 BC Premier David Eby had a ‘frank discussion’ with US ambassador Pete Hoekstra on the lumber dispute and tariffs. In related news: Canada is investing $229M to help retrain tariff-hit Ontario workers; and the US Department of Labor is supporting laidoff workers at Roseburg’s Dillard mill. Meanwhile: Domtar’s Seth Kursman responds to report claiming Canadian firms supported US election deniers; and Sweden’s Södras pulp mill pursues renewable hydrogen.
BC Premier David Eby had a ‘frank discussion’ with US ambassador Pete Hoekstra on the lumber dispute and tariffs. In related news: Canada is investing $229M to help retrain tariff-hit Ontario workers; and the US Department of Labor is supporting laidoff workers at Roseburg’s Dillard mill. Meanwhile: Domtar’s Seth Kursman responds to report claiming Canadian firms supported US election deniers; and Sweden’s Södras pulp mill pursues renewable hydrogen.
In Forestry news: Quesnel City Council endorses Forestry is a Solution campaign; the importance of Mosaic’s new stewardship pilot in the Kohsilah watershed is stressed; access to Washington’s private forests is said to be in decline; the Roadless Rule gets more pushback from Oregon and Montana ENGOs; and IKEA faces timber traceability test un EU Deforestation Regulation.
Finally, the WorkSafeBC surplus debate: prudent rate management—or a rainy-day fund already spent?
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor




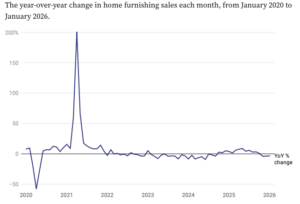 Unfortunately for retailers in the home sector, 2026 will likely look an awful lot like 2025. …While the pandemic offered a temporary financial boost, broad economic uncertainty caused many consumers to pull back on discretionary spending, leading to a decline in the high-ticket purchases. …The category has consistently seen year-over-year sales declines, according to the US Department of Commerce. …As was the case over the past few years, the weak housing market — driven by a lack of inventory and elevated interest rates — poses one of the biggest threats to the home sector this year. “The housing market is just stuck in neutral,” Zak Stambor said. “By and large, just few people are moving, and the lack of housing turnover means there’s a smaller-than-normal market for home goods.” “It’s the uncertainty that’s really driving the hesitation on the consumer side — where they should go, when they should buy, what they should buy in this market.”
Unfortunately for retailers in the home sector, 2026 will likely look an awful lot like 2025. …While the pandemic offered a temporary financial boost, broad economic uncertainty caused many consumers to pull back on discretionary spending, leading to a decline in the high-ticket purchases. …The category has consistently seen year-over-year sales declines, according to the US Department of Commerce. …As was the case over the past few years, the weak housing market — driven by a lack of inventory and elevated interest rates — poses one of the biggest threats to the home sector this year. “The housing market is just stuck in neutral,” Zak Stambor said. “By and large, just few people are moving, and the lack of housing turnover means there’s a smaller-than-normal market for home goods.” “It’s the uncertainty that’s really driving the hesitation on the consumer side — where they should go, when they should buy, what they should buy in this market.” City of Powell River councillors were provided an overview on March 5 of Tla’amin Nation’s negotiations to repatriate access to forest lands currently held by Western Forest Products (WFP). Adam Culos, general manager of Thichum Forest Products, said that Tla’amin had announced a milestone agreement, where Thichum Forest Products, through Tla’amin, is working on an agreement with WFP to acquire Tree Farm Licence 39 block one. Seanna McConnell, Western Forest Products vice-president, Indigenous partnerships, said Qwoqwnes Forestry Holdings Limited Partnership, wholly owned by Tla’amin, will be purchasing 100 per cent ownership of WFP’s Stillwater forest operation for $80 million. …Culos said the acquisition … supports Thichum’s long-term success through investment in their business and the future of the community, [adding] that almost all the wood supplies domestic mills, so there are three fibre supply agreements. One will be WFP, supporting the company’s five coastal mills, along with Mosaic Forest Management and Domtar.
City of Powell River councillors were provided an overview on March 5 of Tla’amin Nation’s negotiations to repatriate access to forest lands currently held by Western Forest Products (WFP). Adam Culos, general manager of Thichum Forest Products, said that Tla’amin had announced a milestone agreement, where Thichum Forest Products, through Tla’amin, is working on an agreement with WFP to acquire Tree Farm Licence 39 block one. Seanna McConnell, Western Forest Products vice-president, Indigenous partnerships, said Qwoqwnes Forestry Holdings Limited Partnership, wholly owned by Tla’amin, will be purchasing 100 per cent ownership of WFP’s Stillwater forest operation for $80 million. …Culos said the acquisition … supports Thichum’s long-term success through investment in their business and the future of the community, [adding] that almost all the wood supplies domestic mills, so there are three fibre supply agreements. One will be WFP, supporting the company’s five coastal mills, along with Mosaic Forest Management and Domtar.
 Quesnel City Council has endorsed the “Forestry is a Solution” campaign. Erin Robinson, Forestry Initiatives Manager at the City, talked about the “Forestry is a Solution” campaign at the most recent Council meeting. “It was launched in January at the BC Natural Resources Forum in Prince George. The “Forestry is a Solution” campaign is led by a coalition of forest sector organizations, community leaders, workers, and industry advocates to demonstrate strong public support for British Columbia’s forest sector. The initiative highlights forestry’s role in: supporting affordable housing, reducing wildfire risk through active forest management, sustaining family-supporting jobs, generating public revenues, and contributing to lower carbon construction.” Robinson said it is in line with Council’s concerns over the current state of the industry.
Quesnel City Council has endorsed the “Forestry is a Solution” campaign. Erin Robinson, Forestry Initiatives Manager at the City, talked about the “Forestry is a Solution” campaign at the most recent Council meeting. “It was launched in January at the BC Natural Resources Forum in Prince George. The “Forestry is a Solution” campaign is led by a coalition of forest sector organizations, community leaders, workers, and industry advocates to demonstrate strong public support for British Columbia’s forest sector. The initiative highlights forestry’s role in: supporting affordable housing, reducing wildfire risk through active forest management, sustaining family-supporting jobs, generating public revenues, and contributing to lower carbon construction.” Robinson said it is in line with Council’s concerns over the current state of the industry.
 ELOCHOMAN RIVER VALLEY, Washington — Investment companies have whittled away the land hunters can use in Wahkiakum and Pacific counties. Access to tens of thousands of acres of longtime hunting grounds is now blocked because a new generation of private landowners won’t offer access. The landowners are often investment companies, not based in the region or even the country. Not only is hunting off limits on their lands, they also often block access to adjacent properties that are state-owned — and therefore should be public — or adjacent privately owned property that still allows free hunting. Steve Ogden, an assistant manager for land operations at Washington Department of Natural Resources, said the agency’s hands are tied — private landowners can’t be forced to allow people on their land. The companies’ land restrictions have begun to erase generations-old family traditions, especially among the working class, and reduce access to affordable foods, like elk, in Washington’s second-poorest county.
ELOCHOMAN RIVER VALLEY, Washington — Investment companies have whittled away the land hunters can use in Wahkiakum and Pacific counties. Access to tens of thousands of acres of longtime hunting grounds is now blocked because a new generation of private landowners won’t offer access. The landowners are often investment companies, not based in the region or even the country. Not only is hunting off limits on their lands, they also often block access to adjacent properties that are state-owned — and therefore should be public — or adjacent privately owned property that still allows free hunting. Steve Ogden, an assistant manager for land operations at Washington Department of Natural Resources, said the agency’s hands are tied — private landowners can’t be forced to allow people on their land. The companies’ land restrictions have begun to erase generations-old family traditions, especially among the working class, and reduce access to affordable foods, like elk, in Washington’s second-poorest county.
 Four Montana-based Conservation Groups — Alliance for the Wild Rockies, Gallatin Wildlife Association, Native Ecosystems Council, and Council on Fish & Wildlife — sued the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service and U.S. Forest Service for removing wildlife protections on 1.1 million acres of the Beaverhead-Deerlodge National Forest in Montana. The federal government agencies issued a “Forest Plan Amendment” in 2025 to remove protections on 1.1 million acres of habitat that was formerly mapped and protected as “lynx habitat” for the Canada lynx, a threatened species listed under the Endangered Species Act. …The lynx population in the Greater Yellowstone Area is currently at risk of extinction, but if managed properly, the Beaverhead-Deerlodge National Forest could aid the recovery of the imperiled Greater Yellowstone lynx population by serving as a connectivity corridor with the healthier lynx populations in Northern Montana.
Four Montana-based Conservation Groups — Alliance for the Wild Rockies, Gallatin Wildlife Association, Native Ecosystems Council, and Council on Fish & Wildlife — sued the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service and U.S. Forest Service for removing wildlife protections on 1.1 million acres of the Beaverhead-Deerlodge National Forest in Montana. The federal government agencies issued a “Forest Plan Amendment” in 2025 to remove protections on 1.1 million acres of habitat that was formerly mapped and protected as “lynx habitat” for the Canada lynx, a threatened species listed under the Endangered Species Act. …The lynx population in the Greater Yellowstone Area is currently at risk of extinction, but if managed properly, the Beaverhead-Deerlodge National Forest could aid the recovery of the imperiled Greater Yellowstone lynx population by serving as a connectivity corridor with the healthier lynx populations in Northern Montana.  As the EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) nears implementation this year, furniture giant IKEA may need stronger traceability systems to prove its timber isn’t linked to post-2020 deforestation. Although nearly all IKEA wood is FSC-certified or recycled, past investigations show this voluntary scheme can miss illegal or unsustainable logging. The EUDR requires geolocation data and stricter due diligence than existing certifications or regulations, but repeated delays and possible rule changes have created uncertainty for companies like IKEA preparing to comply. Industry watchdogs say high-profile companies like IKEA can “do more” to champion the landmark regulation and implement leading wood traceability systems, rather than relying solely on existing — voluntary— certification schemes.
As the EU’s Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) nears implementation this year, furniture giant IKEA may need stronger traceability systems to prove its timber isn’t linked to post-2020 deforestation. Although nearly all IKEA wood is FSC-certified or recycled, past investigations show this voluntary scheme can miss illegal or unsustainable logging. The EUDR requires geolocation data and stricter due diligence than existing certifications or regulations, but repeated delays and possible rule changes have created uncertainty for companies like IKEA preparing to comply. Industry watchdogs say high-profile companies like IKEA can “do more” to champion the landmark regulation and implement leading wood traceability systems, rather than relying solely on existing — voluntary— certification schemes.
 When it comes to WorkSafeBC, one of the most misunderstood issues we hear about from business groups is the surplus. Specifically, many small-business associations have been calling on WorkSafeBC to rebate the surplus back to employers since our funding level is above target. For background, the funding level is simply a ratio of assets over liabilities on a funding basis. …What is also not well understood is that WorkSafeBC has been returning significant amounts of surplus funds to employers annually to keep rates both stable and below the actual costs of the system. …The reality is that if WorkSafeBC refunded the entire surplus to employers we would no longer be able to price premiums below system costs, meaning rates would have to be raised in subsequent years. …Rate stability for employers is a priority for WorkSafeBC. Some sectors benefiting from rate reductions in 2026 include sawmills (down 40%), framing and residential forming (down 40%).
When it comes to WorkSafeBC, one of the most misunderstood issues we hear about from business groups is the surplus. Specifically, many small-business associations have been calling on WorkSafeBC to rebate the surplus back to employers since our funding level is above target. For background, the funding level is simply a ratio of assets over liabilities on a funding basis. …What is also not well understood is that WorkSafeBC has been returning significant amounts of surplus funds to employers annually to keep rates both stable and below the actual costs of the system. …The reality is that if WorkSafeBC refunded the entire surplus to employers we would no longer be able to price premiums below system costs, meaning rates would have to be raised in subsequent years. …Rate stability for employers is a priority for WorkSafeBC. Some sectors benefiting from rate reductions in 2026 include sawmills (down 40%), framing and residential forming (down 40%). One of the most persistent myths in BC business circles is that WorkSafeBC is sitting on a massive surplus—a piggy bank that should be cracked open and handed back to employers. Manitoba did it, Ontario did it. …So why not BC? Because the surplus is depleted. It didn’t disappear overnight. It was frittered away, year by year, policy by policy, under an NDP government. …And now, BC’s small business owners are staring down the consequences. …According to WorkSafeBC’s own financial statements, in 2019 the system was funded at 153%—a full 23 points above the 130% floor set by policy and insurance best practices. That cushion, billions built up over decades, was a rainy day fund. It was never meant to finance an ever-expanding bureaucratic empire. …In 2019, WorkSafeBC’s rate of $1.55 per $100 of assessable payroll was among the lowest in Canada—only three provinces were cheaper. By 2024, that same $1.55 is higher than every province except two.
One of the most persistent myths in BC business circles is that WorkSafeBC is sitting on a massive surplus—a piggy bank that should be cracked open and handed back to employers. Manitoba did it, Ontario did it. …So why not BC? Because the surplus is depleted. It didn’t disappear overnight. It was frittered away, year by year, policy by policy, under an NDP government. …And now, BC’s small business owners are staring down the consequences. …According to WorkSafeBC’s own financial statements, in 2019 the system was funded at 153%—a full 23 points above the 130% floor set by policy and insurance best practices. That cushion, billions built up over decades, was a rainy day fund. It was never meant to finance an ever-expanding bureaucratic empire. …In 2019, WorkSafeBC’s rate of $1.55 per $100 of assessable payroll was among the lowest in Canada—only three provinces were cheaper. By 2024, that same $1.55 is higher than every province except two.