 BC’s Premier and forest industry leaders demand Ottawa treat lumber tariffs as a national priority. In related news: Gorman’s Nick Arkle is pushing for “equal treatment”; BC Conservatives say “BC should get tougher”; The Conversation argues that tariffs won’t drive much US investment, and Realtor.com and the Wall Street Journal focus on rising lumber and homebuilding costs.
BC’s Premier and forest industry leaders demand Ottawa treat lumber tariffs as a national priority. In related news: Gorman’s Nick Arkle is pushing for “equal treatment”; BC Conservatives say “BC should get tougher”; The Conversation argues that tariffs won’t drive much US investment, and Realtor.com and the Wall Street Journal focus on rising lumber and homebuilding costs.
In other news: Canadian Forest Owners support carbon storage research; Ontario launches Boreal Springboard to grow the sector; BC First Nations push to reshape forestry; and the University of Idaho has a new Forest Innovations Institute. Meanwhile: six UBC forestry faculty receive Canada Foundation for Innovation awards; UBC’s Malcolm Knapp Research Forest is recognized by the CIF; registration opens for the TLA’s 81st convention; and the latest market news from Canada Wood.
Finally, how China’s pulp and paper overcapacity is reshaping global competitiveness.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor
 The US imports about 40% of the softwood lumber the nation uses each year, more than 80% of that from Canada. President Trump says that the US has the capacity to meet 95% of softwood lumber demand and directed federal officials to update policies and regulatory guidelines to expand domestic timber harvesting and curb the arrival of foreign lumber. …As researchers studying the forestry sector and international trade, we recognize that the US has ample forest resources. But replacing imports with domestic lumber isn’t as simple as it sounds. There are differences in tree species and quality, and U.S. lumber often comes at a higher cost, even with tariffs on imports. Challenges like limited labor and manufacturing capacity require long-term investments, which temporary tariffs and uncertain trade policies often fail to encourage. In addition, the amount of lumber imported tends to mirror the boom-and-bust cycles of housing construction, a dynamic that tariffs alone are unlikely to change.
The US imports about 40% of the softwood lumber the nation uses each year, more than 80% of that from Canada. President Trump says that the US has the capacity to meet 95% of softwood lumber demand and directed federal officials to update policies and regulatory guidelines to expand domestic timber harvesting and curb the arrival of foreign lumber. …As researchers studying the forestry sector and international trade, we recognize that the US has ample forest resources. But replacing imports with domestic lumber isn’t as simple as it sounds. There are differences in tree species and quality, and U.S. lumber often comes at a higher cost, even with tariffs on imports. Challenges like limited labor and manufacturing capacity require long-term investments, which temporary tariffs and uncertain trade policies often fail to encourage. In addition, the amount of lumber imported tends to mirror the boom-and-bust cycles of housing construction, a dynamic that tariffs alone are unlikely to change.


 President Trump’s new tariffs on imported lumber and wooden fixtures have taken effect, potentially raising the cost of home construction and renovations. …“These new tariffs will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market by further raising construction and renovation costs,” says NAHB Chairman Buddy Hughes. …According to an NAHB analysis, U.S. sawmills are operating at just 64% of their potential capacity, a figure that has dropped steadily since 2017. “It will take years until domestic lumber production ramps up to meet the needs of our citizens,” the trade group says”. …Framing costs, including the roof, averaged about $49,763 for new single-family homes last year, accounting for about 12% of the total cost of a new build, according to an NAHB breakdown. Cabinets and countertops cost $19,056 on average, accounting for 4.5% of the total, the analysis found. …Builder profit margins have already been shrinking, and many companies have pulled back on new construction.
President Trump’s new tariffs on imported lumber and wooden fixtures have taken effect, potentially raising the cost of home construction and renovations. …“These new tariffs will create additional headwinds for an already challenged housing market by further raising construction and renovation costs,” says NAHB Chairman Buddy Hughes. …According to an NAHB analysis, U.S. sawmills are operating at just 64% of their potential capacity, a figure that has dropped steadily since 2017. “It will take years until domestic lumber production ramps up to meet the needs of our citizens,” the trade group says”. …Framing costs, including the roof, averaged about $49,763 for new single-family homes last year, accounting for about 12% of the total cost of a new build, according to an NAHB breakdown. Cabinets and countertops cost $19,056 on average, accounting for 4.5% of the total, the analysis found. …Builder profit margins have already been shrinking, and many companies have pulled back on new construction.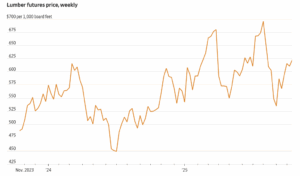 Lumber futures have risen about 19% from a low hit in early September, driven by the production cuts, hopes that declining interest rates will revive the housing market and Trump’s import tax. The 10% levy is on top of steep duties on Canadian lumber, which are adjusted annually in a heavily litigated process that is the result of a decades-long trade dispute. Those antidumping and countervailing duties rose in August to about 35% for most Canadian producers, up from roughly 15%. Canada’s sawmills are by far the largest source of softwood lumber from beyond U.S. borders, fulfilling about 24% of domestic consumption last year. Other significant importers of softwood lumber, the type used to frame houses, include Brazil and European countries such as Germany and Sweden. Homebuilders argue that import taxes will raise construction costs. U.S. lumber producers and timberland owners, however, urged Trump to enact a tariff.
Lumber futures have risen about 19% from a low hit in early September, driven by the production cuts, hopes that declining interest rates will revive the housing market and Trump’s import tax. The 10% levy is on top of steep duties on Canadian lumber, which are adjusted annually in a heavily litigated process that is the result of a decades-long trade dispute. Those antidumping and countervailing duties rose in August to about 35% for most Canadian producers, up from roughly 15%. Canada’s sawmills are by far the largest source of softwood lumber from beyond U.S. borders, fulfilling about 24% of domestic consumption last year. Other significant importers of softwood lumber, the type used to frame houses, include Brazil and European countries such as Germany and Sweden. Homebuilders argue that import taxes will raise construction costs. U.S. lumber producers and timberland owners, however, urged Trump to enact a tariff.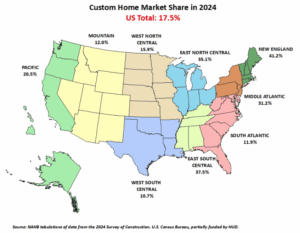 In 2024, 17.5% of all new single-family homes started were custom homes. This share decreased from 18.8% in 2023 and from 20.4% in 2022, according to data tabulated from the Census Bureau’s Survey of Construction (SOC). The custom home market consists of contractor-built and owner-built homes—homes built for owner occupancy on the owner’s land, with either the owner or a builder acting as a general contractor. The alternatives are homes built-for-sale (on the builder’s land, often in subdivisions, with the intention of selling the house and land in one transaction) and homes built-for-rent. In 2024, 73.1% of the single-family homes started were built-for-sale and 9.3% were built-for-rent. At a 17.5% share, the number of custom homes started in 2024 was 176,932, falling from 177,850 in 2023.
In 2024, 17.5% of all new single-family homes started were custom homes. This share decreased from 18.8% in 2023 and from 20.4% in 2022, according to data tabulated from the Census Bureau’s Survey of Construction (SOC). The custom home market consists of contractor-built and owner-built homes—homes built for owner occupancy on the owner’s land, with either the owner or a builder acting as a general contractor. The alternatives are homes built-for-sale (on the builder’s land, often in subdivisions, with the intention of selling the house and land in one transaction) and homes built-for-rent. In 2024, 73.1% of the single-family homes started were built-for-sale and 9.3% were built-for-rent. At a 17.5% share, the number of custom homes started in 2024 was 176,932, falling from 177,850 in 2023.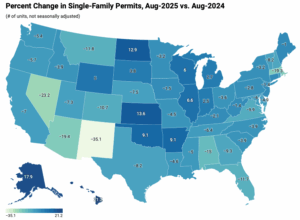 In August, single-family permit activity softened, reflecting caution among developers amid persistent economic headwinds. This trend has been consistent for eight continuous months. On the multifamily front, permitting also cooled in August but remains in the positive territory. While single-family continues to bear the brunt of affordability headwinds, the multifamily space is showing tentative signs of rebalancing. Over the first eight months of 2025, the total number of single-family permits issued year-to-date (YTD) nationwide reached 637,096. On a year-over-year (YoY) basis, this is a decline of 7.1% over the August 2024 level of 685,923. For multifamily, the total number of permits issued nationwide reached 330,617. This is 1.4% higher compared to the August 2024 level of 326,080. HBGI analysis indicates that this growth for multifamily development has been concentrated in lower density areas and among smaller builders.
In August, single-family permit activity softened, reflecting caution among developers amid persistent economic headwinds. This trend has been consistent for eight continuous months. On the multifamily front, permitting also cooled in August but remains in the positive territory. While single-family continues to bear the brunt of affordability headwinds, the multifamily space is showing tentative signs of rebalancing. Over the first eight months of 2025, the total number of single-family permits issued year-to-date (YTD) nationwide reached 637,096. On a year-over-year (YoY) basis, this is a decline of 7.1% over the August 2024 level of 685,923. For multifamily, the total number of permits issued nationwide reached 330,617. This is 1.4% higher compared to the August 2024 level of 326,080. HBGI analysis indicates that this growth for multifamily development has been concentrated in lower density areas and among smaller builders. China’s pulp and paper industry continues to expand at an unprecedented pace, with new mill projects, advanced technologies, and state-backed financing driving record output. What began as a push to meet domestic demand has now evolved into an era of overcapacity and a structural imbalance that is reshaping trade dynamics, pricing strategies, and sustainability priorities worldwide. This expansion has far-reaching effects: global producers are contending with lower-priced exports, disrupted supply chains, and a shifting balance of power that challenges traditional market leaders in North America and Europe. …Industry observers expect consolidation in China’s pulp and paper sector, as smaller and less efficient mills struggle to survive. Strategic investments in transparency, benchmarking, and efficiency will be crucial for staying competitive in a tightening global market.
China’s pulp and paper industry continues to expand at an unprecedented pace, with new mill projects, advanced technologies, and state-backed financing driving record output. What began as a push to meet domestic demand has now evolved into an era of overcapacity and a structural imbalance that is reshaping trade dynamics, pricing strategies, and sustainability priorities worldwide. This expansion has far-reaching effects: global producers are contending with lower-priced exports, disrupted supply chains, and a shifting balance of power that challenges traditional market leaders in North America and Europe. …Industry observers expect consolidation in China’s pulp and paper sector, as smaller and less efficient mills struggle to survive. Strategic investments in transparency, benchmarking, and efficiency will be crucial for staying competitive in a tightening global market.
 The October newsletter includes these headlines and more:
The October newsletter includes these headlines and more:
 At the Kelsey Bay log sort near the town of Sayward, B.C., pulverized cedar bark [is] evidence of the millions of trees that departed from here, never to return. “We’ve seen our territories decimated,” Wei Wai Kum Chief Christopher Roberts explains. Behind him, five freshly cut, old-growth cedars line the warming pavement. These trees, Roberts says, help explain why the nation is here today. …nations are claiming sizable stakes in an industry that has long excluded them. Wei Wai Kum is one of four First Nations to purchase a $36-million stake in La-kwa sa mukw Forestry Partnership, a joint operation with logging company Western Forest Products Ltd. Their partnership came after companies agreed to leave canoe-carving trees in their communities. A sign, for Roberts, that the industry was willing to change. …Now … First Nations’ tenure opportunities have exploded as B.C.’s biggest forest companies sell off major parts of their long-held licences.
At the Kelsey Bay log sort near the town of Sayward, B.C., pulverized cedar bark [is] evidence of the millions of trees that departed from here, never to return. “We’ve seen our territories decimated,” Wei Wai Kum Chief Christopher Roberts explains. Behind him, five freshly cut, old-growth cedars line the warming pavement. These trees, Roberts says, help explain why the nation is here today. …nations are claiming sizable stakes in an industry that has long excluded them. Wei Wai Kum is one of four First Nations to purchase a $36-million stake in La-kwa sa mukw Forestry Partnership, a joint operation with logging company Western Forest Products Ltd. Their partnership came after companies agreed to leave canoe-carving trees in their communities. A sign, for Roberts, that the industry was willing to change. …Now … First Nations’ tenure opportunities have exploded as B.C.’s biggest forest companies sell off major parts of their long-held licences.  Maple Ridge’s greenery is being recognized and awarded on a national scale. Malcolm Knapp Research Forest is one of two forests operated by the University of B.C. (UBC) that was recently acknowledged with a Canadian Institute of Forestry – Canadian Forest Management Group Achievement Award. …The award recognizes outstanding achievements by teams of managers in the field of natural resource management in Canada, and the local forest was praised for its “pivotal role” in advancing forest education, research, and management across B.C. and beyond, explained Helene Marcoux, local research forest director who was on hand for the recent awards presentation. …Through the coordination of more than 1,400 research projects and the delivery of experiential learning programs to thousands of students and professionals, the research forests have significantly shaped forest policy, sustainable management practices, and public understanding of forestry, said presenters of the national awards.
Maple Ridge’s greenery is being recognized and awarded on a national scale. Malcolm Knapp Research Forest is one of two forests operated by the University of B.C. (UBC) that was recently acknowledged with a Canadian Institute of Forestry – Canadian Forest Management Group Achievement Award. …The award recognizes outstanding achievements by teams of managers in the field of natural resource management in Canada, and the local forest was praised for its “pivotal role” in advancing forest education, research, and management across B.C. and beyond, explained Helene Marcoux, local research forest director who was on hand for the recent awards presentation. …Through the coordination of more than 1,400 research projects and the delivery of experiential learning programs to thousands of students and professionals, the research forests have significantly shaped forest policy, sustainable management practices, and public understanding of forestry, said presenters of the national awards. ONTARIO — The Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre has partnered with the Thunder Bay Community Economic Development Commission (CEDC), the Centre for Research and Innovation in the Bio-Economy (CRIBE), Lakehead University and Confederation College to launch the Boreal Springboard, an innovative initiative aimed at strengthening and diversifying the forestry sector in Northwestern Ontario. Graham Bracken, at the Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre, said the launch comes at a critical time for forestry in the region. …“The trade pressures were really the impetus to focus people’s minds,” Bracken said. “The sector is really integrated, and any threat to protection on the sawmill side weakens the rest of the sector. There’s a real drive to look to trade diversification and try and develop new value-added products that we can access other markets with.” Bracken says these investors will bring skills, technologies, and solutions that can be adapted to strengthen and grow the sector.
ONTARIO — The Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre has partnered with the Thunder Bay Community Economic Development Commission (CEDC), the Centre for Research and Innovation in the Bio-Economy (CRIBE), Lakehead University and Confederation College to launch the Boreal Springboard, an innovative initiative aimed at strengthening and diversifying the forestry sector in Northwestern Ontario. Graham Bracken, at the Northwestern Ontario Innovation Centre, said the launch comes at a critical time for forestry in the region. …“The trade pressures were really the impetus to focus people’s minds,” Bracken said. “The sector is really integrated, and any threat to protection on the sawmill side weakens the rest of the sector. There’s a real drive to look to trade diversification and try and develop new value-added products that we can access other markets with.” Bracken says these investors will bring skills, technologies, and solutions that can be adapted to strengthen and grow the sector.