 Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada union says cuts at Natural Resources Canada threaten science-based expertise on forest fires and sustainable resource management. In related news: Western Forest Products sawmill curtailments to extend into 2026; Packaging Corporation of America to partially close its Wallula, Washington containerboard plant; and Campbell River mayor says Crofton mill closure is a warning BC can no longer ignore.
Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada union says cuts at Natural Resources Canada threaten science-based expertise on forest fires and sustainable resource management. In related news: Western Forest Products sawmill curtailments to extend into 2026; Packaging Corporation of America to partially close its Wallula, Washington containerboard plant; and Campbell River mayor says Crofton mill closure is a warning BC can no longer ignore.
In Forestry/Climate news: 2025 wildfire emissions reach records in Europe and Canada; EU Council and Parliament reach deal on deforestation regulation; Ontario’s logging roads provide vital infrastructure; BC Timber Sales to harvest old-growth in the northwest; and an Okanagan activist says loggers use fire mitigation for profit. Meanwhile: the Washington Forest Industry gears up for 2026 legislative session; and the implications of Australia’s new forestry standards remains unclear.
Finally, optimism for salmon stream restoration near Gold River, BC—with Western Forest Product’s support.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor

 Over 600 public servants were notified this week that their jobs are on the line, with Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) feeling the brunt of the potential cuts. The Public Service Alliance of Canada (PSAC) said in a news release that 219 workers at NRCan received warning that their position could be cut. In addition, the Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada (PIPSC) told Radio-Canada that 200 of its members at NRCan were also given notices of a potential layoff. …Jean Bérubé, a forest pathologist at NRCan who is also a union rep for 3,000 federal research scientists, said he was informed his position is being eliminated.The federal government’s cuts to the public service feel similar to those occurring south of the border under the second administration of U.S. President Donald Trump, he said. …Bérubé pointed to the emergence of the invasive Emerald ash borer that has killed millions of ash trees in Canada’s urban areas.
Over 600 public servants were notified this week that their jobs are on the line, with Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) feeling the brunt of the potential cuts. The Public Service Alliance of Canada (PSAC) said in a news release that 219 workers at NRCan received warning that their position could be cut. In addition, the Professional Institute of the Public Service of Canada (PIPSC) told Radio-Canada that 200 of its members at NRCan were also given notices of a potential layoff. …Jean Bérubé, a forest pathologist at NRCan who is also a union rep for 3,000 federal research scientists, said he was informed his position is being eliminated.The federal government’s cuts to the public service feel similar to those occurring south of the border under the second administration of U.S. President Donald Trump, he said. …Bérubé pointed to the emergence of the invasive Emerald ash borer that has killed millions of ash trees in Canada’s urban areas. Western Forest Products says the temporary curtailment at its Chemainus sawmill will extend into the new year, while work slowdowns are expected at its other mills across Vancouver Island in December. The WFP curtailment in Chemainus began in June, affecting about 150 workers, with work yet to resume. …Meanwhile, reduced hours are expected at other work sites on the Island later this month. “In the latter half of December, we will take temporary downtime at our Saltair mill in Ladysmith, Duke Point mill in Nanaimo, and Cowichan Bay mill in Duncan,” said Babita Khunkhun, senior director of communications at WFP. “This will involve reduced operating hours, an extended holiday break and adjusted shift schedules.” Khunkhun says regular operations are expected to resume at all of those mills – except for Chemainus – on Jan. 6 “depending on market conditions and available log supply.”
Western Forest Products says the temporary curtailment at its Chemainus sawmill will extend into the new year, while work slowdowns are expected at its other mills across Vancouver Island in December. The WFP curtailment in Chemainus began in June, affecting about 150 workers, with work yet to resume. …Meanwhile, reduced hours are expected at other work sites on the Island later this month. “In the latter half of December, we will take temporary downtime at our Saltair mill in Ladysmith, Duke Point mill in Nanaimo, and Cowichan Bay mill in Duncan,” said Babita Khunkhun, senior director of communications at WFP. “This will involve reduced operating hours, an extended holiday break and adjusted shift schedules.” Khunkhun says regular operations are expected to resume at all of those mills – except for Chemainus – on Jan. 6 “depending on market conditions and available log supply.”
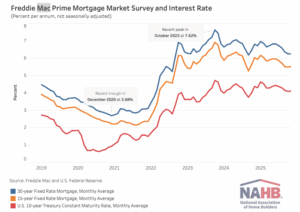 The average mortgage rate in November continued to trend lower to its lowest level in over a year. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.24% in November, 2 basis points (bps) lower than in October. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate increased 3 bps to 5.51%. Both the 30-year and 15-year rates remain lower than a year ago, dropping by 57 bps and 52 bps year-over-year, respectively. …Falling mortgage rates have shown some impact on housing activity. Mortgage application activity continues to strengthen, led by increases in adjustable-rate mortgages and refinancing applications. Additionally, existing home sales rose to an eight-month high in October. There is no data available for new home sales in October due to the government shutdown.
The average mortgage rate in November continued to trend lower to its lowest level in over a year. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.24% in November, 2 basis points (bps) lower than in October. Meanwhile, the 15-year rate increased 3 bps to 5.51%. Both the 30-year and 15-year rates remain lower than a year ago, dropping by 57 bps and 52 bps year-over-year, respectively. …Falling mortgage rates have shown some impact on housing activity. Mortgage application activity continues to strengthen, led by increases in adjustable-rate mortgages and refinancing applications. Additionally, existing home sales rose to an eight-month high in October. There is no data available for new home sales in October due to the government shutdown.
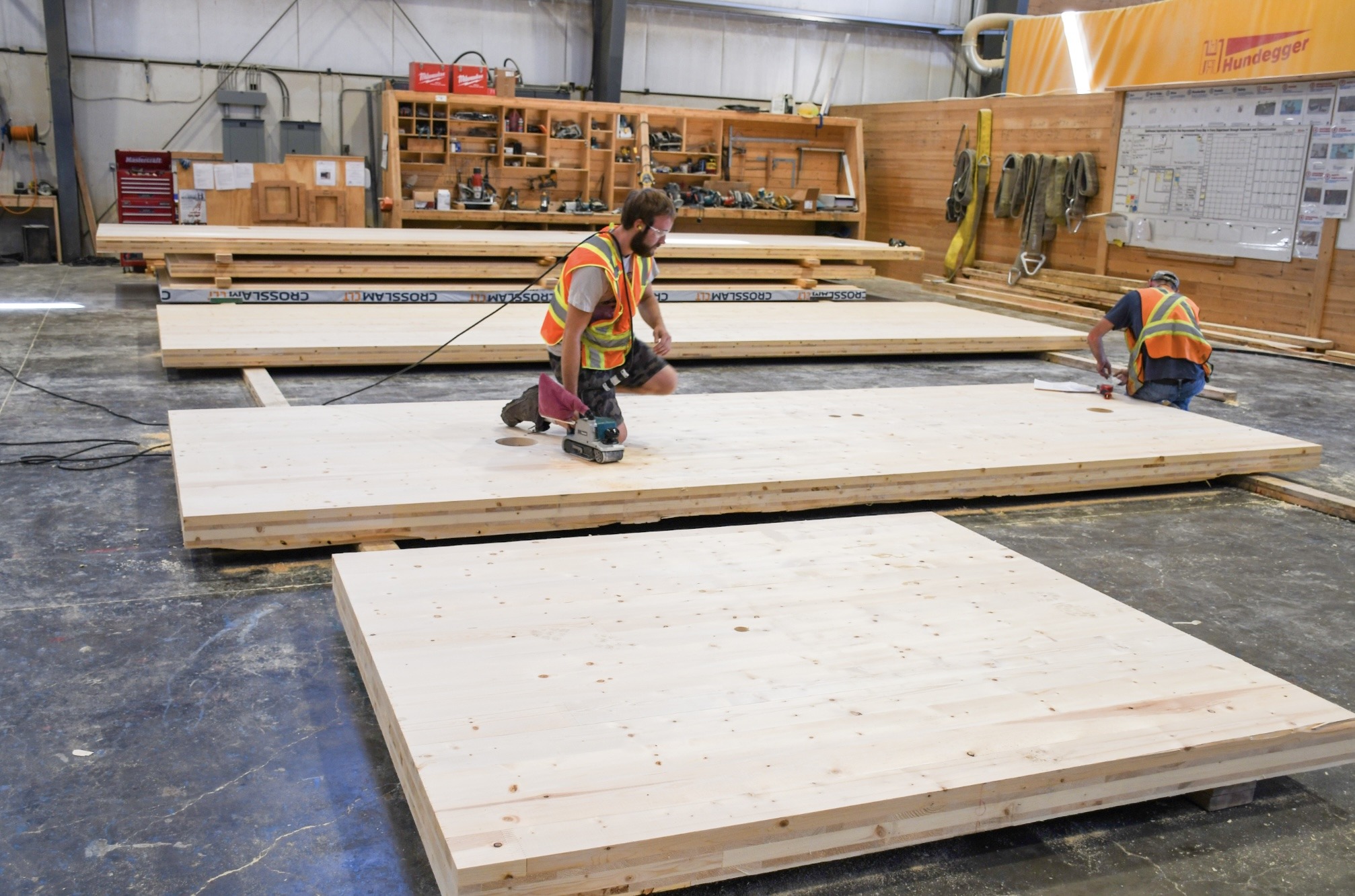 When Prime Minister Mark Carney toured Intelligent City’s advanced manufacturing facility in Delta, B.C. this spring, it was more than just another campaign stop. It signalled that prefabricated and modular construction has moved from the margins to the mainstream of Canada’s housing conversation. That recognition is overdue. If we are serious about tackling Canada’s housing affordability crisis by delivering more homes at scale, governments need to stop paying lip service to the huge potential of off- site construction and start putting it into policy and practice. …First, governments should publish a multi-year prefabricated housing procurement roadmap. Off-site manufacturing depends on predictable, portfolio-scale demand. A provincial roadmap in British Columbia, for example, that consolidates housing needs across ministries, Crown agencies, and municipalities would give factories the confidence to invest in automation, skilled labour, and supply chains.
When Prime Minister Mark Carney toured Intelligent City’s advanced manufacturing facility in Delta, B.C. this spring, it was more than just another campaign stop. It signalled that prefabricated and modular construction has moved from the margins to the mainstream of Canada’s housing conversation. That recognition is overdue. If we are serious about tackling Canada’s housing affordability crisis by delivering more homes at scale, governments need to stop paying lip service to the huge potential of off- site construction and start putting it into policy and practice. …First, governments should publish a multi-year prefabricated housing procurement roadmap. Off-site manufacturing depends on predictable, portfolio-scale demand. A provincial roadmap in British Columbia, for example, that consolidates housing needs across ministries, Crown agencies, and municipalities would give factories the confidence to invest in automation, skilled labour, and supply chains.
 NOOTKA SOUND, BC — Optimism for the future of Chinook salmon is swimming up Muchalat River near the town of Gold River, BC in Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations (MMFN) territory. Kent O’Neill, of the Nootka Sound Watershed Society (NSWS), says he observed hundreds of fish using a newly restored gravel spawning pad this fall. …Navigating a storm of challenges from historical logging practices to droughty summers, Chinook salmon in the region were assessed as Threatened by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada in 2020. To revive local Chinook salmon stocks, a collective effort led by NSWS, Ecofish Research, a Trinity Consultants Canada team, MMFN and the Pacific Salmon Foundation (PSF) was hatched. …Western Forest Products (WFP) also played a major role by providing the gravel and access to the forest service roads. “We wouldn’t have been able to do this project without WFP,” said O’Neill.
NOOTKA SOUND, BC — Optimism for the future of Chinook salmon is swimming up Muchalat River near the town of Gold River, BC in Mowachaht/Muchalaht First Nations (MMFN) territory. Kent O’Neill, of the Nootka Sound Watershed Society (NSWS), says he observed hundreds of fish using a newly restored gravel spawning pad this fall. …Navigating a storm of challenges from historical logging practices to droughty summers, Chinook salmon in the region were assessed as Threatened by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada in 2020. To revive local Chinook salmon stocks, a collective effort led by NSWS, Ecofish Research, a Trinity Consultants Canada team, MMFN and the Pacific Salmon Foundation (PSF) was hatched. …Western Forest Products (WFP) also played a major role by providing the gravel and access to the forest service roads. “We wouldn’t have been able to do this project without WFP,” said O’Neill.
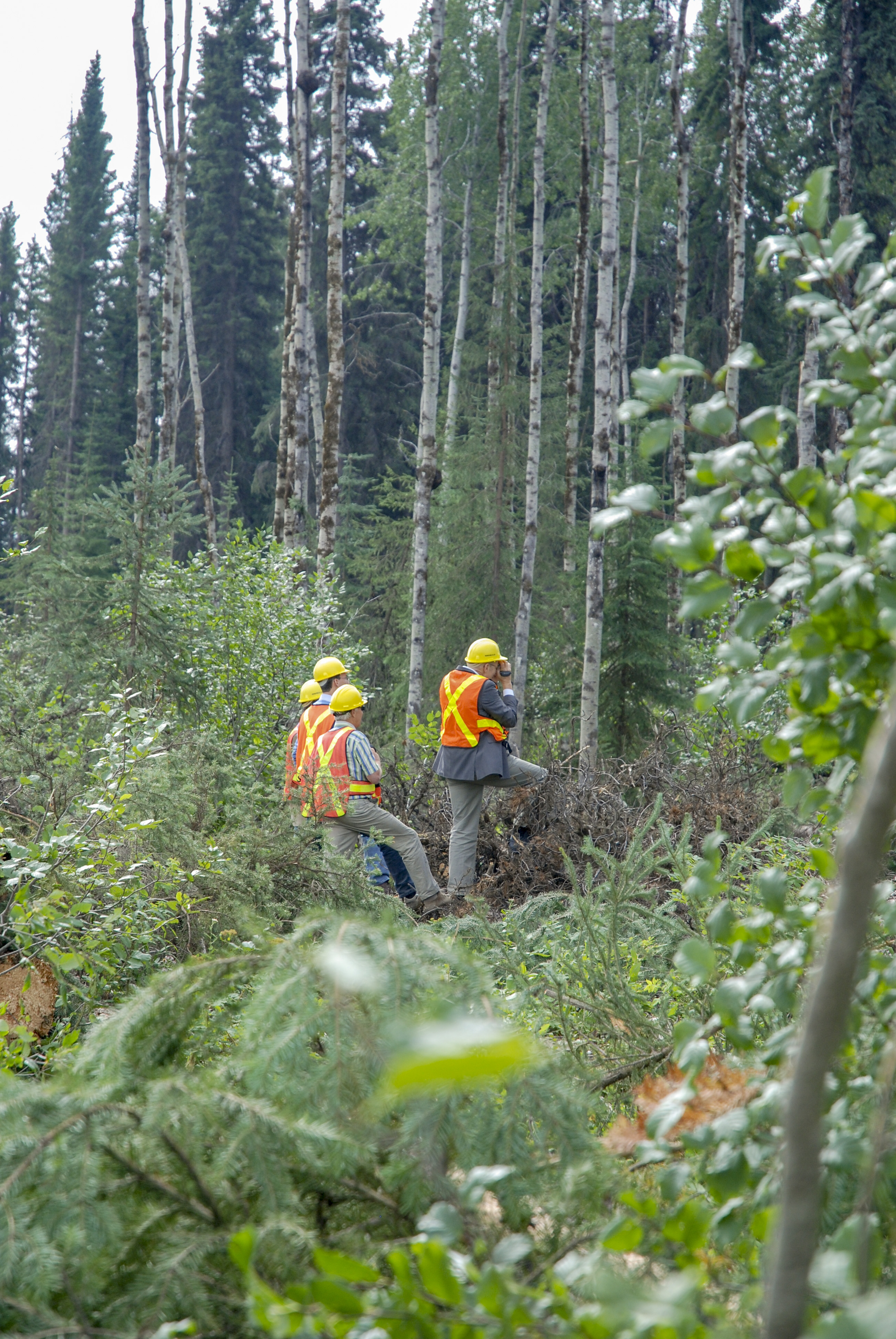
 British Columbia’s logging agency has changed a policy that conserved remnant old-growth forest in the province’s northwest, with a government briefing note showing a plan to open those areas for harvesting has been approved. The note, obtained by The Canadian Press and written by a BC Timber Sales manager in the Babine region, acknowledged the shift “may invoke scrutiny” from conservationist environmental groups. It says First Nations in the Bulkley, Morice and Lakes timber supply areas do not support old-growth logging deferrals recommended by a provincially appointed panel in 2021,and continuing to conserve remnant stands “does not demonstrate respect of the First Nations’ responses” to that process. …Independent ecologist Rachel Holt says the briefing note demonstrates a lack of understanding within BC Timber Sales about “the importance of … these irrecoverable ecological values.” But the crisis in B.C.’s forests is not just ecological.
British Columbia’s logging agency has changed a policy that conserved remnant old-growth forest in the province’s northwest, with a government briefing note showing a plan to open those areas for harvesting has been approved. The note, obtained by The Canadian Press and written by a BC Timber Sales manager in the Babine region, acknowledged the shift “may invoke scrutiny” from conservationist environmental groups. It says First Nations in the Bulkley, Morice and Lakes timber supply areas do not support old-growth logging deferrals recommended by a provincially appointed panel in 2021,and continuing to conserve remnant stands “does not demonstrate respect of the First Nations’ responses” to that process. …Independent ecologist Rachel Holt says the briefing note demonstrates a lack of understanding within BC Timber Sales about “the importance of … these irrecoverable ecological values.” But the crisis in B.C.’s forests is not just ecological.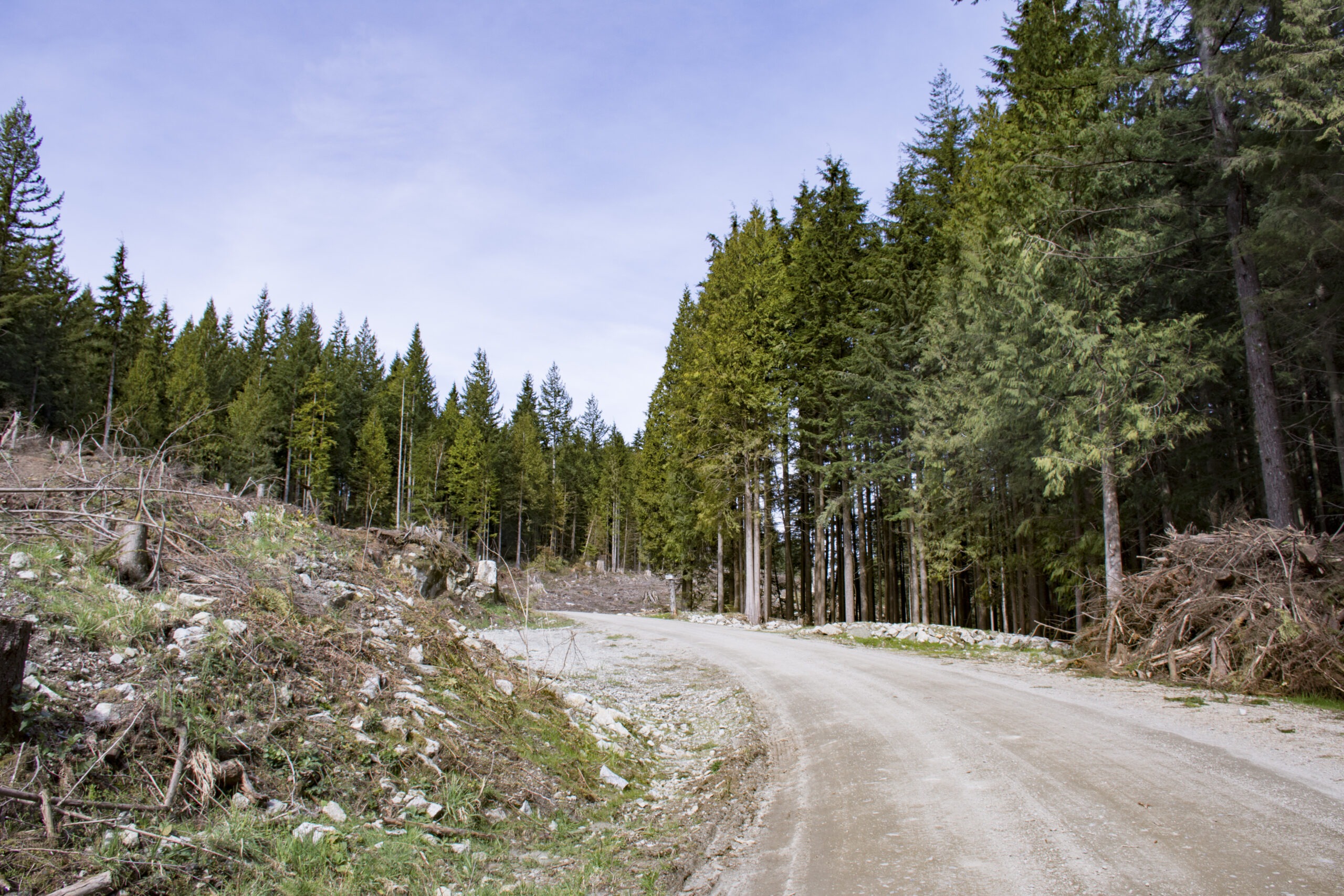 We tend to take logging roads for granted as an inherent right of access to Crown land. Their importance was recently reinforced when, just before the first snowfall, we travelled on one of the longest continuous and scenic forestry roads in the province. Ontario’s forest industry is critical to the provincial economy and many northern and rural communities. In 2023, the forest industry contributed $5.4 billion to Ontario’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and generated $21.6 billion in total revenue. The sector supported approximately 128,000 direct, indirect, and induced jobs in 2024, many of which are in Indigenous, rural, and northern communities. …The Ontario Forest Industries Association’s policy advisor, Adrian Smith said, “Forest access roads serve far more than the forestry sector. Built and maintained by our sector, they provide vital infrastructure. Forestry companies invest millions of dollars in grading, resurfacing, bridge and culvert upkeep, and winter snow clearing to keep this extensive network safe and reliable.
We tend to take logging roads for granted as an inherent right of access to Crown land. Their importance was recently reinforced when, just before the first snowfall, we travelled on one of the longest continuous and scenic forestry roads in the province. Ontario’s forest industry is critical to the provincial economy and many northern and rural communities. In 2023, the forest industry contributed $5.4 billion to Ontario’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and generated $21.6 billion in total revenue. The sector supported approximately 128,000 direct, indirect, and induced jobs in 2024, many of which are in Indigenous, rural, and northern communities. …The Ontario Forest Industries Association’s policy advisor, Adrian Smith said, “Forest access roads serve far more than the forestry sector. Built and maintained by our sector, they provide vital infrastructure. Forestry companies invest millions of dollars in grading, resurfacing, bridge and culvert upkeep, and winter snow clearing to keep this extensive network safe and reliable.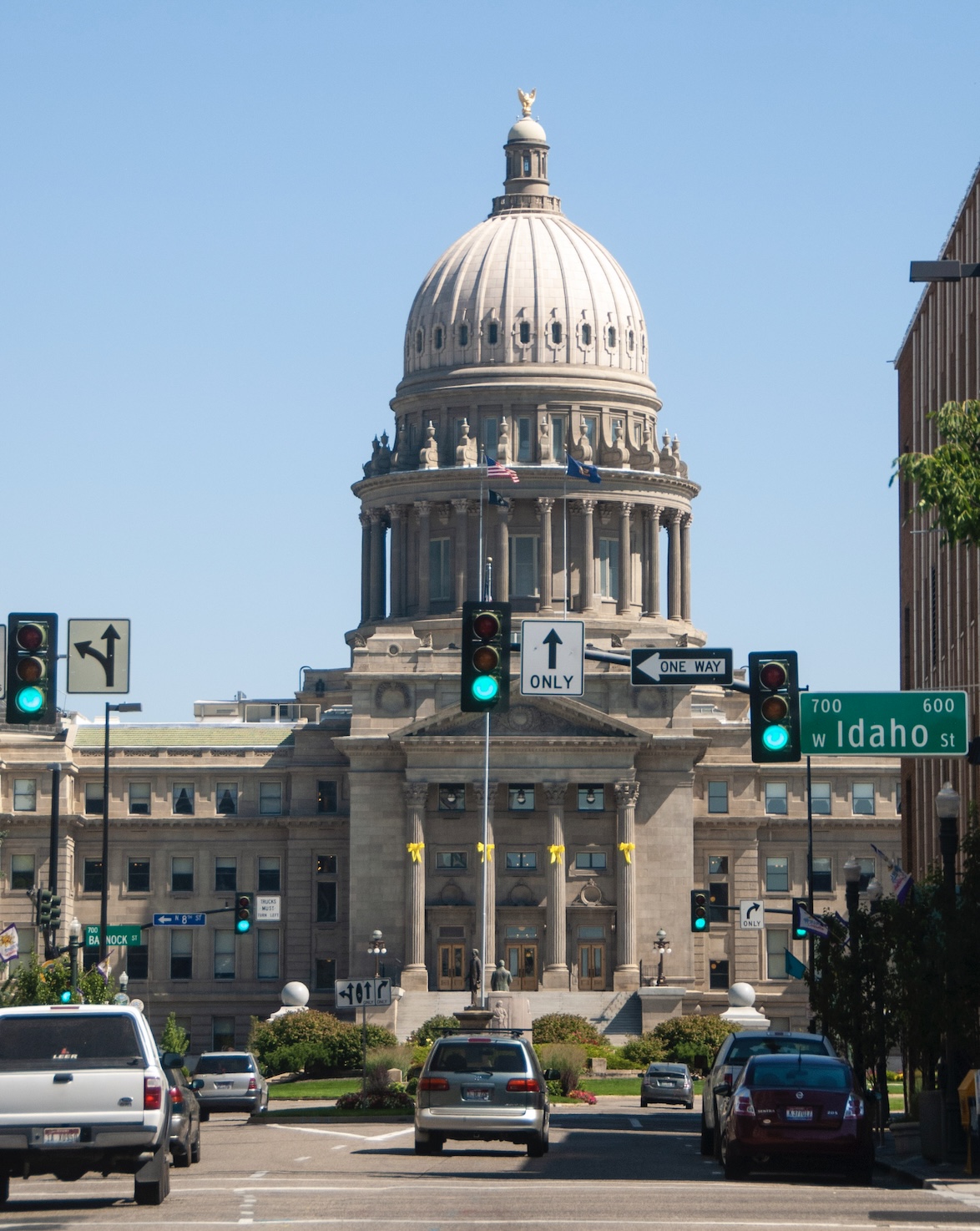 BOISE, Idaho — Governor Brad Little joined U.S. Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Idaho Department of Lands Director Dustin Miller on Friday to renew and expand Idaho’s Shared Stewardship agreement with the federal government — a move aimed at increasing the pace and scale of forest management across the state. The updated agreement establishes a collaborative framework between the U.S. Forest Service and the State of Idaho to strengthen policies related to forest restoration, land management, and wildfire mitigation “across Idaho’s forests and nearby communities.” Building on the landmark 2018 Shared Stewardship agreement, the new plan deepens joint efforts to boost timber production, accelerate wildland restoration, and expand forest health projects on national forests and adjacent state and private lands. The partnership reaffirms each side’s commitment to proactive landscape management as fire seasons grow increasingly longer and more intense.
BOISE, Idaho — Governor Brad Little joined U.S. Forest Service Chief Tom Schultz and Idaho Department of Lands Director Dustin Miller on Friday to renew and expand Idaho’s Shared Stewardship agreement with the federal government — a move aimed at increasing the pace and scale of forest management across the state. The updated agreement establishes a collaborative framework between the U.S. Forest Service and the State of Idaho to strengthen policies related to forest restoration, land management, and wildfire mitigation “across Idaho’s forests and nearby communities.” Building on the landmark 2018 Shared Stewardship agreement, the new plan deepens joint efforts to boost timber production, accelerate wildland restoration, and expand forest health projects on national forests and adjacent state and private lands. The partnership reaffirms each side’s commitment to proactive landscape management as fire seasons grow increasingly longer and more intense. Reforms to Australia’s nature laws have passed federal parliament. A longstanding exemption that meant federal environment laws did not apply to native logging has finally been removed from the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act. Native forest logging will now be subject to national environmental standards – legally binding rules supposed to set clear goals for environmental protection. This should be a win for the environment, and some have celebrated it as an end to native forest logging in Australia. But the reality is such celebrations are premature. We don’t have all the details of the new standards, or know how they will be enforced and monitored. Federal Environment Minister Murray Watt has told the forestry industry, including in Tasmania, that native forest operations will continue as usual. In an interview with ABC Radio Hobart, he said the changes keep day-to-day forestry approvals with the state government, but introduce stronger federal oversight.
Reforms to Australia’s nature laws have passed federal parliament. A longstanding exemption that meant federal environment laws did not apply to native logging has finally been removed from the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act. Native forest logging will now be subject to national environmental standards – legally binding rules supposed to set clear goals for environmental protection. This should be a win for the environment, and some have celebrated it as an end to native forest logging in Australia. But the reality is such celebrations are premature. We don’t have all the details of the new standards, or know how they will be enforced and monitored. Federal Environment Minister Murray Watt has told the forestry industry, including in Tasmania, that native forest operations will continue as usual. In an interview with ABC Radio Hobart, he said the changes keep day-to-day forestry approvals with the state government, but introduce stronger federal oversight.
 The Climate Risk Institute (CRI), in collaboration with the Canadian Institute of Forestry/Institut forestier du Canada (CIF-IFC) and with contributions from the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR), have developed a Climate Adaptation and Resilience Professional Development Program for Forest Professionals in Canada. This course is designed to provide forestry professionals and practitioners with new knowledge of climate change, climate impacts and adaptation strategies to complement their existing knowledge base, strengthen climate resilience in forest management, and build capacity across the sector to integrate adaptation measures into daily practice. Funded in part by Natural Resources Canada through the
The Climate Risk Institute (CRI), in collaboration with the Canadian Institute of Forestry/Institut forestier du Canada (CIF-IFC) and with contributions from the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR), have developed a Climate Adaptation and Resilience Professional Development Program for Forest Professionals in Canada. This course is designed to provide forestry professionals and practitioners with new knowledge of climate change, climate impacts and adaptation strategies to complement their existing knowledge base, strengthen climate resilience in forest management, and build capacity across the sector to integrate adaptation measures into daily practice. Funded in part by Natural Resources Canada through the 
 Thunder Bay – For more than 100 years, the pulp and paper mill in Dryden has been the most important building in this small city in northwestern Ontario. It was the engine of the local economy, providing jobs for generations and connecting Dryden to a larger network of forest products that includes Thunder Bay and other communities in the area. But the same industrial complex also caused one of Canada’s worst environmental disasters. In the 1960s and 1970s, a chlor-alkali plant that was part of the mill dumped an estimated 9,000 to 10,000 kilograms (about 10 metric tons) of mercury into the English–Wabigoon River system. …People have lived with symptoms of mercury poisoning for generations, including Minamata disease. Commercial fishing was stopped, and guiding jobs disappeared. The main question is still painfully unanswered decades later: Who should pay to clean up the river, fix the land, and help the people who were hurt?
Thunder Bay – For more than 100 years, the pulp and paper mill in Dryden has been the most important building in this small city in northwestern Ontario. It was the engine of the local economy, providing jobs for generations and connecting Dryden to a larger network of forest products that includes Thunder Bay and other communities in the area. But the same industrial complex also caused one of Canada’s worst environmental disasters. In the 1960s and 1970s, a chlor-alkali plant that was part of the mill dumped an estimated 9,000 to 10,000 kilograms (about 10 metric tons) of mercury into the English–Wabigoon River system. …People have lived with symptoms of mercury poisoning for generations, including Minamata disease. Commercial fishing was stopped, and guiding jobs disappeared. The main question is still painfully unanswered decades later: Who should pay to clean up the river, fix the land, and help the people who were hurt?