 A US trade court judge has extended the deadline for refunding $166 billion in tariffs, citing the administrative challenge facing US Customs. In related news: the Steelworks’ Jeff Bromley says Canada’s tariff response still still leaves some workers behind; Canada engages FPAC to create a Talent Pipeline Management Pilot for the forest sector; and municipal procurement can be part of the solution to help improve prospects for Canada’s forestry sector. Meanwhile: mass timber highlights and advancements from Vancouver, BC; Lakewood, Washington; and London, England.
A US trade court judge has extended the deadline for refunding $166 billion in tariffs, citing the administrative challenge facing US Customs. In related news: the Steelworks’ Jeff Bromley says Canada’s tariff response still still leaves some workers behind; Canada engages FPAC to create a Talent Pipeline Management Pilot for the forest sector; and municipal procurement can be part of the solution to help improve prospects for Canada’s forestry sector. Meanwhile: mass timber highlights and advancements from Vancouver, BC; Lakewood, Washington; and London, England.
In Forestry news: Mosaic Forest Management is testing a new approach to forest management in the Koksilah watershed; the City of Mission sees profits from timber sales; the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) launched a new climate and biodiversity strategy; Montana and US Forest Service operationalize their new forestry agreement; and a University of BC webinar—Uninvited guests: Invasive pests, diseases and the fate of our forests.
Finally, the Pittsburgh Penguins buy forest carbon credits to offset their footprint.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor

 Richard Eaton, senior judge on the US Court of International Trade, has extended the US administration’s deadline for refunding about US$166 billion in tariffs. Eaton had orginally ordered US Customs and Border Protection to begin the refunding process at the start of the month after the US Supreme Court struck down global tariffs set by president Trump. …The administration has been inundated with lawsuits from companies like Costco, FedEx, and Pandora Jewelry – all looking to get their money back since Eaton’s order meant that everyone who had paid tariffs was entitled to a refund. Barnes, Richardson & Colburn partner
Richard Eaton, senior judge on the US Court of International Trade, has extended the US administration’s deadline for refunding about US$166 billion in tariffs. Eaton had orginally ordered US Customs and Border Protection to begin the refunding process at the start of the month after the US Supreme Court struck down global tariffs set by president Trump. …The administration has been inundated with lawsuits from companies like Costco, FedEx, and Pandora Jewelry – all looking to get their money back since Eaton’s order meant that everyone who had paid tariffs was entitled to a refund. Barnes, Richardson & Colburn partner 


 OTTAWA — The federal government is being accused of creating an uneven playing field in Canada’s shipping industry, and critics claim the Prime Minister’s Office is unwilling to rectify it. Later this spring, Ottawa is expected to launch a federal subsidy program to help reduce the cost of shipping lumber and steel between provinces by 50%. But the subsidies — promised by Carney back in November — will only go to rail companies. “We support this initiative to give a boost to those Canadian industries. But what we were asking was for parity because many destinations and commodities, only maritime transport can handle that,” said Etienne Duchesne, business development project manager at Desgagnés, a maritime shipping company based in Quebec. …In the House of Commons last week, Bloc Québécois MP Claude DeBellefeuille said the government was creating “unfair competition between rail transportation and marine transportation,” putting jobs and supply chains at risk.
OTTAWA — The federal government is being accused of creating an uneven playing field in Canada’s shipping industry, and critics claim the Prime Minister’s Office is unwilling to rectify it. Later this spring, Ottawa is expected to launch a federal subsidy program to help reduce the cost of shipping lumber and steel between provinces by 50%. But the subsidies — promised by Carney back in November — will only go to rail companies. “We support this initiative to give a boost to those Canadian industries. But what we were asking was for parity because many destinations and commodities, only maritime transport can handle that,” said Etienne Duchesne, business development project manager at Desgagnés, a maritime shipping company based in Quebec. …In the House of Commons last week, Bloc Québécois MP Claude DeBellefeuille said the government was creating “unfair competition between rail transportation and marine transportation,” putting jobs and supply chains at risk. US President Trump’s administration on Wednesday launched a trade investigation into excess industrial capacity in 16 major trading partners in a move to rebuild tariff pressure after the U.S. Supreme Court tore down the centerpiece of Trump’s trade policy last month. Canada is not named as one of the targets of the new probe. US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer said the Section 301 unfair trade practices investigation could lead to new tariffs imposed against China, the European Union, India, Japan, Mexico and South Korea by this summer. Other trading partners subject to the excess capacity probe include Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Cambodia, Singapore, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Switzerland and Norway. Trump and his team have made clear they’re seeking to replace the hundreds of billions of dollars in lost revenues after the Supreme Court’s February ruling. In this case, the administration is starting investigations under Section 301 of the Trade Act.
US President Trump’s administration on Wednesday launched a trade investigation into excess industrial capacity in 16 major trading partners in a move to rebuild tariff pressure after the U.S. Supreme Court tore down the centerpiece of Trump’s trade policy last month. Canada is not named as one of the targets of the new probe. US Trade Representative Jamieson Greer said the Section 301 unfair trade practices investigation could lead to new tariffs imposed against China, the European Union, India, Japan, Mexico and South Korea by this summer. Other trading partners subject to the excess capacity probe include Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Cambodia, Singapore, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Switzerland and Norway. Trump and his team have made clear they’re seeking to replace the hundreds of billions of dollars in lost revenues after the Supreme Court’s February ruling. In this case, the administration is starting investigations under Section 301 of the Trade Act.
 The outsized impact that oil prices have on the global economy means higher fuel and energy prices are all but guaranteed for many countries, not just those in the conflict region. …In the forest products sector, softwood lumber trade is one of the most directly exposed segments. Europe accounts for about one-third of the global softwood supply. Sweden and Finland are among Europe’s top exporters, along with Germany and Austria. …Lumber shipments out of Europe rely heavily on shipping routes through the Mediterranean, the Suez Canal, and the Gulf. Shipping costs are expected to escalate as fuel prices and risk premiums rise. Spikes in freight and insurance, along with rising energy costs in production and transport, could quickly start to make Nordic lumber less competitive while tightening margins. …Prolonged disruption in that region could force Nordic lumber producers to redirect volumes to Europe, North Africa, and Asia, causing price pressures in those markets.
The outsized impact that oil prices have on the global economy means higher fuel and energy prices are all but guaranteed for many countries, not just those in the conflict region. …In the forest products sector, softwood lumber trade is one of the most directly exposed segments. Europe accounts for about one-third of the global softwood supply. Sweden and Finland are among Europe’s top exporters, along with Germany and Austria. …Lumber shipments out of Europe rely heavily on shipping routes through the Mediterranean, the Suez Canal, and the Gulf. Shipping costs are expected to escalate as fuel prices and risk premiums rise. Spikes in freight and insurance, along with rising energy costs in production and transport, could quickly start to make Nordic lumber less competitive while tightening margins. …Prolonged disruption in that region could force Nordic lumber producers to redirect volumes to Europe, North Africa, and Asia, causing price pressures in those markets. OTTAWA–Housing starts in Canada are set to decline over the next three years due to higher construction costs, weaker demand and elevated levels of unsold inventory, the country’s housing agency said Wednesday. The outlook from Canada Mortgage and Housing Corp. represents another setback for the country’s residential real-estate sector, where prices and sales have declined following a prolonged period of strength fueled by immigration. It’s also a sign that, unlike in the recent past, housing-market activity won’t help propel the Canadian economy into a higher gear. Canada’s economy is struggling with slow growth, with manufacturers under duress from hefty U.S. tariffs. Furthermore, firms are scaling back spending and hiring plans as the future of a North American trade treaty is in doubt. CMHC said in a report that it expects housing starts to drop during the 2026-to-2028 period. [
OTTAWA–Housing starts in Canada are set to decline over the next three years due to higher construction costs, weaker demand and elevated levels of unsold inventory, the country’s housing agency said Wednesday. The outlook from Canada Mortgage and Housing Corp. represents another setback for the country’s residential real-estate sector, where prices and sales have declined following a prolonged period of strength fueled by immigration. It’s also a sign that, unlike in the recent past, housing-market activity won’t help propel the Canadian economy into a higher gear. Canada’s economy is struggling with slow growth, with manufacturers under duress from hefty U.S. tariffs. Furthermore, firms are scaling back spending and hiring plans as the future of a North American trade treaty is in doubt. CMHC said in a report that it expects housing starts to drop during the 2026-to-2028 period. [ Canada’s housing agency says the country made “meaningful” supply gains last year thanks to record rental construction and more “missing middle” type housing, however short-term imbalances remain for several markets. Housing construction rose 6% year-over-year in 2025 to 259,000 units, with activity exceeding the 10-year average across most major markets, according to CMHC’s spring housing supply report. …Rentals drove overall new housing supply in Canada last year, with the number of rental units under construction nearly doubling the 10-year average. …The trend led to increased vacancy rates and slower rent price rises compared with recent years. The report also highlighted the growth of “missing middle” housing — a term referring to gentle-to-medium density types such as accessory suites, multiplexes, row homes, stacked townhouses and low-rise apartments, which have often been under-represented in new supply. …Despite some encouraging trends, particularly for the rental market, housing construction for the home ownership market weakened overall.
Canada’s housing agency says the country made “meaningful” supply gains last year thanks to record rental construction and more “missing middle” type housing, however short-term imbalances remain for several markets. Housing construction rose 6% year-over-year in 2025 to 259,000 units, with activity exceeding the 10-year average across most major markets, according to CMHC’s spring housing supply report. …Rentals drove overall new housing supply in Canada last year, with the number of rental units under construction nearly doubling the 10-year average. …The trend led to increased vacancy rates and slower rent price rises compared with recent years. The report also highlighted the growth of “missing middle” housing — a term referring to gentle-to-medium density types such as accessory suites, multiplexes, row homes, stacked townhouses and low-rise apartments, which have often been under-represented in new supply. …Despite some encouraging trends, particularly for the rental market, housing construction for the home ownership market weakened overall.
 VANCOUVER, BC – Canfor Pulp Products announced that at the special meeting of the holders of common shares in the capital of the Company held earlier, the Shareholders voted in favour of approving the special resolution authorizing the previously announced arrangement whereby Canfor Corporation will acquire all of the issued and outstanding Common Shares that it and its affiliates do not already own by way of a statutory plan of arrangement. …The Arrangement was approved by 96.02% of the Shareholders and 84.42% of the Shareholders excluding any votes of the Purchaser and its affiliates and any other Shareholders whose votes were required to be excluded. …Assuming that all remaining approvals are obtained and all other remaining conditions precedent to the completion of the Arrangement are satisfied or waived, the Company anticipates that the Arrangement will be completed on or about March 17, 2026.
VANCOUVER, BC – Canfor Pulp Products announced that at the special meeting of the holders of common shares in the capital of the Company held earlier, the Shareholders voted in favour of approving the special resolution authorizing the previously announced arrangement whereby Canfor Corporation will acquire all of the issued and outstanding Common Shares that it and its affiliates do not already own by way of a statutory plan of arrangement. …The Arrangement was approved by 96.02% of the Shareholders and 84.42% of the Shareholders excluding any votes of the Purchaser and its affiliates and any other Shareholders whose votes were required to be excluded. …Assuming that all remaining approvals are obtained and all other remaining conditions precedent to the completion of the Arrangement are satisfied or waived, the Company anticipates that the Arrangement will be completed on or about March 17, 2026. US applications for unemployment benefits inched down modestly last week as layoffs remain at historically healthy levels despite a weakening job market. The number of Americans filing for jobless aid for the week ending March 7 fell by 1,000 to 213,000 the previous week, the Labor Department reported Thursday. Analysts surveyed by the data firm FactSet forecast 215,000 new benefit applications. Filings for unemployment benefits are viewed as a proxy for U.S. layoffs and are close to a real-time indicator of the health of the job market. While weekly layoffs have remained in a historically low range mostly between 200,000 and 250,000 for the past few years, a number of high-profile companies have announced job cuts recently, including Morgan Stanley,Block, UPSand Amazon in recent weeks. …For now, the U.S. job market appears stuck in what economists call a “low-hire, low-fire” state that has kept the unemployment rate historically low, but has left those out of work struggling to find a new job.
US applications for unemployment benefits inched down modestly last week as layoffs remain at historically healthy levels despite a weakening job market. The number of Americans filing for jobless aid for the week ending March 7 fell by 1,000 to 213,000 the previous week, the Labor Department reported Thursday. Analysts surveyed by the data firm FactSet forecast 215,000 new benefit applications. Filings for unemployment benefits are viewed as a proxy for U.S. layoffs and are close to a real-time indicator of the health of the job market. While weekly layoffs have remained in a historically low range mostly between 200,000 and 250,000 for the past few years, a number of high-profile companies have announced job cuts recently, including Morgan Stanley,Block, UPSand Amazon in recent weeks. …For now, the U.S. job market appears stuck in what economists call a “low-hire, low-fire” state that has kept the unemployment rate historically low, but has left those out of work struggling to find a new job.

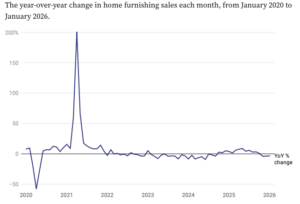 Unfortunately for retailers in the home sector, 2026 will likely look an awful lot like 2025. …While the pandemic offered a temporary financial boost, broad economic uncertainty caused many consumers to pull back on discretionary spending, leading to a decline in the high-ticket purchases. …The category has consistently seen year-over-year sales declines, according to the US Department of Commerce. …As was the case over the past few years, the weak housing market — driven by a lack of inventory and elevated interest rates — poses one of the biggest threats to the home sector this year. “The housing market is just stuck in neutral,” Zak Stambor said. “By and large, just few people are moving, and the lack of housing turnover means there’s a smaller-than-normal market for home goods.” “It’s the uncertainty that’s really driving the hesitation on the consumer side — where they should go, when they should buy, what they should buy in this market.”
Unfortunately for retailers in the home sector, 2026 will likely look an awful lot like 2025. …While the pandemic offered a temporary financial boost, broad economic uncertainty caused many consumers to pull back on discretionary spending, leading to a decline in the high-ticket purchases. …The category has consistently seen year-over-year sales declines, according to the US Department of Commerce. …As was the case over the past few years, the weak housing market — driven by a lack of inventory and elevated interest rates — poses one of the biggest threats to the home sector this year. “The housing market is just stuck in neutral,” Zak Stambor said. “By and large, just few people are moving, and the lack of housing turnover means there’s a smaller-than-normal market for home goods.” “It’s the uncertainty that’s really driving the hesitation on the consumer side — where they should go, when they should buy, what they should buy in this market.” NEW YORK — Stocks fell and oil prices traded above $100 per barrel Monday as investors grappled with a potential energy crisis caused by the war with Iran. …Stocks have been jolted by nerves about the Middle East conflict disrupting the global flow of oil and reigniting inflation at a time when the US labor market appears to be on shaky ground. Oil prices Monday surged to their highest level since mid-2022 when markets were rocked by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. US crude oil surged 11%, to $101 per barrel. Brent crude, the international benchmark, was also up 11%, to $103 per barrel. …The war with Iran has effectively halted the flow of oil through the Strait of Hormuz, the narrow waterway off Iran’s coast through which 20% of global oil consumption flows. …Wall Street’s fear gauge, the VIX, jumped 5% and hit its highest level since April, when markets were rocked by uncertainty about tariffs.
NEW YORK — Stocks fell and oil prices traded above $100 per barrel Monday as investors grappled with a potential energy crisis caused by the war with Iran. …Stocks have been jolted by nerves about the Middle East conflict disrupting the global flow of oil and reigniting inflation at a time when the US labor market appears to be on shaky ground. Oil prices Monday surged to their highest level since mid-2022 when markets were rocked by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. US crude oil surged 11%, to $101 per barrel. Brent crude, the international benchmark, was also up 11%, to $103 per barrel. …The war with Iran has effectively halted the flow of oil through the Strait of Hormuz, the narrow waterway off Iran’s coast through which 20% of global oil consumption flows. …Wall Street’s fear gauge, the VIX, jumped 5% and hit its highest level since April, when markets were rocked by uncertainty about tariffs. 
 WASHINGTON — American employers unexpectedly cut 92,000 jobs last month, a sign that the labor market remains under strain. The unemployment rate blipped up to 4.4%. The
WASHINGTON — American employers unexpectedly cut 92,000 jobs last month, a sign that the labor market remains under strain. The unemployment rate blipped up to 4.4%. The  A recent
A recent  Leveraging locally made forest products supports local jobs, efficient builds, and community resilience. …Forestry is more than just an industry; it is the lifeblood of some 300 Canadian communities. In the face of trade and market headwinds, some forest-dependent communities across the country are experiencing a worrying trend: the hollowing out of their economic base. Recent trade and market impacts on forestry have reduced production or closed mills, eliminated jobs, and reduced municipal revenues. With new challenges bring new opportunity – to take action on what we control. To streamline regulations to make our industries more competitive, diversify export markets, and do more here at home with Canadian grown and made products. Municipalities across the country can be part of the solution to help improve prospects for the forestry sector and its employees. Municipalities have the power to choose Canadian wood and wood fibre-based products in local projects.
Leveraging locally made forest products supports local jobs, efficient builds, and community resilience. …Forestry is more than just an industry; it is the lifeblood of some 300 Canadian communities. In the face of trade and market headwinds, some forest-dependent communities across the country are experiencing a worrying trend: the hollowing out of their economic base. Recent trade and market impacts on forestry have reduced production or closed mills, eliminated jobs, and reduced municipal revenues. With new challenges bring new opportunity – to take action on what we control. To streamline regulations to make our industries more competitive, diversify export markets, and do more here at home with Canadian grown and made products. Municipalities across the country can be part of the solution to help improve prospects for the forestry sector and its employees. Municipalities have the power to choose Canadian wood and wood fibre-based products in local projects.


 City of Powell River Council has officially endorsed the Forestry is a Solution campaign led by a broad coalition of community leaders, workers and forest industry advocates. At the March 6 city council meeting, councillors reviewed correspondence from Kim Haakstad, CEO of BC Council of Forest Industries, which has the goal to demonstrate deep public support for BC’s forest sector and ensure it remains a strategic asset for the future. The request had three components. The first was to officially endorse the Forestry is a Solution campaign. Secondly, encourage community members to visit the forestryisasolution.com website to sign a petition and send a letter to their MLA, the minister of forests, the premier and the official opposition forest critic… and share information about the campaign. Mayor Ron Woznow said he had worked with 22 other mayors regarding the importance of forestry… especially in terms of the significant debt the province is facing.
City of Powell River Council has officially endorsed the Forestry is a Solution campaign led by a broad coalition of community leaders, workers and forest industry advocates. At the March 6 city council meeting, councillors reviewed correspondence from Kim Haakstad, CEO of BC Council of Forest Industries, which has the goal to demonstrate deep public support for BC’s forest sector and ensure it remains a strategic asset for the future. The request had three components. The first was to officially endorse the Forestry is a Solution campaign. Secondly, encourage community members to visit the forestryisasolution.com website to sign a petition and send a letter to their MLA, the minister of forests, the premier and the official opposition forest critic… and share information about the campaign. Mayor Ron Woznow said he had worked with 22 other mayors regarding the importance of forestry… especially in terms of the significant debt the province is facing.
 OLMYPIA, Washington – Washington state is poised to significantly expand its efforts to combat climate change with a proposed agreement to link its carbon market with those of California and Quebec. The move, announced Tuesday by the Washington Department of Ecology, aims to stabilize and reduce the costs associated with decarbonizing the state’s economy. The draft linkage agreement is now open for public comment until May 1, 2026, with the shared market potentially launching as early as 2027. This collaboration represents a major step forward in regional climate action, building upon Washington’s 2021 Climate Commitment Act. …The linkage would allow businesses in all three jurisdictions to participate in joint auctions and trade carbon allowances freely. This expanded market is expected to stabilize Washington’s relatively new and more expensive carbon market, as California and Quebec have been operating linked markets since 2014. While aligning with California and Quebec, Washington maintains distinct climate goals.
OLMYPIA, Washington – Washington state is poised to significantly expand its efforts to combat climate change with a proposed agreement to link its carbon market with those of California and Quebec. The move, announced Tuesday by the Washington Department of Ecology, aims to stabilize and reduce the costs associated with decarbonizing the state’s economy. The draft linkage agreement is now open for public comment until May 1, 2026, with the shared market potentially launching as early as 2027. This collaboration represents a major step forward in regional climate action, building upon Washington’s 2021 Climate Commitment Act. …The linkage would allow businesses in all three jurisdictions to participate in joint auctions and trade carbon allowances freely. This expanded market is expected to stabilize Washington’s relatively new and more expensive carbon market, as California and Quebec have been operating linked markets since 2014. While aligning with California and Quebec, Washington maintains distinct climate goals. 

 A new study with EFI contribution,
A new study with EFI contribution,  When it comes to WorkSafeBC, one of the most misunderstood issues we hear about from business groups is the surplus. Specifically, many small-business associations have been calling on WorkSafeBC to rebate the surplus back to employers since our funding level is above target. For background, the funding level is simply a ratio of assets over liabilities on a funding basis. …What is also not well understood is that WorkSafeBC has been returning significant amounts of surplus funds to employers annually to keep rates both stable and below the actual costs of the system. …The reality is that if WorkSafeBC refunded the entire surplus to employers we would no longer be able to price premiums below system costs, meaning rates would have to be raised in subsequent years. …Rate stability for employers is a priority for WorkSafeBC. Some sectors benefiting from rate reductions in 2026 include sawmills (down 40%), framing and residential forming (down 40%).
When it comes to WorkSafeBC, one of the most misunderstood issues we hear about from business groups is the surplus. Specifically, many small-business associations have been calling on WorkSafeBC to rebate the surplus back to employers since our funding level is above target. For background, the funding level is simply a ratio of assets over liabilities on a funding basis. …What is also not well understood is that WorkSafeBC has been returning significant amounts of surplus funds to employers annually to keep rates both stable and below the actual costs of the system. …The reality is that if WorkSafeBC refunded the entire surplus to employers we would no longer be able to price premiums below system costs, meaning rates would have to be raised in subsequent years. …Rate stability for employers is a priority for WorkSafeBC. Some sectors benefiting from rate reductions in 2026 include sawmills (down 40%), framing and residential forming (down 40%). One of the most persistent myths in BC business circles is that WorkSafeBC is sitting on a massive surplus—a piggy bank that should be cracked open and handed back to employers. Manitoba did it, Ontario did it. …So why not BC? Because the surplus is depleted. It didn’t disappear overnight. It was frittered away, year by year, policy by policy, under an NDP government. …And now, BC’s small business owners are staring down the consequences. …According to WorkSafeBC’s own financial statements, in 2019 the system was funded at 153%—a full 23 points above the 130% floor set by policy and insurance best practices. That cushion, billions built up over decades, was a rainy day fund. It was never meant to finance an ever-expanding bureaucratic empire. …In 2019, WorkSafeBC’s rate of $1.55 per $100 of assessable payroll was among the lowest in Canada—only three provinces were cheaper. By 2024, that same $1.55 is higher than every province except two.
One of the most persistent myths in BC business circles is that WorkSafeBC is sitting on a massive surplus—a piggy bank that should be cracked open and handed back to employers. Manitoba did it, Ontario did it. …So why not BC? Because the surplus is depleted. It didn’t disappear overnight. It was frittered away, year by year, policy by policy, under an NDP government. …And now, BC’s small business owners are staring down the consequences. …According to WorkSafeBC’s own financial statements, in 2019 the system was funded at 153%—a full 23 points above the 130% floor set by policy and insurance best practices. That cushion, billions built up over decades, was a rainy day fund. It was never meant to finance an ever-expanding bureaucratic empire. …In 2019, WorkSafeBC’s rate of $1.55 per $100 of assessable payroll was among the lowest in Canada—only three provinces were cheaper. By 2024, that same $1.55 is higher than every province except two.