TORONTO — Canada is aiming to cut its emissions in half by 2035 compared to 2005 levels, the federal government announced Thursday, a target more modest than what a federal advisory body had previously recommended. The target of reducing emissions by 45% to 50% balances both ambition and what is achievable, Environment and Climate Change Minister Steven Guilbeault said. …He added that the target’s lower end accounts for potential headwinds, including how United States president-elect Donald Trump approaches key climate policies. …”As a responsible government, we have to account for the possibilities that it may be more difficult in the coming years to continue moving forward because our major trading partner may decide to take a different course when it comes to tackling climate change,” Guilbeault said. Canada’s Net-Zero Advisory Body recommended an emissions reduction target of 50% to 55%. …Catherine Abreu, a climate policy analyst, called the target “pathetic”.
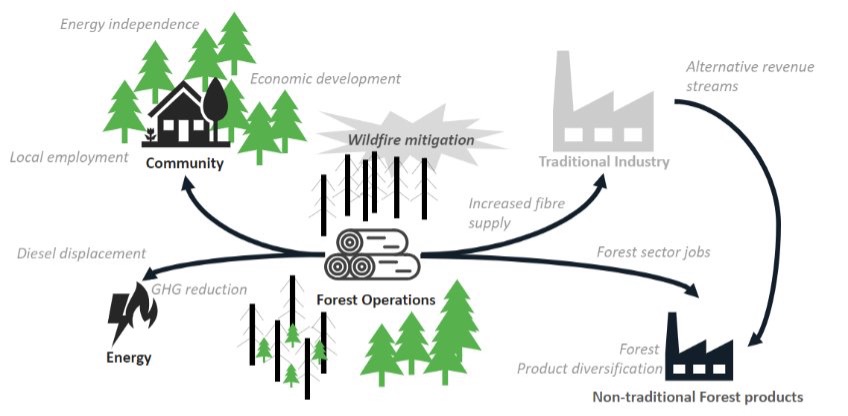
 Scrap wood fibre in the Rainy River district could get a new life, thanks to a partnership working towards a green fuel production facility. Ten First Nations in the Rainy River District near Fort Frances have joined forces to create ground-breaking Wanagekong-Biiwega’iganan Clean Energy Corporation (WBCEC). In partnership with Highbury Energy Inc., a Vancouver-based clean energy innovator, the initiative aims to transform wood waste—including bark, sawdust, and logging debris—into low-carbon transportation fuels. …The corporation is currently engaging with industry stakeholders such as Boundary Waters Forest Management Corporation, West Fraser OSB, Manitou Forest Products, Nickel Lake Lumber, and Resolute Forest Products (Sapawe Sawmill) to secure local wood waste as feedstock for a proposed biorefinery in Fort Frances. …This initiative aligns with similar projects Highbury Energy is involved in, including one in British Columbia to replace natural gas with a clean renewable fuel gas in a pulp mill lime-kiln.
Scrap wood fibre in the Rainy River district could get a new life, thanks to a partnership working towards a green fuel production facility. Ten First Nations in the Rainy River District near Fort Frances have joined forces to create ground-breaking Wanagekong-Biiwega’iganan Clean Energy Corporation (WBCEC). In partnership with Highbury Energy Inc., a Vancouver-based clean energy innovator, the initiative aims to transform wood waste—including bark, sawdust, and logging debris—into low-carbon transportation fuels. …The corporation is currently engaging with industry stakeholders such as Boundary Waters Forest Management Corporation, West Fraser OSB, Manitou Forest Products, Nickel Lake Lumber, and Resolute Forest Products (Sapawe Sawmill) to secure local wood waste as feedstock for a proposed biorefinery in Fort Frances. …This initiative aligns with similar projects Highbury Energy is involved in, including one in British Columbia to replace natural gas with a clean renewable fuel gas in a pulp mill lime-kiln. Renewables are currently expected to account for 23% of U.S. electricity generation this year, increasing to 25% in 2025, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s latest Short-Term Energy Outlook, released Dec. 10. Renewables accounted for 22% of U.S. electricity generation last year. Biomass is currently expected to account for 2.18% of U.S. renewable electricity generation this year, falling to 2% next year. Biomass accounted for 2.44% of renewable electricity generation in 2023. According to the EIA, biomass is expected to be used to generate 20.6 billion kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity in 2024, increasing to 21.1 billion kWh in 2025. Biomass generation was at 21.4 billion kWh in 2023.
Renewables are currently expected to account for 23% of U.S. electricity generation this year, increasing to 25% in 2025, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s latest Short-Term Energy Outlook, released Dec. 10. Renewables accounted for 22% of U.S. electricity generation last year. Biomass is currently expected to account for 2.18% of U.S. renewable electricity generation this year, falling to 2% next year. Biomass accounted for 2.44% of renewable electricity generation in 2023. According to the EIA, biomass is expected to be used to generate 20.6 billion kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity in 2024, increasing to 21.1 billion kWh in 2025. Biomass generation was at 21.4 billion kWh in 2023.