
President Trump says he’ll seek a swift Supreme Court ruling after a federal appeals court declared many of his tariffs illegal. In other Business news: Weyerhaeuser closed the sale of its Princeton, BC mill to Gorman; Western Forest Products unveiled a refreshed brand; lumber futures remain under pressure; and US construction spending fell 2.2% through July. Meanwhile: BC’s public service unions began job action; the BC Provincial Forest Advisory Council launched its engagement process; and the Canadian Institute of Forestry named Curtis Cook its new Executive Director.
In Forestry/Wildfire news: new analysis shows Canadian wildfire emissions quadrupled since the 1990s; Nova Scotia’s woodland travel ban faces a constitutional challenge; AI applications bring cautious optimism to the forest sector; and wildfires continue near Fort Providence, NWT, the Oregon Cascades, and Northern California. Meanwhile: rice husk boards are promoted as a substitute for lumber; and the latest market news from Canada Wood Group.
Finally, the 22nd Global Buyers Mission kicks off in Whistler tomorrow—uniting wood manufacturers and buyers.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor
 BC Wood is set to welcome delegates and buyers from British Columbia and around the world to the 22nd Annual Global Buyers Mission (GBM), kicking off tomorrow in Whistler, BC. This signature event brings Canadian wood manufacturers together with pre-qualified international buyers in an exclusive, business-focused environment. The GBM opens with a welcome breakfast, where Premier David Eby will address participants and officially launch the trade show. His presence underscores the critical role of BC’s wood and forestry sector in driving innovation, sustainability, and economic growth. Nearly 800 attendees are expected, a testament to the GBM’s significance in connecting Canadian producers with global markets.
BC Wood is set to welcome delegates and buyers from British Columbia and around the world to the 22nd Annual Global Buyers Mission (GBM), kicking off tomorrow in Whistler, BC. This signature event brings Canadian wood manufacturers together with pre-qualified international buyers in an exclusive, business-focused environment. The GBM opens with a welcome breakfast, where Premier David Eby will address participants and officially launch the trade show. His presence underscores the critical role of BC’s wood and forestry sector in driving innovation, sustainability, and economic growth. Nearly 800 attendees are expected, a testament to the GBM’s significance in connecting Canadian producers with global markets. WASHINGTON — US President Trump is indicating that he’ll ask the Supreme Court tomorrow to overturn a federal appeals court ruling that found many of his
WASHINGTON — US President Trump is indicating that he’ll ask the Supreme Court tomorrow to overturn a federal appeals court ruling that found many of his 


 Western is proud to launch a refreshed brand that better reflects who we are, where we’re going and what our customers, communities, and partners expect from us. Our refreshed brand is rooted in our belief that wood plays a vital role in building a more sustainable future. Wood has always been part of everyday life – in the homes we live in, the furniture we use and the warmth and comfort we seek in natural materials. At Western, we are proud to carry that legacy forward by helping meet today’s demand for beautiful, low-carbon building materials. This brand refresh is grounded in our long-term strategy and shaped by the people who make Western what it is. It reflects our continued commitment to quality, sustainability and stewardship. Explore the rest of our site to see how our refreshed brand reflects the care we put into everything we do, from forest to finished product.
Western is proud to launch a refreshed brand that better reflects who we are, where we’re going and what our customers, communities, and partners expect from us. Our refreshed brand is rooted in our belief that wood plays a vital role in building a more sustainable future. Wood has always been part of everyday life – in the homes we live in, the furniture we use and the warmth and comfort we seek in natural materials. At Western, we are proud to carry that legacy forward by helping meet today’s demand for beautiful, low-carbon building materials. This brand refresh is grounded in our long-term strategy and shaped by the people who make Western what it is. It reflects our continued commitment to quality, sustainability and stewardship. Explore the rest of our site to see how our refreshed brand reflects the care we put into everything we do, from forest to finished product.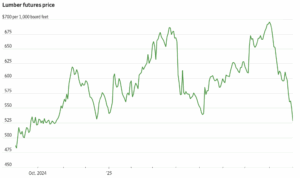 Lumber prices, which shed more than 20% in August, have continued to fall to start September, hitting their lowest price this year thanks to a glut of wood that was piled up ahead of a big increase in duties on Canadian imports. “There has clearly been a speculative inventory accumulation at every level from mills to single location lumber dealers,” said Matt Layman, who publishes Layman’s Lumber Guide “For the first time in my 40-plus year career there is indeed a wall of wood that must be liquidated.” As with many raw materials, the lumber market has been whipsawed by President Trump’s tariff threats. The White House is studying tariffs on imported lumber in the name of national security. …Any lumber tariff will come on top of duties on Canadian softwood lumber that rose to about 35% for most producers, from 15% last year. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
Lumber prices, which shed more than 20% in August, have continued to fall to start September, hitting their lowest price this year thanks to a glut of wood that was piled up ahead of a big increase in duties on Canadian imports. “There has clearly been a speculative inventory accumulation at every level from mills to single location lumber dealers,” said Matt Layman, who publishes Layman’s Lumber Guide “For the first time in my 40-plus year career there is indeed a wall of wood that must be liquidated.” As with many raw materials, the lumber market has been whipsawed by President Trump’s tariff threats. The White House is studying tariffs on imported lumber in the name of national security. …Any lumber tariff will come on top of duties on Canadian softwood lumber that rose to about 35% for most producers, from 15% last year. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]

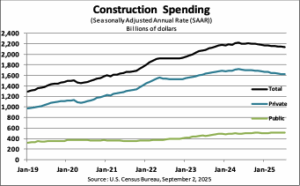 Construction spending in the United States reached $1,232.7 billion during the first seven months of 2025, a 2.2% decrease from $1,259.9 billion in the same period of 2024. Residential construction accounted for $524.7 billion, down 4.0%, while nonresidential construction declined 0.8% to $707.9 billion, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Private construction dropped 3.8% year-to-date to $946.5 billion. …Public construction increased 3.8% to $286.2 billion over the same period. …For the month of July 2025, construction spending was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $2,139.1 billion, down 0.1% from June and 2.8% below July 2024. Private sector construction decreased 0.2% from the previous month, while public construction rose 0.3%.
Construction spending in the United States reached $1,232.7 billion during the first seven months of 2025, a 2.2% decrease from $1,259.9 billion in the same period of 2024. Residential construction accounted for $524.7 billion, down 4.0%, while nonresidential construction declined 0.8% to $707.9 billion, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Private construction dropped 3.8% year-to-date to $946.5 billion. …Public construction increased 3.8% to $286.2 billion over the same period. …For the month of July 2025, construction spending was at a seasonally adjusted annual rate of $2,139.1 billion, down 0.1% from June and 2.8% below July 2024. Private sector construction decreased 0.2% from the previous month, while public construction rose 0.3%. The Canada Wood Group Newsletter includes these headlines and more:
The Canada Wood Group Newsletter includes these headlines and more:
 Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, remote piloting, and robotics are beginning to have a profound impact on the forest industry as we have known it, from forest management to log harvesting and delivery and right through to lumber production. This is only the beginning. In a recent interview, Bill Gates said that AI will have a more profound impact on humanity than the personal computer (PC) did. …From a forest management perspective, AI offers incredible potential for planning forest cutblocks and reforestation. In the face of climate change, forest companies will have no choice but to design forests that are more resilient to forest fires, pest and pathogens. The ability of AI to provide a variety of solutions in minutes, based on collating and analyzing past research, will make a forest technician’s job easier, while providing better solutions. This is a clear example of using AI for good—and we should make the most of it.
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, remote piloting, and robotics are beginning to have a profound impact on the forest industry as we have known it, from forest management to log harvesting and delivery and right through to lumber production. This is only the beginning. In a recent interview, Bill Gates said that AI will have a more profound impact on humanity than the personal computer (PC) did. …From a forest management perspective, AI offers incredible potential for planning forest cutblocks and reforestation. In the face of climate change, forest companies will have no choice but to design forests that are more resilient to forest fires, pest and pathogens. The ability of AI to provide a variety of solutions in minutes, based on collating and analyzing past research, will make a forest technician’s job easier, while providing better solutions. This is a clear example of using AI for good—and we should make the most of it.
 Colorado’s state-specific rule for largely protecting roadless areas in its national forests will be spared from a Trump administration effort to remove such protections on a broader basis. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins said in a news release on Wednesday that a public comment period is opening on her previously announced proposal to do away with the 2001 national roadless rule. But the Agriculture Department also said in the news release that state-specific rules in Colorado and Idaho won’t be affected by the proposal. Altogether, the proposal would apply to nearly 45 million acres, the release said. Eliminating the rule would open roadless areas to road-building. The existing rule has limited activities such as logging in those areas, and was instituted at the end of the Clinton administration.
Colorado’s state-specific rule for largely protecting roadless areas in its national forests will be spared from a Trump administration effort to remove such protections on a broader basis. Agriculture Secretary Brooke Rollins said in a news release on Wednesday that a public comment period is opening on her previously announced proposal to do away with the 2001 national roadless rule. But the Agriculture Department also said in the news release that state-specific rules in Colorado and Idaho won’t be affected by the proposal. Altogether, the proposal would apply to nearly 45 million acres, the release said. Eliminating the rule would open roadless areas to road-building. The existing rule has limited activities such as logging in those areas, and was instituted at the end of the Clinton administration. The Amazon rainforest is one of Earth’s most diverse ecosystems, playing a key role in maintaining regional and global climate stability. However, recent changes in land use, vegetation, and the climate have disrupted biosphere-atmosphere interactions, leading to significant alterations in the water, energy, and carbon cycles. …Here, we quantify the relative contributions of deforestation and global climate change to observed shifts in key Amazonian climate parameters. We analyzed long-term atmospheric and land cover change data across 29 areas in the Brazilian Legal Amazon from 1985 to 2020. …While the rise in atmospheric methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) mixing ratios is primarily driven by global emissions, deforestation has significantly increased surface air temperatures and reduced precipitation during the Amazonian dry season. Over the past 35 years, deforestation has accounted for approximately 74% of the ~ 21 mm dry season decline and 16.5% of the 2°C rise in maximum surface air temperature.
The Amazon rainforest is one of Earth’s most diverse ecosystems, playing a key role in maintaining regional and global climate stability. However, recent changes in land use, vegetation, and the climate have disrupted biosphere-atmosphere interactions, leading to significant alterations in the water, energy, and carbon cycles. …Here, we quantify the relative contributions of deforestation and global climate change to observed shifts in key Amazonian climate parameters. We analyzed long-term atmospheric and land cover change data across 29 areas in the Brazilian Legal Amazon from 1985 to 2020. …While the rise in atmospheric methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) mixing ratios is primarily driven by global emissions, deforestation has significantly increased surface air temperatures and reduced precipitation during the Amazonian dry season. Over the past 35 years, deforestation has accounted for approximately 74% of the ~ 21 mm dry season decline and 16.5% of the 2°C rise in maximum surface air temperature.  The federal government is attempting to abandon years of climate science and regulation, and officials from Washington state are warning those efforts will drastically slow the country’s ability to cut greenhouse gas emissions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency no longer wants to classify greenhouse gas emissions as dangerous and, therefore, something that must be regulated. The agency is now in the middle of a public comment process to reverse its long-standing course. Public officials and climate change experts from across the country are testifying against the federal government’s new direction. Among those in opposition is Joel Creswell, who manages the climate pollution reduction program with Washington state’s Department of Ecology. He said the EPA’s process is built on unscientific research and cherry-picked data. It’s also likely illegal, Creswell said. The federal government is trying to provide the “appearance of a science-based reason” not to regulate greenhouse gases, Creswell said.
The federal government is attempting to abandon years of climate science and regulation, and officials from Washington state are warning those efforts will drastically slow the country’s ability to cut greenhouse gas emissions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency no longer wants to classify greenhouse gas emissions as dangerous and, therefore, something that must be regulated. The agency is now in the middle of a public comment process to reverse its long-standing course. Public officials and climate change experts from across the country are testifying against the federal government’s new direction. Among those in opposition is Joel Creswell, who manages the climate pollution reduction program with Washington state’s Department of Ecology. He said the EPA’s process is built on unscientific research and cherry-picked data. It’s also likely illegal, Creswell said. The federal government is trying to provide the “appearance of a science-based reason” not to regulate greenhouse gases, Creswell said.

