 As world leaders gathered for the G7 summit last week in Kananaskis, Alberta, more than 50 wildfires burned across the province. The leaders’ joint statements included the Kananaskis Wildfire Charter, the first G7 document explicitly dedicated to co-ordinating international action on wildfire prevention, mitigation, response and recovery. It was agreed to by all the G7 leaders, as well as the heads of Australia, India, Mexico, South Korea and South Africa, non-G7 governments also invited to join this year’s summit. The charter outlines initiatives ranging from geospatial mapping and early warning systems to the adoption of wildfire-resilient infrastructure. Mathieu Bourbonnais, an assistant professor in environmental science at the University of British Columbia Okanagan and UBC research chair in wildfire management, said he is trying to be positive about the statement’s approach. “The other thing is, we’re doing a lot of this already”.
As world leaders gathered for the G7 summit last week in Kananaskis, Alberta, more than 50 wildfires burned across the province. The leaders’ joint statements included the Kananaskis Wildfire Charter, the first G7 document explicitly dedicated to co-ordinating international action on wildfire prevention, mitigation, response and recovery. It was agreed to by all the G7 leaders, as well as the heads of Australia, India, Mexico, South Korea and South Africa, non-G7 governments also invited to join this year’s summit. The charter outlines initiatives ranging from geospatial mapping and early warning systems to the adoption of wildfire-resilient infrastructure. Mathieu Bourbonnais, an assistant professor in environmental science at the University of British Columbia Okanagan and UBC research chair in wildfire management, said he is trying to be positive about the statement’s approach. “The other thing is, we’re doing a lot of this already”.

 Over 7,600 people shared their views on outdoor recreation in a first-ever public survey conducted by Mosaic. “The feedback we received tells us how important Mosaic’s managed forests are to people’s lives,” said Jimmie Hodgson at Mosaic. “It reinforces our responsibility to work toward solutions that reflect what we heard.” Early findings show:
Over 7,600 people shared their views on outdoor recreation in a first-ever public survey conducted by Mosaic. “The feedback we received tells us how important Mosaic’s managed forests are to people’s lives,” said Jimmie Hodgson at Mosaic. “It reinforces our responsibility to work toward solutions that reflect what we heard.” Early findings show:
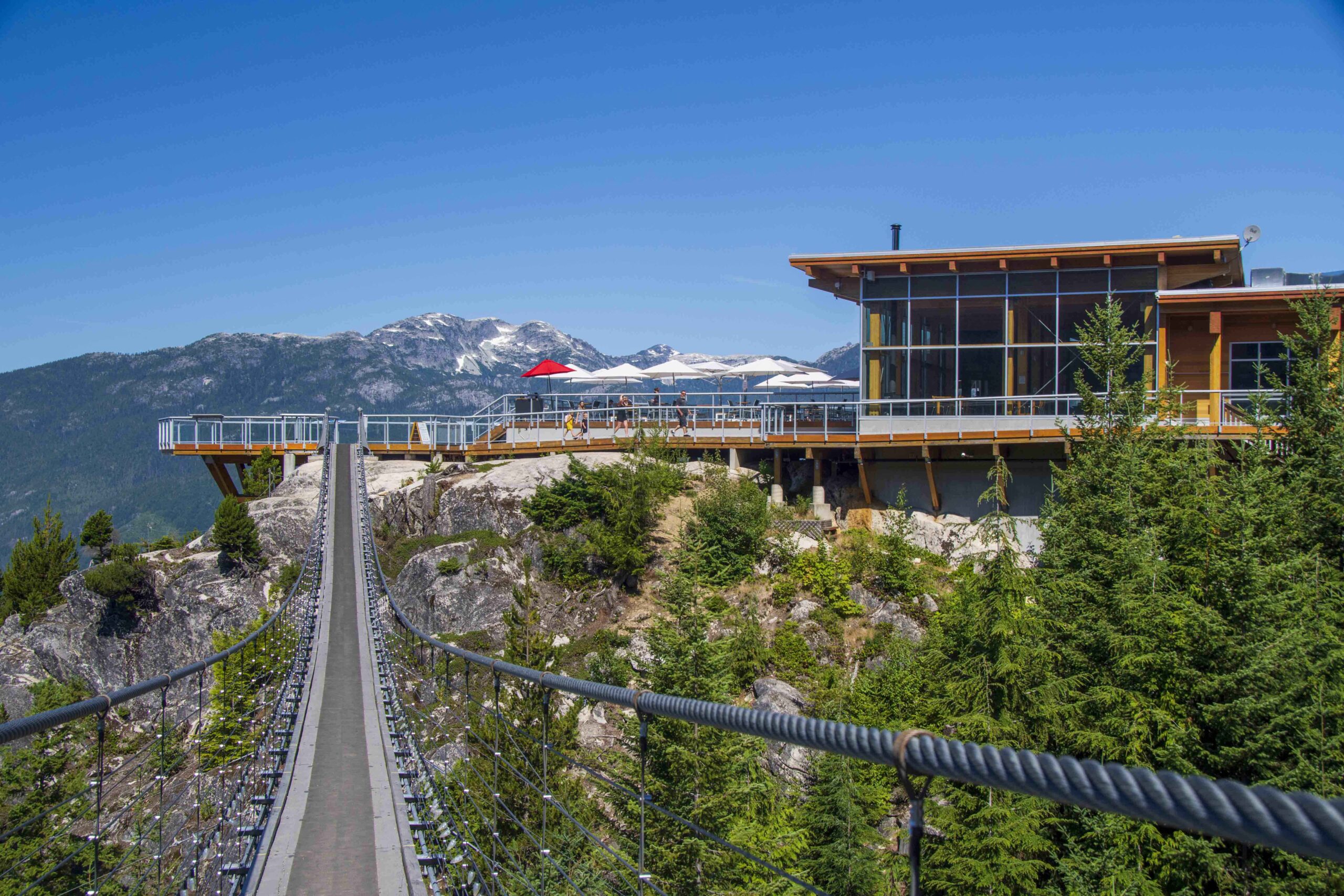 Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw (Squamish Nation) and the Province have signed an agreement to guide forest stewardship in Squamish Nation territory at a ceremony held at the top of the Sea-to-Sky gondola overlooking Átl’ḵa7tsem (Howe Sound). “This agreement will ensure our cultural sites and key environmental areas are protected for future generations. These have been our lands for thousands of years, and the fact they are now back under our direct control provides a greater sense of security for our people, and a strong optimism for our future,” said Sxwíxwtn Wilson Williams, Councillor and elected spokesperson, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw (Squamish Nation). …The next step will be to complete a ministerial order, which will include consultation with First Nations, and engagement with the public. It aims to establish objectives for the forestry sector to follow in alignment with the agreement and provide the Squamish Nation certainty in sites of high value.
Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw (Squamish Nation) and the Province have signed an agreement to guide forest stewardship in Squamish Nation territory at a ceremony held at the top of the Sea-to-Sky gondola overlooking Átl’ḵa7tsem (Howe Sound). “This agreement will ensure our cultural sites and key environmental areas are protected for future generations. These have been our lands for thousands of years, and the fact they are now back under our direct control provides a greater sense of security for our people, and a strong optimism for our future,” said Sxwíxwtn Wilson Williams, Councillor and elected spokesperson, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw (Squamish Nation). …The next step will be to complete a ministerial order, which will include consultation with First Nations, and engagement with the public. It aims to establish objectives for the forestry sector to follow in alignment with the agreement and provide the Squamish Nation certainty in sites of high value.
 Firefighters are urging hikers and mountain bikers not to enter trails closed due to a wildfire just north of Squamish, B.C., ahead of the Canada Day long weekend. The Dryden Creek wildfire, which was discovered on June 9, is considered under control by the B.C. Wildfire Service, but a local state of emergency remains in Squamish and a campfire ban remains in effect for the district. Fire suppression work is ongoing in the area, and evacuation orders and alerts remain due to the danger of trees falling and rocks rolling loose. Despite that, firefighters say they’re seeing people disobey trail closures, which could prove to be a risky decision. “Especially last weekend, numerous hikers and mountain bikers accessed trails that were closed,” said B.C. Wildfire fire information officer Jennifer Lohmeyer on Tuesday. “Some people even moved barriers that had been put in place to indicate that the trail was closed,” she added.
Firefighters are urging hikers and mountain bikers not to enter trails closed due to a wildfire just north of Squamish, B.C., ahead of the Canada Day long weekend. The Dryden Creek wildfire, which was discovered on June 9, is considered under control by the B.C. Wildfire Service, but a local state of emergency remains in Squamish and a campfire ban remains in effect for the district. Fire suppression work is ongoing in the area, and evacuation orders and alerts remain due to the danger of trees falling and rocks rolling loose. Despite that, firefighters say they’re seeing people disobey trail closures, which could prove to be a risky decision. “Especially last weekend, numerous hikers and mountain bikers accessed trails that were closed,” said B.C. Wildfire fire information officer Jennifer Lohmeyer on Tuesday. “Some people even moved barriers that had been put in place to indicate that the trail was closed,” she added. The City of Delta is undertaking an inventory of its trees. Crews started last week in Ladner, collecting data on street and park trees as part of Delta’s Urban Forest Strategy. In its request for proposals this spring for a qualified arboricultural consultant to conduct the urban forest subsection inventory of individual city-owned urban trees, the city noted it wanted to focus on street and park specimen trees. The project does not include trees on private property, nor is it the intent to include larger stands of trees in the city’s natural areas. The purpose of the project is to expand a tree inventory that was started in-house in 2023, improve asset management, as well as gain an accurate cost of a city-wide tree inventory for areas with low, medium and high canopy coverage.
The City of Delta is undertaking an inventory of its trees. Crews started last week in Ladner, collecting data on street and park trees as part of Delta’s Urban Forest Strategy. In its request for proposals this spring for a qualified arboricultural consultant to conduct the urban forest subsection inventory of individual city-owned urban trees, the city noted it wanted to focus on street and park specimen trees. The project does not include trees on private property, nor is it the intent to include larger stands of trees in the city’s natural areas. The purpose of the project is to expand a tree inventory that was started in-house in 2023, improve asset management, as well as gain an accurate cost of a city-wide tree inventory for areas with low, medium and high canopy coverage.
 It’s been hot in southern Ontario [with] apocalyptic news coverage out of Toronto…. “The world is burning,” announces the headline of a parenting advice column in The Globe and Mail. “Should we tell our children?” The author’s children are not told about forest fires… They are not told about the huge, ongoing increase in greenhouse gas emissions in Asia, cancelling out many times over the modest reductions achieved at great cost in North America and Europe. …The answer… is that natural variability is larger than the trend line produced by statistics. It’s true that Canada has seen more communities damaged or destroyed by fire, but that’s largely because there are more communities. …The Second World War was nearing its end, but the war on forest fires was just beginning, with the deployment of heavy equipment as well as aircraft. Saving timber was the goal, and the unintended consequences have piled up ever since.
It’s been hot in southern Ontario [with] apocalyptic news coverage out of Toronto…. “The world is burning,” announces the headline of a parenting advice column in The Globe and Mail. “Should we tell our children?” The author’s children are not told about forest fires… They are not told about the huge, ongoing increase in greenhouse gas emissions in Asia, cancelling out many times over the modest reductions achieved at great cost in North America and Europe. …The answer… is that natural variability is larger than the trend line produced by statistics. It’s true that Canada has seen more communities damaged or destroyed by fire, but that’s largely because there are more communities. …The Second World War was nearing its end, but the war on forest fires was just beginning, with the deployment of heavy equipment as well as aircraft. Saving timber was the goal, and the unintended consequences have piled up ever since. New film reveals the roots of B.C.’s wildfire crisis—and what we must do to stop it. A powerful new documentary exploring the causes and consequences of British Columbia’s escalating wildfire crisis will premiere to the public at the Vernon Performing Arts Centre Thursday June 26 at 7:00 pm. Titled B.C. is Burning, the 45-minute film delivers a sobering but hopeful look at what’s fueling today’s megafires—and the science-based solutions that could protect our forests, our communities, and our future. B.C. is Burning was independently produced and funded through community support, with Homestead Foods generously contributing half of the total budget. We also gratefully acknowledge major support from Skyline Helicopters, Padoin Reforestation, and Kalesnikoff.
New film reveals the roots of B.C.’s wildfire crisis—and what we must do to stop it. A powerful new documentary exploring the causes and consequences of British Columbia’s escalating wildfire crisis will premiere to the public at the Vernon Performing Arts Centre Thursday June 26 at 7:00 pm. Titled B.C. is Burning, the 45-minute film delivers a sobering but hopeful look at what’s fueling today’s megafires—and the science-based solutions that could protect our forests, our communities, and our future. B.C. is Burning was independently produced and funded through community support, with Homestead Foods generously contributing half of the total budget. We also gratefully acknowledge major support from Skyline Helicopters, Padoin Reforestation, and Kalesnikoff.

 For years, forest firefighters in Ontario have been calling on the provincial government to reclassify their jobs to recognize them as an emergency service in a bid to stem recruitment and retention issues. It’s a change the Ford government promised it would take on after sustained pressure from front-line staff and union officials. The province now says work to reclassify forest firefighters — officially called resource technicians — has been “completed,” and is blaming the Ontario Public Service Employees Union for a delay in announcing the move. Whether the terms the government has put forward address the substantive changes called for by forest firefighters is contested. Draft information seen by Global News shows the reclassification involves renaming positions within the existing union structure — and moving people one category further up the grid, for a raise of roughly $3 per hour.
For years, forest firefighters in Ontario have been calling on the provincial government to reclassify their jobs to recognize them as an emergency service in a bid to stem recruitment and retention issues. It’s a change the Ford government promised it would take on after sustained pressure from front-line staff and union officials. The province now says work to reclassify forest firefighters — officially called resource technicians — has been “completed,” and is blaming the Ontario Public Service Employees Union for a delay in announcing the move. Whether the terms the government has put forward address the substantive changes called for by forest firefighters is contested. Draft information seen by Global News shows the reclassification involves renaming positions within the existing union structure — and moving people one category further up the grid, for a raise of roughly $3 per hour.
 The U.S. Forest Service has proposed lifting the rule that bars roads in designated wilderness areas. The change could open 1.2 million acres of federal land in Arizona to logging. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins proposed canceling the 25-year-old “roadless rule” that created some 58 million acres of wilderness areas throughout the west. Arizona’s forested wilderness areas come to about 1.2 million acres of the 11 million acres of Forest Service land in Arizona. …Environmental groups immediately decried the proposal. They said it would increase the danger of wildfires and destroy wilderness areas essential to wildlife and many forms of recreation. …However, a century of logging, cattle grazing and fire suppression has dramatically increased tree densities across forested Northern Arizona … from about 50 per acre to more like 1,000 per acre in the past century. …The Four Forests Restoration Initiative has tried and mostly failed to ramp up logging on six million acres of non protected forest already criss-crossed with roads.
The U.S. Forest Service has proposed lifting the rule that bars roads in designated wilderness areas. The change could open 1.2 million acres of federal land in Arizona to logging. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins proposed canceling the 25-year-old “roadless rule” that created some 58 million acres of wilderness areas throughout the west. Arizona’s forested wilderness areas come to about 1.2 million acres of the 11 million acres of Forest Service land in Arizona. …Environmental groups immediately decried the proposal. They said it would increase the danger of wildfires and destroy wilderness areas essential to wildlife and many forms of recreation. …However, a century of logging, cattle grazing and fire suppression has dramatically increased tree densities across forested Northern Arizona … from about 50 per acre to more like 1,000 per acre in the past century. …The Four Forests Restoration Initiative has tried and mostly failed to ramp up logging on six million acres of non protected forest already criss-crossed with roads. President Trump’s Executive Order (EO) “Empowering Commonsense Wildfire Prevention and Response” is the latest of several significant federal policy efforts aimed at tackling the wildfire crisis. The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) focuses on embedding science, data, and technology into government to support communities in preparing for, responding to, and recovering from wildfires. FAS applauds several elements of President Trump’s EO. For instance, the EO correctly recognizes that wildfire technology and prescribed fire are powerful tools for reducing risk and strengthening wildfire resilience. FAS is also glad to see the Administration promote interagency coordination; emphasize the importance of state, local, and Tribal leadership; and recognize the intersection of wildfire resilience and other sectors, such as the grid and our bioeconomy. We are encouraged that the Administration and Congress are recognizing the severity of the wildfire crisis and elevating it as a national priority. Yet the devil is in the details when it comes to making real-world progress.
President Trump’s Executive Order (EO) “Empowering Commonsense Wildfire Prevention and Response” is the latest of several significant federal policy efforts aimed at tackling the wildfire crisis. The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) focuses on embedding science, data, and technology into government to support communities in preparing for, responding to, and recovering from wildfires. FAS applauds several elements of President Trump’s EO. For instance, the EO correctly recognizes that wildfire technology and prescribed fire are powerful tools for reducing risk and strengthening wildfire resilience. FAS is also glad to see the Administration promote interagency coordination; emphasize the importance of state, local, and Tribal leadership; and recognize the intersection of wildfire resilience and other sectors, such as the grid and our bioeconomy. We are encouraged that the Administration and Congress are recognizing the severity of the wildfire crisis and elevating it as a national priority. Yet the devil is in the details when it comes to making real-world progress. A proposal to sell public lands through the U.S. Senate’s budget reconciliation bill died by the sword of parliamentary procedure Monday, though the budgetary battle over public lands is not yet over. The Senate parliamentarian … nixed a provision to sell up to three million acres of Bureau of Land Management and U.S. Forest Service land across 11 states, including Wyoming, finding that it violated a rule limiting budget reconciliation bills to measures that are directly related to federal spending. The provision, which framed the sale as a way to alleviate the housing crisis by opening up more land for development, has roiled Westerners of all political persuasions since it was unveiled June 11. …U.S. Sen. Mike Lee, R-Utah, the architect of the provision, will introduce a new measure removing Forest Service land from the bill and narrowing the amount of BLM land for sale to tracts within 5 miles of population centers.
A proposal to sell public lands through the U.S. Senate’s budget reconciliation bill died by the sword of parliamentary procedure Monday, though the budgetary battle over public lands is not yet over. The Senate parliamentarian … nixed a provision to sell up to three million acres of Bureau of Land Management and U.S. Forest Service land across 11 states, including Wyoming, finding that it violated a rule limiting budget reconciliation bills to measures that are directly related to federal spending. The provision, which framed the sale as a way to alleviate the housing crisis by opening up more land for development, has roiled Westerners of all political persuasions since it was unveiled June 11. …U.S. Sen. Mike Lee, R-Utah, the architect of the provision, will introduce a new measure removing Forest Service land from the bill and narrowing the amount of BLM land for sale to tracts within 5 miles of population centers. A plan to sell more than 2 million acres of federal land in Oregon, Washington and 9 other Western states has been ruled out of Republicans’ big tax and spending cut bill after the Senate parliamentarian determined the proposal by Senate Energy Chairman Mike Lee would violate the chamber’s rules. Lee, an Utah Republican, has proposed selling public lands to states or other entities for use as housing or infrastructure. The plan would revive a longtime ambition of Western conservatives to cede lands to local control after a similar proposal failed in the House earlier this year.The proposal received a mixed reception Monday from the governors of Western states. New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham, a Democrat, called it problematic in her state because of the close relationship residents have with public lands. …Lee said he would keep trying. …Environmental advocates celebrated the ruling late Monday, but cautioned that Lee’s proposal was far from dead.
A plan to sell more than 2 million acres of federal land in Oregon, Washington and 9 other Western states has been ruled out of Republicans’ big tax and spending cut bill after the Senate parliamentarian determined the proposal by Senate Energy Chairman Mike Lee would violate the chamber’s rules. Lee, an Utah Republican, has proposed selling public lands to states or other entities for use as housing or infrastructure. The plan would revive a longtime ambition of Western conservatives to cede lands to local control after a similar proposal failed in the House earlier this year.The proposal received a mixed reception Monday from the governors of Western states. New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham, a Democrat, called it problematic in her state because of the close relationship residents have with public lands. …Lee said he would keep trying. …Environmental advocates celebrated the ruling late Monday, but cautioned that Lee’s proposal was far from dead.

 HELENA, Montana — US Secretary of Agriculture Brooke L. Rollins announced US Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Montana Governor Greg Gianforte signed a historic Shared Stewardship Memorandum of Understanding, establishing a new framework between the US Forest Service (USFS) and the State of Montana to advance forest restoration and reduce wildfire risk across the state. Montana’s Shared Stewardship Agreement expands collaborative efforts to accelerate active forest management, safeguard communities, and support sustainable timber production. …“By cutting burdensome, unnecessary red tape and empowering Montana to lead, we’re proving that through real partnership, conservation and economic growth can go hand-in-hand. …The Forest Service and Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) will jointly identify and execute large-scale forest management projects, initially focusing on approximately 200,000 acres in northwest Montana.
HELENA, Montana — US Secretary of Agriculture Brooke L. Rollins announced US Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Montana Governor Greg Gianforte signed a historic Shared Stewardship Memorandum of Understanding, establishing a new framework between the US Forest Service (USFS) and the State of Montana to advance forest restoration and reduce wildfire risk across the state. Montana’s Shared Stewardship Agreement expands collaborative efforts to accelerate active forest management, safeguard communities, and support sustainable timber production. …“By cutting burdensome, unnecessary red tape and empowering Montana to lead, we’re proving that through real partnership, conservation and economic growth can go hand-in-hand. …The Forest Service and Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) will jointly identify and execute large-scale forest management projects, initially focusing on approximately 200,000 acres in northwest Montana.

 WHITE SULPHUR SPRINGS, Montana — The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest has released a final decision for the Bonanza Project, located in the Castle Mountains just east of White Sulphur Springs. Primary management activities planned include timber harvest and prescribed fire. “The project area is highly impacted by the mountain pine beetle and some areas have experienced 90% tree mortality,” said District Ranger Jason Oltrogge. “The timber generated from this project will provide wood products to local companies and prescribed fire will restore forests and reduce wildfire severity.” The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest partnered with the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation to plan this project, and the joint effort made this project a reality. …The project includes commercial timber harvest on 1,980 acres and prescribed burning on 918 acres. Project implementation is anticipated to start later this summer.
WHITE SULPHUR SPRINGS, Montana — The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest has released a final decision for the Bonanza Project, located in the Castle Mountains just east of White Sulphur Springs. Primary management activities planned include timber harvest and prescribed fire. “The project area is highly impacted by the mountain pine beetle and some areas have experienced 90% tree mortality,” said District Ranger Jason Oltrogge. “The timber generated from this project will provide wood products to local companies and prescribed fire will restore forests and reduce wildfire severity.” The Helena-Lewis and Clark National Forest partnered with the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation to plan this project, and the joint effort made this project a reality. …The project includes commercial timber harvest on 1,980 acres and prescribed burning on 918 acres. Project implementation is anticipated to start later this summer.

 When U.S. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins announced on Monday that her department would be opening up more US Forest Service land to development, she did so with the caveat that just two states — Colorado and Idaho — would not be impacted. Rollins, who serves in President Donald Trump’s cabinet, unveiled the plans during a meeting of Western state governors in Santa Fe, where she told reporters that the Agriculture Department would be rescinding the 2001 “roadless rule” established under former President Bill Clinton. The rule, hailed by conservationists as a landmark preservation effort, protects roughly 58.5 million acres of backcountry Forest Service land from road construction, logging and other development. “For too long, Western states, especially those with large swaths of land administered by our incredible Forest Service, have been inhibited from innovating because of burdensome regulations imposed by the federal government,” Rollins said.
When U.S. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins announced on Monday that her department would be opening up more US Forest Service land to development, she did so with the caveat that just two states — Colorado and Idaho — would not be impacted. Rollins, who serves in President Donald Trump’s cabinet, unveiled the plans during a meeting of Western state governors in Santa Fe, where she told reporters that the Agriculture Department would be rescinding the 2001 “roadless rule” established under former President Bill Clinton. The rule, hailed by conservationists as a landmark preservation effort, protects roughly 58.5 million acres of backcountry Forest Service land from road construction, logging and other development. “For too long, Western states, especially those with large swaths of land administered by our incredible Forest Service, have been inhibited from innovating because of burdensome regulations imposed by the federal government,” Rollins said.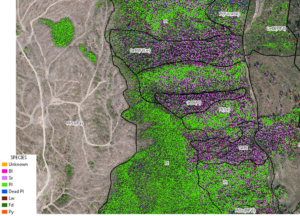 After a longer wait than expected, the a bill that would eliminate the unpopular Oregon Wildfire Hazard Map passed the Oregon House on June 24. Senate Bill 83 repeals a map meant to identify parts of Oregon at high risk of catastrophic wildfires but has become a lightning rod for anger from rural residents who say it places an unfair burden on them. The bill, which passed the Senate in April, now heads to the desk of Gov. Tina Kotek. The map, which was released earlier in 2025 and identifies areas at high wildfire risk, requires stricter building codes and creation of defensible space for roughly 100,000 properties in the name of wildfire prevention. The map was roundly condemned by impacted residents who said it was inaccurate, decreased property values and imposed burdensome regulations.
After a longer wait than expected, the a bill that would eliminate the unpopular Oregon Wildfire Hazard Map passed the Oregon House on June 24. Senate Bill 83 repeals a map meant to identify parts of Oregon at high risk of catastrophic wildfires but has become a lightning rod for anger from rural residents who say it places an unfair burden on them. The bill, which passed the Senate in April, now heads to the desk of Gov. Tina Kotek. The map, which was released earlier in 2025 and identifies areas at high wildfire risk, requires stricter building codes and creation of defensible space for roughly 100,000 properties in the name of wildfire prevention. The map was roundly condemned by impacted residents who said it was inaccurate, decreased property values and imposed burdensome regulations.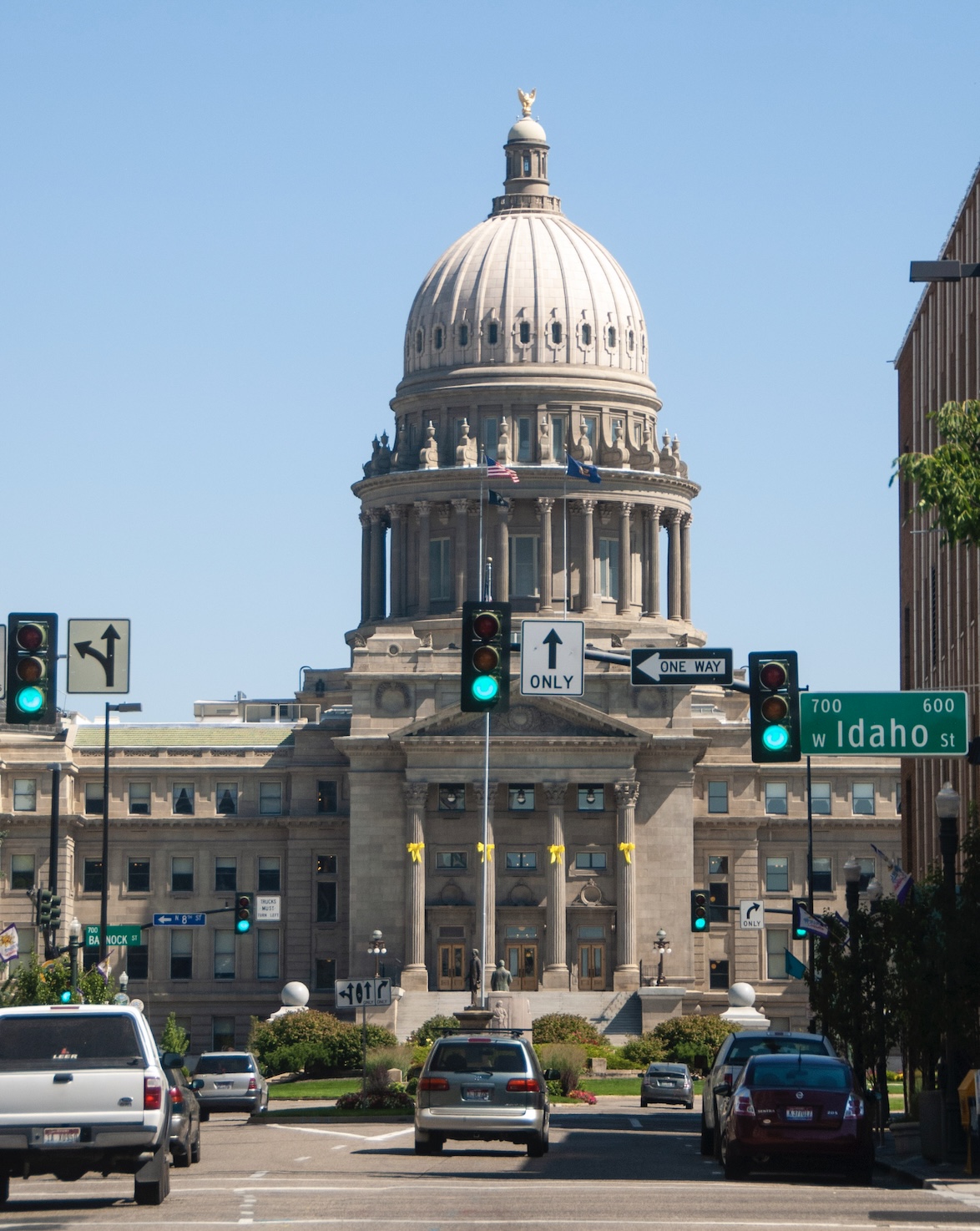 The Idaho roadless rule is not included in the effort by the Trump administration to rescind the national rule. A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Agriculture said, “the Idaho state-specific roadless rule was part of the Administrative Procedures Act petitions and will not be affected by rescinding the 2001 Roadless Rule.” The rule, a collaboratively written offshoot of the national rule, was spearheaded by then-Gov. Jim Risch in 2006. It is more flexible than the national rule and allows limited logging and road building in some of the state’s roadless forests that are not otherwise protected as wilderness areas. But it also offers more stringent protections to the most remote areas. …Risch’s Idaho-specific roadless rule, implemented in 2008, overrides the national rule and forbids logging and roads on 3.2 million acres of the state’s 9 million acres of inventoried roadless areas. Some logging and roads are allowed, under limited circumstances, on the remaining 6 million acres.
The Idaho roadless rule is not included in the effort by the Trump administration to rescind the national rule. A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Agriculture said, “the Idaho state-specific roadless rule was part of the Administrative Procedures Act petitions and will not be affected by rescinding the 2001 Roadless Rule.” The rule, a collaboratively written offshoot of the national rule, was spearheaded by then-Gov. Jim Risch in 2006. It is more flexible than the national rule and allows limited logging and road building in some of the state’s roadless forests that are not otherwise protected as wilderness areas. But it also offers more stringent protections to the most remote areas. …Risch’s Idaho-specific roadless rule, implemented in 2008, overrides the national rule and forbids logging and roads on 3.2 million acres of the state’s 9 million acres of inventoried roadless areas. Some logging and roads are allowed, under limited circumstances, on the remaining 6 million acres. Less than two weeks have passed since the public learned of a Senate proposal to sell off public lands, and now, the U.S. Department of Agriculture has removed roadless protections for more than 58 million acres of federal land across the nation. …Helena Hunters and Anglers …decided to call an emergency meeting for Tuesday to discuss the implications of the announcement. If roadless areas were truly gone, the group might not continue their yearly monitoring of roadless areas. Montana has almost 6.4 million acres of inventoried roadless areas… Helena Hunters and Anglers has been monitoring some of those roadless areas for the past few years to assess their condition, and some of the findings aren’t good. …A number of other conservation organizations immediately criticized the action, calling it another handout to corporations to the detriment of the American public and future generations. The Colorado-based Center for Western Priorities said Rollins’ reasons were suspect.
Less than two weeks have passed since the public learned of a Senate proposal to sell off public lands, and now, the U.S. Department of Agriculture has removed roadless protections for more than 58 million acres of federal land across the nation. …Helena Hunters and Anglers …decided to call an emergency meeting for Tuesday to discuss the implications of the announcement. If roadless areas were truly gone, the group might not continue their yearly monitoring of roadless areas. Montana has almost 6.4 million acres of inventoried roadless areas… Helena Hunters and Anglers has been monitoring some of those roadless areas for the past few years to assess their condition, and some of the findings aren’t good. …A number of other conservation organizations immediately criticized the action, calling it another handout to corporations to the detriment of the American public and future generations. The Colorado-based Center for Western Priorities said Rollins’ reasons were suspect.



