 Prime Minister Mark Carney said Canada probably won’t reach a near-term deal with the United States to lower tariffs on sectors such as steel and aluminum, and negotiations are likely to be rolled into next year’s review of the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement. Canada and the US were close to a pact on metals tariffs, but President Donald Trump then terminated talks in October. …“My judgment is that that is now going to roll into the broader CUSMA negotiation, so we’re unlikely, given the time horizons coming together, to have a sectoral agreement,” Carney said on Thursday. “Although if the United States wants to come back on that in those areas, we’re always ready there — we’re very ready.” …Canada is “very ready on forest products to strike an agreement,” the prime minister added. The U.S. has placed roughly 45% duties and taxes on imports of Canadian softwood lumber, to the frustration of US homebuilders.
Prime Minister Mark Carney said Canada probably won’t reach a near-term deal with the United States to lower tariffs on sectors such as steel and aluminum, and negotiations are likely to be rolled into next year’s review of the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement. Canada and the US were close to a pact on metals tariffs, but President Donald Trump then terminated talks in October. …“My judgment is that that is now going to roll into the broader CUSMA negotiation, so we’re unlikely, given the time horizons coming together, to have a sectoral agreement,” Carney said on Thursday. “Although if the United States wants to come back on that in those areas, we’re always ready there — we’re very ready.” …Canada is “very ready on forest products to strike an agreement,” the prime minister added. The U.S. has placed roughly 45% duties and taxes on imports of Canadian softwood lumber, to the frustration of US homebuilders.
 The federal government’s “Buy Canadian” policy for procurement for large infrastructure and defence projects kicked in on Tuesday as the U.S. trade war continues, Procurement Minister Joël Lightbound says. The policy was announced by Prime Minister Mark Carney in September and is essentially a mandate for the federal government to source components used in major government projects from domestic manufacturers. The procurement policy will extend immediately to government contracts valued at $25 million and over, but will expand to contracts valued at $5 million and over by the spring of 2026, Lightbound said. …Additionally, large federal construction and defence projects valued at $25 million or more will be required to use Canadian-produced steel, aluminum and wood products where the basic supply is available, he added. …In July, Carney had announced Canada would “restrict and reduce foreign steel imports entering the Canadian market.” In August, the policy was extended to Canadian lumber.
The federal government’s “Buy Canadian” policy for procurement for large infrastructure and defence projects kicked in on Tuesday as the U.S. trade war continues, Procurement Minister Joël Lightbound says. The policy was announced by Prime Minister Mark Carney in September and is essentially a mandate for the federal government to source components used in major government projects from domestic manufacturers. The procurement policy will extend immediately to government contracts valued at $25 million and over, but will expand to contracts valued at $5 million and over by the spring of 2026, Lightbound said. …Additionally, large federal construction and defence projects valued at $25 million or more will be required to use Canadian-produced steel, aluminum and wood products where the basic supply is available, he added. …In July, Carney had announced Canada would “restrict and reduce foreign steel imports entering the Canadian market.” In August, the policy was extended to Canadian lumber. The trade war launched by Donald Trump continues to intensify, striking Canadian workers. In addition to the 50% tariffs on steel and aluminum imposed earlier this year and the duties on non-CUSMA-compliant automobiles and parts, Washington added a 50% tariff on copper in July. More recently, a new 10% duty on softwood lumber was introduced, on top of the existing countervailing and anti-dumping duties. …Thanks to the mobilization and constant pressure of the United Steelworkers, several long-standing union demands have finally been adopted in Ottawa. …The federal government announced that it will now require the use of Canadian-made products in publicly funded projects and has announced new investments to strengthen Canada’s industrial capacity and the resilience of our supply chains. …Canada must go further and adopt a strong industrial strategy to reduce our dependence on the U.S. market, protect jobs, and ensure that we never again find ourselves in such a vulnerable position.
The trade war launched by Donald Trump continues to intensify, striking Canadian workers. In addition to the 50% tariffs on steel and aluminum imposed earlier this year and the duties on non-CUSMA-compliant automobiles and parts, Washington added a 50% tariff on copper in July. More recently, a new 10% duty on softwood lumber was introduced, on top of the existing countervailing and anti-dumping duties. …Thanks to the mobilization and constant pressure of the United Steelworkers, several long-standing union demands have finally been adopted in Ottawa. …The federal government announced that it will now require the use of Canadian-made products in publicly funded projects and has announced new investments to strengthen Canada’s industrial capacity and the resilience of our supply chains. …Canada must go further and adopt a strong industrial strategy to reduce our dependence on the U.S. market, protect jobs, and ensure that we never again find ourselves in such a vulnerable position.  “We’re just waiting for the dust to settle.” That sentiment was expressed recently by Nick Arkle, CEO of Gorman Bros., regarding the current 45% tariff on Canadian lumber exported to the US. In other words, what the industry is seeking more than anything else is clarity. …Complicating this scenario for lumber producers—and one that should not and cannot be overlooked—is provincial government policy, especially in BC, Ontario and Quebec. …If there is a potential silver lining in Canada to the ongoing tariff soap opera, it’s the promise by the Canadian Liberal government to build 500,000 new, affordable homes per year, thus theoretically creating significant domestic demand for building materials like softwood lumber. …While the experts are skeptical that the federal government will meet its goal of building 500,000 new homes per year… it will be worthwhile watching to see if Canadian softwood lumber producers will step up and benefit from this initiative.
“We’re just waiting for the dust to settle.” That sentiment was expressed recently by Nick Arkle, CEO of Gorman Bros., regarding the current 45% tariff on Canadian lumber exported to the US. In other words, what the industry is seeking more than anything else is clarity. …Complicating this scenario for lumber producers—and one that should not and cannot be overlooked—is provincial government policy, especially in BC, Ontario and Quebec. …If there is a potential silver lining in Canada to the ongoing tariff soap opera, it’s the promise by the Canadian Liberal government to build 500,000 new, affordable homes per year, thus theoretically creating significant domestic demand for building materials like softwood lumber. …While the experts are skeptical that the federal government will meet its goal of building 500,000 new homes per year… it will be worthwhile watching to see if Canadian softwood lumber producers will step up and benefit from this initiative.
 CHEMAINUS, BC — Western Forest Products’ value-added division in Chemainus is receiving up to $7.5 million from the province to add two new continuous dry kilns to its manufacturing operations. The investment, from the province’s BC Manufacturing Jobs Fund, will allow WFP’s facility on River Road to expand the production of high-value products and create new opportunities for second-growth hemlock to produce higher-value products, as well as increasing the stability of the forest company’s operations on Vancouver Island. Minister of Jobs and Economic Growth Ravi Kahlon and Forest Minister Ravi Parmar joined Steven Hofer, CEO of WFP, to make the funding announcement, which is expected to strengthen Vancouver Island’s manufacturing sector. In addition, the ministers announced that
CHEMAINUS, BC — Western Forest Products’ value-added division in Chemainus is receiving up to $7.5 million from the province to add two new continuous dry kilns to its manufacturing operations. The investment, from the province’s BC Manufacturing Jobs Fund, will allow WFP’s facility on River Road to expand the production of high-value products and create new opportunities for second-growth hemlock to produce higher-value products, as well as increasing the stability of the forest company’s operations on Vancouver Island. Minister of Jobs and Economic Growth Ravi Kahlon and Forest Minister Ravi Parmar joined Steven Hofer, CEO of WFP, to make the funding announcement, which is expected to strengthen Vancouver Island’s manufacturing sector. In addition, the ministers announced that  Nine more forestry companies are being supported to modernize, innovate and diversify their product lines and fibre sources to make more high-value, made-in-BC products, and help protect and create jobs. “It’s no secret our forestry sector is facing many challenges, making these investments timely,” said Minister of Forests, Ravi Parmar. …Through the BC Manufacturing Jobs Fund, the Province is contributing $2.5 million to plan or complete capital projects. For example, Canadian Bavarian Millwork and Lumber in Chemainus will receive as much as $1.4 million to help build its new facility. …Additional investments include:
Nine more forestry companies are being supported to modernize, innovate and diversify their product lines and fibre sources to make more high-value, made-in-BC products, and help protect and create jobs. “It’s no secret our forestry sector is facing many challenges, making these investments timely,” said Minister of Forests, Ravi Parmar. …Through the BC Manufacturing Jobs Fund, the Province is contributing $2.5 million to plan or complete capital projects. For example, Canadian Bavarian Millwork and Lumber in Chemainus will receive as much as $1.4 million to help build its new facility. …Additional investments include: Many laid-off workers at Western Forest Products’ Chemainus sawmill are increasingly frustrated with the company for the delays in the reopening of the mill, and with the state of the coastal forest industry overall. Brian Bull, Randy Robertson and Robert Joyce, who collectively have 95 years working in the forest industry, have been laid off since WFP temporarily curtailed operations at the mill on June 18. WFP recently announced that the shutdown at the mill, which employees approximately 150 workers, would extend into 2026 due to poor market conditions, high American lumber tariffs, and log-supply issues. Robertson said the company has not given the workers any indication of when the mill will reopen. …Bull said the mill’s workers’… employment insurance benefits are running out and they’re only making about half of the money they make at the mill even with the EI benefits.
Many laid-off workers at Western Forest Products’ Chemainus sawmill are increasingly frustrated with the company for the delays in the reopening of the mill, and with the state of the coastal forest industry overall. Brian Bull, Randy Robertson and Robert Joyce, who collectively have 95 years working in the forest industry, have been laid off since WFP temporarily curtailed operations at the mill on June 18. WFP recently announced that the shutdown at the mill, which employees approximately 150 workers, would extend into 2026 due to poor market conditions, high American lumber tariffs, and log-supply issues. Robertson said the company has not given the workers any indication of when the mill will reopen. …Bull said the mill’s workers’… employment insurance benefits are running out and they’re only making about half of the money they make at the mill even with the EI benefits.  NANAIMO — Exploratory discussions around potentially restricting industrial business activities in Nanaimo irked representatives of Nanaimo Forest Products (NFP), which operates Duke Point’s Harmac Pacific pulp mill. The narrowly approved Nov. 17 notice of motion from Nanaimo city councillor Paul Manly. …Harmac Pacific is actively attempting to rezone a pair of adjacent Phoenix Way lots involving a combined 244 acres bordering Cedar’s Cable Bay Trail. “If this bylaw were to become a reality, it would threaten the ability of our business to continue. …Mayor Leonard Krog is heavily opposed to the motion. “This motion basically says to anyone who wants to invest in this community ‘Don’t bother going to Nanaimo, don’t bother worrying about whether the land is zoned for heavy industry because Nanaimo wants to limit everything that might actually create some real jobs…’” …Harmac Pacific employs roughly 340 employees at its specialty pulp operation, which features a unique employee-owned ownership model.
NANAIMO — Exploratory discussions around potentially restricting industrial business activities in Nanaimo irked representatives of Nanaimo Forest Products (NFP), which operates Duke Point’s Harmac Pacific pulp mill. The narrowly approved Nov. 17 notice of motion from Nanaimo city councillor Paul Manly. …Harmac Pacific is actively attempting to rezone a pair of adjacent Phoenix Way lots involving a combined 244 acres bordering Cedar’s Cable Bay Trail. “If this bylaw were to become a reality, it would threaten the ability of our business to continue. …Mayor Leonard Krog is heavily opposed to the motion. “This motion basically says to anyone who wants to invest in this community ‘Don’t bother going to Nanaimo, don’t bother worrying about whether the land is zoned for heavy industry because Nanaimo wants to limit everything that might actually create some real jobs…’” …Harmac Pacific employs roughly 340 employees at its specialty pulp operation, which features a unique employee-owned ownership model. For Crofton mill workers it was like getting a lump of coal in their stockings. Last week owners of the Domtar pulp mill announced they were shuttering the operation …Who and what is to blame is a complicated tangle, encompassing questions about the future of the forest industry in this province. …While we must confront these questions, the closure also highlights the dangers of community dependence on a particular operation, or even industry. While the workers will, of course, be the most affected, North Cowichan residents will also feel the pain from the mill closure, as it is the municipality’s single biggest taxpayer. ….We can all hope that there will still be a future for the Crofton mill site… but that’s in no way a given. The municipality will be facing some very difficult decisions about services and what it can afford. The larger community will also feel the loss of all of those well paying jobs.
For Crofton mill workers it was like getting a lump of coal in their stockings. Last week owners of the Domtar pulp mill announced they were shuttering the operation …Who and what is to blame is a complicated tangle, encompassing questions about the future of the forest industry in this province. …While we must confront these questions, the closure also highlights the dangers of community dependence on a particular operation, or even industry. While the workers will, of course, be the most affected, North Cowichan residents will also feel the pain from the mill closure, as it is the municipality’s single biggest taxpayer. ….We can all hope that there will still be a future for the Crofton mill site… but that’s in no way a given. The municipality will be facing some very difficult decisions about services and what it can afford. The larger community will also feel the loss of all of those well paying jobs.
 The Court of International Trade on Dec. 18 again
The Court of International Trade on Dec. 18 again  NORTH CAROLINA — After reviewing public comments, the
NORTH CAROLINA — After reviewing public comments, the  Maine timber companies are in line to receive substantial incentives to manage forests and grow healthier, more valuable trees. A $32 million award to the New England Forestry Foundation was recently finalized by the US Department of Agriculture. The funding package, through the Advancing Markets for Producers initiative, replaces similar funding provided under the “climate smart commodities” program. While there are some adjustments to the program, it achieves the same purpose, according to the foundation Deputy Director Andi Colnes. The grant will largely subsidize commercial and pre-commercial thinning, Colnes said. It will also provide funding to expand market opportunities, particularly for mass timber construction, she added. …According to Colnes, the program is able to cover about 50,000 acres of New England forests, mostly commercial timberland in Maine. The foundation said 23 commercial, conservation and public forest owners are already enrolled in the project.
Maine timber companies are in line to receive substantial incentives to manage forests and grow healthier, more valuable trees. A $32 million award to the New England Forestry Foundation was recently finalized by the US Department of Agriculture. The funding package, through the Advancing Markets for Producers initiative, replaces similar funding provided under the “climate smart commodities” program. While there are some adjustments to the program, it achieves the same purpose, according to the foundation Deputy Director Andi Colnes. The grant will largely subsidize commercial and pre-commercial thinning, Colnes said. It will also provide funding to expand market opportunities, particularly for mass timber construction, she added. …According to Colnes, the program is able to cover about 50,000 acres of New England forests, mostly commercial timberland in Maine. The foundation said 23 commercial, conservation and public forest owners are already enrolled in the project.
 President Trump’s tariff and trade policies dominated the world’s political discourse through 2025. …The good news is that the BC economy has been fairly resilient through 2025. …BC trade resilience can also be attributed to a broader export commodity mix, dominated by forestry, agricultural and seafood products, as well as mining and oil and gas. …Forest products were tagged with a sectoral tariff of 10 per cent in October 2025, on top of new anti-dumping and countervailing tariffs on softwood lumber. …This has put tremendous pressure on an industry. …It’s difficult to disentangle the impact of tariffs from overall adverse trends in the BC forest industry, many mill closures and curtailments in recent years. BC forestry exports are among the most exposed to the US market, with about 75% of forestry exports headed south. Exports of softwood lumber were down 26% in August 2025 compared to August 2024. Pulp and paper exports were also down 9% on a year-to-date basis compared to 2024.
President Trump’s tariff and trade policies dominated the world’s political discourse through 2025. …The good news is that the BC economy has been fairly resilient through 2025. …BC trade resilience can also be attributed to a broader export commodity mix, dominated by forestry, agricultural and seafood products, as well as mining and oil and gas. …Forest products were tagged with a sectoral tariff of 10 per cent in October 2025, on top of new anti-dumping and countervailing tariffs on softwood lumber. …This has put tremendous pressure on an industry. …It’s difficult to disentangle the impact of tariffs from overall adverse trends in the BC forest industry, many mill closures and curtailments in recent years. BC forestry exports are among the most exposed to the US market, with about 75% of forestry exports headed south. Exports of softwood lumber were down 26% in August 2025 compared to August 2024. Pulp and paper exports were also down 9% on a year-to-date basis compared to 2024.

 The
The 

 Nonfarm payrolls grew slightly more than expected in November but slumped in October while unemployment hit its highest in four years, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Tuesday in numbers delayed by the government shutdown. Job growth totaled a seasonally adjusted 64,000 for the month, better than the Dow Jones estimate of 45,000 and up from a sharp decline in October. The unemployment rate rose to 4.6%, more than expected and its highest level since September 2021. A more encompassing measure that includes discouraged workers and those holding part-time jobs for economic reasons swelled to 8.7%, its peak going back to August 2021. In addition to the November report, the BLS released an abbreviated October count that showed payrolls down 105,000. While there was no official estimate, Wall Street economists were largely expecting a decline following a surprise increase of 108,000 in September.
Nonfarm payrolls grew slightly more than expected in November but slumped in October while unemployment hit its highest in four years, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Tuesday in numbers delayed by the government shutdown. Job growth totaled a seasonally adjusted 64,000 for the month, better than the Dow Jones estimate of 45,000 and up from a sharp decline in October. The unemployment rate rose to 4.6%, more than expected and its highest level since September 2021. A more encompassing measure that includes discouraged workers and those holding part-time jobs for economic reasons swelled to 8.7%, its peak going back to August 2021. In addition to the November report, the BLS released an abbreviated October count that showed payrolls down 105,000. While there was no official estimate, Wall Street economists were largely expecting a decline following a surprise increase of 108,000 in September.
 The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) welcomes the announcement made today by the Honourable Tim Hodgson, Minister of Energy and Natural Resources. The event celebrated funding for projects that strengthen Canada’s forestry sector and foster innovation in wood-based solutions. CWC received $8.5 million since 2023 to expand the use of wood-based products, broaden education on wood construction and contribute to the advancement of the National Building Code. …This funding has allowed CWC and its WoodWorks program to support design and construction professionals with expert resources, tools, and guidance that help accelerate the adoption of wood construction nationwide. As we continue this work, we will help catalyze sustainable demand for construction solutions that are not only innovative but also replicable and rapidly deployed, approaches that will help address Canada’s housing and affordability challenges at scale.
The Canadian Wood Council (CWC) welcomes the announcement made today by the Honourable Tim Hodgson, Minister of Energy and Natural Resources. The event celebrated funding for projects that strengthen Canada’s forestry sector and foster innovation in wood-based solutions. CWC received $8.5 million since 2023 to expand the use of wood-based products, broaden education on wood construction and contribute to the advancement of the National Building Code. …This funding has allowed CWC and its WoodWorks program to support design and construction professionals with expert resources, tools, and guidance that help accelerate the adoption of wood construction nationwide. As we continue this work, we will help catalyze sustainable demand for construction solutions that are not only innovative but also replicable and rapidly deployed, approaches that will help address Canada’s housing and affordability challenges at scale.
 Mark Latino is the CEO of Lee Display, a Fairfield, California-based company… that still makes artificial Christmas trees, producing around 10,000 each year. Tariffs shone a twinkling light this year on fake Christmas trees — and the extent to which America depends on other countries for its plastic fir trees. Prices for fake trees rose 10% to 15% this year due to the new import taxes, according to the American Christmas Tree Association, a trade group. Tree sellers cut their orders and paid higher tariffs for the stock they brought in. Despite those issues, tree companies say they aren’t likely to shift large-scale production back to the US after decades in Asia. Fake trees are labor-intensive and require holiday lights and other components the US doesn’t make. …About 80% of the US residents who put up a Christmas tree this year planned to use a fake one. …That percentage has been unchanged for at least 15 years.
Mark Latino is the CEO of Lee Display, a Fairfield, California-based company… that still makes artificial Christmas trees, producing around 10,000 each year. Tariffs shone a twinkling light this year on fake Christmas trees — and the extent to which America depends on other countries for its plastic fir trees. Prices for fake trees rose 10% to 15% this year due to the new import taxes, according to the American Christmas Tree Association, a trade group. Tree sellers cut their orders and paid higher tariffs for the stock they brought in. Despite those issues, tree companies say they aren’t likely to shift large-scale production back to the US after decades in Asia. Fake trees are labor-intensive and require holiday lights and other components the US doesn’t make. …About 80% of the US residents who put up a Christmas tree this year planned to use a fake one. …That percentage has been unchanged for at least 15 years.
 Over an hour of discussion followed BC Timber Sales’ (BCTS) presentation at the Sunshine Coast Regional District’s (SCRD) Dec. 11 committee of the whole meeting. …BCTS representatives, a delegation at the committee meeting, faced a direct ask from Gibsons area alternate director Annemarie De Andrade to pause harvesting activities on TA0519, in the Gibsons aquifer recharge area pending further study of the impacts of such logging. “We can continue to listen and continue with a light footprint, but we cannot pause,” was the response from BCTS’s Chinook Business Area timber sales manager Stacey Gould. She explained BCTS has a role as a revenue generator for the province. …That “lighter” BCTS footprint… is havesting about half of the volume it is permitted to on the lower Sunshine Coast. To make up for that, higher levels of harvesting need to be undertaking in other locations.
Over an hour of discussion followed BC Timber Sales’ (BCTS) presentation at the Sunshine Coast Regional District’s (SCRD) Dec. 11 committee of the whole meeting. …BCTS representatives, a delegation at the committee meeting, faced a direct ask from Gibsons area alternate director Annemarie De Andrade to pause harvesting activities on TA0519, in the Gibsons aquifer recharge area pending further study of the impacts of such logging. “We can continue to listen and continue with a light footprint, but we cannot pause,” was the response from BCTS’s Chinook Business Area timber sales manager Stacey Gould. She explained BCTS has a role as a revenue generator for the province. …That “lighter” BCTS footprint… is havesting about half of the volume it is permitted to on the lower Sunshine Coast. To make up for that, higher levels of harvesting need to be undertaking in other locations.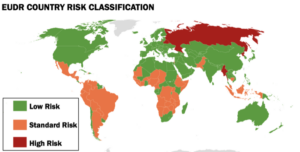 The EU Deforestation Rule has already caused supply chain hurdles for American farmers, ranchers and foresters, and the rule has not even begun being enforced. EU farmers themselves have raised concerns over their compliance requirements and received additional flexibilities, and member governments are still navigating how to implement the complex auditing system. With these logistical challenges clear even to EU officials, the European Commission has voted to once again delay the rule’s implementation until 2026 and 2027 for large and small businesses, respectively. However, as long as the rule stands as currently drafted, agricultural supply chains will be strained from the looming enforcement deadline. Overall, the EU fails to recognize the long-standing position of American farmers and ranchers as global leaders in agricultural production with environmental stewardship. A rule that was originally targeted to penalize bad actors in the global marketplace has now hindered some of the most productive producers in the world.
The EU Deforestation Rule has already caused supply chain hurdles for American farmers, ranchers and foresters, and the rule has not even begun being enforced. EU farmers themselves have raised concerns over their compliance requirements and received additional flexibilities, and member governments are still navigating how to implement the complex auditing system. With these logistical challenges clear even to EU officials, the European Commission has voted to once again delay the rule’s implementation until 2026 and 2027 for large and small businesses, respectively. However, as long as the rule stands as currently drafted, agricultural supply chains will be strained from the looming enforcement deadline. Overall, the EU fails to recognize the long-standing position of American farmers and ranchers as global leaders in agricultural production with environmental stewardship. A rule that was originally targeted to penalize bad actors in the global marketplace has now hindered some of the most productive producers in the world.
 Gov. Jared Polis signed an
Gov. Jared Polis signed an  NEW YORK, NY – Mercer International announced that its subsidiary, Mercer Peace River Pulp (MPR), and Svante Technologies (Svante) have commenced operation of a previously announced carbon dioxide (CO₂) capture demonstration unit at the Mercer Peace River pulp mill in northern Alberta. The pilot project is designed to evaluate Svante’s solid sorbent carbon capture technology on biogenic CO₂ emissions from the mill’s recovery boiler flue gas. As a cost-efficient step, this stage builds on the previously announced Front-End Engineering and Design Phase 2. …“Commissioning this demonstration unit… allows us to evaluate carbon capture performance in our operating environment and gather practical data on what would be required for any future scale-up,” said Bill Adams. “The results from this on-site demonstration will help us evaluate the decarbonization potential of this technology for biogenic emissions and inform longer-term planning across our pulp operations.”
NEW YORK, NY – Mercer International announced that its subsidiary, Mercer Peace River Pulp (MPR), and Svante Technologies (Svante) have commenced operation of a previously announced carbon dioxide (CO₂) capture demonstration unit at the Mercer Peace River pulp mill in northern Alberta. The pilot project is designed to evaluate Svante’s solid sorbent carbon capture technology on biogenic CO₂ emissions from the mill’s recovery boiler flue gas. As a cost-efficient step, this stage builds on the previously announced Front-End Engineering and Design Phase 2. …“Commissioning this demonstration unit… allows us to evaluate carbon capture performance in our operating environment and gather practical data on what would be required for any future scale-up,” said Bill Adams. “The results from this on-site demonstration will help us evaluate the decarbonization potential of this technology for biogenic emissions and inform longer-term planning across our pulp operations.”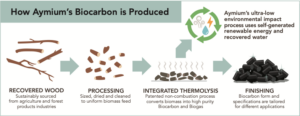 Weyerhaeuser, America’s largest private landowner, said it has launched a venture to turn runty trees and sawdust from its fleet of mills into a replacement for metallurgical coal used in steel making. The forest-products company said it expects production to begin in 2027 at a facility being built next to its sawmill in McComb, Mississippi—the first of several biocarbon plants planned by Weyerhaeuser and partner Aymium. It is the latest effort to find a market for the trees too small or otherwise unsuitable for making lumber. Such wood has typically been sent to pulp and paper mills, but U.S. wood-pulp consumption capacity has plunged due to waning paper demand. …Stockfish said he envisions the venture with Aymium operating as many as 10 or 11 biocarbon production facilities across Weyerhaeuser’s U.S. properties. …Aymium CEO James Mennell said the company’s process works with all species of wood as well as agricultural residues. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
Weyerhaeuser, America’s largest private landowner, said it has launched a venture to turn runty trees and sawdust from its fleet of mills into a replacement for metallurgical coal used in steel making. The forest-products company said it expects production to begin in 2027 at a facility being built next to its sawmill in McComb, Mississippi—the first of several biocarbon plants planned by Weyerhaeuser and partner Aymium. It is the latest effort to find a market for the trees too small or otherwise unsuitable for making lumber. Such wood has typically been sent to pulp and paper mills, but U.S. wood-pulp consumption capacity has plunged due to waning paper demand. …Stockfish said he envisions the venture with Aymium operating as many as 10 or 11 biocarbon production facilities across Weyerhaeuser’s U.S. properties. …Aymium CEO James Mennell said the company’s process works with all species of wood as well as agricultural residues. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required] NEW ZEALAND — Let’s not sugar coat it: this year was a tough year for forestry in the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). It’s especially frustrating as we had begun to believe the government’s promise, made just after it took power in late 2023, to “restore credibility in the ETS”. Indeed, this promise looked plausible up until quite recently. After all, the LUC restrictions, while unpopular among forestry companies and investors, had been clearly communicated long before the 2023 election. So no surprises there – except for a pleasant surprise in August, when the government announced it would not adopt the Climate Change Commission’s somewhat perplexing recommendation to reinject about 14 million of unsold auction NZUs from 2028 to 2030. The positive streak finally ended in October when the government began a staccato of policy tweaks that have cumulatively undermined confidence in the government’s commitment to climate change mitigation and, by extension, the ETS.
NEW ZEALAND — Let’s not sugar coat it: this year was a tough year for forestry in the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). It’s especially frustrating as we had begun to believe the government’s promise, made just after it took power in late 2023, to “restore credibility in the ETS”. Indeed, this promise looked plausible up until quite recently. After all, the LUC restrictions, while unpopular among forestry companies and investors, had been clearly communicated long before the 2023 election. So no surprises there – except for a pleasant surprise in August, when the government announced it would not adopt the Climate Change Commission’s somewhat perplexing recommendation to reinject about 14 million of unsold auction NZUs from 2028 to 2030. The positive streak finally ended in October when the government began a staccato of policy tweaks that have cumulatively undermined confidence in the government’s commitment to climate change mitigation and, by extension, the ETS.