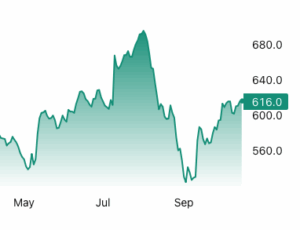
 Lumber futures rose past $610 per thousand board feet in mid-October, approaching monthly highs as markets priced in tighter near-term supply and looming trade restrictions. Under newly announced US Section 232 tariffs that take effect on October 14th, imported softwood lumber will face a 10% duty and finished wood goods such as cabinets and furniture will face higher levies, prompting importers to front-load purchases and draw down inventories. Domestic output is also constrained as sawmills run cautiously after years of underinvestment, logging curbs in sensitive regions and slow capacity restarts have limited production. The cost and delay of switching suppliers is material given that Canadian lumber, which supplies much of US demand, already carries elevated antidumping and countervailing duties, intensifying the supply squeeze.
Lumber futures rose past $610 per thousand board feet in mid-October, approaching monthly highs as markets priced in tighter near-term supply and looming trade restrictions. Under newly announced US Section 232 tariffs that take effect on October 14th, imported softwood lumber will face a 10% duty and finished wood goods such as cabinets and furniture will face higher levies, prompting importers to front-load purchases and draw down inventories. Domestic output is also constrained as sawmills run cautiously after years of underinvestment, logging curbs in sensitive regions and slow capacity restarts have limited production. The cost and delay of switching suppliers is material given that Canadian lumber, which supplies much of US demand, already carries elevated antidumping and countervailing duties, intensifying the supply squeeze.
 North America’s softwood lumber market looks likely to end 2025 no more settled than it was at the beginning. Producers and buyers alike continue navigating a landscape shaped by fluctuating demand, shifting trade patterns, and an uncertain housing outlook. Despite modest production declines in early 2025, the lumber market remains oversupplied. Mills across the US and Canada are contending with high inventories built up earlier in the year. Expectations of tariff hikes spurred an early rush of exports from Canada to the US, flooding the market while demand was soft. However, in the first half of 2025 softwood lumber exports from Canada to the US declined, while US imports from Europe in the first seven months of 2025 increased by 6% year-over-year. Underlying these supply pressures is a US housing market stuck in the doldrums. August saw an 8.5% decline in overall housing starts, with single-family construction down nearly 7%.
North America’s softwood lumber market looks likely to end 2025 no more settled than it was at the beginning. Producers and buyers alike continue navigating a landscape shaped by fluctuating demand, shifting trade patterns, and an uncertain housing outlook. Despite modest production declines in early 2025, the lumber market remains oversupplied. Mills across the US and Canada are contending with high inventories built up earlier in the year. Expectations of tariff hikes spurred an early rush of exports from Canada to the US, flooding the market while demand was soft. However, in the first half of 2025 softwood lumber exports from Canada to the US declined, while US imports from Europe in the first seven months of 2025 increased by 6% year-over-year. Underlying these supply pressures is a US housing market stuck in the doldrums. August saw an 8.5% decline in overall housing starts, with single-family construction down nearly 7%. President Trump unveiled sweeping tariffs on imported lumber and wood products that his administration says are needed to protect the US economy and boost domestic manufacturing. Starting Oct. 14, softwood lumber will face 10% duties, while kitchen cabinets, bathroom vanities, and other finished wood goods will be hit with 25% tariffs that rise further in January. The biggest blow will fall on Canada, the US’s top lumber supplier, whose lumber exports are already subject to separate duties totaling 35.19%. …Though Canada dominates exports of lumber to the US, many other countries export wood products to the US. The Section 232 tariffs on lumber and wood products affect them in varying ways; some countries benefit from trade deals with the US that cap the rates, and others bear the full brunt. …Though lumber accounts for less than 20% of building costs, the National Association of Homebuilders has long said that restrictions on Canadian lumber translate to higher construction costs. [to access the full story a Bloomberg subscription is required]
President Trump unveiled sweeping tariffs on imported lumber and wood products that his administration says are needed to protect the US economy and boost domestic manufacturing. Starting Oct. 14, softwood lumber will face 10% duties, while kitchen cabinets, bathroom vanities, and other finished wood goods will be hit with 25% tariffs that rise further in January. The biggest blow will fall on Canada, the US’s top lumber supplier, whose lumber exports are already subject to separate duties totaling 35.19%. …Though Canada dominates exports of lumber to the US, many other countries export wood products to the US. The Section 232 tariffs on lumber and wood products affect them in varying ways; some countries benefit from trade deals with the US that cap the rates, and others bear the full brunt. …Though lumber accounts for less than 20% of building costs, the National Association of Homebuilders has long said that restrictions on Canadian lumber translate to higher construction costs. [to access the full story a Bloomberg subscription is required] Canada’s international trade deficit swelled to $6.3 billion in August, its second-largest shortfall on record, as new United States tariffs took a heavy toll on key exports and injected fresh volatility into cross-border flows. The latest figures, released by Statistics Canada, show how US trade policy continues to affect Canadian exporters and make the Bank of Canada’s next interest rate decision more complicated. Exports in August fell 3% by value and 3.2% in volume, led by sharp declines in copper ore and lumber shipments, both of which were hit by new US tariffs. …Imports, meanwhile, rose 0.9%, buoyed by higher consumer goods, a sign of resilient household demand, even as business investment remained soft. …Exports to the US, Canada’s largest trading partner, fell 3.4% in August after three consecutive monthly gains, and were down 8% year-over-year. Exports to non-US destinations edged up 1.8% from a year ago but slipped 2% from July.
Canada’s international trade deficit swelled to $6.3 billion in August, its second-largest shortfall on record, as new United States tariffs took a heavy toll on key exports and injected fresh volatility into cross-border flows. The latest figures, released by Statistics Canada, show how US trade policy continues to affect Canadian exporters and make the Bank of Canada’s next interest rate decision more complicated. Exports in August fell 3% by value and 3.2% in volume, led by sharp declines in copper ore and lumber shipments, both of which were hit by new US tariffs. …Imports, meanwhile, rose 0.9%, buoyed by higher consumer goods, a sign of resilient household demand, even as business investment remained soft. …Exports to the US, Canada’s largest trading partner, fell 3.4% in August after three consecutive monthly gains, and were down 8% year-over-year. Exports to non-US destinations edged up 1.8% from a year ago but slipped 2% from July. Canada’s merchandise trade deficit widened in August to C$6.32 billion ($4.53 billion) as exports fell faster in both value and volume than the rise in imports on a monthly basis, official government statistics showed on Tuesday. The trade deficit in August was led by drop in exports not only to its top trading partner the U.S. but also because its shipments to the rest of the world shrank in the month. Canada’s international trade numbers took a beating early this year as US President Trump imposed sectoral tariffs on the country, forcing businesses to reorient supply chain from its biggest trading partner. But the shift has been volatile and erratic. Analysts polled by Reuters had forecast the August trade deficit at C$5.55 billion, up from an upwardly revised C$3.82 billion in the prior month. Total exports dropped by 3% while imports increased 0.9%, StatsCan said.
Canada’s merchandise trade deficit widened in August to C$6.32 billion ($4.53 billion) as exports fell faster in both value and volume than the rise in imports on a monthly basis, official government statistics showed on Tuesday. The trade deficit in August was led by drop in exports not only to its top trading partner the U.S. but also because its shipments to the rest of the world shrank in the month. Canada’s international trade numbers took a beating early this year as US President Trump imposed sectoral tariffs on the country, forcing businesses to reorient supply chain from its biggest trading partner. But the shift has been volatile and erratic. Analysts polled by Reuters had forecast the August trade deficit at C$5.55 billion, up from an upwardly revised C$3.82 billion in the prior month. Total exports dropped by 3% while imports increased 0.9%, StatsCan said. It’s hard to find anything good to say about Canadian forestry stocks right now. Some of the biggest names in the sector have been on a downward slide for the past three years. … But the onslaught of grim news has highlighted some bargains. …Okay, the definition of attractive rests on an assumption that risk-averse investors might not want to embrace just yet: Despite Mr. Trump’s bluster, the US still needs Canadian lumber in a big way to feed its lumber-intensive home construction industry. Says who? The National Association of Home Builders, for one. …Some analysts believe that US forestry companies will struggle to replace Canadian softwood. Ben Isaacson, at Bank of Nova Scotia, estimates that US producers would have to build 50 new mills to become fully independent of Canadian lumber. Just two companies build the specialized equipment required in mills. They would struggle to supply even two mills a year. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
It’s hard to find anything good to say about Canadian forestry stocks right now. Some of the biggest names in the sector have been on a downward slide for the past three years. … But the onslaught of grim news has highlighted some bargains. …Okay, the definition of attractive rests on an assumption that risk-averse investors might not want to embrace just yet: Despite Mr. Trump’s bluster, the US still needs Canadian lumber in a big way to feed its lumber-intensive home construction industry. Says who? The National Association of Home Builders, for one. …Some analysts believe that US forestry companies will struggle to replace Canadian softwood. Ben Isaacson, at Bank of Nova Scotia, estimates that US producers would have to build 50 new mills to become fully independent of Canadian lumber. Just two companies build the specialized equipment required in mills. They would struggle to supply even two mills a year. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]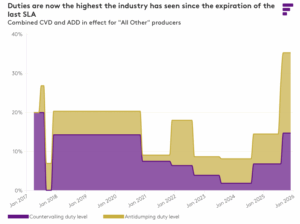 Although we are skeptical how effective the C$500 million in “transition” funding will be, the C$700 million in loan guarantees, which are clearly designed as a short-term lifeline for companies to weather the storm, seem pretty meaningful to the Canadian industry at first glance. …If Canadian producers were to simply absorb the incremental duty rate increase, using today’s FOB price for most Canadian softwood lumber and last year’s export volumes to the US translates to a “just pay it” cost of C$1.6-1.7 billion in additional duty payments over the next 12 months. Canadian mill operators are not in a financial position to simply absorb an additional 21-percentage-point increase in duties, so this is an extreme estimate of the true cost. Mills will curtail output rather than continue producing at heavy losses until prices adjust accordingly. Additionally, there is usually some degree of passthrough from the buyer to the seller.
Although we are skeptical how effective the C$500 million in “transition” funding will be, the C$700 million in loan guarantees, which are clearly designed as a short-term lifeline for companies to weather the storm, seem pretty meaningful to the Canadian industry at first glance. …If Canadian producers were to simply absorb the incremental duty rate increase, using today’s FOB price for most Canadian softwood lumber and last year’s export volumes to the US translates to a “just pay it” cost of C$1.6-1.7 billion in additional duty payments over the next 12 months. Canadian mill operators are not in a financial position to simply absorb an additional 21-percentage-point increase in duties, so this is an extreme estimate of the true cost. Mills will curtail output rather than continue producing at heavy losses until prices adjust accordingly. Additionally, there is usually some degree of passthrough from the buyer to the seller. The softwood lumber trade dispute between the US and Canada, which has led to ever-higher US import duties on Canadian lumber, has lasted for decades. …Canadian lumber has the backing NAHB, which sees lumber tariffs as exacerbating high costs for builders and worsening the US housing affordability crisis. There is currently a “Wall of Wood” in the US, after Canadian producers increased shipments to the US in anticipation of the hike to existing ADD and CVD duties in August. Expectations that a large increase in duties would force the closure of Canadian sawmills, lead to shortages, and a boost in lumber prices, overlooked the current weak US demand for lumber, according to Matt Layman. …As US homebuilders now face additional tariff-driven costs, including a 50% tariff on cabinets and vanities, it’s hard to see the lumber demand situation improving, even if more Canadian suppliers have to curtail production or close sawmills.
The softwood lumber trade dispute between the US and Canada, which has led to ever-higher US import duties on Canadian lumber, has lasted for decades. …Canadian lumber has the backing NAHB, which sees lumber tariffs as exacerbating high costs for builders and worsening the US housing affordability crisis. There is currently a “Wall of Wood” in the US, after Canadian producers increased shipments to the US in anticipation of the hike to existing ADD and CVD duties in August. Expectations that a large increase in duties would force the closure of Canadian sawmills, lead to shortages, and a boost in lumber prices, overlooked the current weak US demand for lumber, according to Matt Layman. …As US homebuilders now face additional tariff-driven costs, including a 50% tariff on cabinets and vanities, it’s hard to see the lumber demand situation improving, even if more Canadian suppliers have to curtail production or close sawmills.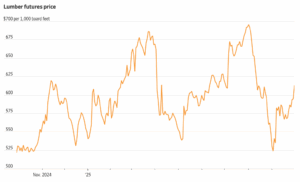 Lumber futures prices are trading higher after President Trump slapped a 10% tariff on wood imports. Lumber prices have been on a rollercoaster this year, lifted by higher import taxes and tugged lower by the deteriorating housing and construction markets. …Trump’s executive order said the additional 10% tariff, which will also raise the price of lumber from European suppliers like Germany and Sweden, is aimed at protecting domestic sawmills. …Analysts expect the tariff to benefit domestic sawyers and timberland owners, such as Weyerhaeuser and PotlatchDeltic, at the expense of competitors north of the border, who have been losing US market share because of the duties, challenges supplying their sawmills with logs and the abundance of cheap US pine. “Canadian lumber producers’ cash costs should further increase, resulting in capacity closures and a tightening of lumber supply-demand dynamics,” said Michael Roxland of Truist Securities. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
Lumber futures prices are trading higher after President Trump slapped a 10% tariff on wood imports. Lumber prices have been on a rollercoaster this year, lifted by higher import taxes and tugged lower by the deteriorating housing and construction markets. …Trump’s executive order said the additional 10% tariff, which will also raise the price of lumber from European suppliers like Germany and Sweden, is aimed at protecting domestic sawmills. …Analysts expect the tariff to benefit domestic sawyers and timberland owners, such as Weyerhaeuser and PotlatchDeltic, at the expense of competitors north of the border, who have been losing US market share because of the duties, challenges supplying their sawmills with logs and the abundance of cheap US pine. “Canadian lumber producers’ cash costs should further increase, resulting in capacity closures and a tightening of lumber supply-demand dynamics,” said Michael Roxland of Truist Securities. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required] The Trump administration’s latest tariffs on housing materials could raise the average cost of building a single-family home by nearly $9,000, according to a report Tuesday from UBS. Research analyst John Lovallo said the new levies include “an incremental 10% Section 232 tariff on softwood timber and lumber imports, as well as 25% levies on kitchen cabinets, vanities and upholstered wood products.” UBS estimates the lumber tariff will add about $720 per home, while cabinet and vanity tariffs could tack on another $280. Upholstered wood products were not included in the calculation because they are generally purchased by homeowners rather than builders. “As a result, we now estimate the total tariff impact on the cost to construct an average home at approximately $8.9K,” Lovallo wrote. …“Importantly, we continue to believe this cost impact will be spread throughout the entire housing value chain, with the builders perhaps best positioned to push back on suppliers,” he said.
The Trump administration’s latest tariffs on housing materials could raise the average cost of building a single-family home by nearly $9,000, according to a report Tuesday from UBS. Research analyst John Lovallo said the new levies include “an incremental 10% Section 232 tariff on softwood timber and lumber imports, as well as 25% levies on kitchen cabinets, vanities and upholstered wood products.” UBS estimates the lumber tariff will add about $720 per home, while cabinet and vanity tariffs could tack on another $280. Upholstered wood products were not included in the calculation because they are generally purchased by homeowners rather than builders. “As a result, we now estimate the total tariff impact on the cost to construct an average home at approximately $8.9K,” Lovallo wrote. …“Importantly, we continue to believe this cost impact will be spread throughout the entire housing value chain, with the builders perhaps best positioned to push back on suppliers,” he said. President Trump ordered fresh tariffs on softwood timber, lumber, and wood furnishings, even as housing groups warn the move could drive up construction costs and furniture-industry advocates said the levies would lead to US job losses. The tariffs may, however, prove more legally durable than Trump’s reciprocal country-by-country penalties because they fall under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act, the same legal tool the White House has used to justify duties on steel and aluminum. …The measures hit Canada especially hard because the country already faces duties of more than 35%, a result of recent but separate trade initiatives. Publicly traded lumber producers most directly exposed include Canada’s West Fraser Timber, Canfor, and Interfor. In the US, Weyerhaeuser, Boise Cascade, and Louisiana-Pacific are the closest listed peers, with stocks prices that often move in step with lumber tariffs and demand. US-based furniture retailers may also experience pain, with many dependent on foreign wood.
President Trump ordered fresh tariffs on softwood timber, lumber, and wood furnishings, even as housing groups warn the move could drive up construction costs and furniture-industry advocates said the levies would lead to US job losses. The tariffs may, however, prove more legally durable than Trump’s reciprocal country-by-country penalties because they fall under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act, the same legal tool the White House has used to justify duties on steel and aluminum. …The measures hit Canada especially hard because the country already faces duties of more than 35%, a result of recent but separate trade initiatives. Publicly traded lumber producers most directly exposed include Canada’s West Fraser Timber, Canfor, and Interfor. In the US, Weyerhaeuser, Boise Cascade, and Louisiana-Pacific are the closest listed peers, with stocks prices that often move in step with lumber tariffs and demand. US-based furniture retailers may also experience pain, with many dependent on foreign wood.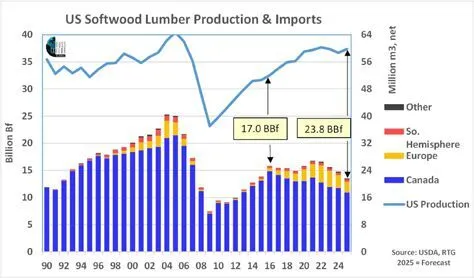
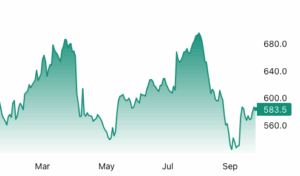 Lumber futures traded above $580 per thousand board feet in September, holding above earlier month lows as supply tightened and housing demand showed signs of renewal. Major producers such as Interfor reduced output through maintenance and shift cuts and mill idling while Canadian softwood flows remained constrained by tariff uncertainty which compressed prompt availability. Expectations of Fed further rate cuts later in 2025 encouraged forward looking builders to replenish inventories. New single family sales rose 20.5% to an 800k seasonally adjusted annualized rate in August which was the largest monthly rise since August 2022. Existing home sales held at a 4.00m SAAR in August and housing inventory stood at 1.53m units equivalent to 4.6 months of supply.
Lumber futures traded above $580 per thousand board feet in September, holding above earlier month lows as supply tightened and housing demand showed signs of renewal. Major producers such as Interfor reduced output through maintenance and shift cuts and mill idling while Canadian softwood flows remained constrained by tariff uncertainty which compressed prompt availability. Expectations of Fed further rate cuts later in 2025 encouraged forward looking builders to replenish inventories. New single family sales rose 20.5% to an 800k seasonally adjusted annualized rate in August which was the largest monthly rise since August 2022. Existing home sales held at a 4.00m SAAR in August and housing inventory stood at 1.53m units equivalent to 4.6 months of supply.

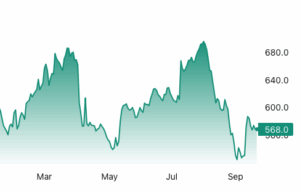 Lumber futures fell back below $570 per thousand board feet in September, reflecting the struggles in the US housing market. Builders are scaling back new construction amid a recent inventory glut and growing economic uncertainty, while the Trump administration’s fluctuating stance on tariffs for imported lumber over the past few months has added further volatility. Meanwhile, a significant gap remains between the number of homes for sale and the demand from Americans seeking housing. Affordability challenges have caused many buyers to withdraw in recent months, keeping construction activity muted throughout 2025. However, recent cuts in US interest rates, along with prospects of further easing, have helped curb some of the losses. Without a substantial increase in new home demand, the subdued pace of construction is likely to persist, as builders continue to compete with the steadily growing inventory of existing homes. [END]
Lumber futures fell back below $570 per thousand board feet in September, reflecting the struggles in the US housing market. Builders are scaling back new construction amid a recent inventory glut and growing economic uncertainty, while the Trump administration’s fluctuating stance on tariffs for imported lumber over the past few months has added further volatility. Meanwhile, a significant gap remains between the number of homes for sale and the demand from Americans seeking housing. Affordability challenges have caused many buyers to withdraw in recent months, keeping construction activity muted throughout 2025. However, recent cuts in US interest rates, along with prospects of further easing, have helped curb some of the losses. Without a substantial increase in new home demand, the subdued pace of construction is likely to persist, as builders continue to compete with the steadily growing inventory of existing homes. [END] BURNABY, BC — Interfor announced that it has entered into an agreement with a syndicate of underwriters led by RBC Capital Markets and Scotiabank, under which the Underwriters have agreed to purchase, on a bought deal basis, 12,437,800 common shares of the Company at a price of $10.05 per Common Share for gross proceeds of $125 million. The Company has agreed to grant the Underwriters an over-allotment option to purchase up to an additional 15% of the Common Shares. …The Company intends to use the net proceeds of the Offering to pay down existing indebtedness and for general corporate purposes. …Proceeds of the Offering are expected to further enhance Interfor’s flexibility to navigate near-term market volatility. The Offering is scheduled to close on or about October 1, 2025.
BURNABY, BC — Interfor announced that it has entered into an agreement with a syndicate of underwriters led by RBC Capital Markets and Scotiabank, under which the Underwriters have agreed to purchase, on a bought deal basis, 12,437,800 common shares of the Company at a price of $10.05 per Common Share for gross proceeds of $125 million. The Company has agreed to grant the Underwriters an over-allotment option to purchase up to an additional 15% of the Common Shares. …The Company intends to use the net proceeds of the Offering to pay down existing indebtedness and for general corporate purposes. …Proceeds of the Offering are expected to further enhance Interfor’s flexibility to navigate near-term market volatility. The Offering is scheduled to close on or about October 1, 2025. Housing starts and pre-sales in much of Southern Ontario have earned failing grades and are on track to get even worse, a new study warns — a situation that “should alarm policymakers across all three orders of government.” The report from University of Ottawa’s Missing Middle Initiative compares housing starts and sales in 34 municipalities across the Greater Toronto Area and neighbouring Southern Ontario cities for the first six months of 2025 with the same period from 2021–2024. It found starts are down 40% relative to that four-year average, with pre-construction condo sales plunging 89 per cent and other homes 70 per cent. The reduction in starts has direct employment implications, and the collapse in pre-construction sales, the study says, is “a clear indication that Ontario’s housing situation will get worse before it gets better, and that market weakness is not isolated to the condo market.” …The study paints a similarly bleak picture for the first half of 2025.
Housing starts and pre-sales in much of Southern Ontario have earned failing grades and are on track to get even worse, a new study warns — a situation that “should alarm policymakers across all three orders of government.” The report from University of Ottawa’s Missing Middle Initiative compares housing starts and sales in 34 municipalities across the Greater Toronto Area and neighbouring Southern Ontario cities for the first six months of 2025 with the same period from 2021–2024. It found starts are down 40% relative to that four-year average, with pre-construction condo sales plunging 89 per cent and other homes 70 per cent. The reduction in starts has direct employment implications, and the collapse in pre-construction sales, the study says, is “a clear indication that Ontario’s housing situation will get worse before it gets better, and that market weakness is not isolated to the condo market.” …The study paints a similarly bleak picture for the first half of 2025.)
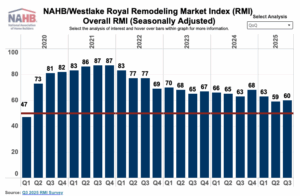 In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB/Westlake Royal Remodeling Market Index (RMI) posted a reading of 60, up one point compared to the previous quarter. With the reading of 60, the RMI remains solidly in positive territory above 50, but lower than it had been at any time from 2021 through 2024. Overall, remodelers remain optimistic about the market, although slightly less optimistic than they were at this time last year. The most significant headwinds they are facing include high material and labor costs, as well as economic and political uncertainty making some of their potential customers cautious about moving forward with remodeling projects. The small quarter-over-quarter improvement is consistent with flat construction spending trends and the current wait-and-see demand environment.
In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB/Westlake Royal Remodeling Market Index (RMI) posted a reading of 60, up one point compared to the previous quarter. With the reading of 60, the RMI remains solidly in positive territory above 50, but lower than it had been at any time from 2021 through 2024. Overall, remodelers remain optimistic about the market, although slightly less optimistic than they were at this time last year. The most significant headwinds they are facing include high material and labor costs, as well as economic and political uncertainty making some of their potential customers cautious about moving forward with remodeling projects. The small quarter-over-quarter improvement is consistent with flat construction spending trends and the current wait-and-see demand environment.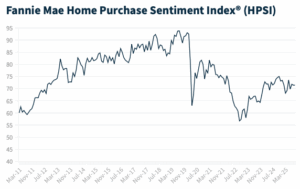 WASHINGTON, DC – Fannie Mae published the results of its September 2025
WASHINGTON, DC – Fannie Mae published the results of its September 2025 
 President Donald Trump has reignited debate over the nation’s housing shortage, calling on Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to spur a wave of new home construction. Trump accused large homebuilders of “sitting on 2 million empty lots, a record,” and likened their behavior to OPEC’s control of oil prices. …“I’m asking Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to get Big Homebuilders going and, by so doing, help restore the American Dream!” The president’s comments come as housing inventory has rebounded from historic lows in 2022, but builders continue to face limited incentives to ramp up construction. …Since taking office, Trump has made housing a central policy focus, including an executive order for emergency price relief and a campaign to pressure the Federal Reserve for lower rates. …Despite Trump’s calls, the mechanics of how Fannie and Freddie might spur more homebuilding remain unclear.
President Donald Trump has reignited debate over the nation’s housing shortage, calling on Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to spur a wave of new home construction. Trump accused large homebuilders of “sitting on 2 million empty lots, a record,” and likened their behavior to OPEC’s control of oil prices. …“I’m asking Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to get Big Homebuilders going and, by so doing, help restore the American Dream!” The president’s comments come as housing inventory has rebounded from historic lows in 2022, but builders continue to face limited incentives to ramp up construction. …Since taking office, Trump has made housing a central policy focus, including an executive order for emergency price relief and a campaign to pressure the Federal Reserve for lower rates. …Despite Trump’s calls, the mechanics of how Fannie and Freddie might spur more homebuilding remain unclear. 


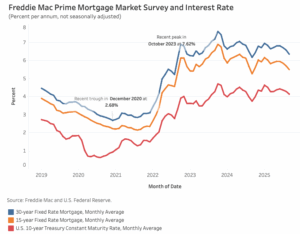 Average mortgage rates in September trended lower as the bond market priced in expectations of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.35%, 24 basis points (bps) lower than August. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 21 bps to 5.50%. Despite the recent drop, rates remain higher than a year ago as last September saw the lowest levels in about two years. The 30-year rate is currently higher by 17 basis points (bps), and the 15-year rate is higher by 24 bps, year-over-year. …Markets began pricing in rate cuts from the Fed at the start of the month, particularly after news that jobless claims rose while inflation remained modest. On September 17, the Federal Reserve announced a 25 bps cut to the federal funds rate, bringing the target range to 4.00% – 4.25%. Falling mortgage rates have already shown an impact on housing activity.
Average mortgage rates in September trended lower as the bond market priced in expectations of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.35%, 24 basis points (bps) lower than August. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate declined 21 bps to 5.50%. Despite the recent drop, rates remain higher than a year ago as last September saw the lowest levels in about two years. The 30-year rate is currently higher by 17 basis points (bps), and the 15-year rate is higher by 24 bps, year-over-year. …Markets began pricing in rate cuts from the Fed at the start of the month, particularly after news that jobless claims rose while inflation remained modest. On September 17, the Federal Reserve announced a 25 bps cut to the federal funds rate, bringing the target range to 4.00% – 4.25%. Falling mortgage rates have already shown an impact on housing activity. 

 Housing is the foundation of the economy. …It’s not a surprise, then, that the Trump administration recently said it was considering declaring the housing crisis a national emergency. The federal government alone can’t solve the housing crisis. That said, the administration could take steps that would meaningfully help make American housing more affordable. …One of the biggest issues is supply. …But
Housing is the foundation of the economy. …It’s not a surprise, then, that the Trump administration recently said it was considering declaring the housing crisis a national emergency. The federal government alone can’t solve the housing crisis. That said, the administration could take steps that would meaningfully help make American housing more affordable. …One of the biggest issues is supply. …But  Cardboard-box demand is slumping, flashing a potential warning about the health of the American consumer given that goods ranging from pizzas to ovens are transported in corrugated packaging. A historic run of pulp-mill closures is also signaling problems for the companies that make corrugated packaging as well as the timberland owners who sell them wood. International Paper, the country’s biggest box maker, announced last month the shutdown of two US containerboard mills, which make the brown paper that is folded into corrugated packaging. …It is a surprising turn in the e-commerce era. Box makers and analysts say demand presently suffers from uncertainty in US boardrooms and export markets because of President Trump’s tariffs as well as from weakening consumer spending. The sputtering housing market has also hurt, reducing the need for moving boxes as well as packaging for building products and appliances. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
Cardboard-box demand is slumping, flashing a potential warning about the health of the American consumer given that goods ranging from pizzas to ovens are transported in corrugated packaging. A historic run of pulp-mill closures is also signaling problems for the companies that make corrugated packaging as well as the timberland owners who sell them wood. International Paper, the country’s biggest box maker, announced last month the shutdown of two US containerboard mills, which make the brown paper that is folded into corrugated packaging. …It is a surprising turn in the e-commerce era. Box makers and analysts say demand presently suffers from uncertainty in US boardrooms and export markets because of President Trump’s tariffs as well as from weakening consumer spending. The sputtering housing market has also hurt, reducing the need for moving boxes as well as packaging for building products and appliances. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required] The UK timber industry is currently experiencing a crisis, even as it reports record sales of softwood, raising concerns over supply chain challenges, rising costs, and sustainability issues. The surge in softwood sales, particularly in the construction and woodworking sectors, has overshadowed the ongoing difficulties facing the industry. While the demand for timber has been high, particularly due to the growing construction boom and a shift toward more sustainable building materials, the challenges related to timber shortages and price increases remain deeply concerning for businesses across the sector. …The Timber Trade Federation (TTF) reports that softwood sales in the UK reached record levels in 2024. However, one of the most pressing issues facing the UK timber sector is the disruption of supply chains. The UK has faced considerable difficulty in securing a steady supply of raw timber. The global timber shortage has exacerbated the situation.
The UK timber industry is currently experiencing a crisis, even as it reports record sales of softwood, raising concerns over supply chain challenges, rising costs, and sustainability issues. The surge in softwood sales, particularly in the construction and woodworking sectors, has overshadowed the ongoing difficulties facing the industry. While the demand for timber has been high, particularly due to the growing construction boom and a shift toward more sustainable building materials, the challenges related to timber shortages and price increases remain deeply concerning for businesses across the sector. …The Timber Trade Federation (TTF) reports that softwood sales in the UK reached record levels in 2024. However, one of the most pressing issues facing the UK timber sector is the disruption of supply chains. The UK has faced considerable difficulty in securing a steady supply of raw timber. The global timber shortage has exacerbated the situation. Shares in packaging and paper group Mondi fell sharply on Monday after the company issued a cautionary outlook, citing weak demand and falling prices across pulp and paper grades. The warning rattled investor confidence in the paper and packaging sector, dragging Mondi shares to a 12-year low. The company said volumes remained subdued and selling prices declined in most grades, particularly in fine paper and corrugated segments. Citing fragile demand, Mondi described the trading environment as challenging and flagged continued weakness for the rest of the year. CEO Andrew King told analysts that demand for packaging “has not become worse, nor has it become better,” and that weakness in the fine paper market persisted. …Mondi’s warning underscores continued strain across the paper and packaging industry. Oversupply in key markets, weak industrial demand in Europe, and aggressive pricing competition are pressuring margins and volumes across the sector.
Shares in packaging and paper group Mondi fell sharply on Monday after the company issued a cautionary outlook, citing weak demand and falling prices across pulp and paper grades. The warning rattled investor confidence in the paper and packaging sector, dragging Mondi shares to a 12-year low. The company said volumes remained subdued and selling prices declined in most grades, particularly in fine paper and corrugated segments. Citing fragile demand, Mondi described the trading environment as challenging and flagged continued weakness for the rest of the year. CEO Andrew King told analysts that demand for packaging “has not become worse, nor has it become better,” and that weakness in the fine paper market persisted. …Mondi’s warning underscores continued strain across the paper and packaging industry. Oversupply in key markets, weak industrial demand in Europe, and aggressive pricing competition are pressuring margins and volumes across the sector.