Kevin Mason
The US tariff regime is far from over despite a US Supreme Court ruling striking down last year’s tariffs authorized by President Trump under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA). Although the court noted in its ruling that the president overstepped his authority in applying reciprocal tariffs on virtually all trading partners, it did leave the door open for other means of tariff application—and the US Administration has wasted no time in charging through that door, turning to Section 122 of the Trade Act of 1974 to impose new global tariffs of 10% (likely moving to 15%). Tariffs under Section 122 expire after 150 days without congressional approval, but we assume other options will be put in place before expiry (Section 232, 301 or some other creative mechanism).
With respect to the forest products industry, cessation of IEEPA tariffs and application of these new Section 122 tariffs have no impact on existing lumber duties (35% remains intact), nor for any existing tariffs under Section 232 (at 10%) or goods currently compliant under USMCA (such goods remain tariff-free under Section 122). Although USMCA-compliant goods are safe from tariffs for now, with that trade deal being reviewed this summer the tariff-free flow of goods among the US, Mexico and Canada could be upended. Since almost all newsprint supply comes from Canada (see page 19), that fear is ostensibly already causing U.S. buyers to accelerate purchases. Our table details what we know at the moment about the new tariff regime (Section 122 at 10% but probably moving to 15%). Brazil and China appear to be winners in these latest moves, but, with other mechanisms available to Trump, we don’t think these recent tariff reductions are going to lead to any dramatic increase in imports from these countries (uncertainty seems to be part of the goal under Trump’s methods).


 A judge with the US Court of International Trade ordered refunds for companies that paid tariffs that were later struck down by the United States Supreme Court. …The Supreme Court ruling did not say whether there should be refunds, leaving companies that paid the duties to sue the federal government. In Wednesday’s decision in the New York trade court, Judge Richard Eaton said all importers who paid IEEPA duties are “entitled to the benefit” of the Supreme Court’s decision. Eaton was ruling specifically on a case brought by Atmus Filtration, a filtration company in Tennessee, but said he will be the only judge to hear cases about refunds. Eaton ordered the Trump administration to finalize import paperwork without charging companies the IEEPA tariffs. …A coalition of more than 1,000 small businesses called it a victory and called on the Trump administration to act swiftly. …The White House has not yet responded.
A judge with the US Court of International Trade ordered refunds for companies that paid tariffs that were later struck down by the United States Supreme Court. …The Supreme Court ruling did not say whether there should be refunds, leaving companies that paid the duties to sue the federal government. In Wednesday’s decision in the New York trade court, Judge Richard Eaton said all importers who paid IEEPA duties are “entitled to the benefit” of the Supreme Court’s decision. Eaton was ruling specifically on a case brought by Atmus Filtration, a filtration company in Tennessee, but said he will be the only judge to hear cases about refunds. Eaton ordered the Trump administration to finalize import paperwork without charging companies the IEEPA tariffs. …A coalition of more than 1,000 small businesses called it a victory and called on the Trump administration to act swiftly. …The White House has not yet responded.
 Fiber and glass are among the packaging substrates hardest hit by February closure and layoff announcements. Here are the North American facilities that have announced downsizing efforts:
Fiber and glass are among the packaging substrates hardest hit by February closure and layoff announcements. Here are the North American facilities that have announced downsizing efforts: The escalating crisis in the Middle East could extend transport times for Finnish forest industry products to Asia by several weeks. At the same time, freight costs may rise, and container availability could become increasingly uncertain. Iran has announced the closure of the Strait of Hormuz. According to international reporting, several major shipping lines have also paused or reduced traffic through the Suez Canal, redirecting vessels around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope on routes to Asia. The Strait of Hormuz is a critical artery for global oil trade, and disruptions there primarily push up energy prices. For Finland’s forest industry, however, access through the Suez Canal is more directly decisive. Approximately 20 percent of the forest industry’s exports go to Asia, and the majority of those shipments pass through the Suez Canal, says Maarit Lindström, Director and Chief Economist at Metsäteollisuus ry.
The escalating crisis in the Middle East could extend transport times for Finnish forest industry products to Asia by several weeks. At the same time, freight costs may rise, and container availability could become increasingly uncertain. Iran has announced the closure of the Strait of Hormuz. According to international reporting, several major shipping lines have also paused or reduced traffic through the Suez Canal, redirecting vessels around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope on routes to Asia. The Strait of Hormuz is a critical artery for global oil trade, and disruptions there primarily push up energy prices. For Finland’s forest industry, however, access through the Suez Canal is more directly decisive. Approximately 20 percent of the forest industry’s exports go to Asia, and the majority of those shipments pass through the Suez Canal, says Maarit Lindström, Director and Chief Economist at Metsäteollisuus ry.  Portland based Hampton Lumber, one of the nation’s largest lumber manufacturers, confirmed on Thursday that it has parted ways with CEO Randy Schillinger. Steve Zika, vice chair of the Hampton board and its chief executive for 20 years before Schillinger was named to the position in June 2023 has served in an interim capacity since early December, the company said in an emailed statement. [A Portland Business Journal subscription is required to access this full story]
Portland based Hampton Lumber, one of the nation’s largest lumber manufacturers, confirmed on Thursday that it has parted ways with CEO Randy Schillinger. Steve Zika, vice chair of the Hampton board and its chief executive for 20 years before Schillinger was named to the position in June 2023 has served in an interim capacity since early December, the company said in an emailed statement. [A Portland Business Journal subscription is required to access this full story]
 NEOPIT, Wisconsin — A Neopit wood mill is closed Tuesday after it experienced an early morning fire. Menominee Tribal Enterprises says it lost its stacker building and associated equipment. Some lumber inventory was damaged in the fire as well. All employees are safe and no injuries were reported. Production operations are closed for the day as the organization assesses the damage and begins determining the next steps for recovery and continuity of operations. The Menominee Tribal Enterprises store and main office remain open and are operating during regular business hours.
NEOPIT, Wisconsin — A Neopit wood mill is closed Tuesday after it experienced an early morning fire. Menominee Tribal Enterprises says it lost its stacker building and associated equipment. Some lumber inventory was damaged in the fire as well. All employees are safe and no injuries were reported. Production operations are closed for the day as the organization assesses the damage and begins determining the next steps for recovery and continuity of operations. The Menominee Tribal Enterprises store and main office remain open and are operating during regular business hours.
 A recent
A recent  WASHINGTON — American employers unexpectedly cut 92,000 jobs last month, a sign that the labor market remains under strain. The unemployment rate blipped up to 4.4%. The
WASHINGTON — American employers unexpectedly cut 92,000 jobs last month, a sign that the labor market remains under strain. The unemployment rate blipped up to 4.4%. The 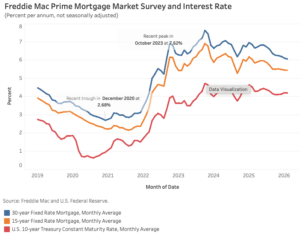 Mortgage rates continued to decline in February, dipping below 6% in the last week of February. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.05% last month, 5 basis points (bps) lower than January. Meanwhile, the average 15-year rate declined only a basis point to 5.43%. Compared to a year ago, the 30-year and 15-year rates are lower by 79 bps and 60 bps, respectively. The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term borrowing, held relatively steady for most of February with an average 4.18% – a marginal decrease of 2 bps from the previous month. However, yields fell significantly in the final week of February. …Following the recent escalation of conflict in the Middle East, the 10-year Treasury yield has shown signs of reversing course. Investors are closely monitoring how protracted the conflict may become and its potential implications for global energy markets. If oil prices rise significantly, inflation pressures could intensify, potentially pushing Treasury yields higher.
Mortgage rates continued to decline in February, dipping below 6% in the last week of February. According to Freddie Mac, the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 6.05% last month, 5 basis points (bps) lower than January. Meanwhile, the average 15-year rate declined only a basis point to 5.43%. Compared to a year ago, the 30-year and 15-year rates are lower by 79 bps and 60 bps, respectively. The 10-year Treasury yield, a key benchmark for long-term borrowing, held relatively steady for most of February with an average 4.18% – a marginal decrease of 2 bps from the previous month. However, yields fell significantly in the final week of February. …Following the recent escalation of conflict in the Middle East, the 10-year Treasury yield has shown signs of reversing course. Investors are closely monitoring how protracted the conflict may become and its potential implications for global energy markets. If oil prices rise significantly, inflation pressures could intensify, potentially pushing Treasury yields higher.
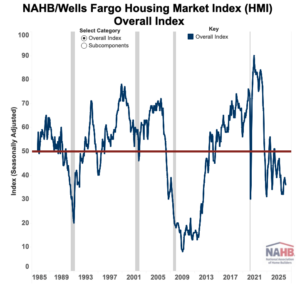
 If enacted, the new legislation would aim to streamline tariff exclusions for goods used in home construction, help stabilize material pricing, and support efforts to expand housing supply nationwide U.S. Sens. Jacky Rosen (D‑NV) and Chris Coons (D‑DE) have introduced legislation aimed at easing construction costs and addressing America’s housing affordability crisis by excluding key homebuilding materials from tariffs imposed under the Trump administration. The Housing Tariff Exclusion Act would create a process to automatically exempt many building materials from current and future tariffs and allow importers to apply for exemptions on other essential construction inputs. The bill comes amid ongoing concerns that tariffs on imported materials such as lumber, steel, and other construction inputs have driven up costs for builders, contributing to higher home prices and exacerbating supply shortages. …The bill has garnered support from industry groups including the NAHB.
If enacted, the new legislation would aim to streamline tariff exclusions for goods used in home construction, help stabilize material pricing, and support efforts to expand housing supply nationwide U.S. Sens. Jacky Rosen (D‑NV) and Chris Coons (D‑DE) have introduced legislation aimed at easing construction costs and addressing America’s housing affordability crisis by excluding key homebuilding materials from tariffs imposed under the Trump administration. The Housing Tariff Exclusion Act would create a process to automatically exempt many building materials from current and future tariffs and allow importers to apply for exemptions on other essential construction inputs. The bill comes amid ongoing concerns that tariffs on imported materials such as lumber, steel, and other construction inputs have driven up costs for builders, contributing to higher home prices and exacerbating supply shortages. …The bill has garnered support from industry groups including the NAHB.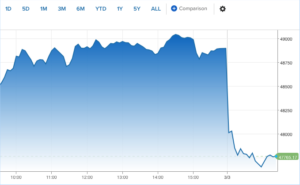 US equities tumbled on Tuesday, undoing a Monday equity comeback, as oil prices spiked again and traders began to worry the U.S.-Iran conflict could drag on longer than anticipated. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 1,238 points, or 2.5%. If that holds, it would mark the blue-chip index’s first 1,000-point decline since April 10, 2025. The S&P 500 slipped 2.2%, while the Nasdaq Composite was down 2.3%. Brent crude oil, the international benchmark, topped $84 a barrel, up 8% Tuesday following a 6% spike Monday. WTI crude jumped 8% to above $77 a barrel after a 6% jump as well on Monday. Iranian Revolutionary Guard commander said the Strait of Hormuz — the world’s most vital transit route for crude oil — is closed and that Iran would set ablaze ships attempting the route, Reuters reported, citing Iranian media.
US equities tumbled on Tuesday, undoing a Monday equity comeback, as oil prices spiked again and traders began to worry the U.S.-Iran conflict could drag on longer than anticipated. The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 1,238 points, or 2.5%. If that holds, it would mark the blue-chip index’s first 1,000-point decline since April 10, 2025. The S&P 500 slipped 2.2%, while the Nasdaq Composite was down 2.3%. Brent crude oil, the international benchmark, topped $84 a barrel, up 8% Tuesday following a 6% spike Monday. WTI crude jumped 8% to above $77 a barrel after a 6% jump as well on Monday. Iranian Revolutionary Guard commander said the Strait of Hormuz — the world’s most vital transit route for crude oil — is closed and that Iran would set ablaze ships attempting the route, Reuters reported, citing Iranian media. Real estate professionals active in the Los Angeles market are bracing themselves for another wave of tariff-induced uncertainty following the US Supreme Court’s ruling. …Despite the Feb. 20 ruling, President Donald Trump has been adamant that he will find other avenues to impose his tariffs. Trump’s tariff policies have already caused upheaval for local businesses, and now the country’s heightened situation with tariffs will further disrupt L.A.’s real estate market, according to experts across development, manufacturing and finance. “This is a very shifting landscape for American companies,” said Ken Calligar, founder of RSG 3•D. …Garret Weyand, at Cedar Street Partners, said, “If costs are too high because of these tariffs, then projects don’t get built.” Banks will likely make borrowers increase the amount of equity so that the bank is covered in the event tariffs and inflation raise project costs.
Real estate professionals active in the Los Angeles market are bracing themselves for another wave of tariff-induced uncertainty following the US Supreme Court’s ruling. …Despite the Feb. 20 ruling, President Donald Trump has been adamant that he will find other avenues to impose his tariffs. Trump’s tariff policies have already caused upheaval for local businesses, and now the country’s heightened situation with tariffs will further disrupt L.A.’s real estate market, according to experts across development, manufacturing and finance. “This is a very shifting landscape for American companies,” said Ken Calligar, founder of RSG 3•D. …Garret Weyand, at Cedar Street Partners, said, “If costs are too high because of these tariffs, then projects don’t get built.” Banks will likely make borrowers increase the amount of equity so that the bank is covered in the event tariffs and inflation raise project costs.
 Logging and forest trucking industry added an estimated $1.3 billion to the Northeast region in 2024, with Maine contributing $534 million of that amount, according to a study released this week. Maine’s figure included $283 million in total labor earnings and an estimated $23 million in state tax revenues. The Pine Tree State numbers represented 2,744 direct logging and trucking jobs, along with an additional 1,715 indirect jobs, for a total of about 4,460 jobs statewide. The Augusta-based Professional Logging Contractors of the Northeast released the results of its first-ever regional study on Wednesday, conducted by Wallace Economic Advisers LLC. It showed that in 2024, logging and forest trucking supported around 6,930 jobs in the region, generated $393 million in labor income, pumped an estimated $61 million into state and local tax coffers, and remained critical to a range of industries and communities.
Logging and forest trucking industry added an estimated $1.3 billion to the Northeast region in 2024, with Maine contributing $534 million of that amount, according to a study released this week. Maine’s figure included $283 million in total labor earnings and an estimated $23 million in state tax revenues. The Pine Tree State numbers represented 2,744 direct logging and trucking jobs, along with an additional 1,715 indirect jobs, for a total of about 4,460 jobs statewide. The Augusta-based Professional Logging Contractors of the Northeast released the results of its first-ever regional study on Wednesday, conducted by Wallace Economic Advisers LLC. It showed that in 2024, logging and forest trucking supported around 6,930 jobs in the region, generated $393 million in labor income, pumped an estimated $61 million into state and local tax coffers, and remained critical to a range of industries and communities.


 The mass timber supply chain has spent more than a decade proving the product works. …Now, research produced by Michigan State University argues that none of it matters much if the system surrounding the product isn’t built to match. Led by George Berghorn, Modular Mass Timber for Housing Construction, research published in the
The mass timber supply chain has spent more than a decade proving the product works. …Now, research produced by Michigan State University argues that none of it matters much if the system surrounding the product isn’t built to match. Led by George Berghorn, Modular Mass Timber for Housing Construction, research published in the 

 OREGON — The Pacific Northwest isn’t known as maple syrup country, but a burgeoning syrup industry in Oregon and Washington is trying to change that perception, one gallon of sap at a time. The Northwest’s more temperate climate and more watery maple sap make it harder to make syrup at a commercial scale. Producers can invest in technology, much of it developed in Canada, to improve their harvests, but that means steeper initial investments for farmers, and it doesn’t solve the fact that making bigleaf maple syrup still requires long, grueling hours that producers say can be a barrier to entry. Because of that, the Northwest maple syrup industry has required more effort to get off the ground. But those passionate about local syrup say the delicious, boutique product is well worth the trouble.
OREGON — The Pacific Northwest isn’t known as maple syrup country, but a burgeoning syrup industry in Oregon and Washington is trying to change that perception, one gallon of sap at a time. The Northwest’s more temperate climate and more watery maple sap make it harder to make syrup at a commercial scale. Producers can invest in technology, much of it developed in Canada, to improve their harvests, but that means steeper initial investments for farmers, and it doesn’t solve the fact that making bigleaf maple syrup still requires long, grueling hours that producers say can be a barrier to entry. Because of that, the Northwest maple syrup industry has required more effort to get off the ground. But those passionate about local syrup say the delicious, boutique product is well worth the trouble. The Trump administration is turning to rarely used laws to circumvent environmental restrictions and expand logging in certain Pacific Northwest forests, legal analysts and advocates say. In plans announced in February to expand logging in Alaska’s Tongass National Forest and on federal land in western Oregon … administration is using the 1990 Tongass Timber Reform Act to prioritize logging in the largest national forest in the US, and BLM is citing a 1937 law, the Oregon and California Revested Railroad Lands Act, to do so on its land in western Oregon. Both apply only to specific forests and envision logging as a primary use of those lands. The agencies are using federal laws that “privilege timber harvesting and will use that argument to short circuit environmental protections,” especially at the expense of endangered species, said Andrew Mergen, a Harvard Law School professor who was previously a lawyer at the Justice Department’s Environment & Natural Resources Division.
The Trump administration is turning to rarely used laws to circumvent environmental restrictions and expand logging in certain Pacific Northwest forests, legal analysts and advocates say. In plans announced in February to expand logging in Alaska’s Tongass National Forest and on federal land in western Oregon … administration is using the 1990 Tongass Timber Reform Act to prioritize logging in the largest national forest in the US, and BLM is citing a 1937 law, the Oregon and California Revested Railroad Lands Act, to do so on its land in western Oregon. Both apply only to specific forests and envision logging as a primary use of those lands. The agencies are using federal laws that “privilege timber harvesting and will use that argument to short circuit environmental protections,” especially at the expense of endangered species, said Andrew Mergen, a Harvard Law School professor who was previously a lawyer at the Justice Department’s Environment & Natural Resources Division.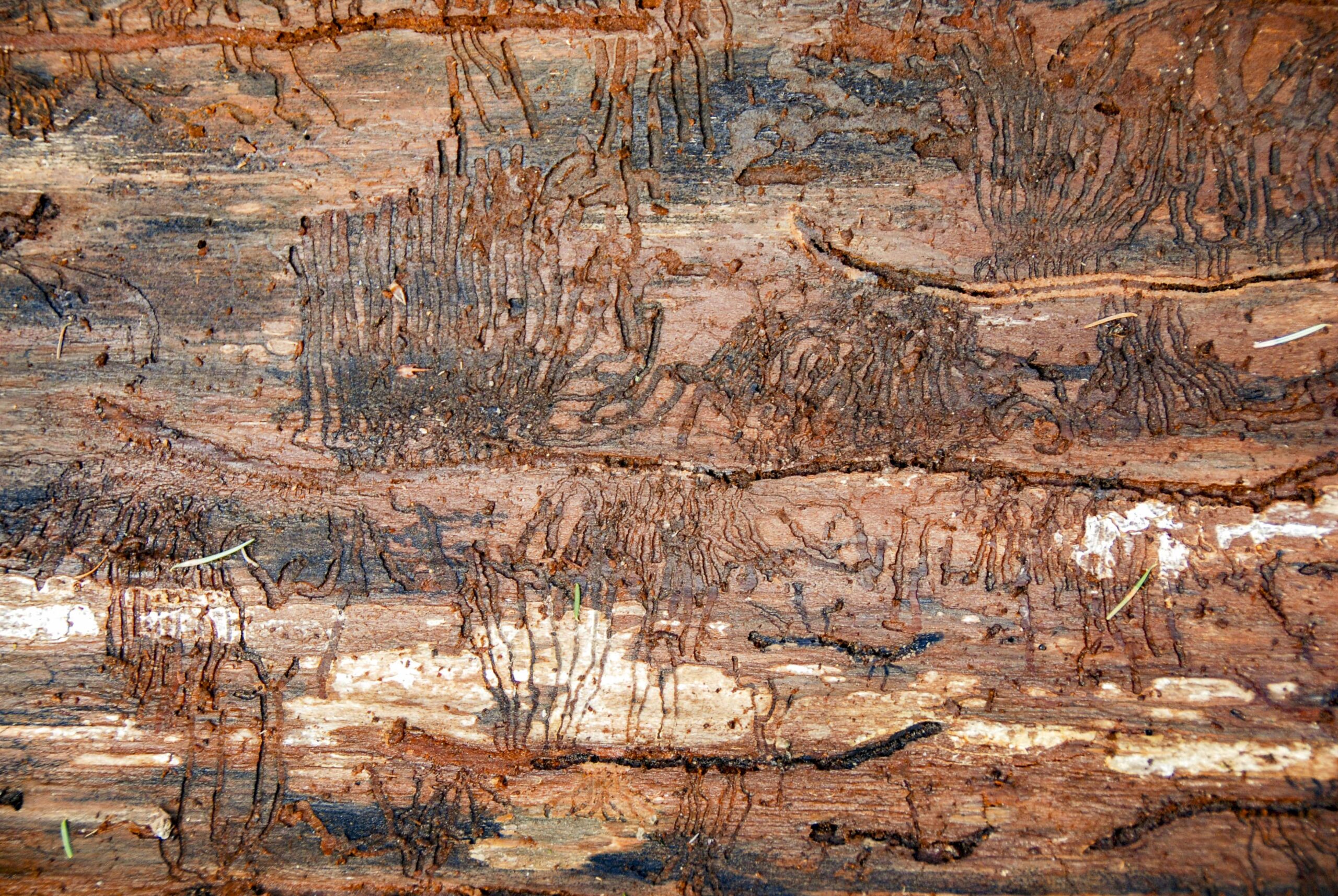 Across the Front Range, century-old, iconic ponderosa pines span thousands of acres …But over the past three years, that landscape has noticeably shifted. More hillsides are now marked by … signs of a growing pine beetle outbreak, according to the state’s Forest Service lead entomologist, Dan West. “The ability for these small, little insects to work in concert to all attack one tree all at the same time and to overcome the tree’s defenses that have been there for a century is truly staggering,” West said. It only took a few years for these tiny insects, no bigger than a grain of rice, to explode across the Front Range and impact more than 7,000 acres of forested land. Now, Gov. Jared Polis has launched an aggressive response. …Whether the state’s new task force can slow the outbreak remains to be seen.
Across the Front Range, century-old, iconic ponderosa pines span thousands of acres …But over the past three years, that landscape has noticeably shifted. More hillsides are now marked by … signs of a growing pine beetle outbreak, according to the state’s Forest Service lead entomologist, Dan West. “The ability for these small, little insects to work in concert to all attack one tree all at the same time and to overcome the tree’s defenses that have been there for a century is truly staggering,” West said. It only took a few years for these tiny insects, no bigger than a grain of rice, to explode across the Front Range and impact more than 7,000 acres of forested land. Now, Gov. Jared Polis has launched an aggressive response. …Whether the state’s new task force can slow the outbreak remains to be seen. 
 OREGON — A historic state-tribal collaboration in Oregon has stalled after a charitable foundation pulled out of a potential land deal. The Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife was preparing to purchase 11,438 acres of private timberland using a federal grant. The area is about 10 miles southwest of La Grande in the Blue Mountains. The agency planned to manage the land alongside the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation — the first such collaboration in Oregon. But the landowner, the Harry A. Merlo Foundation, has withdrawn from the deal “for undisclosed reasons,” according to the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife. The state wildlife department and tribes had secured $22 million in federal funding to acquire and co-manage the land. …The plan was to restore this swath of forests and meadows for elk and salmon habitat.
OREGON — A historic state-tribal collaboration in Oregon has stalled after a charitable foundation pulled out of a potential land deal. The Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife was preparing to purchase 11,438 acres of private timberland using a federal grant. The area is about 10 miles southwest of La Grande in the Blue Mountains. The agency planned to manage the land alongside the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation — the first such collaboration in Oregon. But the landowner, the Harry A. Merlo Foundation, has withdrawn from the deal “for undisclosed reasons,” according to the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife. The state wildlife department and tribes had secured $22 million in federal funding to acquire and co-manage the land. …The plan was to restore this swath of forests and meadows for elk and salmon habitat.

