 Stacked doughnuts and “damn fine coffee” welcomed a small but eager group of visitors Thursday morning to the World Forestry Center. These die-hard fans had traveled — at least one from out of state — to see the log. But not just any log. This lump of ponderosa pine, hand selected by David Lynch, is the most famous prop from his cult classic TV series, “Twin Peaks.” It was lovingly carried by actress Catherine Coulson, who portrayed the wise and mysterious Margaret “The Log Lady” Lanterman on the show. The pop-up exhibit, “What the Log Saw: Honoring the legacy of Catherine ‘The Log Lady’ Coulson,” celebrates both the on-screen character and the woman who portrayed her, while making connections between “The Log Lady” and sustainable forestry practices. …Coulson’s daughter, Zoey Yinger of Portland, approached the World Forest Center in January about displaying the log after the devastating Los Angeles wildfires.
Stacked doughnuts and “damn fine coffee” welcomed a small but eager group of visitors Thursday morning to the World Forestry Center. These die-hard fans had traveled — at least one from out of state — to see the log. But not just any log. This lump of ponderosa pine, hand selected by David Lynch, is the most famous prop from his cult classic TV series, “Twin Peaks.” It was lovingly carried by actress Catherine Coulson, who portrayed the wise and mysterious Margaret “The Log Lady” Lanterman on the show. The pop-up exhibit, “What the Log Saw: Honoring the legacy of Catherine ‘The Log Lady’ Coulson,” celebrates both the on-screen character and the woman who portrayed her, while making connections between “The Log Lady” and sustainable forestry practices. …Coulson’s daughter, Zoey Yinger of Portland, approached the World Forest Center in January about displaying the log after the devastating Los Angeles wildfires.

 WASHINGTON, DC — The American Kitchen Cabinet Alliance (AKCA) recently submitted formal comments as part of the Section 232 investigation on Timber, Lumber and Derivatives (including cabinets). Unfairly traded cabinet imports many of them sold at prices that are often over 60% below that of the domestic market are flooding into the US. …“American cabinet manufacturing plants cannot compete with foreign countries flooding the market with unfairly traded cabinets which has resulted in an estimated $6.5 billion in lost revenue to the domestic industry over the last five years,” remarked Perry Miller, President of Kountry Wood Products. “Foreign imports primarily from Cambodia, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, Vietnam that are heavily subsidized are destroying American cabinet jobs. …“The domestic cabinet industry is on the brink of collapse. “We are asking for a Section 232 tariff of at least 60%, to level the playing field and stop the cheating as we seek to protect over 250,000 American jobs.”
WASHINGTON, DC — The American Kitchen Cabinet Alliance (AKCA) recently submitted formal comments as part of the Section 232 investigation on Timber, Lumber and Derivatives (including cabinets). Unfairly traded cabinet imports many of them sold at prices that are often over 60% below that of the domestic market are flooding into the US. …“American cabinet manufacturing plants cannot compete with foreign countries flooding the market with unfairly traded cabinets which has resulted in an estimated $6.5 billion in lost revenue to the domestic industry over the last five years,” remarked Perry Miller, President of Kountry Wood Products. “Foreign imports primarily from Cambodia, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, Vietnam that are heavily subsidized are destroying American cabinet jobs. …“The domestic cabinet industry is on the brink of collapse. “We are asking for a Section 232 tariff of at least 60%, to level the playing field and stop the cheating as we seek to protect over 250,000 American jobs.” New York — Some of the last cargo ships carrying Chinese goods without crippling tariffs are arriving at US ports. Come next week, that will change. Cargo on ships from China loaded after April 9 will carry with them the 145% tariff President Donald Trump slapped on goods from that nation last month. Next week there will be fewer ships carrying less cargo. For many importers, it is too expensive to do business with China. Yet China is still one of America’s most important trading partners. It’s where we get most of our clothes, footwear, electronics and microchips, which power appliances, thermostats and anything else that beeps. …Forty-five percent of supply chain leaders expect they’ll pass the higher cost from tariffs down to their customers, according to a new survey by Gartner, a corporate research firm. …With fewer cargo ships expected at US ports, local economies will suffer immediately, Gene Seroka, executive director of the Port of Los Angeles said.
New York — Some of the last cargo ships carrying Chinese goods without crippling tariffs are arriving at US ports. Come next week, that will change. Cargo on ships from China loaded after April 9 will carry with them the 145% tariff President Donald Trump slapped on goods from that nation last month. Next week there will be fewer ships carrying less cargo. For many importers, it is too expensive to do business with China. Yet China is still one of America’s most important trading partners. It’s where we get most of our clothes, footwear, electronics and microchips, which power appliances, thermostats and anything else that beeps. …Forty-five percent of supply chain leaders expect they’ll pass the higher cost from tariffs down to their customers, according to a new survey by Gartner, a corporate research firm. …With fewer cargo ships expected at US ports, local economies will suffer immediately, Gene Seroka, executive director of the Port of Los Angeles said. BINGEN, Washington — A plywood mill in the southern Washington city of Bingen will close next month and lay off all 81 workers, the plant’s operator said Thursday. The SDS facility has been operating — with occasional stoppages — since 1949. It uses older equipment, according to Wilkins, Kaiser & Olsen, which was part of a consortium of firms that acquired the mill in 2021. “Regrettably, the long-term challenges and the magnitude of the required investment render continued operation unsustainable,” the mill’s operators said. An adjacent stud mill, planer mill and marine facility will continue operating. Bingen is a small city just across the Columbia River from Hood River. WKO and an affiliated business, Mt. Hood Forest Products, are adding 60 full-time positions to increase their output by 35%. The firms said they will consider hiring some of the laid-off workers.
BINGEN, Washington — A plywood mill in the southern Washington city of Bingen will close next month and lay off all 81 workers, the plant’s operator said Thursday. The SDS facility has been operating — with occasional stoppages — since 1949. It uses older equipment, according to Wilkins, Kaiser & Olsen, which was part of a consortium of firms that acquired the mill in 2021. “Regrettably, the long-term challenges and the magnitude of the required investment render continued operation unsustainable,” the mill’s operators said. An adjacent stud mill, planer mill and marine facility will continue operating. Bingen is a small city just across the Columbia River from Hood River. WKO and an affiliated business, Mt. Hood Forest Products, are adding 60 full-time positions to increase their output by 35%. The firms said they will consider hiring some of the laid-off workers.

 Gross domestic product (GDP) contracted in the first quarter by 0.3%, with imported goods being a large contributor to the decline as the suppliers prepared for President Trump’s tariff proposals once he took office. NAHB estimates this should even out in the second quarter. Other economic data of note are inflation, which is still elevated but creeping downward, and the unemployment rate, which remains low but may edge up among economic uncertainty. …NAHB Chief Economist Robert Dietz hasn’t hit the panic button yet. And I still think that we don’t know what President Trump’s economy really is yet. It’s been policy by sledgehammer, and now they’re going to start putting the pieces back together.” NAHB Senior Officers and staff continue to actively engage with lawmakers on this and other policies, including a special BUILD-PAC Capital Club event this week featuring an interview with Sen. Tim Sheehy.
Gross domestic product (GDP) contracted in the first quarter by 0.3%, with imported goods being a large contributor to the decline as the suppliers prepared for President Trump’s tariff proposals once he took office. NAHB estimates this should even out in the second quarter. Other economic data of note are inflation, which is still elevated but creeping downward, and the unemployment rate, which remains low but may edge up among economic uncertainty. …NAHB Chief Economist Robert Dietz hasn’t hit the panic button yet. And I still think that we don’t know what President Trump’s economy really is yet. It’s been policy by sledgehammer, and now they’re going to start putting the pieces back together.” NAHB Senior Officers and staff continue to actively engage with lawmakers on this and other policies, including a special BUILD-PAC Capital Club event this week featuring an interview with Sen. Tim Sheehy. Tuesday marked the 100th day of President Trump’s second term in office and there are signs of stress and jitters in the US construction industry, with rising prices, falling confidence, and a sharp uptick in abandoned projects. “Lumber and metals prices shot up in March, while contractors’ inboxes are bulging with ‘Dear Valued Customer’ letters announcing further increases for many products,” said Ken Simonson, chief economist at AGC. “Rapid-fire changes in tariffs threaten to drive prices higher for many essential construction goods,” he added. The price of materials and services used in nonresidential construction rose 0.4% in March, the third monthly increase in a row, AGC said. It was the first time since September 2023 that input prices had risen for three consecutive months, and comes after more than a year of stable or falling prices, Simonson said. …Within the 0.4% hike, lumber and plywood rose 2.7%.
Tuesday marked the 100th day of President Trump’s second term in office and there are signs of stress and jitters in the US construction industry, with rising prices, falling confidence, and a sharp uptick in abandoned projects. “Lumber and metals prices shot up in March, while contractors’ inboxes are bulging with ‘Dear Valued Customer’ letters announcing further increases for many products,” said Ken Simonson, chief economist at AGC. “Rapid-fire changes in tariffs threaten to drive prices higher for many essential construction goods,” he added. The price of materials and services used in nonresidential construction rose 0.4% in March, the third monthly increase in a row, AGC said. It was the first time since September 2023 that input prices had risen for three consecutive months, and comes after more than a year of stable or falling prices, Simonson said. …Within the 0.4% hike, lumber and plywood rose 2.7%.
 To kick off National Home Remodeling Month in May, which promotes the benefits of hiring a professional remodeler, the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) has highlighted
To kick off National Home Remodeling Month in May, which promotes the benefits of hiring a professional remodeler, the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) has highlighted 
 The US economy contracted in the first three months of 2025 on an import surge at the start of President Trump’s second term in office as he wages a potentially costly trade war. Gross domestic product fell at a 0.3% annualized pace, according to a Commerce Department report adjusted for seasonal factors and inflation. This was the first quarter of negative growth since Q1 of 2022. Economists had been looking for a gain of 0.4% after GDP rose by 2.4% in the fourth quarter of 2024. However, over the past day or so some Wall Street economists changed their outlook to negative growth, largely because of an unexpected rise in imports as companies and consumers sought to get ahead of the Trump tariffs implemented in early April. …The more telling number for the future of the expansion was consumer spending, and it grew, but at a relatively weak pace,” said Robert Frick.
The US economy contracted in the first three months of 2025 on an import surge at the start of President Trump’s second term in office as he wages a potentially costly trade war. Gross domestic product fell at a 0.3% annualized pace, according to a Commerce Department report adjusted for seasonal factors and inflation. This was the first quarter of negative growth since Q1 of 2022. Economists had been looking for a gain of 0.4% after GDP rose by 2.4% in the fourth quarter of 2024. However, over the past day or so some Wall Street economists changed their outlook to negative growth, largely because of an unexpected rise in imports as companies and consumers sought to get ahead of the Trump tariffs implemented in early April. …The more telling number for the future of the expansion was consumer spending, and it grew, but at a relatively weak pace,” said Robert Frick. 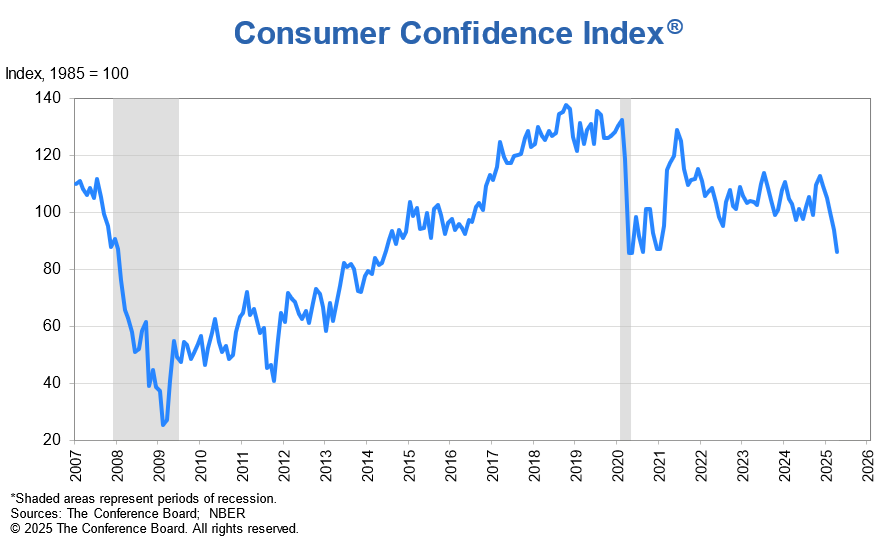



 The April Monthly Update includes these stories and more:
The April Monthly Update includes these stories and more:
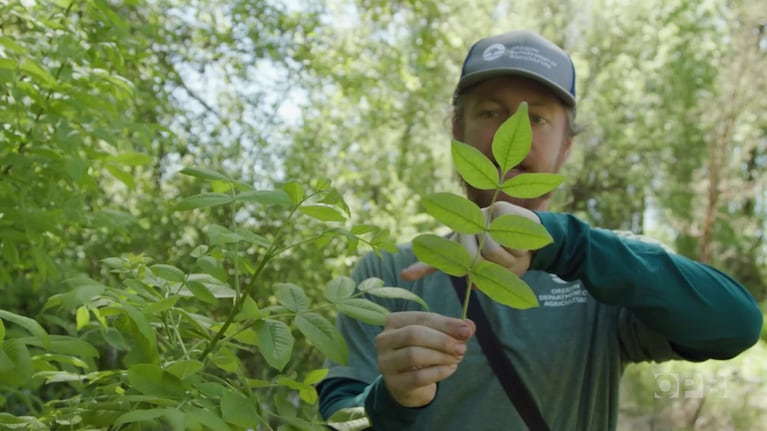







 The Washington State Department of Natural Resources recently began a multi-faceted forest restoration project across approximately 150 acres of the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest near Verlot. The Pilchuck Restoration Project is led by the Department of Natural Resources (DNR) Federal Lands Program under the agency’s Good Neighbor Authority agreement with the USDA Forest Service. Established in 2014, the GNA allows DNR to leverage its resources with federal and local partners to perform a variety of restoration activities on federal lands. Operators are following a carefully designed prescription focused on thinning out the small-diameter, younger trees that, due to past management practices, are overcrowding tree stands to the detriment of the larger, older trees.
The Washington State Department of Natural Resources recently began a multi-faceted forest restoration project across approximately 150 acres of the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest near Verlot. The Pilchuck Restoration Project is led by the Department of Natural Resources (DNR) Federal Lands Program under the agency’s Good Neighbor Authority agreement with the USDA Forest Service. Established in 2014, the GNA allows DNR to leverage its resources with federal and local partners to perform a variety of restoration activities on federal lands. Operators are following a carefully designed prescription focused on thinning out the small-diameter, younger trees that, due to past management practices, are overcrowding tree stands to the detriment of the larger, older trees.

