 The Wood Pellet Association of Canada, Firefly, FutureMetrics, Hanwa and Ørsted are conducting a one-day workshop—Safe Wood Pellet Storage: Preventing, Detecting, and Managing Self-Heating Incidents in Tokyo, Japan, on March 12, 2026. This workshop is a must-attend for professionals seeking to enhance pellet storage safety, mitigate fire risks, and improve operational resilience in large-scale storage environments. Join industry experts for a crucial discussion on the risks, detection, and prevention of self-heating incidents in wood pellet storage. This workshop will offer invaluable insights into major incidents, technical causes, risk mitigation strategies, and emergency response procedures, assisting professionals in enhancing safety standards across storage facilities. Don’t miss this opportunity to engage with leading specialists and drive industry-wide improvements forward.
The Wood Pellet Association of Canada, Firefly, FutureMetrics, Hanwa and Ørsted are conducting a one-day workshop—Safe Wood Pellet Storage: Preventing, Detecting, and Managing Self-Heating Incidents in Tokyo, Japan, on March 12, 2026. This workshop is a must-attend for professionals seeking to enhance pellet storage safety, mitigate fire risks, and improve operational resilience in large-scale storage environments. Join industry experts for a crucial discussion on the risks, detection, and prevention of self-heating incidents in wood pellet storage. This workshop will offer invaluable insights into major incidents, technical causes, risk mitigation strategies, and emergency response procedures, assisting professionals in enhancing safety standards across storage facilities. Don’t miss this opportunity to engage with leading specialists and drive industry-wide improvements forward.
 Welcome to the Wood Pellet Association of Canada’s Spring 2026 newsletter. We hope you enjoy reading it, and we welcome your feedback.
Welcome to the Wood Pellet Association of Canada’s Spring 2026 newsletter. We hope you enjoy reading it, and we welcome your feedback. Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington.
Drax Group is launching a strategic review of its Canadian pellet operations due to a constrained fiber market and low margins. …CEO Will Gardiner discussed the company’s changing pellet production strategy. …“Our US business is fundamentally part of our UK supply chain. That business is doing very well As you will have seen, our Canadian business is more challenged, and we’ve been talking about this for some time as margins have come down due to fiber costs rising in Canada more rapidly than indexed power prices in Asia. As we noted last year, this dynamic contributed to the decision we’ve made to close one of our pellet plants in Williams Lake towards the end of last year.” As a result, Drax is not currently expecting to commit any additional capital to the pellet production segment, including the paused pellet plant planned for development in Longview, Washington.
 Canada should ensure its ‘project of national interest’ designation is helping build competitive clean industries, starting with four key focus areas, according to a new report from the
Canada should ensure its ‘project of national interest’ designation is helping build competitive clean industries, starting with four key focus areas, according to a new report from the 
 With global temperature rising and extreme weather becoming the new normal, ballooning insurance premiums and shrinking coverage are hitting Canadians hard. Basement floods and severe winter storms have brought the financial fallout of climate change home—it is no longer a hypothetical. …“The fact that every insurance company has climate scientists on staff and insurance companies are all pricing in climate risk; there is no financial incentive for them to do that if it wasn’t real,” said Dr. Kate Marvel, a NASA climate scientist. If climate change were a hoax, insurers would simply undercut one another, offering cheaper coverage and dismissing long-term risk, Marvel explained. Instead, they are doing the opposite; quietly rewriting the rules of risk as extreme weather becomes more frequent, more destructive and more expensive. …The question is whether governments will act quickly enough to adapt to a warming climate and confront who pays for the damage when they don’t.
With global temperature rising and extreme weather becoming the new normal, ballooning insurance premiums and shrinking coverage are hitting Canadians hard. Basement floods and severe winter storms have brought the financial fallout of climate change home—it is no longer a hypothetical. …“The fact that every insurance company has climate scientists on staff and insurance companies are all pricing in climate risk; there is no financial incentive for them to do that if it wasn’t real,” said Dr. Kate Marvel, a NASA climate scientist. If climate change were a hoax, insurers would simply undercut one another, offering cheaper coverage and dismissing long-term risk, Marvel explained. Instead, they are doing the opposite; quietly rewriting the rules of risk as extreme weather becomes more frequent, more destructive and more expensive. …The question is whether governments will act quickly enough to adapt to a warming climate and confront who pays for the damage when they don’t. The 2026 Arctic Bioenergy Summit and Tour brought together over 125 northern energy leaders, policymakers, and bioenergy experts in Yellowknife from January 26–28 to explore sustainable heating solutions for remote and Arctic communities. The event, hosted by the Arctic Energy Alliance and the Wood Pellet Association of Canada, showcased the theme Sustainable Bioenergy for Northern Communities: Reliable. Affordable. Local. Sessions emphasized that bioenergy continues to offer meaningful economic, environmental, and energy‑security benefits for northern and remote communities—especially when paired with strong local leadership and practical, scalable project design. The event also provided valuable networking opportunities, connecting community representatives, government officials, and industry innovators.
The 2026 Arctic Bioenergy Summit and Tour brought together over 125 northern energy leaders, policymakers, and bioenergy experts in Yellowknife from January 26–28 to explore sustainable heating solutions for remote and Arctic communities. The event, hosted by the Arctic Energy Alliance and the Wood Pellet Association of Canada, showcased the theme Sustainable Bioenergy for Northern Communities: Reliable. Affordable. Local. Sessions emphasized that bioenergy continues to offer meaningful economic, environmental, and energy‑security benefits for northern and remote communities—especially when paired with strong local leadership and practical, scalable project design. The event also provided valuable networking opportunities, connecting community representatives, government officials, and industry innovators. A new study finds that Canada could remove at least five times its annual carbon emissions with strategic planting of more than six million trees along the northern edge of the boreal forest. The
A new study finds that Canada could remove at least five times its annual carbon emissions with strategic planting of more than six million trees along the northern edge of the boreal forest. The  Nature markets are systems for measuring an ecological improvement on some land, then creating a representation of that improvement as a credit, which can then be bought and sold. In theory, they allow governments to attract more private investment and diversify funds that help restore nature. The reality is much more complicated. I recently
Nature markets are systems for measuring an ecological improvement on some land, then creating a representation of that improvement as a credit, which can then be bought and sold. In theory, they allow governments to attract more private investment and diversify funds that help restore nature. The reality is much more complicated. I recently  Record forest fires, under-utilized agricultural residues like straw and husks and struggling sawmills have left Canada with an abundance of undervalued biomass. If carefully and strategically managed, this resource could become a powerful ally in the fight against climate change. Canada’s biomass sectors are facing significant uncertainty because of political and natural disruptions. The forestry sector was hit last year by new American tariffs announced by the Donald Trump administration on Canadian forest products, bringing the total duties imposed on Canadian lumber to 45 per cent. The agricultural and agri-food sector is also particularly vulnerable, since it exports more than 70 per cent of its main crops. In addition to facing these political uncertainties, biomass sectors are increasingly experiencing the effects of climate disasters.
Record forest fires, under-utilized agricultural residues like straw and husks and struggling sawmills have left Canada with an abundance of undervalued biomass. If carefully and strategically managed, this resource could become a powerful ally in the fight against climate change. Canada’s biomass sectors are facing significant uncertainty because of political and natural disruptions. The forestry sector was hit last year by new American tariffs announced by the Donald Trump administration on Canadian forest products, bringing the total duties imposed on Canadian lumber to 45 per cent. The agricultural and agri-food sector is also particularly vulnerable, since it exports more than 70 per cent of its main crops. In addition to facing these political uncertainties, biomass sectors are increasingly experiencing the effects of climate disasters.  OTTAWA, ON
OTTAWA, ON 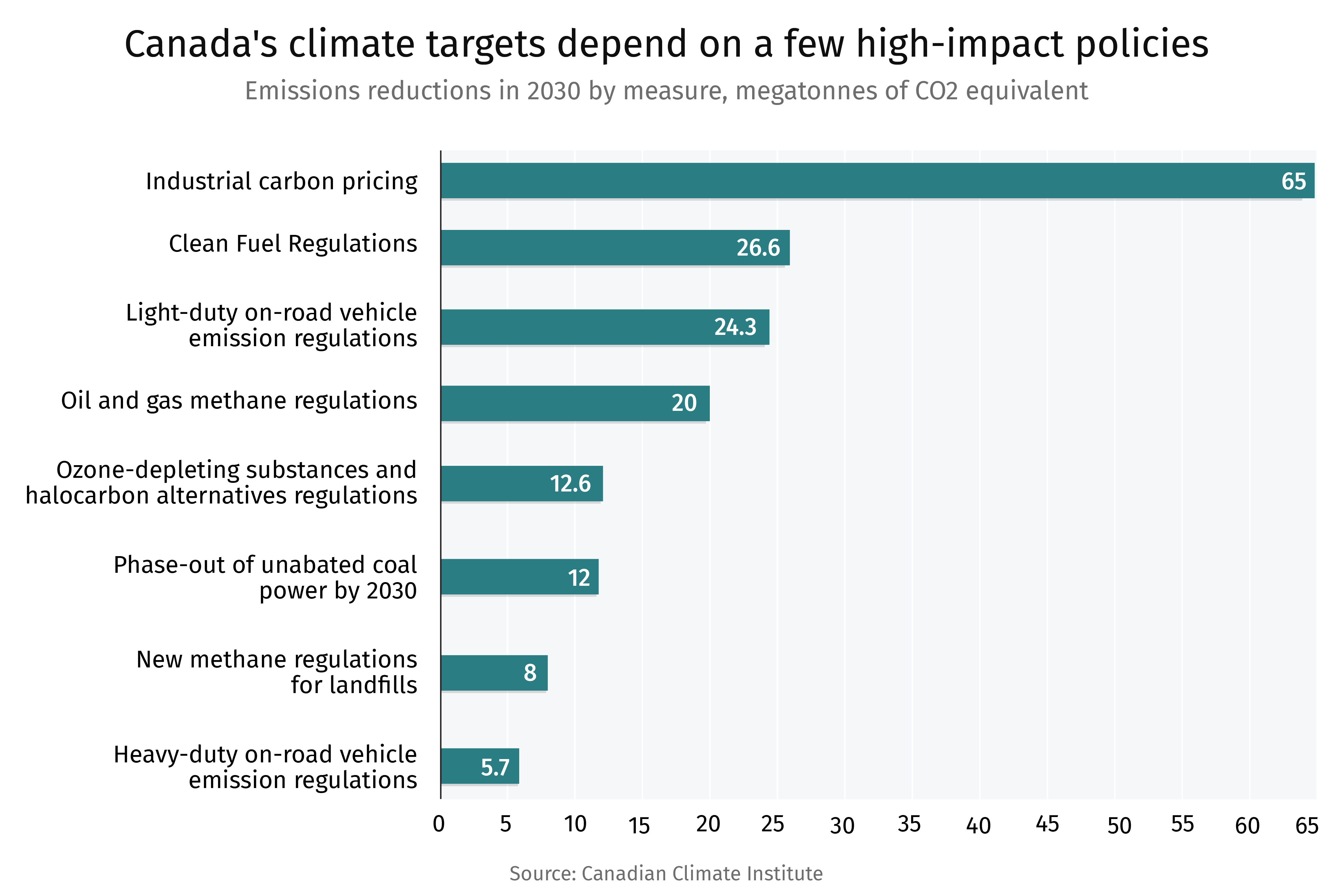
 Strategically planting trees along the northern edge of Canada’s boreal forest could remove multiple gigatonnes of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by the end of the century, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Waterloo. The research, published in
Strategically planting trees along the northern edge of Canada’s boreal forest could remove multiple gigatonnes of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by the end of the century, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Waterloo. The research, published in  The Quebec government says it’s pushing back its greenhouse gas reduction target by five years to protect the economy and jobs. Environment Minister Bernard Drainville announced today that the government will not meet its goal of reducing emissions by 37.5 per cent below 1990 levels by 2030. This target has now been set for 2035— a timeline the government describes as ambitious yet realistic. Drainville says in a news release that Quebec has reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 20 per cent since 1990. He says achieving the other half of the target in just five years would risk economic damage at a time of uncertainty and tariff threats from the US. In response, environment group Equiterre says the government is letting young Quebecers down.
The Quebec government says it’s pushing back its greenhouse gas reduction target by five years to protect the economy and jobs. Environment Minister Bernard Drainville announced today that the government will not meet its goal of reducing emissions by 37.5 per cent below 1990 levels by 2030. This target has now been set for 2035— a timeline the government describes as ambitious yet realistic. Drainville says in a news release that Quebec has reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 20 per cent since 1990. He says achieving the other half of the target in just five years would risk economic damage at a time of uncertainty and tariff threats from the US. In response, environment group Equiterre says the government is letting young Quebecers down. A coalition of health and environmental groups sued the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Wednesday, challenging the rescinding of a scientific finding that has been the central basis for U.S. action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change. A rule finalized by the EPA last week revoked
A coalition of health and environmental groups sued the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Wednesday, challenging the rescinding of a scientific finding that has been the central basis for U.S. action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change. A rule finalized by the EPA last week revoked  The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say.
The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say. WASHINGTON — The Trump administration on Thursday will revoke a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the White House announced. The Environmental Protection Agency will issue a final rule rescinding a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding. That Obama-era policy determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. …White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt said… the action “will save $1.3 trillion in crushing regulations,” she said. …The endangerment finding is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. It is used to justify regulations, such as auto emissions standards, intended to protect against threats made increasingly severe by climate change — deadly floods, extreme heat waves, catastrophic wildfires and other natural disasters.
WASHINGTON — The Trump administration on Thursday will revoke a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the White House announced. The Environmental Protection Agency will issue a final rule rescinding a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding. That Obama-era policy determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. …White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt said… the action “will save $1.3 trillion in crushing regulations,” she said. …The endangerment finding is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. It is used to justify regulations, such as auto emissions standards, intended to protect against threats made increasingly severe by climate change — deadly floods, extreme heat waves, catastrophic wildfires and other natural disasters. Misleading. Unjustified. Hypocritical. Those are just some of the words that Department of Energy scientists used to describe a 141-page report on climate change that was commissioned by DOE Secretary Chris Wright. The feedback appears in newly revealed emails that were made public as part of a court fight between DOE and public interest groups. And they show that criticism of the report isn’t limited to scientists outside the Trump administration. The department’s own internal reviewers took issue with the document, which was written by five climate contrarians from outside DOE who were handpicked by Wright. …One DOE reviewer echoed that opinion and said it was “misleading” for the report to talk about how climate change could boost plant growth without mentioning its other drawbacks. Another comment described the report’s criticism of climate modeling as an “unjustified (and at worst a biased) judgement.”
Misleading. Unjustified. Hypocritical. Those are just some of the words that Department of Energy scientists used to describe a 141-page report on climate change that was commissioned by DOE Secretary Chris Wright. The feedback appears in newly revealed emails that were made public as part of a court fight between DOE and public interest groups. And they show that criticism of the report isn’t limited to scientists outside the Trump administration. The department’s own internal reviewers took issue with the document, which was written by five climate contrarians from outside DOE who were handpicked by Wright. …One DOE reviewer echoed that opinion and said it was “misleading” for the report to talk about how climate change could boost plant growth without mentioning its other drawbacks. Another comment described the report’s criticism of climate modeling as an “unjustified (and at worst a biased) judgement.” 
 NEW YORK
NEW YORK UK energy company Drax’s ambitions of becoming a significant wood pellet supplier to Asia are in danger of faltering as Japanese policymakers wind back generous subsidies for the biomass sector. Japan is set to soon surpass the UK as the world’s largest wood pellet importer after a post-Fukushima push to diversify power sources that caused hundreds of plants to spring up that burn wood pellets, palm kernel shells — a palm oil byproduct — and other organic materials. But policymakers in Japan are pulling support for the controversial industry after realising the hurdles to bringing down fuel costs. Tokyo has already cut subsidies for new projects of more than 10 megawatts. “The real intention is quite simple: no new government support, phasing out. We don’t see any clear path of bringing down costs in the foreseeable future,” said one government official. “Existing projects might survive but no new projects are coming.”
UK energy company Drax’s ambitions of becoming a significant wood pellet supplier to Asia are in danger of faltering as Japanese policymakers wind back generous subsidies for the biomass sector. Japan is set to soon surpass the UK as the world’s largest wood pellet importer after a post-Fukushima push to diversify power sources that caused hundreds of plants to spring up that burn wood pellets, palm kernel shells — a palm oil byproduct — and other organic materials. But policymakers in Japan are pulling support for the controversial industry after realising the hurdles to bringing down fuel costs. Tokyo has already cut subsidies for new projects of more than 10 megawatts. “The real intention is quite simple: no new government support, phasing out. We don’t see any clear path of bringing down costs in the foreseeable future,” said one government official. “Existing projects might survive but no new projects are coming.” CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet at increased risk of a “hothouse” trajectory driven by feedback loops that can amplify the consequences of global warming. “The risk of a hothouse Earth
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Scientists say multiple Earth system components appear closer to destabilization than previously believed, putting the planet at increased risk of a “hothouse” trajectory driven by feedback loops that can amplify the consequences of global warming. “The risk of a hothouse Earth  …Timber prices have been low for a long time; they never really recovered from the 2008 housing crash. Nearly a dozen paper mills closed across the South in recent years, and Hurricane Helene tore down trees in much of Georgia and the Carolinas. It’s left many in Georgia, one of the leading states for forestry, with a dilemma: what do you do when your income relies on a forest but nobody wants to buy your trees? A group of researchers and industry leaders thinks paying landowners for carbon storage could help. “We may see a decline in the number of acres that are kept in forests and the quality of the land that is forested,” said David Eady with Georgia Tech’s business school. Losing those trees would shrink the industry and be devastating for the environment. …So Eady and others asked: why not use that carbon storage to keep foresters in business?
…Timber prices have been low for a long time; they never really recovered from the 2008 housing crash. Nearly a dozen paper mills closed across the South in recent years, and Hurricane Helene tore down trees in much of Georgia and the Carolinas. It’s left many in Georgia, one of the leading states for forestry, with a dilemma: what do you do when your income relies on a forest but nobody wants to buy your trees? A group of researchers and industry leaders thinks paying landowners for carbon storage could help. “We may see a decline in the number of acres that are kept in forests and the quality of the land that is forested,” said David Eady with Georgia Tech’s business school. Losing those trees would shrink the industry and be devastating for the environment. …So Eady and others asked: why not use that carbon storage to keep foresters in business?
 With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe.
With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe. When the time is right, a good love song can make all the difference. A study from the University of California, Davis, found that temperature affects the sound and quality of male frogs’ mating calls. In the colder, early weeks of spring, their songs start off sluggishly. In warmer weather, their songs pick up the pace, and female frogs take note. Better songs make the males more attractive mates and suggest to females that conditions are suitable for reproduction. …The results carry implications for conservation amid climate change. …Understanding when frogs breed, how that may shift as the climate warms, and what is driving those shifts is critical to their conservation. …females do not necessarily come to the pond just because the males are calling. The time has to be right for her eggs to survive. That clue lies in the quality of the male’s song, which is more attractive once it’s warmer.
When the time is right, a good love song can make all the difference. A study from the University of California, Davis, found that temperature affects the sound and quality of male frogs’ mating calls. In the colder, early weeks of spring, their songs start off sluggishly. In warmer weather, their songs pick up the pace, and female frogs take note. Better songs make the males more attractive mates and suggest to females that conditions are suitable for reproduction. …The results carry implications for conservation amid climate change. …Understanding when frogs breed, how that may shift as the climate warms, and what is driving those shifts is critical to their conservation. …females do not necessarily come to the pond just because the males are calling. The time has to be right for her eggs to survive. That clue lies in the quality of the male’s song, which is more attractive once it’s warmer.  BUENOS AIRES, Argentina — Human-caused climate change had an important impact on the recent ferocious wildfires that engulfed parts of Chile and Argentina’s Patagonia region, making the extremely high-risk conditions that led to widespread burning up to three times more likely than in a world without global warming, a team of researchers warned on Wednesday. The hot, dry and gusty weather that fed last month’s deadly wildfires in central and southern Chile was made around 200% more likely by human-made greenhouse gas emissions while the high-fire-risk conditions that fueled the blazes still racing through southern Argentina were made 150% more likely, according to World Weather Attribution, a scientific initiative that investigates extreme weather events soon after they happen. That probability will only increase, the experts added, as humans continue to blanket the planet with heat-trapping gases.
BUENOS AIRES, Argentina — Human-caused climate change had an important impact on the recent ferocious wildfires that engulfed parts of Chile and Argentina’s Patagonia region, making the extremely high-risk conditions that led to widespread burning up to three times more likely than in a world without global warming, a team of researchers warned on Wednesday. The hot, dry and gusty weather that fed last month’s deadly wildfires in central and southern Chile was made around 200% more likely by human-made greenhouse gas emissions while the high-fire-risk conditions that fueled the blazes still racing through southern Argentina were made 150% more likely, according to World Weather Attribution, a scientific initiative that investigates extreme weather events soon after they happen. That probability will only increase, the experts added, as humans continue to blanket the planet with heat-trapping gases. Scotland would have to plant several hundred thousand hectares of new woodland to achieve net-zero carbon emissions in the livestock sector by 2050 through afforestation alone, a new study has shown. The study by The James Hutton Institute, which was recently published in the journal Science of The Total Environment, investigated how multi-functional afforestation and livestock reduction could contribute to helping Scotland achieve net-zero emissions in the livestock sector by 2050. This goal aligns with the Paris Agreement on climate change. Researchers have simulated a scenario in which approximately 30,000ha per year of new woodland and agroforestry were planted in Scotland between 2020 and 2025. …It is often assumed such planting can only occur at the expense of grazing area, so the researchers coupled this planting effort with a linear decrease in livestock, with an estimated total reduction of approximately 50% of the present herd numbers.
Scotland would have to plant several hundred thousand hectares of new woodland to achieve net-zero carbon emissions in the livestock sector by 2050 through afforestation alone, a new study has shown. The study by The James Hutton Institute, which was recently published in the journal Science of The Total Environment, investigated how multi-functional afforestation and livestock reduction could contribute to helping Scotland achieve net-zero emissions in the livestock sector by 2050. This goal aligns with the Paris Agreement on climate change. Researchers have simulated a scenario in which approximately 30,000ha per year of new woodland and agroforestry were planted in Scotland between 2020 and 2025. …It is often assumed such planting can only occur at the expense of grazing area, so the researchers coupled this planting effort with a linear decrease in livestock, with an estimated total reduction of approximately 50% of the present herd numbers. Boreal ecosystems store twice as much carbon as the atmosphere and warm faster than the global average. The current paradigm based on boreal forests and tundra considers that warming will accelerate boreal carbon loss. However, the warming response of Sphagnum peatlands, storing ~40% of boreal carbon stocks, remains under-investigated. …investigations into two long-term warming experiments in Finnish peatlands, we demonstrate that warming enhances soil carbon accumulation in boreal Sphagnum peatlands. This result sharply contrasts with warming-induced carbon loss from boreal forests and tundra, owing to the unique metabolic response of Sphagnum… Our estimates suggest that warming-induced increase of soil carbon in boreal Sphagnum peatlands (assuming no hydrological changes or plant species shifts) may offset nearly half the boreal forest carbon-sink decline or heterotrophic respiration increases in Arctic tundra under warming. These findings highlight the vital but overlooked role of Sphagnum peatlands in counteracting boreal carbon loss under future warming.
Boreal ecosystems store twice as much carbon as the atmosphere and warm faster than the global average. The current paradigm based on boreal forests and tundra considers that warming will accelerate boreal carbon loss. However, the warming response of Sphagnum peatlands, storing ~40% of boreal carbon stocks, remains under-investigated. …investigations into two long-term warming experiments in Finnish peatlands, we demonstrate that warming enhances soil carbon accumulation in boreal Sphagnum peatlands. This result sharply contrasts with warming-induced carbon loss from boreal forests and tundra, owing to the unique metabolic response of Sphagnum… Our estimates suggest that warming-induced increase of soil carbon in boreal Sphagnum peatlands (assuming no hydrological changes or plant species shifts) may offset nearly half the boreal forest carbon-sink decline or heterotrophic respiration increases in Arctic tundra under warming. These findings highlight the vital but overlooked role of Sphagnum peatlands in counteracting boreal carbon loss under future warming.
 A door company in Ireland says it holds the key to turning wood dust into electricity to help power its factory. It’s part of a new multimillion-pound investment by O&S Doors. The company says the onsite renewable heat and energy technology is “a first on the island of Ireland”. Currently the company takes wood dust left over from the manufacturing process and ships it to England where it is used as animal bedding or sent to landfill. But the company – located just outside Benburb in County Tyrone – has revealed new details of its plans to install a biomass-fuelled combined heat and power system. It will turn the dust into millions of units of electricity that can reused to power parts of the factory. …O&S Doors says its biomass-fuelled combined heat and power system will harness MDF dust.
A door company in Ireland says it holds the key to turning wood dust into electricity to help power its factory. It’s part of a new multimillion-pound investment by O&S Doors. The company says the onsite renewable heat and energy technology is “a first on the island of Ireland”. Currently the company takes wood dust left over from the manufacturing process and ships it to England where it is used as animal bedding or sent to landfill. But the company – located just outside Benburb in County Tyrone – has revealed new details of its plans to install a biomass-fuelled combined heat and power system. It will turn the dust into millions of units of electricity that can reused to power parts of the factory. …O&S Doors says its biomass-fuelled combined heat and power system will harness MDF dust. The energy industry initially sold wood pellets as a way to clean up coal. And governments bought into that assumption. But now policymakers are questioning that position and even reversing course. At the center of this debate is a UK-based power company called Drax, which converted Europe’s largest coal plant into a biomass facility—one fueled by wood pellets that it imported from southern states in the United States. The debate raises a multitude of questions, namely those centered on pollution and costs. That is, if the additive creates more pollution than either wind or solar energy, why bother, especially since it comes from a power source that depends on subsidies? Merry Dickinson, campaign director for the Dogwood Alliance, told me that Drax now operates entirely on woody biomass… “The amount of wood required … is beyond what is available as waste wood,” Dickinson says. “…much of the supply consists of whole trees.” [Forbes allows 4 free articles per month]
The energy industry initially sold wood pellets as a way to clean up coal. And governments bought into that assumption. But now policymakers are questioning that position and even reversing course. At the center of this debate is a UK-based power company called Drax, which converted Europe’s largest coal plant into a biomass facility—one fueled by wood pellets that it imported from southern states in the United States. The debate raises a multitude of questions, namely those centered on pollution and costs. That is, if the additive creates more pollution than either wind or solar energy, why bother, especially since it comes from a power source that depends on subsidies? Merry Dickinson, campaign director for the Dogwood Alliance, told me that Drax now operates entirely on woody biomass… “The amount of wood required … is beyond what is available as waste wood,” Dickinson says. “…much of the supply consists of whole trees.” [Forbes allows 4 free articles per month]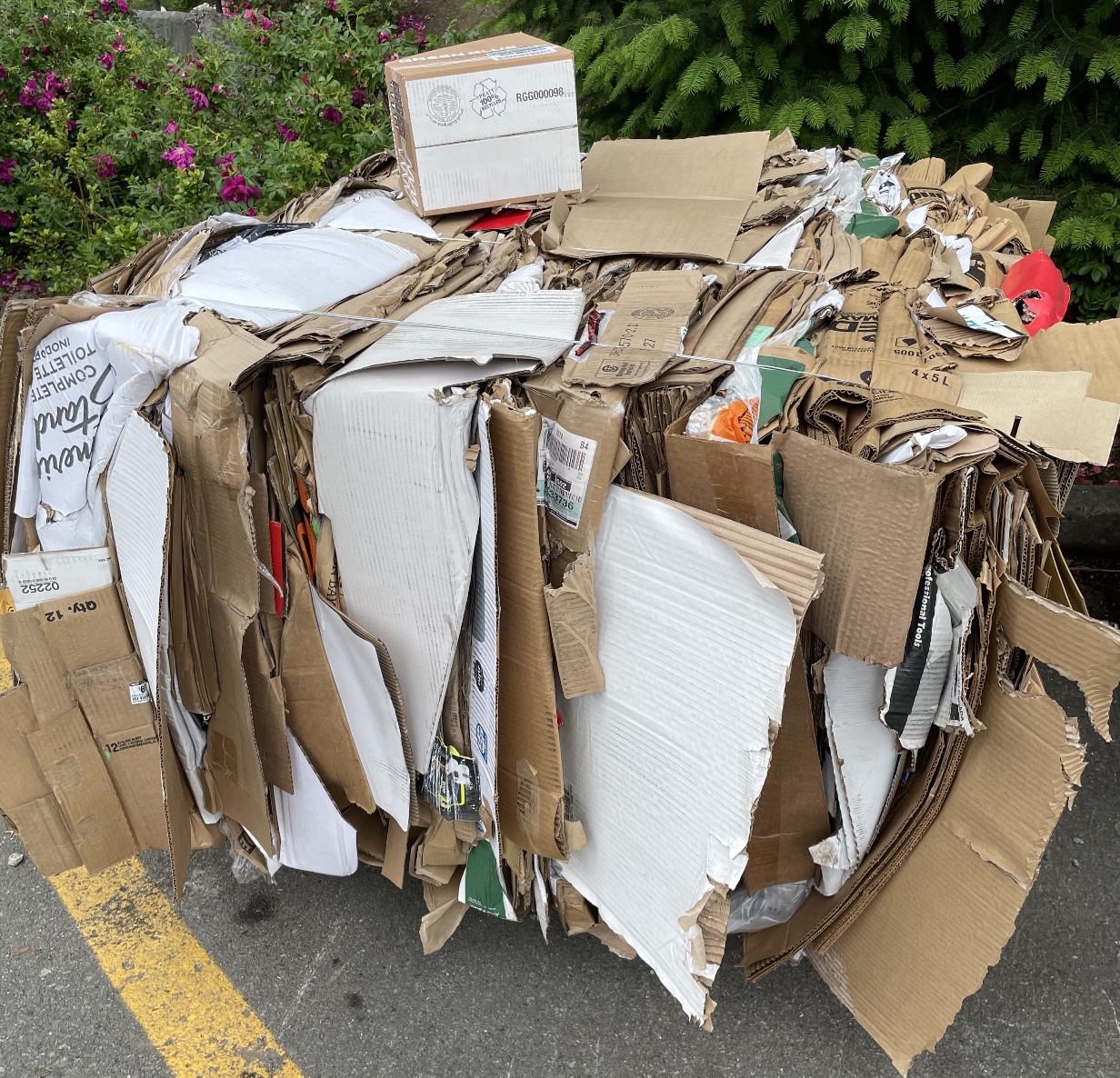 A new study has shown for the first time that waste cardboard can be used as an effective source of biomass fuel for large-scale power generation, offering a potential new domestic resource to support the UK’s renewable energy sector. Engineers from the University of Nottingham have carried out the first comprehensive characterisation of cardboard as a fuel source and developed a new method to assess its composition. The research … provides a practical tool for evaluating different grades of cardboard for use in energy production. The study found that cardboard displays distinct physical and chemical properties compared with traditional biomass fuels. These include lower carbon content, a reduced heating value and a high level of calcium carbonate fillers, particularly in printed grades. Calcium carbonate is commonly added to cardboard to improve stiffness and optical qualities, but during combustion it forms ash that can reduce boiler performance.
A new study has shown for the first time that waste cardboard can be used as an effective source of biomass fuel for large-scale power generation, offering a potential new domestic resource to support the UK’s renewable energy sector. Engineers from the University of Nottingham have carried out the first comprehensive characterisation of cardboard as a fuel source and developed a new method to assess its composition. The research … provides a practical tool for evaluating different grades of cardboard for use in energy production. The study found that cardboard displays distinct physical and chemical properties compared with traditional biomass fuels. These include lower carbon content, a reduced heating value and a high level of calcium carbonate fillers, particularly in printed grades. Calcium carbonate is commonly added to cardboard to improve stiffness and optical qualities, but during combustion it forms ash that can reduce boiler performance.