firefighters to share resources and respond across jurisdictional lines during emergencies. “This complex operating environment within California and the challenges we face year-round require this collaborative approach,” Jaime Gamboa, fire director for the Forest Service’s Pacific Southwest Region, said. The agreement emphasizes a united front in wildfire emergencies, prioritizing the closest available resources to protect lives and property. It also covers hazardous fuels reduction and streamlines training and equipment sharing.
VALLEJO, Calif. — The USDA Forest Service Pacific Southwest Region and CAL FIRE have renewed their commitment to battling wildfires across California. This renewal extends the California Fire Master Agreement for another five years. The agreement, signed by Pacific Southwest interim Regional Forester Jacque Buchanan and CAL FIRE Chief Joe Tyler on Dec. 12, allows for a cooperative approach to wildfire response. According to the USDA Forest Service, this collaboration enables firefighters to share resources and respond across jurisdictional lines during emergencies. “This complex operating environment within California and the challenges we face year-round require this collaborative approach,” Jaime Gamboa, fire director for the Forest Service’s Pacific Southwest Region, said. The agreement emphasizes a united front in wildfire emergencies, prioritizing the closest available resources to protect lives and property. It also covers hazardous fuels reduction and streamlines training and equipment sharing.



 OREGON– The Bureau of Land Management’s state office in Oregon increased its timber sales in 2025, leading to one of its largest years for sales by board-feet and dollars in decades. The increase coincides with a provision of the tax and spending bill approved by Congress in July, that requires BLM to increase the timber it makes available for harvest by 20 million board-feet each year through 2034. BLM data show that the timber sales through the office totalled 290.6 million board-feet this year, an increase of 66.8 million from the previous year. …2025 was the third-highest year for BLM timber sales through the Oregon office by both board-feet and sale price, topped only by 2019 and 2021. Sales this year brought in $63.7 million.
OREGON– The Bureau of Land Management’s state office in Oregon increased its timber sales in 2025, leading to one of its largest years for sales by board-feet and dollars in decades. The increase coincides with a provision of the tax and spending bill approved by Congress in July, that requires BLM to increase the timber it makes available for harvest by 20 million board-feet each year through 2034. BLM data show that the timber sales through the office totalled 290.6 million board-feet this year, an increase of 66.8 million from the previous year. …2025 was the third-highest year for BLM timber sales through the Oregon office by both board-feet and sale price, topped only by 2019 and 2021. Sales this year brought in $63.7 million.

 DENVER — Vast swaths of the ponderosa pine forests that blanket Colorado’s Front Range mountains could turn rust-colored and die over the next five years as pine beetles begin to spread aggressively, new federal forecasts show. Aerial surveys conducted by the U.S. Forest Service over the last year found evidence of rapidly spreading beetle infestations along the mountains and foothills that stretch from southern Larimer County to southern El Paso County, including the western flank of metro Denver. Already, pockets of dead trees are visible from Interstate 70 and U.S. 285. The rapid uptick in beetle-killed trees near the state’s largest cities and major highways prompted state leaders to form a task force this month to grapple with the outbreak. Gov. Jared Polis
DENVER — Vast swaths of the ponderosa pine forests that blanket Colorado’s Front Range mountains could turn rust-colored and die over the next five years as pine beetles begin to spread aggressively, new federal forecasts show. Aerial surveys conducted by the U.S. Forest Service over the last year found evidence of rapidly spreading beetle infestations along the mountains and foothills that stretch from southern Larimer County to southern El Paso County, including the western flank of metro Denver. Already, pockets of dead trees are visible from Interstate 70 and U.S. 285. The rapid uptick in beetle-killed trees near the state’s largest cities and major highways prompted state leaders to form a task force this month to grapple with the outbreak. Gov. Jared Polis 
 Washington state officials admitted Jan. 6 they overstated by more than 80% how much projects funded by cap-and-trade taxes have reduced greenhouse gases. The Department of Commerce blamed data entry errors for inflating the benefits of eight grants that helped low- and moderate income households buy energy-efficient electric appliances. The state reported in November the eight grants will cut emissions by 7.5 million metric tons and accounted for 86% of all reductions over two years. The actual reduction was only 78,000 tons, according to Commerce. Commerce’s correction confirmed calculations by Washington Policy Center vice president for research Todd Myers. Earlier in the day, Myers posted online that 86% of the purported reductions were “probably fake.” …The Department of Ecology compiled and issued the faulty report. The report was a comprehensive accounting of how 37 state agencies and universities spent $1.5 billion in cap-and-trade taxes during the 2023-25 biennium, Ecology said.
Washington state officials admitted Jan. 6 they overstated by more than 80% how much projects funded by cap-and-trade taxes have reduced greenhouse gases. The Department of Commerce blamed data entry errors for inflating the benefits of eight grants that helped low- and moderate income households buy energy-efficient electric appliances. The state reported in November the eight grants will cut emissions by 7.5 million metric tons and accounted for 86% of all reductions over two years. The actual reduction was only 78,000 tons, according to Commerce. Commerce’s correction confirmed calculations by Washington Policy Center vice president for research Todd Myers. Earlier in the day, Myers posted online that 86% of the purported reductions were “probably fake.” …The Department of Ecology compiled and issued the faulty report. The report was a comprehensive accounting of how 37 state agencies and universities spent $1.5 billion in cap-and-trade taxes during the 2023-25 biennium, Ecology said.