MONTREAL – The Quebec government is trying to ease rising tensions between forestry workers and Indigenous protesters who oppose a new bill. Natural Resources Minister Maïté Blanchette Vézina and Indigenous Affairs Minister Ian Lafrenière announced Tuesday they were meeting with three Atikamekw communities in Quebec’s Mauricie region, roughly 200 kilometres north of Montreal. The region has been the site of recent tense confrontations between protesters and industry workers over a series of blockades that have disrupted operations for some in the forestry sector. …The Assembly of First Nations Quebec–Labrador is expected to meet with the office of Premier François Legault on Wednesday. The conflict stems from a bill tabled in the Quebec legislature this spring that aimed to protect communities dependent on the forestry industry. …Indigenous leaders were quick to criticize the bill, saying it infringed on their rights. …The blockades have led to hostile exchanges between the group’s members and forestry workers.
Updated coverage: Quebec government renews promise to make changes to forestry reform bill

 A proposed sale of Northern Pulp’s vast timberlands appears to leave nothing for the cleanup of its former kraft pulp mill in Pictou County or for the money owed to taxpayers. But the companies that provided interim financing to Northern Pulp through its five-year insolvency, and potentially a significant portion of its underfunded pension obligation to former mill employees, would get paid. On Monday, Northern Pulp filed a proposed “stalking horse” (a minimum bid) of $104 million for Northern Timber with the BC Supreme Court as part of its insolvency proceedings. It is also seeking the extension of creditor protection, leaving the potential that a higher bid could come in for its valuable forest lands. …No estimated cost has been released publicly for cleaning up the Abercrombie site that housed Northern Pulp for 50 years. …On Monday, Northern Pulp said it had provided a cleanup plan to the Department of Environment.
A proposed sale of Northern Pulp’s vast timberlands appears to leave nothing for the cleanup of its former kraft pulp mill in Pictou County or for the money owed to taxpayers. But the companies that provided interim financing to Northern Pulp through its five-year insolvency, and potentially a significant portion of its underfunded pension obligation to former mill employees, would get paid. On Monday, Northern Pulp filed a proposed “stalking horse” (a minimum bid) of $104 million for Northern Timber with the BC Supreme Court as part of its insolvency proceedings. It is also seeking the extension of creditor protection, leaving the potential that a higher bid could come in for its valuable forest lands. …No estimated cost has been released publicly for cleaning up the Abercrombie site that housed Northern Pulp for 50 years. …On Monday, Northern Pulp said it had provided a cleanup plan to the Department of Environment.



 OTTAWA — Canada’s housing crisis may get worse before it starts to show much relief, as new projections say that the number of housing starts will actually decrease this year and next. These new estimates, from both public and private sector housing forecasts, contradict political promises from all levels of government to boost supply of homes across the country. The Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) forecasts that the total number of housing starts in Canada this year will be about 237,800, down from 245,367 in 2024. CMHC, a Crown corporation that acts as Canada’s national housing agency, also forecasts a drop to no more than 227,734 next year and 220,016 in 2027. Those forecasts are all below the 267,000 annual output for housing starts from 2021-22 and less than half the 480,000 that the CMHC says Canada needs to add each year over the next decade.
OTTAWA — Canada’s housing crisis may get worse before it starts to show much relief, as new projections say that the number of housing starts will actually decrease this year and next. These new estimates, from both public and private sector housing forecasts, contradict political promises from all levels of government to boost supply of homes across the country. The Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) forecasts that the total number of housing starts in Canada this year will be about 237,800, down from 245,367 in 2024. CMHC, a Crown corporation that acts as Canada’s national housing agency, also forecasts a drop to no more than 227,734 next year and 220,016 in 2027. Those forecasts are all below the 267,000 annual output for housing starts from 2021-22 and less than half the 480,000 that the CMHC says Canada needs to add each year over the next decade. EDMUNDSTON, New Brunswick – Acadian Timber reported financial and operating results for the three months ended June 28, 2025. “During the second quarter, Acadian delivered mixed results,” said Adam Sheparski, CEO. …Acadian generated sales of $17.1 million, compared to $41.2 million in the prior year period. The second quarter of 2024 included $19.7 million in carbon credit sales, while no carbon credit sales occurred in the second quarter of 2025. Acadian generated $0.8 million of Free Cash Flow during the second quarter and declared dividends of $5.2 million or $0.29 per share to our shareholders. …While the second quarter of the year is traditionally our weakest due to seasonal operating conditions, operating activity in Maine was impacted by prolonged wet conditions which significantly delayed the commencement of deliveries in the spring.
EDMUNDSTON, New Brunswick – Acadian Timber reported financial and operating results for the three months ended June 28, 2025. “During the second quarter, Acadian delivered mixed results,” said Adam Sheparski, CEO. …Acadian generated sales of $17.1 million, compared to $41.2 million in the prior year period. The second quarter of 2024 included $19.7 million in carbon credit sales, while no carbon credit sales occurred in the second quarter of 2025. Acadian generated $0.8 million of Free Cash Flow during the second quarter and declared dividends of $5.2 million or $0.29 per share to our shareholders. …While the second quarter of the year is traditionally our weakest due to seasonal operating conditions, operating activity in Maine was impacted by prolonged wet conditions which significantly delayed the commencement of deliveries in the spring. TORONTO — George Brown College’s (GBC) Limberlost Place has helped trigger major changes to Ontario’s building codes and is playing a key role in the province’s strategy to grow its mass timber construction sector, college officials say. The 10-storey academic building—Canada’s first institutional structure made from mass timber and designed to achieve net-zero carbon emissions—has served as a catalyst for the Ontario government’s Advanced Wood Construction Action Plan, unveiled on June 26. The action plan outlines four goals: Promote awareness and use of advanced wood construction; Remove regulatory barriers in codes and standards; Stimulate innovation and investment in advanced manufacturing; and Showcase successful projects to build industry confidence. Limberlost Place embodies all four goals. …By demonstrating the viability and benefits of mass timber at scale, George Brown College has positioned itself—and Ontario—as a leader in sustainable construction and advanced wood manufacturing.
TORONTO — George Brown College’s (GBC) Limberlost Place has helped trigger major changes to Ontario’s building codes and is playing a key role in the province’s strategy to grow its mass timber construction sector, college officials say. The 10-storey academic building—Canada’s first institutional structure made from mass timber and designed to achieve net-zero carbon emissions—has served as a catalyst for the Ontario government’s Advanced Wood Construction Action Plan, unveiled on June 26. The action plan outlines four goals: Promote awareness and use of advanced wood construction; Remove regulatory barriers in codes and standards; Stimulate innovation and investment in advanced manufacturing; and Showcase successful projects to build industry confidence. Limberlost Place embodies all four goals. …By demonstrating the viability and benefits of mass timber at scale, George Brown College has positioned itself—and Ontario—as a leader in sustainable construction and advanced wood manufacturing. There may have been dissension surrounding the Morris Street bikeway, but the Halifax mayor and regional council found common ground with mass timber. Mayor Andy Fillmore tabled a motion at Tuesday’s council meeting to direct the chief administrative officer to prepare a staff report that, with changes to land-use bylaws and amendments to a municipal planning strategy, would knock down barriers to mass timber construction to help expedite housing builds. That would include the potential to increase the height of built-form requirements from 10 to 12 storeys for mass timber construction. The motion passed unanimously. “The principal reason (for supporting the mayor’s motion) is that this unlocks some newfound potential in local supply,” Coun. Jean St-Amand (Bedford-Wentworth) said. “I think that’s something that can have a very positive impact to the acceleration of our ability and our capacity to build.
There may have been dissension surrounding the Morris Street bikeway, but the Halifax mayor and regional council found common ground with mass timber. Mayor Andy Fillmore tabled a motion at Tuesday’s council meeting to direct the chief administrative officer to prepare a staff report that, with changes to land-use bylaws and amendments to a municipal planning strategy, would knock down barriers to mass timber construction to help expedite housing builds. That would include the potential to increase the height of built-form requirements from 10 to 12 storeys for mass timber construction. The motion passed unanimously. “The principal reason (for supporting the mayor’s motion) is that this unlocks some newfound potential in local supply,” Coun. Jean St-Amand (Bedford-Wentworth) said. “I think that’s something that can have a very positive impact to the acceleration of our ability and our capacity to build.
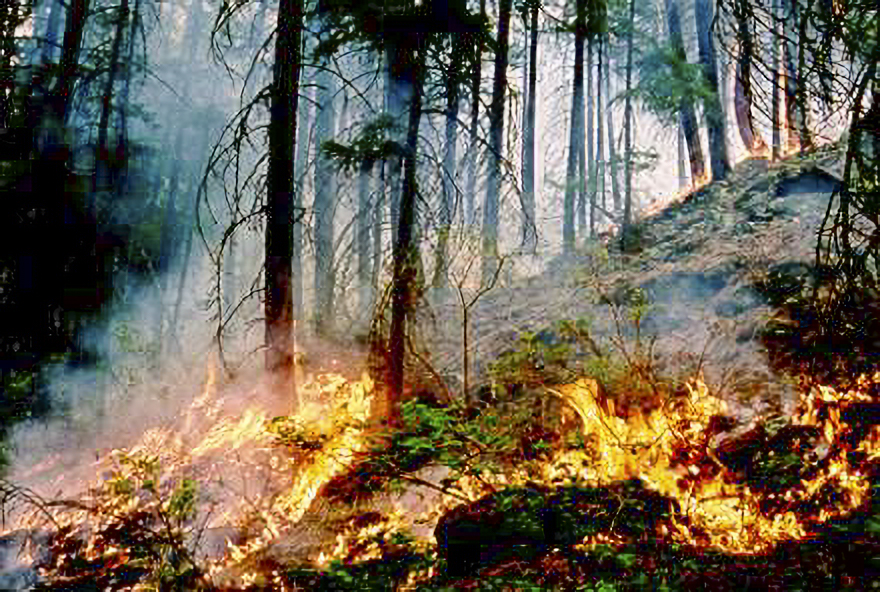
 The historic wildfires that ripped through Quebec in 2023, destroying millions of hectares of forest and impacting thousands of people, is estimated to have cost over $8 billion. That’s according to a new provincially funded study published Wednesday by Nada Conseils — a climate action consultancy firm — highlighting the impacts and collective costs of the fires on citizens, governments, businesses and ecosystems. According to SOPFEU, the agency responsible for wildfire prevention and suppression in Quebec, the 2023 wildfire season was the worst in over 100 years with 713 fires — 99.9 per cent of which were caused by lightening — burning 4.3 million hectares of forest. …For governments, much of the costs incurred stemmed from firefighting operations, emergency services including evacuations and housing evacuees, and financial assistance programs. …The report notes that some of the most significant costs for citizens were linked to property damage, as well as financial impacts related to lost income and increased expenses.
The historic wildfires that ripped through Quebec in 2023, destroying millions of hectares of forest and impacting thousands of people, is estimated to have cost over $8 billion. That’s according to a new provincially funded study published Wednesday by Nada Conseils — a climate action consultancy firm — highlighting the impacts and collective costs of the fires on citizens, governments, businesses and ecosystems. According to SOPFEU, the agency responsible for wildfire prevention and suppression in Quebec, the 2023 wildfire season was the worst in over 100 years with 713 fires — 99.9 per cent of which were caused by lightening — burning 4.3 million hectares of forest. …For governments, much of the costs incurred stemmed from firefighting operations, emergency services including evacuations and housing evacuees, and financial assistance programs. …The report notes that some of the most significant costs for citizens were linked to property damage, as well as financial impacts related to lost income and increased expenses. LAKE HURON, Ontario — Jenifer Brousseau often picks berries and traditional medicines in the bush around her community in northeastern Ontario. But in recent years, Brousseau and many others from Serpent River have been concerned about the forestry industry’s use of herbicides that contain the chemical glyphosate. …Environmental groups — including Friends of the Earth Canada, the David Suzuki Foundation, Safe Food Matters and Environmental Defence Canada — have launched a court challenge of Health Canada’s conclusions on glyphosate. …Some small municipalities in northern Ontario have also started to petition the province in their effort to get the ban. …Fred Pinto, an adjunct professor of forestry at the University of Toronto said herbicides are just one tool used by forestry companies to manage vegetation. Pinto said herbicide spraying is often done using aircraft in areas that have little to no road access.
LAKE HURON, Ontario — Jenifer Brousseau often picks berries and traditional medicines in the bush around her community in northeastern Ontario. But in recent years, Brousseau and many others from Serpent River have been concerned about the forestry industry’s use of herbicides that contain the chemical glyphosate. …Environmental groups — including Friends of the Earth Canada, the David Suzuki Foundation, Safe Food Matters and Environmental Defence Canada — have launched a court challenge of Health Canada’s conclusions on glyphosate. …Some small municipalities in northern Ontario have also started to petition the province in their effort to get the ban. …Fred Pinto, an adjunct professor of forestry at the University of Toronto said herbicides are just one tool used by forestry companies to manage vegetation. Pinto said herbicide spraying is often done using aircraft in areas that have little to no road access.

 Worsening dry conditions across New Brunswick — which sparked a provincewide burn ban and led this week to an uncontrolled wildfire near Miramichi — have prompted the provincial government to impose restrictions on some industrial activities in forested areas. The Department of Natural Resources said in a news release Friday that some forestry operations would be banned for the next several days given the high risk of another wildfire. …From midnight on Aug. 8 to midnight on Aug. 12, harvesting, forwarding, skidding, scarification, chipping and all pre-commercial thinning and cleaning are all banned. That restriction applies to all forestry on both Crown and private lands. Trucking, road construction and maintenance, vegetation management and tree planting are allowed to continue. …Except for the possibility of a shower Saturday afternoon in northern New Brunswick, the province could see at least six more days of dry, hot weather, according to Environment Canada forecasts.
Worsening dry conditions across New Brunswick — which sparked a provincewide burn ban and led this week to an uncontrolled wildfire near Miramichi — have prompted the provincial government to impose restrictions on some industrial activities in forested areas. The Department of Natural Resources said in a news release Friday that some forestry operations would be banned for the next several days given the high risk of another wildfire. …From midnight on Aug. 8 to midnight on Aug. 12, harvesting, forwarding, skidding, scarification, chipping and all pre-commercial thinning and cleaning are all banned. That restriction applies to all forestry on both Crown and private lands. Trucking, road construction and maintenance, vegetation management and tree planting are allowed to continue. …Except for the possibility of a shower Saturday afternoon in northern New Brunswick, the province could see at least six more days of dry, hot weather, according to Environment Canada forecasts.

 MIRAMICHI, New Brunswick — In response to the increased wildfire risk, some forestry operations in New Brunswick will be restricted over the next couple of days. A release from the province’s Department of Natural Resources says the move is to protect both the forests and people living in the province. On Friday, the natural resources minister said in the release the restrictions will be on both Crown and private lands. “These measures will help protect our forests, animals, natural habitats and our communities, as well as our wildland fire crews,” John Herron said. As of midnight Friday, harvesting, forwarding, skidding, scarification, chipping and all pre-commercial thinning and cleaning are restricted until Tuesday. However, trucking, road construction and maintenance, vegetation management and tree planting are still getting the green light. These restrictions apply to all forested lands in the province, both private and Crown.
MIRAMICHI, New Brunswick — In response to the increased wildfire risk, some forestry operations in New Brunswick will be restricted over the next couple of days. A release from the province’s Department of Natural Resources says the move is to protect both the forests and people living in the province. On Friday, the natural resources minister said in the release the restrictions will be on both Crown and private lands. “These measures will help protect our forests, animals, natural habitats and our communities, as well as our wildland fire crews,” John Herron said. As of midnight Friday, harvesting, forwarding, skidding, scarification, chipping and all pre-commercial thinning and cleaning are restricted until Tuesday. However, trucking, road construction and maintenance, vegetation management and tree planting are still getting the green light. These restrictions apply to all forested lands in the province, both private and Crown. Fostering inclusive economic development and ensuring that local communities, including Indigenous partners, benefit from these opportunities are key priorities for the Government of Canada. Today, Claude Guay, Parliamentary Secretary to the Minister of Energy and Natural Resources, concluded a two-day tour of Northern Quebec, where he highlighted the importance of Quebec’s mining and forest sectors in building Canada’s supply chains and export opportunities, creating good jobs, and strengthening reconciliation… Parliamentary Secretary Guay concluded the trip with a visit to Les Chantiers Chibougamau’s Kraft Pulp Mill in Lebel-sur-Quevillon and their head manufacturing plant in Chibougamau. These sites are key examples of Quebec’s forest sector excellence and innovation in modernizing the industry, accelerating affordable housing and promoting green construction using value-added Canadian wood-based products.
Fostering inclusive economic development and ensuring that local communities, including Indigenous partners, benefit from these opportunities are key priorities for the Government of Canada. Today, Claude Guay, Parliamentary Secretary to the Minister of Energy and Natural Resources, concluded a two-day tour of Northern Quebec, where he highlighted the importance of Quebec’s mining and forest sectors in building Canada’s supply chains and export opportunities, creating good jobs, and strengthening reconciliation… Parliamentary Secretary Guay concluded the trip with a visit to Les Chantiers Chibougamau’s Kraft Pulp Mill in Lebel-sur-Quevillon and their head manufacturing plant in Chibougamau. These sites are key examples of Quebec’s forest sector excellence and innovation in modernizing the industry, accelerating affordable housing and promoting green construction using value-added Canadian wood-based products.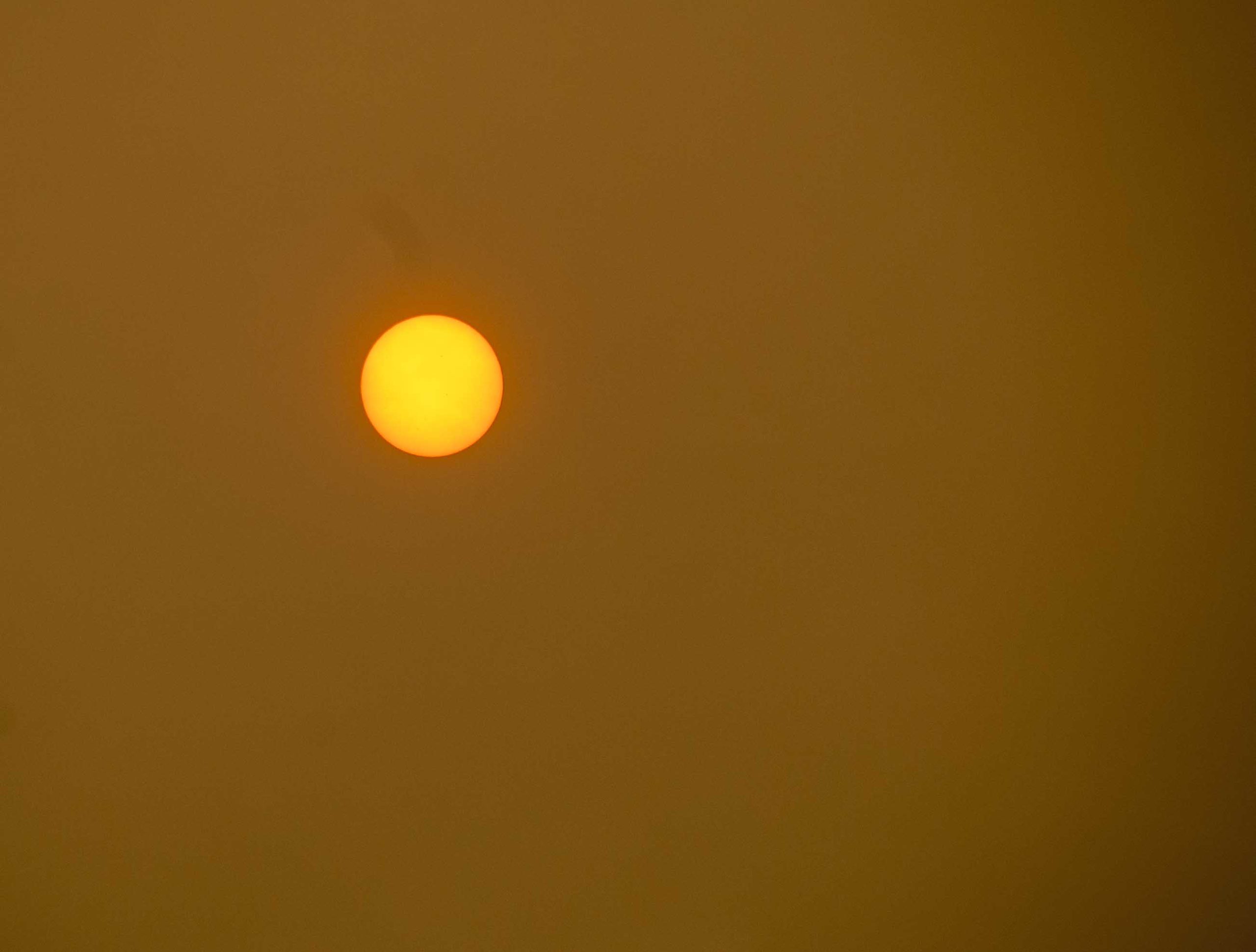 Toronto is among the most polluted cities in the world on Monday morning as the city remains under a special air quality statement for its third consecutive day. Environment Canada said smoke from forest fires is expected to continue to impact much of southern Ontario Monday and may persist into Tuesday before finally easing. “Air quality and visibility due to wildfire smoke can fluctuate over short distances and can vary considerably from hour to hour,” said Environment Canada in a special air quality statement issued Monday morning. …Toronto ranked third in a
Toronto is among the most polluted cities in the world on Monday morning as the city remains under a special air quality statement for its third consecutive day. Environment Canada said smoke from forest fires is expected to continue to impact much of southern Ontario Monday and may persist into Tuesday before finally easing. “Air quality and visibility due to wildfire smoke can fluctuate over short distances and can vary considerably from hour to hour,” said Environment Canada in a special air quality statement issued Monday morning. …Toronto ranked third in a 


 Officials in Nova Scotia say a wildfire in the western part of the province has grown and could force people out of their homes, while cooler temperatures and low winds have helped firefighters in Newfoundland and Labrador. The Long Lake wildfire is expected to grow, said Scott Tingley, manager of forest protection with Nova Scotia’s Natural Resources Department. On Sunday evening, the Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources said the fire had almost doubled in size, growing from 11 square kilometres in the morning to nearly 20 square kilometres. It had spread past Godfrey Lake to the intersection of Fairns and West Dalhousie roads on one side and the south side of Spectacle Lakes on the other, it added. “These are not favourable firefighting conditions,” Tingley told reporters Sunday morning. “It’s very, very dry.” Two contracted helicopters were helping local firefighters along with crews from Prince Edward Island and Ontario, he said.
Officials in Nova Scotia say a wildfire in the western part of the province has grown and could force people out of their homes, while cooler temperatures and low winds have helped firefighters in Newfoundland and Labrador. The Long Lake wildfire is expected to grow, said Scott Tingley, manager of forest protection with Nova Scotia’s Natural Resources Department. On Sunday evening, the Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources said the fire had almost doubled in size, growing from 11 square kilometres in the morning to nearly 20 square kilometres. It had spread past Godfrey Lake to the intersection of Fairns and West Dalhousie roads on one side and the south side of Spectacle Lakes on the other, it added. “These are not favourable firefighting conditions,” Tingley told reporters Sunday morning. “It’s very, very dry.” Two contracted helicopters were helping local firefighters along with crews from Prince Edward Island and Ontario, he said.
 NOVA SCOTIA –More than one hundred homes have been evacuated as an out of control wildfire near West Dalhousie in Annapolis County continues to burn Friday morning. The fire broke out Wednesday on the north side of Long Lake, about 20 kilometres east of Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia. The provincial Department of Natural Resources has said a lightning strike caused the fire. …The national weather forecaster has issued an air quality statement for Annapolis County and parts of Halifax County, saying smoke from the wildfires is reducing air quality in the area, and that people who are more likely to be impacted by smoke — including pregnant people, infants and young children, people with chronic health conditions and people who work outdoors — should avoid strenuous outdoor activities.
NOVA SCOTIA –More than one hundred homes have been evacuated as an out of control wildfire near West Dalhousie in Annapolis County continues to burn Friday morning. The fire broke out Wednesday on the north side of Long Lake, about 20 kilometres east of Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia. The provincial Department of Natural Resources has said a lightning strike caused the fire. …The national weather forecaster has issued an air quality statement for Annapolis County and parts of Halifax County, saying smoke from the wildfires is reducing air quality in the area, and that people who are more likely to be impacted by smoke — including pregnant people, infants and young children, people with chronic health conditions and people who work outdoors — should avoid strenuous outdoor activities.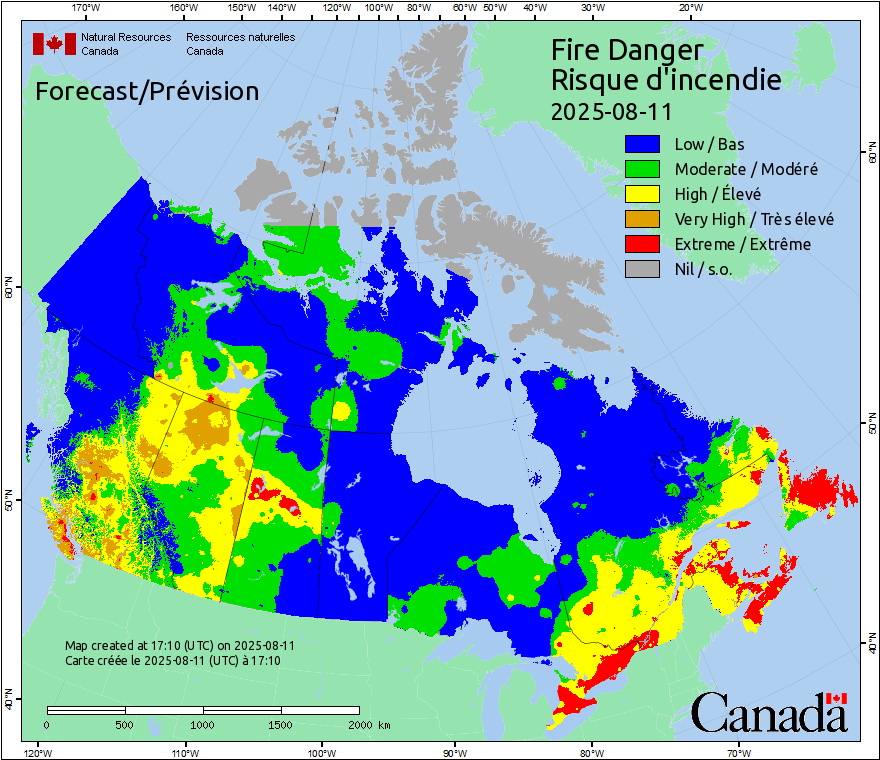
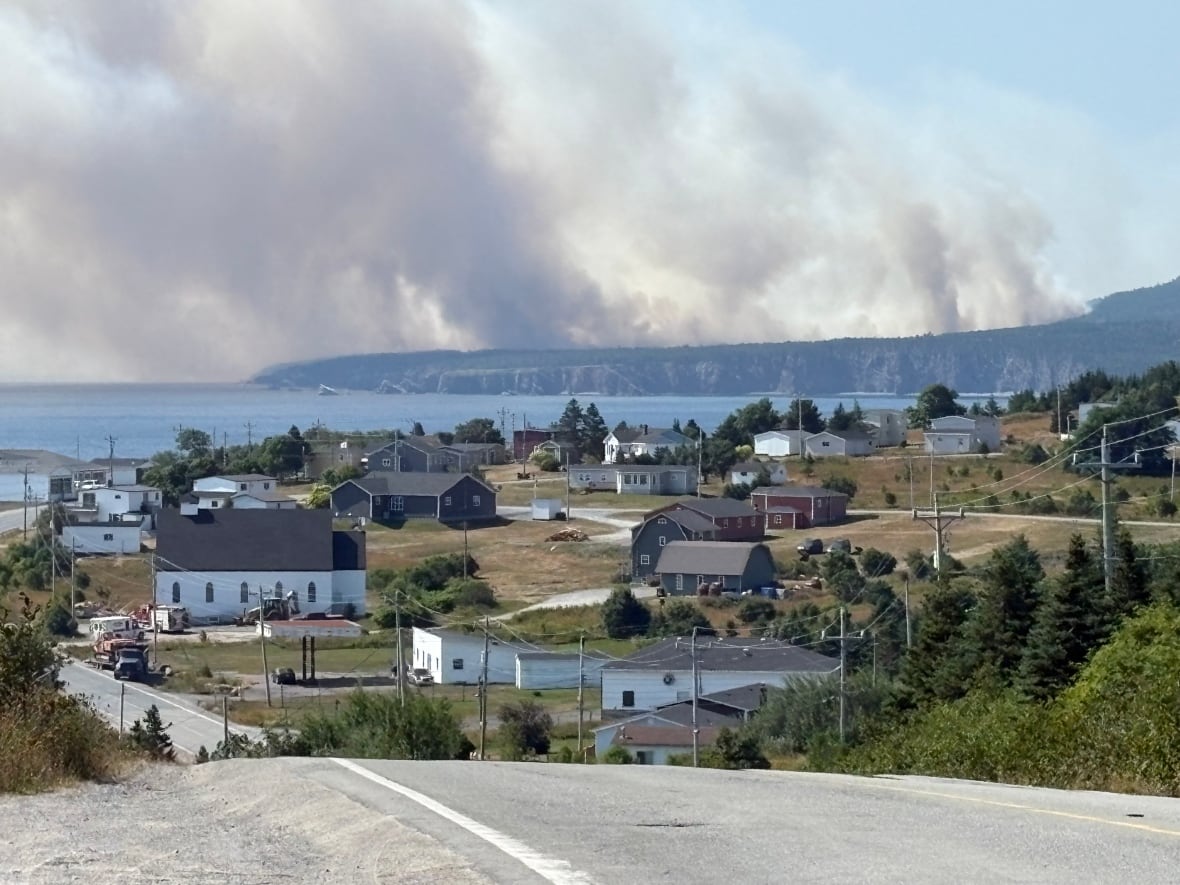
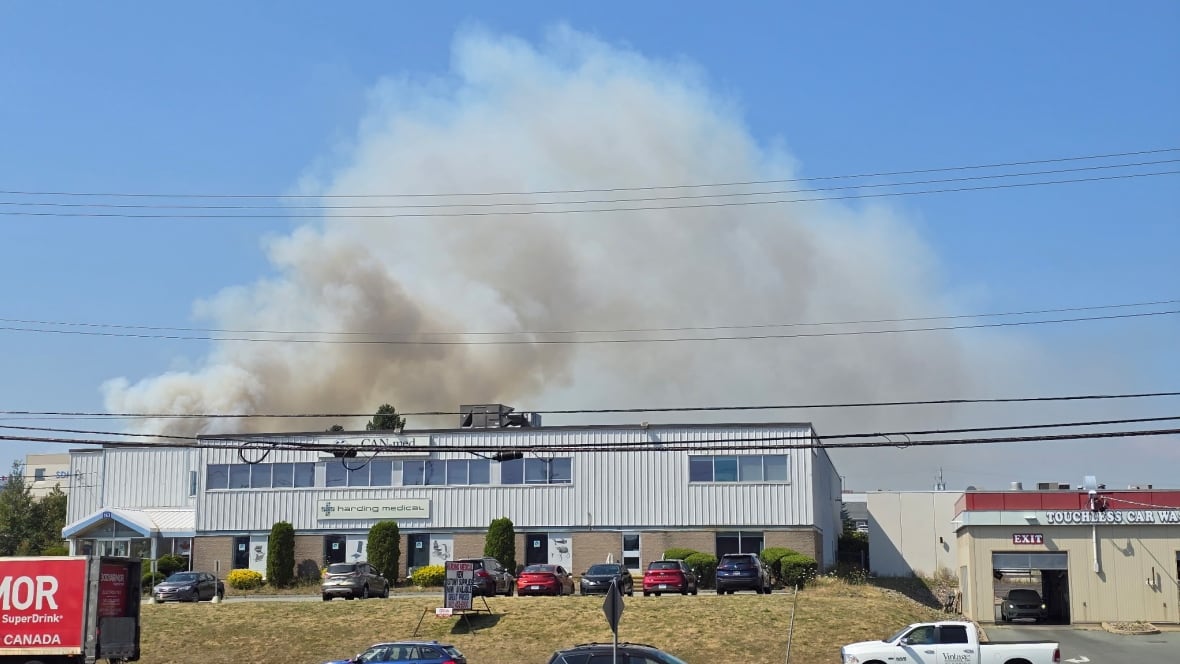




 The air quality has finally improved after several days of wildfire smoke hanging over much of southern Quebec. Montreal, along with several other cities in the province, were dealt an air quality advisory starting Saturday and clearing up Monday evening. But this year, the smoke causing the poor air quality isn’t coming from within the province but rather from the fires raging in the Prairies. While Quebec is seeing a rather tame wildfire season, this year is still gearing up to be another intense season for other parts of Canada. So far, 2025 has seen wildfires consume 6.5 million hectares. Last year the number totalled 5.3 million, and in 2023 — Canada’s worst wildfire season on record — a little over 16 million hectares burned. “The thing that is quite exceptional right now is that we had three years in a row with very, very high fire activity in Canada,” said Boulanger. The three most active fire seasons since 1995 have been recorded between 2023 and 2025, he said.
The air quality has finally improved after several days of wildfire smoke hanging over much of southern Quebec. Montreal, along with several other cities in the province, were dealt an air quality advisory starting Saturday and clearing up Monday evening. But this year, the smoke causing the poor air quality isn’t coming from within the province but rather from the fires raging in the Prairies. While Quebec is seeing a rather tame wildfire season, this year is still gearing up to be another intense season for other parts of Canada. So far, 2025 has seen wildfires consume 6.5 million hectares. Last year the number totalled 5.3 million, and in 2023 — Canada’s worst wildfire season on record — a little over 16 million hectares burned. “The thing that is quite exceptional right now is that we had three years in a row with very, very high fire activity in Canada,” said Boulanger. The three most active fire seasons since 1995 have been recorded between 2023 and 2025, he said.