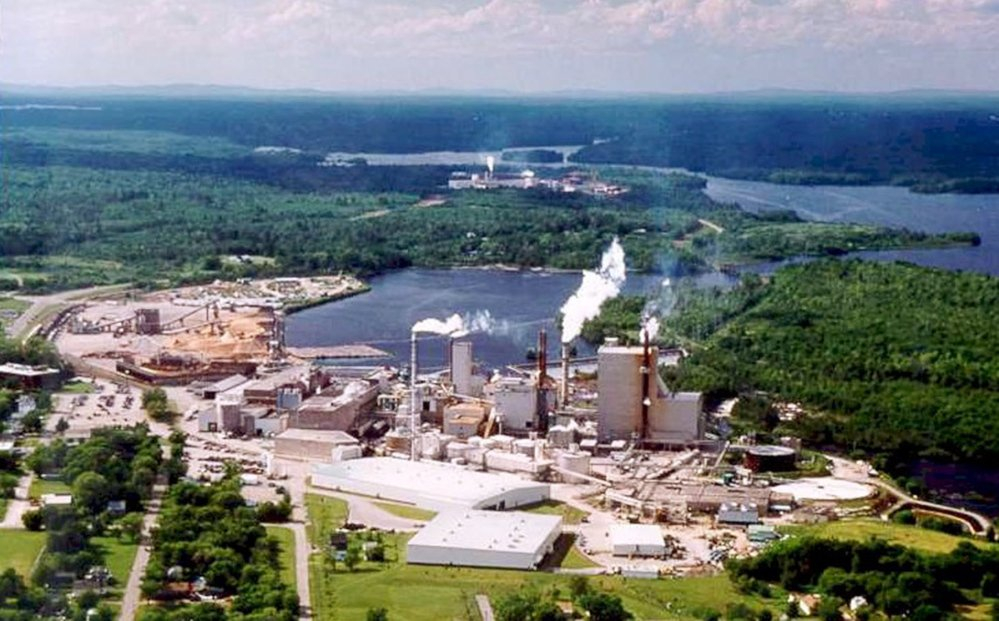
 The past few years have been tough for Canada’s forest industry. …In response to US tariffs and as a partial solution to our continuing housing crisis, Prime Minister Carney has made a commendable move, providing support for the lumber industry and setting a target of doubling housing starts. He’s also announced the Canadian Forest Sector Transformation Task Force. Achieving Mr. Carney’s targets for the forestry sector will require transformation of our wood products and construction industries. …When a log is cut up for lumber, about 40% of the tree is converted to residual chips, and without demand for wood chips to make paper, production of lumber will not be viable. New, alternative uses for those residuals become essential. One option would be to replace a number of idled pulp mills with a couple of large, modern mills.
The past few years have been tough for Canada’s forest industry. …In response to US tariffs and as a partial solution to our continuing housing crisis, Prime Minister Carney has made a commendable move, providing support for the lumber industry and setting a target of doubling housing starts. He’s also announced the Canadian Forest Sector Transformation Task Force. Achieving Mr. Carney’s targets for the forestry sector will require transformation of our wood products and construction industries. …When a log is cut up for lumber, about 40% of the tree is converted to residual chips, and without demand for wood chips to make paper, production of lumber will not be viable. New, alternative uses for those residuals become essential. One option would be to replace a number of idled pulp mills with a couple of large, modern mills.
…New pulp mill designs act as biorefineries, making a range of products. Heat can be exported to district heating plants and power to the grid. Methanol, also known as wood alcohol, can be used in various industrial processes. Currently, methanol is made largely from natural gas, so replacing this product with wood-based spirits offers a carbon advantage. Lignin extracted from pulp mills can be used to displace petroleum-based incumbents in a range of products such as plywood glues and polyurethanes. Currently, because of the steep decline in demand for our pulp and paper products, we are only cutting half the wood that provincial forest ministries deem sustainable. This leaves large amounts of biomass in the forests, which can amplify the threat of wildfires. Reinvesting in our forest sector can help us to lower the risk of catastrophic fires going forward. [to access the full story a Globe and Mail subscription is required]
 Almost three years after declaring bankruptcy, and more than two years under new owners, legal proceedings for Penticton’s Structurlam are continuing through the courts as it fights with the company that sent it into bankruptcy in the first place. In January, the case returned to the BC Supreme Court in Vancouver to order two Canadian engineering firms to produce documents and reports for the proceedings as Structurlam faces $80 million US in claims from Walmart, according to a decision published on Feb. 11. In 2023, Structurlam began bankruptcy proceedings after Walmart ended its contract to build the company’s new home office campus in Arkansas. …In July, Walmart filed a claim for over $80 million US for allegedly defective, nonconforming, rejected, nondelivered, or returned goods that it had paid for and alleged costs to replace said goods. The January 2026 B.C. Supreme Court decision orders two engineering firms to provide their documentation.
Almost three years after declaring bankruptcy, and more than two years under new owners, legal proceedings for Penticton’s Structurlam are continuing through the courts as it fights with the company that sent it into bankruptcy in the first place. In January, the case returned to the BC Supreme Court in Vancouver to order two Canadian engineering firms to produce documents and reports for the proceedings as Structurlam faces $80 million US in claims from Walmart, according to a decision published on Feb. 11. In 2023, Structurlam began bankruptcy proceedings after Walmart ended its contract to build the company’s new home office campus in Arkansas. …In July, Walmart filed a claim for over $80 million US for allegedly defective, nonconforming, rejected, nondelivered, or returned goods that it had paid for and alleged costs to replace said goods. The January 2026 B.C. Supreme Court decision orders two engineering firms to provide their documentation.
 The United Steelworkers union found positives in a difficult BC budget. …Recognizing the uncertainty created by US trade policy… USW Western Canada Director Scott Lunny said… “Today’s budget advances the government’s work towards long-term economic stability, including BC’s goal of securing $200 billion in private-sector investment over the next decade in sectors including mining, forestry and manufacturing”. …USW noted positives, including: a continued commitment in funding to strengthen permitting capacity in resource industries; a $400- million Strategic Investments Special Account to leverage federal government dollars for investment and job creation in key sectors like value-added forestry, responsible mining, manufacturing and clean energy; and unprecedented investment in skilled trades funding as well as a training grant to encourage apprenticeships. …”While we welcome the $20 million to help workers and employers in tariff-impacted sectors like steel and forestry, there is still a missing commitment to stabilizing and sustaining the primary forestry sector,” said Lunny.
The United Steelworkers union found positives in a difficult BC budget. …Recognizing the uncertainty created by US trade policy… USW Western Canada Director Scott Lunny said… “Today’s budget advances the government’s work towards long-term economic stability, including BC’s goal of securing $200 billion in private-sector investment over the next decade in sectors including mining, forestry and manufacturing”. …USW noted positives, including: a continued commitment in funding to strengthen permitting capacity in resource industries; a $400- million Strategic Investments Special Account to leverage federal government dollars for investment and job creation in key sectors like value-added forestry, responsible mining, manufacturing and clean energy; and unprecedented investment in skilled trades funding as well as a training grant to encourage apprenticeships. …”While we welcome the $20 million to help workers and employers in tariff-impacted sectors like steel and forestry, there is still a missing commitment to stabilizing and sustaining the primary forestry sector,” said Lunny. The BC government is forecasting that the natural gas industry will play a larger role as the top driver of provincial resource revenue, while warning about tough times in the former economic powerhouse of forestry. Natural gas royalties are expected to ring in at nearly $1.3-billion for the 12 months ending March 31, 2027, up 38%. …The government is anticipating $521-million in forestry revenue for the 2026-27 fiscal year, up 3%, but still down sharply when compared with several years ago. …In the 2020-21 fiscal year, forestry revenue surpassed $1.3-billion and natural gas royalties reached $196-million. …Tuesday’s budget introduces a temporary Stumpage Payment Deferral Program in an effort to ease the cash crunch for companies. The voluntary program covers the first 11 months of 2026. …The government anticipates that the trend of depressed annual volumes of tree harvesting will continue over the next several years, restricting the production of softwood lumber. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
The BC government is forecasting that the natural gas industry will play a larger role as the top driver of provincial resource revenue, while warning about tough times in the former economic powerhouse of forestry. Natural gas royalties are expected to ring in at nearly $1.3-billion for the 12 months ending March 31, 2027, up 38%. …The government is anticipating $521-million in forestry revenue for the 2026-27 fiscal year, up 3%, but still down sharply when compared with several years ago. …In the 2020-21 fiscal year, forestry revenue surpassed $1.3-billion and natural gas royalties reached $196-million. …Tuesday’s budget introduces a temporary Stumpage Payment Deferral Program in an effort to ease the cash crunch for companies. The voluntary program covers the first 11 months of 2026. …The government anticipates that the trend of depressed annual volumes of tree harvesting will continue over the next several years, restricting the production of softwood lumber. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]








 Canada’s annual inflation rate edged down to 2.3% in January, Statistics Canada said on Tuesday, driven downward by a decline in the cost of gasoline. Economists were largely expecting the rate to remain unchanged from December’s 2.4%. Pump prices put pressure on the headline rate, having fallen 16.7% in January compared to the same period last year. With gas excluded, January’s inflation rate came in at 3%. The Bank of Canada’s preferred measures of core inflation, which strip away volatility from one-time tax changes and gas prices, all ticked down in January — bringing those rates closer to the central bank’s two per cent inflation target. “Overall, this is an encouraging result for the Bank of Canada, with inflation finally nearing the [2%] target on a broader basis,” wrote Douglas Porter, chief economist at Bank of Montreal. ›
Canada’s annual inflation rate edged down to 2.3% in January, Statistics Canada said on Tuesday, driven downward by a decline in the cost of gasoline. Economists were largely expecting the rate to remain unchanged from December’s 2.4%. Pump prices put pressure on the headline rate, having fallen 16.7% in January compared to the same period last year. With gas excluded, January’s inflation rate came in at 3%. The Bank of Canada’s preferred measures of core inflation, which strip away volatility from one-time tax changes and gas prices, all ticked down in January — bringing those rates closer to the central bank’s two per cent inflation target. “Overall, this is an encouraging result for the Bank of Canada, with inflation finally nearing the [2%] target on a broader basis,” wrote Douglas Porter, chief economist at Bank of Montreal. › The pace of homebuilding in Canada continues to slow with no near-term signs of a turnaround, said Canada Mortgage and Housing Corp. on Monday. The national housing agency said the seasonally-adjusted annual pace of housing starts declined 15% in January. Housing starts can vary considerably month-to-month as big projects get started, but the agency’s six-month moving average for annual starts also showed a 3.5% decline. “The six-month trend has decreased for the fourth consecutive month,” said CMHC deputy chief economist Tania Bourassa-Ochoa in a news release. “We expect new construction to continue trending lower going forward as trade and geopolitical uncertainty, high construction costs, weaker demand, and rising inventories continue to constrain developer activity.” She said a near-term turnaround is looking unlikely, and reflects what the agency has been hearing from developers over recent months. The pullback comes amid a variety of pressures, including lower immigration numbers and US trade policy.
The pace of homebuilding in Canada continues to slow with no near-term signs of a turnaround, said Canada Mortgage and Housing Corp. on Monday. The national housing agency said the seasonally-adjusted annual pace of housing starts declined 15% in January. Housing starts can vary considerably month-to-month as big projects get started, but the agency’s six-month moving average for annual starts also showed a 3.5% decline. “The six-month trend has decreased for the fourth consecutive month,” said CMHC deputy chief economist Tania Bourassa-Ochoa in a news release. “We expect new construction to continue trending lower going forward as trade and geopolitical uncertainty, high construction costs, weaker demand, and rising inventories continue to constrain developer activity.” She said a near-term turnaround is looking unlikely, and reflects what the agency has been hearing from developers over recent months. The pullback comes amid a variety of pressures, including lower immigration numbers and US trade policy.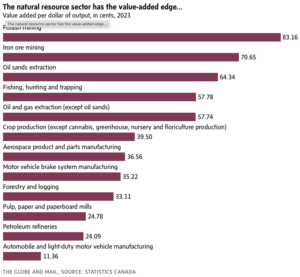 It’s been nearly a century since political economist Harold Innis popularized the phrase “hewers of wood and drawers of water” in decrying Canada’s dependence on natural resources. …Underpinning that cry is the (wrongheaded) assumption that natural resources such as mining, agriculture and energy are second-grade economic activity, less desirable than manufacturing. …That mistake is the foundation for many public policy blunders over many decades. The numbers demolish that myth, and tell a very different story, one in which energy, mining and other natural resources sectors create enormous economic value and are globally competitive. …The federal government needs to get itself out of the way of some of the strongest parts of the Canadian economy. Stop subsidizing inefficient sectors. Stop raising protective tariffs that harm other parts of the economy. Focus on rolling back unjustified regulatory barriers that harm the ability of the entire economy, particularly globally exposed natural resources sectors, to compete. And, most of all, stop the undervaluing Canada’s great natural advantage in natural resources. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
It’s been nearly a century since political economist Harold Innis popularized the phrase “hewers of wood and drawers of water” in decrying Canada’s dependence on natural resources. …Underpinning that cry is the (wrongheaded) assumption that natural resources such as mining, agriculture and energy are second-grade economic activity, less desirable than manufacturing. …That mistake is the foundation for many public policy blunders over many decades. The numbers demolish that myth, and tell a very different story, one in which energy, mining and other natural resources sectors create enormous economic value and are globally competitive. …The federal government needs to get itself out of the way of some of the strongest parts of the Canadian economy. Stop subsidizing inefficient sectors. Stop raising protective tariffs that harm other parts of the economy. Focus on rolling back unjustified regulatory barriers that harm the ability of the entire economy, particularly globally exposed natural resources sectors, to compete. And, most of all, stop the undervaluing Canada’s great natural advantage in natural resources. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required] NEW YORK, New York — Mercer International reported fourth quarter 2025 Operating EBITDA of negative $20.1 million compared to positive $99.2 million in the same quarter of 2024 and negative $28.1 million in the third quarter of 2025. In the fourth quarter of 2025, net loss was $308.7 million compared to net income of $16.7 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and a net loss of $80.8 million in the third quarter of 2025. The net loss in the fourth quarter of 2025 included total non-cash impairments of $238.7 million. This included non-cash impairments of $203.5 million recognized against long-lived assets at our Peace River mill due to the continued down-cycle environment of hardwood pulp markets, $12.2 million against certain obsolete equipment and $23.0 million against pulp inventory due to low prices and high fiber costs. …Mr. Juan Carlos Bueno, CEO: “We continue to prioritize improving liquidity and working capital, committing to rebalancing our asset portfolio and maintaining operating discipline.”
NEW YORK, New York — Mercer International reported fourth quarter 2025 Operating EBITDA of negative $20.1 million compared to positive $99.2 million in the same quarter of 2024 and negative $28.1 million in the third quarter of 2025. In the fourth quarter of 2025, net loss was $308.7 million compared to net income of $16.7 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and a net loss of $80.8 million in the third quarter of 2025. The net loss in the fourth quarter of 2025 included total non-cash impairments of $238.7 million. This included non-cash impairments of $203.5 million recognized against long-lived assets at our Peace River mill due to the continued down-cycle environment of hardwood pulp markets, $12.2 million against certain obsolete equipment and $23.0 million against pulp inventory due to low prices and high fiber costs. …Mr. Juan Carlos Bueno, CEO: “We continue to prioritize improving liquidity and working capital, committing to rebalancing our asset portfolio and maintaining operating discipline.” BURNABY, BC — Interfor recorded a net loss in Q4, 2025 of $104.6 million, compared to a net loss of $215.8 million in Q3’25 and a net loss of $49.9 million in Q4’24. Adjusted EBITDA was a loss of $29.2 million on sales of $600.6 million in Q4’25 versus an Adjusted EBITDA loss of $183.8 million on sales of $689.3 million in Q3’25 and Adjusted EBITDA of $80.4 million on sales of $746.5 million in Q4’24. …During and subsequent to Q4’25, Interfor completed a series of financing transactions. Taken together, these transactions significantly enhance Interfor’s financial flexibility, bolster liquidity and provide meaningful additional runway as the Company continues to navigate volatile lumber market conditions. …Lumber production of 753 million board feet was down 159 million board feet versus the preceding quarter. …Interfor’s strategy of maintaining a diversified portfolio of operations in multiple regions allows the Company to both reduce risk and maximize returns on capital over the business cycle.
BURNABY, BC — Interfor recorded a net loss in Q4, 2025 of $104.6 million, compared to a net loss of $215.8 million in Q3’25 and a net loss of $49.9 million in Q4’24. Adjusted EBITDA was a loss of $29.2 million on sales of $600.6 million in Q4’25 versus an Adjusted EBITDA loss of $183.8 million on sales of $689.3 million in Q3’25 and Adjusted EBITDA of $80.4 million on sales of $746.5 million in Q4’24. …During and subsequent to Q4’25, Interfor completed a series of financing transactions. Taken together, these transactions significantly enhance Interfor’s financial flexibility, bolster liquidity and provide meaningful additional runway as the Company continues to navigate volatile lumber market conditions. …Lumber production of 753 million board feet was down 159 million board feet versus the preceding quarter. …Interfor’s strategy of maintaining a diversified portfolio of operations in multiple regions allows the Company to both reduce risk and maximize returns on capital over the business cycle.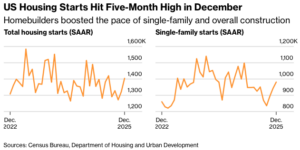 New residential construction in the US rose to a five-month high in December, as homebuilders boosted production to take advantage of lower borrowing costs. Housing starts increased 6.2% to an annual pace of 1.4 million homes in December, according to figures released Wednesday by the government, which were delayed by fall’s federal shutdown. …The advance was broad-based, with both single-family home starts and apartment projects rising at year’s end. The number of one-family homes started was the highest since February. The stronger construction numbers suggest that builders were growing more confident at year’s end even as they continued to sell off a bloated inventory of new houses. For the full year, however, starts notched a fourth-straight annual decline …In December, building permits, which point to future construction, rose 4.3% to an annualized pace of 1.45 million, the highest since March, government data show. Single-family permits fell slightly. [to access the full story a Bloomberg subscription is required]
New residential construction in the US rose to a five-month high in December, as homebuilders boosted production to take advantage of lower borrowing costs. Housing starts increased 6.2% to an annual pace of 1.4 million homes in December, according to figures released Wednesday by the government, which were delayed by fall’s federal shutdown. …The advance was broad-based, with both single-family home starts and apartment projects rising at year’s end. The number of one-family homes started was the highest since February. The stronger construction numbers suggest that builders were growing more confident at year’s end even as they continued to sell off a bloated inventory of new houses. For the full year, however, starts notched a fourth-straight annual decline …In December, building permits, which point to future construction, rose 4.3% to an annualized pace of 1.45 million, the highest since March, government data show. Single-family permits fell slightly. [to access the full story a Bloomberg subscription is required]


 Reality-television stars are rarely consulted on matters of public policy. But in April, Realtor.com asked Tarek El Moussa to comment on the White House’s “Liberation Day” tariffs. The Southern California entrepreneur, who rose to fame on the popularity of HGTV’s Flip or Fop franchise, warned that higher import taxes would harm “new-home builders” and “first-time buyers” the most — after all, “luxury buyers” could absorb greater costs. Aspiring homeowners, he averred, are “usually strapped for cash,” and “doing everything they can just to buy a house.” Now that the second Trump administration has passed its one-year anniversary, all evidence indicates that El Moussa understands his industry well. There is little doubt that his trade war erects a sizable obstacle before those looking to find a place of their own. …The types of wood available in the US are not always the same as what’s available from Canadian imports.
Reality-television stars are rarely consulted on matters of public policy. But in April, Realtor.com asked Tarek El Moussa to comment on the White House’s “Liberation Day” tariffs. The Southern California entrepreneur, who rose to fame on the popularity of HGTV’s Flip or Fop franchise, warned that higher import taxes would harm “new-home builders” and “first-time buyers” the most — after all, “luxury buyers” could absorb greater costs. Aspiring homeowners, he averred, are “usually strapped for cash,” and “doing everything they can just to buy a house.” Now that the second Trump administration has passed its one-year anniversary, all evidence indicates that El Moussa understands his industry well. There is little doubt that his trade war erects a sizable obstacle before those looking to find a place of their own. …The types of wood available in the US are not always the same as what’s available from Canadian imports.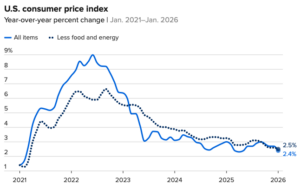 The cost of goods and services rose at a slower annual rate than expected in January, providing hope that the nagging U.S. inflation problem could be starting to ease. The consumer price index for January accelerated 2.4% from the same time a year ago, down 0.3 percentage point from the prior month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Friday. That pulled the inflation rate down to where it was the month after President Donald Trump in April 2025 announced aggressive tariffs on U.S. imports. Excluding food and energy, the core CPI was up 2.5%. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for an annual rate of 2.5% for both readings. On a monthly basis, the all-items index was up a seasonally adjusted 0.2% while core gained 0.3%. …Though the category accounted for much of the CPI gain, shelter costs rose just 0.2% for the month, bringing the annual increase down to 3%.
The cost of goods and services rose at a slower annual rate than expected in January, providing hope that the nagging U.S. inflation problem could be starting to ease. The consumer price index for January accelerated 2.4% from the same time a year ago, down 0.3 percentage point from the prior month, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Friday. That pulled the inflation rate down to where it was the month after President Donald Trump in April 2025 announced aggressive tariffs on U.S. imports. Excluding food and energy, the core CPI was up 2.5%. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for an annual rate of 2.5% for both readings. On a monthly basis, the all-items index was up a seasonally adjusted 0.2% while core gained 0.3%. …Though the category accounted for much of the CPI gain, shelter costs rose just 0.2% for the month, bringing the annual increase down to 3%. 
 As Denmark has recently tightened its standards for new construction with the aim of reducing embodied carbon, what lessons can Canada draw from this experience? In 2023, the Danish Building Code made life-cycle assessment (LCA) mandatory for all new buildings over their first fifty years. …The government also mandated researchers to provide practitioners with a list of generic material data for cases where an Environmental Product Declaration (EPD)—required to perform an LCA. When the regulation came into force in 2023, the entire construction industry was opposed to it, recalls Thomas Graabaek. “ And then slowly there was a movement within architects and engineers that actually we need to have even stricter demands.” …“Unfortunately, in Canada, [architects] have been educated only around operations, [not on its entire life cycle],” explains Kelly Alvarez Doran. He advocates for the establishment of embodied-carbon targets at different regulatory scales.
As Denmark has recently tightened its standards for new construction with the aim of reducing embodied carbon, what lessons can Canada draw from this experience? In 2023, the Danish Building Code made life-cycle assessment (LCA) mandatory for all new buildings over their first fifty years. …The government also mandated researchers to provide practitioners with a list of generic material data for cases where an Environmental Product Declaration (EPD)—required to perform an LCA. When the regulation came into force in 2023, the entire construction industry was opposed to it, recalls Thomas Graabaek. “ And then slowly there was a movement within architects and engineers that actually we need to have even stricter demands.” …“Unfortunately, in Canada, [architects] have been educated only around operations, [not on its entire life cycle],” explains Kelly Alvarez Doran. He advocates for the establishment of embodied-carbon targets at different regulatory scales.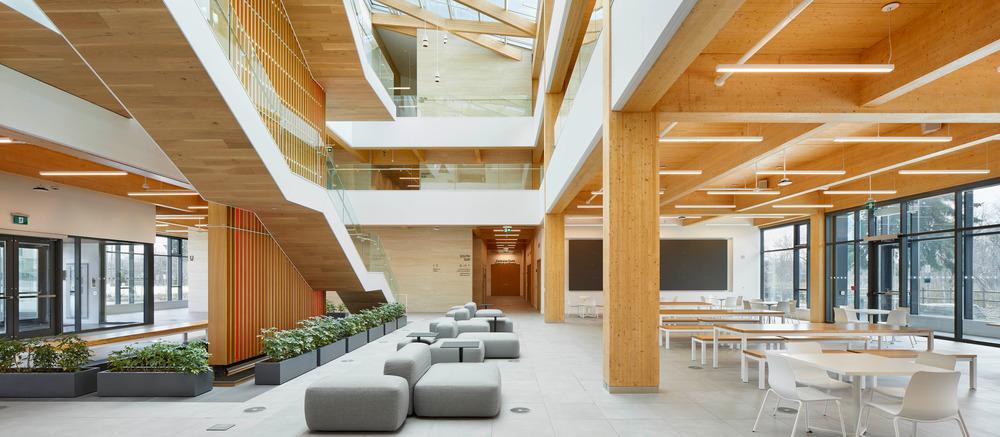 
 Building homes inside a factory has long been seen as a way to revolutionize the American housing industry, ushering in a new era of higher quality homes at lower price. That dream has never quite panned out. Can California finally make it happen? …For decades engineers, architects, futurists, industrialists, investors and politicians have been pining for a better, faster and cheaper way to build homes. Now, amid a national housing shortage, the question felt as pressing as ever: What if construction could harness the speed, efficiency, quality control and cost-savings of the assembly line? …What if the United States could mass-produce its way out of a housing crisis? …This year, state legislators in California believe the turning-point might actually be here. With a little state assistance, they want to make 2026 the Year of the Housing Factory. At long last.
Building homes inside a factory has long been seen as a way to revolutionize the American housing industry, ushering in a new era of higher quality homes at lower price. That dream has never quite panned out. Can California finally make it happen? …For decades engineers, architects, futurists, industrialists, investors and politicians have been pining for a better, faster and cheaper way to build homes. Now, amid a national housing shortage, the question felt as pressing as ever: What if construction could harness the speed, efficiency, quality control and cost-savings of the assembly line? …What if the United States could mass-produce its way out of a housing crisis? …This year, state legislators in California believe the turning-point might actually be here. With a little state assistance, they want to make 2026 the Year of the Housing Factory. At long last.  A BC First Nation in the final stages of treaty negotiation is suing the province for allegedly breaching the “honour of the Crown” after an official extended an expiring timber licence in its traditional territory. Filed in a BC Supreme Court last week, the application for judicial review from ’Wuìk̓inux̌v Nation seeks to overturn an August 2025 decision… that gave Interfor a three-year extension to log an estimated 50,000 cubic metres of timber. The court application argues that allowing a third party to continue harvesting on the nation’s lands—without their consent and against their environmental concerns—is a step backward that the law no longer allows. The claim, which also names Interfor, arrives at a volatile moment for BC politics: by leaning on a landmark legal precedent set in December 2025, it lands squarely in the middle of a heated debate over how the province manages its natural resources in an era of reconciliation.
A BC First Nation in the final stages of treaty negotiation is suing the province for allegedly breaching the “honour of the Crown” after an official extended an expiring timber licence in its traditional territory. Filed in a BC Supreme Court last week, the application for judicial review from ’Wuìk̓inux̌v Nation seeks to overturn an August 2025 decision… that gave Interfor a three-year extension to log an estimated 50,000 cubic metres of timber. The court application argues that allowing a third party to continue harvesting on the nation’s lands—without their consent and against their environmental concerns—is a step backward that the law no longer allows. The claim, which also names Interfor, arrives at a volatile moment for BC politics: by leaning on a landmark legal precedent set in December 2025, it lands squarely in the middle of a heated debate over how the province manages its natural resources in an era of reconciliation. Fire departments across BC are concerned about changes to the FireSmart program and how funding is provided to communities as they plan for wildfires. The Ministry of Forests says it’s moving to a more “holistic approach” based on where risk is the highest but the fire chief who was at the centre of the Wesley Ridge wildfire on Vancouver Island last summer says the program is too important to change. Nick Acciavatti says funding from the provincial FireSmart program was instrumental in saving numerous homes in the Wesley Ridge fire. …The program provides funding to local fire departments that then go into local neighbourhoods to educate and undertake fire prevention work like brush clearing and cleaning properties of combustible materials. But that money may no longer be available to any fire department that applies for it is something Acciavatti is concerned about, considering the changing wildfire conditions here on Vancouver Island.
Fire departments across BC are concerned about changes to the FireSmart program and how funding is provided to communities as they plan for wildfires. The Ministry of Forests says it’s moving to a more “holistic approach” based on where risk is the highest but the fire chief who was at the centre of the Wesley Ridge wildfire on Vancouver Island last summer says the program is too important to change. Nick Acciavatti says funding from the provincial FireSmart program was instrumental in saving numerous homes in the Wesley Ridge fire. …The program provides funding to local fire departments that then go into local neighbourhoods to educate and undertake fire prevention work like brush clearing and cleaning properties of combustible materials. But that money may no longer be available to any fire department that applies for it is something Acciavatti is concerned about, considering the changing wildfire conditions here on Vancouver Island.
 COLORADO — Forest experts are warning that Boulder’s foothills could look markedly different this year as a mountain pine beetle outbreak intensifies, with potentially far-reaching impacts on recreation and fire risk. Landowners are urged to watch for signs of beetle infestation. The state has taken action: Gov. Jared Polis announced a task force in December aimed at protecting Front Range forests from mountain pine beetle over the next decade. Boulder County has seen increased beetle activity in several areas, including upper Lefthand Canyon and Jamestown. Years of drought, warmer temperatures and overcrowded forests have weakened trees, creating ideal conditions for beetles to spread rapidly and overwhelm remaining healthy stands. …The brood of beetles already in trees and poised to spread this summer is substantial, according to Colorado State Forest Service entomologist Dan West. “It’s kind of this cake that’s already being baked,” West told Boulder Reporting Lab.
COLORADO — Forest experts are warning that Boulder’s foothills could look markedly different this year as a mountain pine beetle outbreak intensifies, with potentially far-reaching impacts on recreation and fire risk. Landowners are urged to watch for signs of beetle infestation. The state has taken action: Gov. Jared Polis announced a task force in December aimed at protecting Front Range forests from mountain pine beetle over the next decade. Boulder County has seen increased beetle activity in several areas, including upper Lefthand Canyon and Jamestown. Years of drought, warmer temperatures and overcrowded forests have weakened trees, creating ideal conditions for beetles to spread rapidly and overwhelm remaining healthy stands. …The brood of beetles already in trees and poised to spread this summer is substantial, according to Colorado State Forest Service entomologist Dan West. “It’s kind of this cake that’s already being baked,” West told Boulder Reporting Lab. NEW YORK — BTG Pactual Timberland Investment Group has acquired approximately 107,000 acres of sustainably managed timberlands in Central Virginia from the Weyerhaeuser Company. The acquisition represents one of the largest recent timberland transactions in Virginia, significantly expanding BTG Pactual TIG’s footprint in the region and bringing the firm’s total US portfolio to approximately 1.6 million acres under management. The property is Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certified, consisting primarily of loblolly pine, and will be well-integrated with BTG Pactual TIG’s existing regional operations. …The acquisition also enables BTG Pactual TIG to further expand conservation efforts in the region through its long-term collaboration with NatureVest, The Nature Conservancy’s (TNC’s) in-house impact investing and nature finance team. A preliminary assessment of the asset conducted by TNC found that 25% of the property falls within areas of high ecological and biodiversity value.
NEW YORK — BTG Pactual Timberland Investment Group has acquired approximately 107,000 acres of sustainably managed timberlands in Central Virginia from the Weyerhaeuser Company. The acquisition represents one of the largest recent timberland transactions in Virginia, significantly expanding BTG Pactual TIG’s footprint in the region and bringing the firm’s total US portfolio to approximately 1.6 million acres under management. The property is Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certified, consisting primarily of loblolly pine, and will be well-integrated with BTG Pactual TIG’s existing regional operations. …The acquisition also enables BTG Pactual TIG to further expand conservation efforts in the region through its long-term collaboration with NatureVest, The Nature Conservancy’s (TNC’s) in-house impact investing and nature finance team. A preliminary assessment of the asset conducted by TNC found that 25% of the property falls within areas of high ecological and biodiversity value. The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say.
The Trump administration on Thursday revoked a scientific finding that long has been the central basis for US action to regulate greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change, the most aggressive move by the president to roll back climate regulations. The rule finalized by the Environmental Protection Agency rescinds a 2009 government declaration known as the endangerment finding that determined that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases endanger public health and welfare. The endangerment finding by the Obama administration is the legal underpinning of nearly all climate regulations under the Clean Air Act for motor vehicles, power plants and other pollution sources that are heating the planet. …Legal challenges are certain for an action that repeals all greenhouse gas emissions standards for cars and trucks, and could unleash a broader undoing of climate regulations on stationary sources such as power plants and oil and gas facilities, experts say. With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe.
With European manufacturing output down by up to 40% since 2018, and 200,000 industrial jobs lost last year, the European Confederation of the Paper Industry (Cepi) wants to put biomass, circularity and decarbonization financing back at the heart of the industrial debate. The trade organization relies on a report commissioned from Deloitte. According to this analysis… the use of biomass and efficiency in the circularity of materials are structural advantages for European industry in the face of imported fossil products. The report highlights the fact that the forestry and timber industry, which is already governed by national legislation, has to contend with over a hundred additional European regulations. In Cepi’s view, this overlap is holding back biomass-related industrial development. Moreover, paper collection and recycling remains fragmented across the member states. This heterogeneity complicates the optimization of secondary material flows, despite the fact that paper is one of the most recycled materials in Europe.