
Canada-US lumber trade is at a crossroads—Robert McKellar warns protectionism is not a passing phase; and Andrew Miller declares this is America’s market. In related news: BC Premier Eby rules out retaliatory action; Minister Ravi Parmar says BC’s workers deserve treatment equal to Ontario; Ikea plans to boost its US production; and Interfor’s curtailment hits home in Adams Lake, BC and Ear Falls, Ontario. Meanwhile: Kapuskasing Paper resumes operation with federal and provincial support; 9Wood lays off 9% its workforce in Springfield, Oregon; BMI completes purchase of the Espanola mill; and the US building material dealers elect Frank Addiego as Chair.
In other news: President Trump and the Softwood Lumber Board celebrate National Forest Products Week; and Domtar’s Kingsport mill is recognized by the National Recycling Coalition. Meanwhile: Michelle Gray highlights the University of New Brunswick’s new approaches in digital forestry and forest resilience; and more on the Wildfire Resilience Consortium at Thompson Rivers University.
Finally, tomorrow, Dr. Barry Cooke will discuss the history of debate on budworms—a BC Forest History Association online seminar.
Kelly McCloskey, Tree Frog News Editor




 British Columbia’s forest sector is at a crossroads — facing tough challenges, but also leading the way in solutions that matter most to our province: housing, wildfire resilience, reconciliation, and sustainable economic growth. At the 2026 COFI Convention, leaders from across industry, government, and Indigenous and community partners will come together to rebuild competitiveness and chart the future of a strong, sustainable forest sector. Join us in Vancouver for the largest forest sector gathering in Western Canada. April 8 – 10, 2026 at the JW Marriot Parq Vancouver
British Columbia’s forest sector is at a crossroads — facing tough challenges, but also leading the way in solutions that matter most to our province: housing, wildfire resilience, reconciliation, and sustainable economic growth. At the 2026 COFI Convention, leaders from across industry, government, and Indigenous and community partners will come together to rebuild competitiveness and chart the future of a strong, sustainable forest sector. Join us in Vancouver for the largest forest sector gathering in Western Canada. April 8 – 10, 2026 at the JW Marriot Parq Vancouver
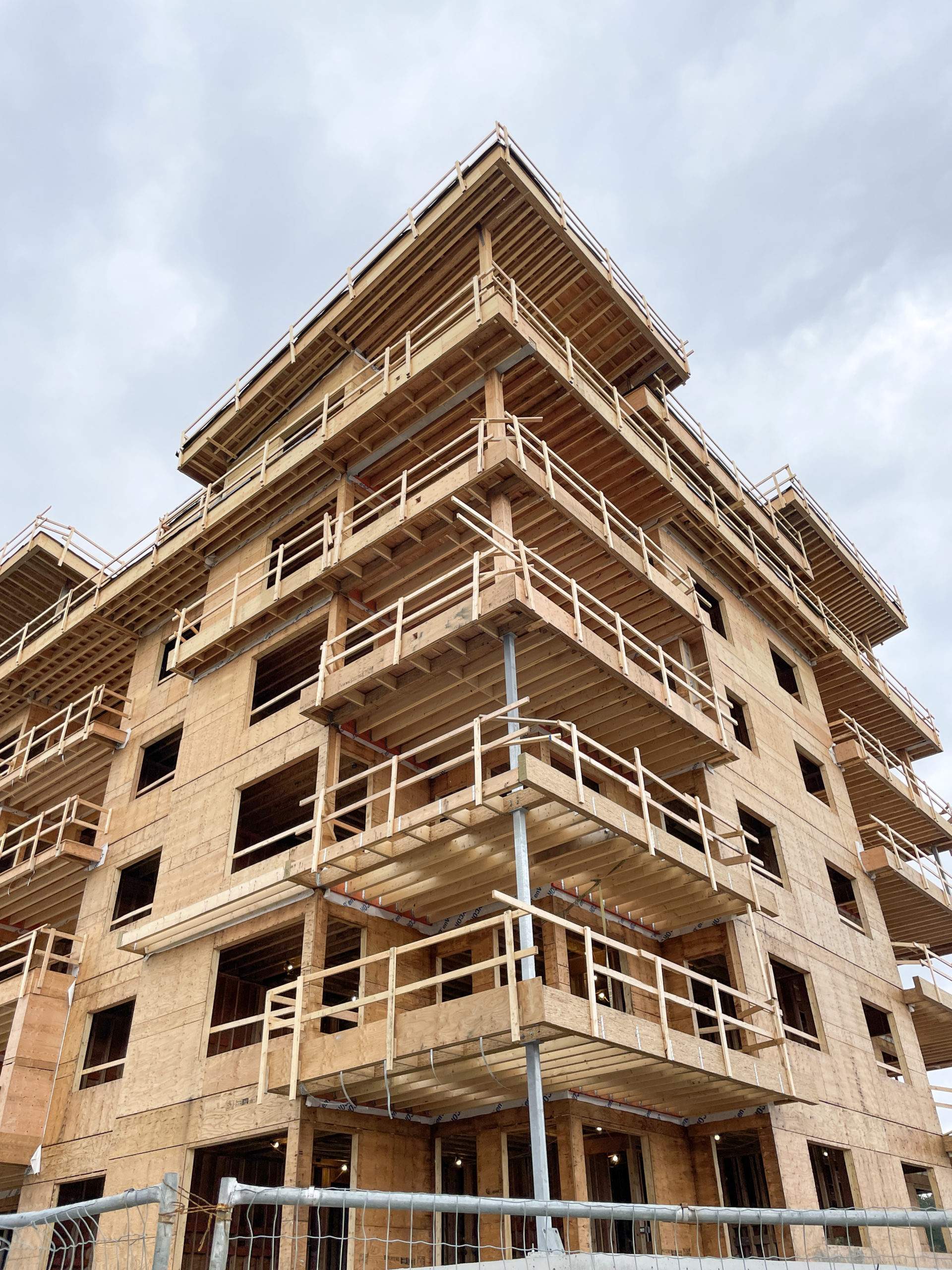


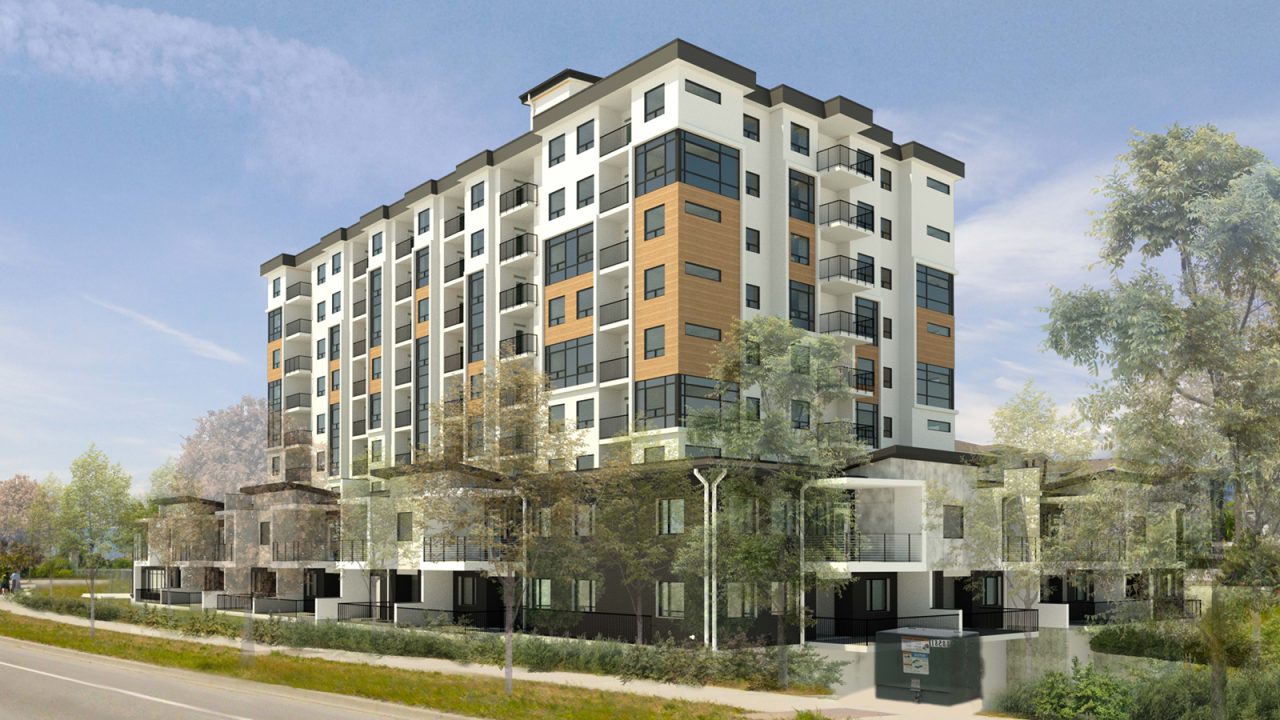
 Canada is facing a housing crisis of historic proportions. With affordability slipping out of reach for millions and supply lagging far behind demand, we need bold, scalable and sustainable solutions. The federal government’s Build Canada Homes initiative is a promising start and an opportunity to scale up the use of Canadian wood in building construction.
Canada is facing a housing crisis of historic proportions. With affordability slipping out of reach for millions and supply lagging far behind demand, we need bold, scalable and sustainable solutions. The federal government’s Build Canada Homes initiative is a promising start and an opportunity to scale up the use of Canadian wood in building construction. 

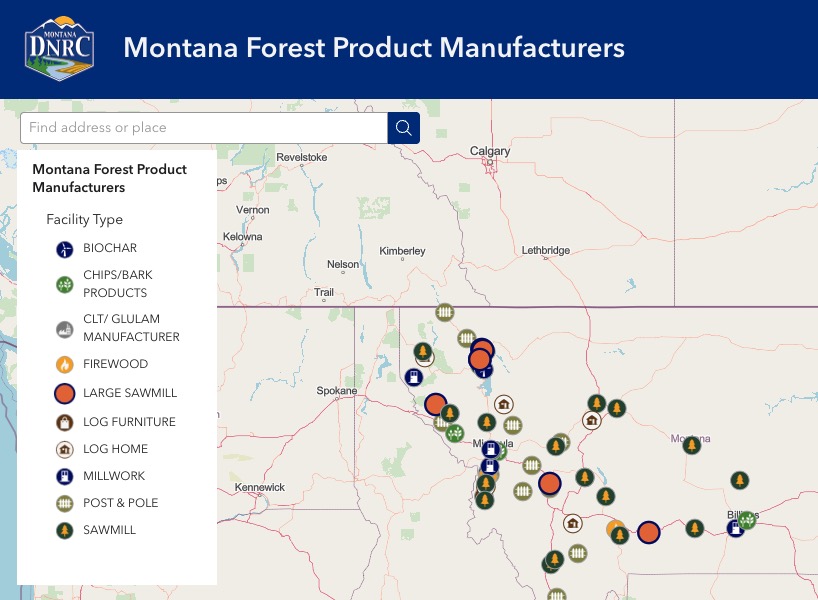 HELENA, Mont. — The Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) has launched an online interactive map showing forest product manufacturers across the state. The new tool helps landowners, contractors, and community members locate nearby mills and connect with partners for forest management and wood processing projects. Each facility listing includes details such as product types, wood species used, and company size, with direct links to their websites. “Beyond helping Montanans find nearby mills, the map highlights manufacturing capacity that supports forest restoration, fuels reduction, and local jobs,” said Marc Vessar, DNRC forest practices program manager.
HELENA, Mont. — The Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC) has launched an online interactive map showing forest product manufacturers across the state. The new tool helps landowners, contractors, and community members locate nearby mills and connect with partners for forest management and wood processing projects. Each facility listing includes details such as product types, wood species used, and company size, with direct links to their websites. “Beyond helping Montanans find nearby mills, the map highlights manufacturing capacity that supports forest restoration, fuels reduction, and local jobs,” said Marc Vessar, DNRC forest practices program manager. Several parliamentarians, key industry players and alternative materials start-ups in hemp, engineered bamboo and engineered timber attended an event designed to focus a spotlight on the new world of possibilities in building materials. The WWF and Forest Alliance NSW event was intended to showcase sustainable alternatives to timber products …with the protection of the proposed Great Koala National Park at the centre of conversations. The event was further by the Parliamentary Friends of Forests. Attending as exhibitors were House of Bamboo, Hemp Inside, Bamboo Society Australia, Australian Hemp Council, iHempNSW, BVN Architecture and betti & knutt. While XLAM … was originally on the list of presenters, an industry source says the pressure from forestry sources had forced the company to pull out. …Susie Russell was particularly inspired by House of Bamboo, realizing that similar products to timber can be made from bamboo, which only takes five years to grow.
Several parliamentarians, key industry players and alternative materials start-ups in hemp, engineered bamboo and engineered timber attended an event designed to focus a spotlight on the new world of possibilities in building materials. The WWF and Forest Alliance NSW event was intended to showcase sustainable alternatives to timber products …with the protection of the proposed Great Koala National Park at the centre of conversations. The event was further by the Parliamentary Friends of Forests. Attending as exhibitors were House of Bamboo, Hemp Inside, Bamboo Society Australia, Australian Hemp Council, iHempNSW, BVN Architecture and betti & knutt. While XLAM … was originally on the list of presenters, an industry source says the pressure from forestry sources had forced the company to pull out. …Susie Russell was particularly inspired by House of Bamboo, realizing that similar products to timber can be made from bamboo, which only takes five years to grow.

 The BC Forest History Association is pleased to welcome Dr. Barry Cooke, Research Scientist with the Canadian Forest Service, as our second speaker of 2025. Dr. Cooke is one of Canada’s leading experts on modeling insect outbreak processes and patterns, with more than 30 years of experience studying spruce budworm population dynamics and forest insect ecology. He has authored over 90 scientific publications, advancing our understanding of budworms, beetles, and other major forest pests through spatial simulation modeling. Join us for this free online presentation, “A History of Debate on Budworms: A BC Perspective.” Tuesday, October 21st 2025 – 7:00 to 8:00 PST
The BC Forest History Association is pleased to welcome Dr. Barry Cooke, Research Scientist with the Canadian Forest Service, as our second speaker of 2025. Dr. Cooke is one of Canada’s leading experts on modeling insect outbreak processes and patterns, with more than 30 years of experience studying spruce budworm population dynamics and forest insect ecology. He has authored over 90 scientific publications, advancing our understanding of budworms, beetles, and other major forest pests through spatial simulation modeling. Join us for this free online presentation, “A History of Debate on Budworms: A BC Perspective.” Tuesday, October 21st 2025 – 7:00 to 8:00 PST 
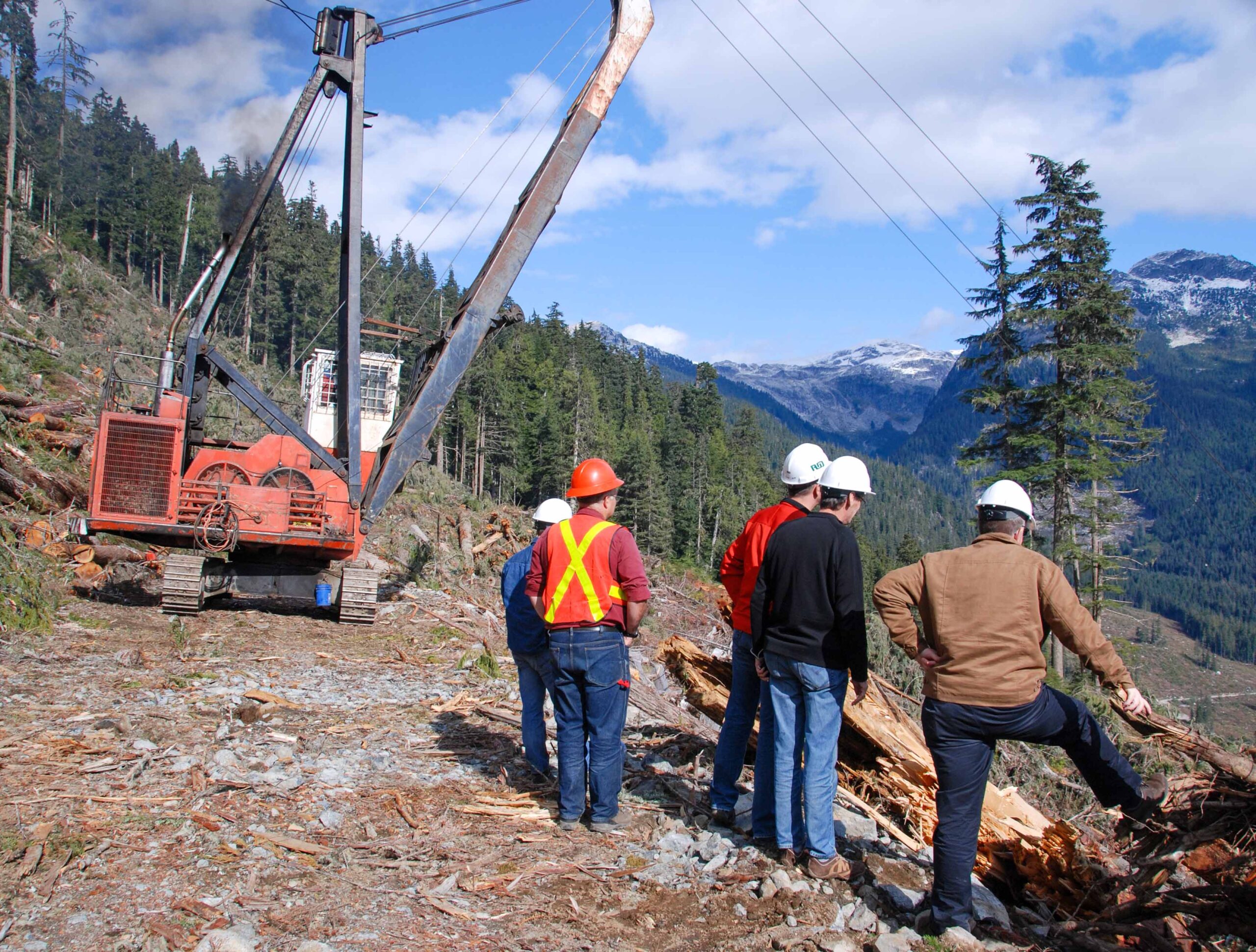 BANFF – A large swath of land will be logged at the base of Sulphur Mountain this winter to help further protect the Banff townsite from a future runaway wildfire similar to one that destroyed part of Jasper last year. As part of Parks Canada’s ongoing work to reduce the threat of wildfire to the townsite, the plan calls for 125 hectares to be logged and thinned in the Spray and Middle Springs area over the next two winters, including about 79 ha this winter. The entire project – which aims to slow the spread of an approaching wildfire and aid in suppression efforts to protect the Banff townsite – is slated to begin by the end of November and wrap up by spring 2027. …The Town of Banff has directed almost $1.5 million to be spent in 2025 wildfire mitigation work in 2025 within the four-km2 townsite.
BANFF – A large swath of land will be logged at the base of Sulphur Mountain this winter to help further protect the Banff townsite from a future runaway wildfire similar to one that destroyed part of Jasper last year. As part of Parks Canada’s ongoing work to reduce the threat of wildfire to the townsite, the plan calls for 125 hectares to be logged and thinned in the Spray and Middle Springs area over the next two winters, including about 79 ha this winter. The entire project – which aims to slow the spread of an approaching wildfire and aid in suppression efforts to protect the Banff townsite – is slated to begin by the end of November and wrap up by spring 2027. …The Town of Banff has directed almost $1.5 million to be spent in 2025 wildfire mitigation work in 2025 within the four-km2 townsite. Environmental advocates and industry officials are divided over whether new logging plans in the Upper Highwood River watershed will provide sufficient protection for the threatened Bull Trout population. West Fraser Cochrane recently obtained Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) authorization under the Fisheries Act and sections 73 and 74 of the Species at Risk Act (SARA) to install 14 temporary crossings for timber harvesting. The company says it is balancing responsible resource use with habitat conservation. “We understand how important it is to protect bull trout and Westslope cutthroat trout habitat in the Highwood– and share that priority,” said West Fraser Cochrane. “…we will monitor conditions before and after harvest to help inform responsible stewardship.” …Both environmental advocates and West Fraser agree on one point: safeguarding the Bull Trout and its habitat is a critical challenge. The question is whether the mitigation steps currently underway will prove sufficient to ensure the species’ long-term survival.
Environmental advocates and industry officials are divided over whether new logging plans in the Upper Highwood River watershed will provide sufficient protection for the threatened Bull Trout population. West Fraser Cochrane recently obtained Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) authorization under the Fisheries Act and sections 73 and 74 of the Species at Risk Act (SARA) to install 14 temporary crossings for timber harvesting. The company says it is balancing responsible resource use with habitat conservation. “We understand how important it is to protect bull trout and Westslope cutthroat trout habitat in the Highwood– and share that priority,” said West Fraser Cochrane. “…we will monitor conditions before and after harvest to help inform responsible stewardship.” …Both environmental advocates and West Fraser agree on one point: safeguarding the Bull Trout and its habitat is a critical challenge. The question is whether the mitigation steps currently underway will prove sufficient to ensure the species’ long-term survival. Local residents are invited to share their input on the development of the West Central Vancouver Island (WCVI) Forest Landscape Plan (FLP), which will guide long-term forest management in the area. …People can share their thoughts through a short survey, open from Wednesday, Oct. 15 until Dec. 15, 2025, or attend an open house in a nearby community. Four in-person open-house engagement sessions are planned so people can learn more about forest landscape planning and comment on the development of the plan in Zeballos, Gold River, Tahsis and Campbell River. FLPs are co-developed with First Nations, with input from communities, subject-matter experts and forest licensees. The WCVI FLP is being developed with the Mowachaht/Muchatlaht First Nation, Ka:yu:’k’t’h’/Che:k’tles7et’h’ First Nations and Ehattesaht Chinehkint First Nation.
Local residents are invited to share their input on the development of the West Central Vancouver Island (WCVI) Forest Landscape Plan (FLP), which will guide long-term forest management in the area. …People can share their thoughts through a short survey, open from Wednesday, Oct. 15 until Dec. 15, 2025, or attend an open house in a nearby community. Four in-person open-house engagement sessions are planned so people can learn more about forest landscape planning and comment on the development of the plan in Zeballos, Gold River, Tahsis and Campbell River. FLPs are co-developed with First Nations, with input from communities, subject-matter experts and forest licensees. The WCVI FLP is being developed with the Mowachaht/Muchatlaht First Nation, Ka:yu:’k’t’h’/Che:k’tles7et’h’ First Nations and Ehattesaht Chinehkint First Nation.
 The man charged after an investigation into the largest wildfire in Nova Scotia history has been fined $25,000. Dalton Stewart, 23, chose not to speak when he was handed the sentence Thursday in Barrington provincial court. The sentence — a joint recommendation from the Crown and defence — also includes an order to complete educational training on wildfire prevention.
The man charged after an investigation into the largest wildfire in Nova Scotia history has been fined $25,000. Dalton Stewart, 23, chose not to speak when he was handed the sentence Thursday in Barrington provincial court. The sentence — a joint recommendation from the Crown and defence — also includes an order to complete educational training on wildfire prevention.  Western Colorado — Communities across the Western Slope need scientifically sound, effective action that actually helps protect our forests and communities. That’s why so many of us are paying attention to the Fix Our Forests Act, now moving through Congress. …The Act leans heavily on boosting logging, and yes, thinning trees in the right places can improve forest health. The problem is that an agenda driven by timber harvesting often causes companies to cut the largest-diameter trees to meet timber quotas set by Washington, D.C. Instead, restoration forestry is the science-backed solution that we really need. …There are real solutions to today’s forestry challenges. …We have the tools – they just need more funding and staff to do the job. …I urge our senators to do all they can to improve the bill before final passage, keeping the public at the table, as they the most to lose if we don’t get this right.
Western Colorado — Communities across the Western Slope need scientifically sound, effective action that actually helps protect our forests and communities. That’s why so many of us are paying attention to the Fix Our Forests Act, now moving through Congress. …The Act leans heavily on boosting logging, and yes, thinning trees in the right places can improve forest health. The problem is that an agenda driven by timber harvesting often causes companies to cut the largest-diameter trees to meet timber quotas set by Washington, D.C. Instead, restoration forestry is the science-backed solution that we really need. …There are real solutions to today’s forestry challenges. …We have the tools – they just need more funding and staff to do the job. …I urge our senators to do all they can to improve the bill before final passage, keeping the public at the table, as they the most to lose if we don’t get this right.
 As the European Commission prepares a further postponement of its Deforestation-free Regulation (EUDR), proposals to simplify the law are abundant in Brussels. The undersigned organizations, representing the U.S. forestry and forest products sector value chain, urge the Commission to avoid a rushed process and take the time necessary to pursue simplification with great care. An additional year provides a valuable opportunity for the Commission to engage in productive dialogue with forest owners and operators in highly forested, low-risk countries like the U.S. to understand implementation challenges and reduce unintended consequences. “Simplifying a law as significant as the EUDR requires thoughtful and purposeful review,” said Eric Gee, executive director of the Southern Forest Products Association (SFPA). “A measured approach will help ensure that any changes both strengthen the law’s effectiveness and uphold fairness for producers in low-risk, sustainably managed regions like the Southeastern United States.”
As the European Commission prepares a further postponement of its Deforestation-free Regulation (EUDR), proposals to simplify the law are abundant in Brussels. The undersigned organizations, representing the U.S. forestry and forest products sector value chain, urge the Commission to avoid a rushed process and take the time necessary to pursue simplification with great care. An additional year provides a valuable opportunity for the Commission to engage in productive dialogue with forest owners and operators in highly forested, low-risk countries like the U.S. to understand implementation challenges and reduce unintended consequences. “Simplifying a law as significant as the EUDR requires thoughtful and purposeful review,” said Eric Gee, executive director of the Southern Forest Products Association (SFPA). “A measured approach will help ensure that any changes both strengthen the law’s effectiveness and uphold fairness for producers in low-risk, sustainably managed regions like the Southeastern United States.”
 As the planet heats up, we need to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. …‘nature-based climate solutions’ are human interventions that utilize natural processes to draw down carbon from the atmosphere. According to William Anderegg, director of the Wilkes Center for Climate Science and Policy at the University of Utah, planting forests is an especially promising option. “The central opportunity here is that we can leverage nature,” Anderegg says, “and forests globally have pretty large potential to help with climate change mitigation.” [However], Anderegg says …there are many problems with the programs that seek to plant forests as a climate solution.
As the planet heats up, we need to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. …‘nature-based climate solutions’ are human interventions that utilize natural processes to draw down carbon from the atmosphere. According to William Anderegg, director of the Wilkes Center for Climate Science and Policy at the University of Utah, planting forests is an especially promising option. “The central opportunity here is that we can leverage nature,” Anderegg says, “and forests globally have pretty large potential to help with climate change mitigation.” [However], Anderegg says …there are many problems with the programs that seek to plant forests as a climate solution.  A study finds that replacing natural gas with electric and biomass power, along with improved energy efficiency, could help some pulp and paper mills reach zero net emissions. Researchers began with a simulation of mills defined by two characteristics: whether they used virgin or recycled fibers, and whether they were integrated or not. A virgin mill creates pulp and paper from fresh wood… while a recycled fiber mill re-uses fibers which may have been previously processed. A mill is considered integrated if it has the capability to turn wood and other biomass into pulp and paper on site, whereas a non-integrated mill uses pulp produced and dried off site. …The final strategy researchers analyzed was the use of low-carbon alternatives, like using waste wood in boilers instead of fossil fuels. The effectiveness changed depending on whether or not the mill was integrated, but all types saw reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
A study finds that replacing natural gas with electric and biomass power, along with improved energy efficiency, could help some pulp and paper mills reach zero net emissions. Researchers began with a simulation of mills defined by two characteristics: whether they used virgin or recycled fibers, and whether they were integrated or not. A virgin mill creates pulp and paper from fresh wood… while a recycled fiber mill re-uses fibers which may have been previously processed. A mill is considered integrated if it has the capability to turn wood and other biomass into pulp and paper on site, whereas a non-integrated mill uses pulp produced and dried off site. …The final strategy researchers analyzed was the use of low-carbon alternatives, like using waste wood in boilers instead of fossil fuels. The effectiveness changed depending on whether or not the mill was integrated, but all types saw reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
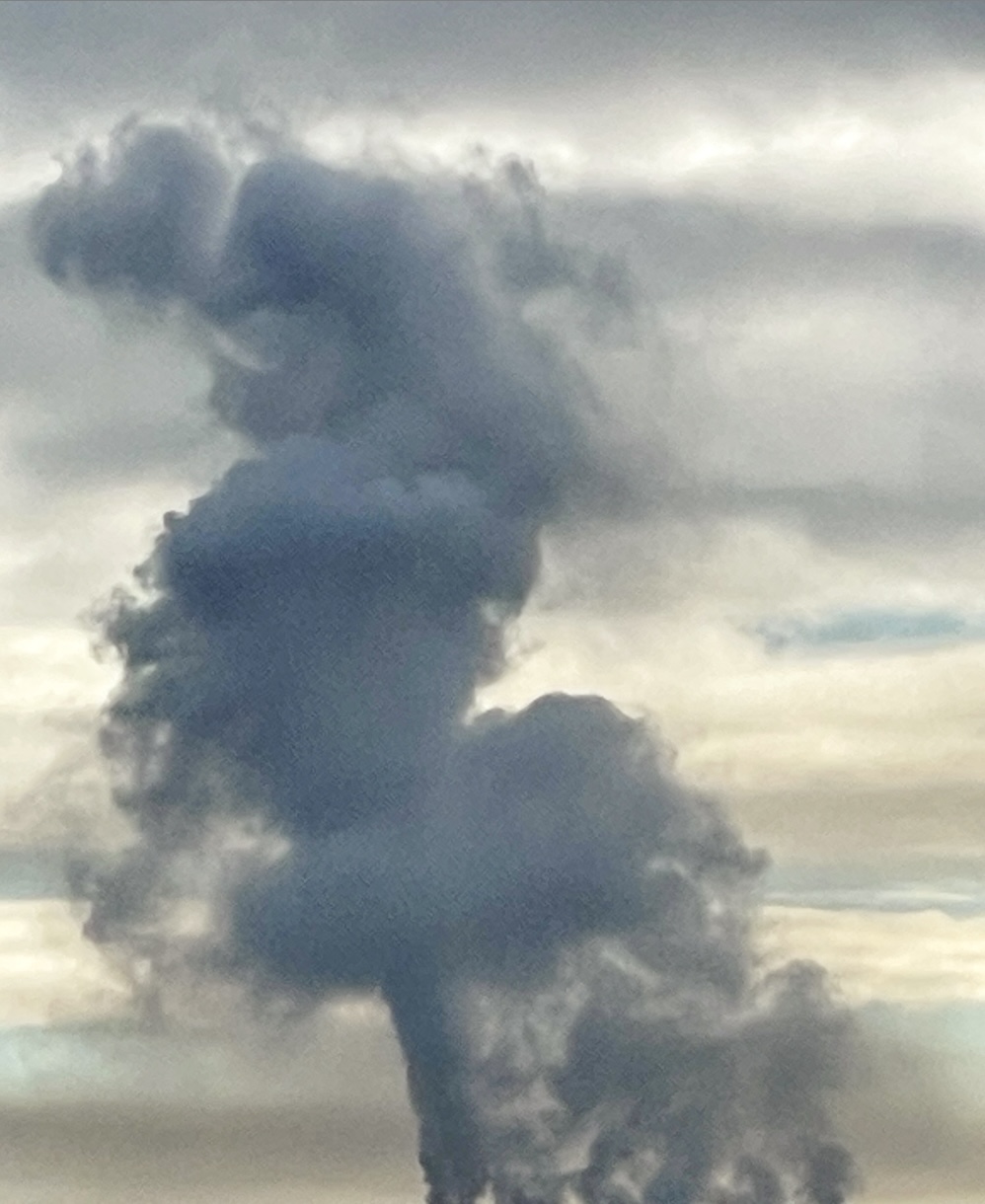 GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.
GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.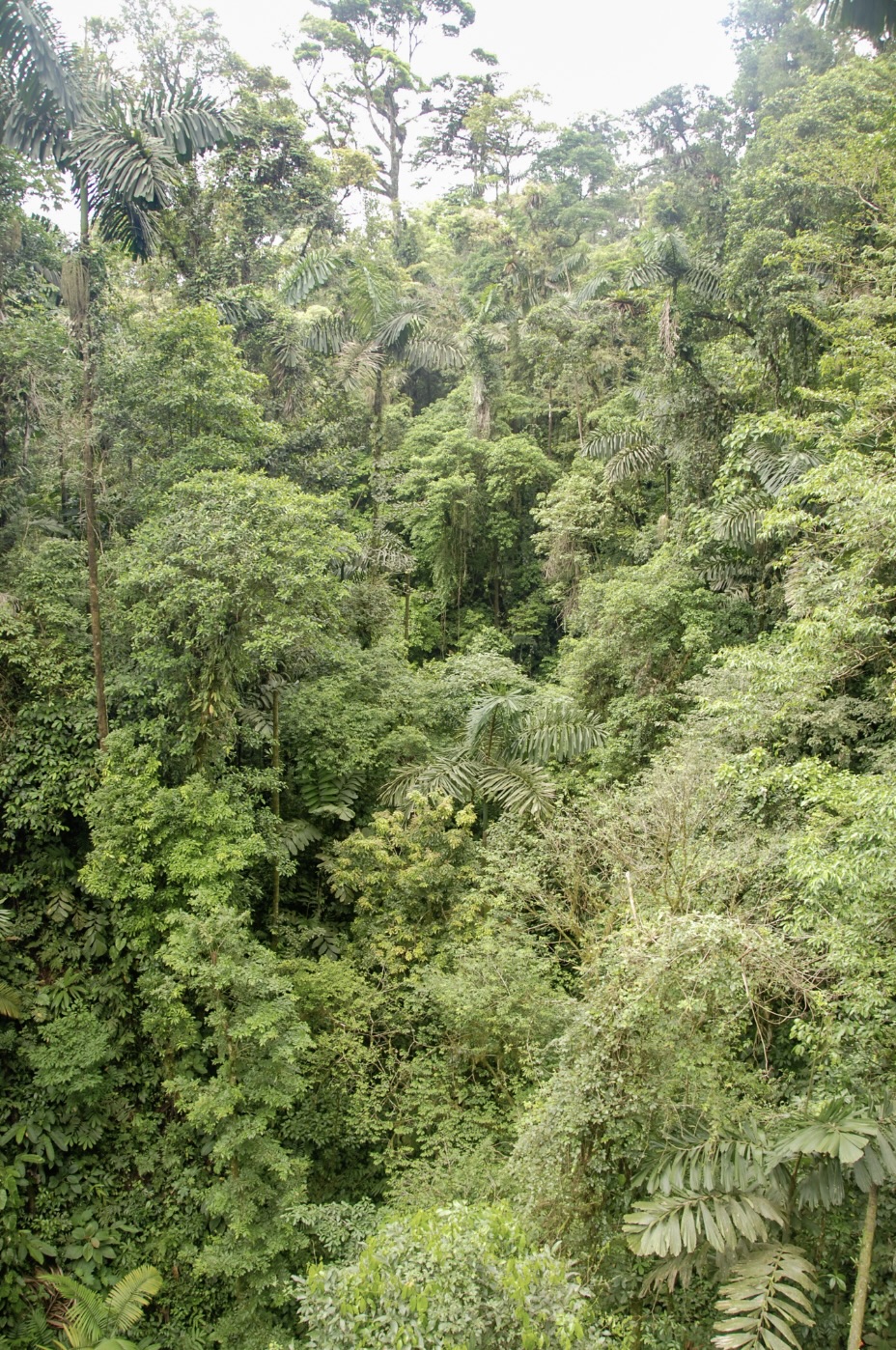 Woody trunks and branches of trees in the wet tropical rainforests of Queensland are losing their ability to absorb excess carbon dioxide. That’s according to an analysis of 49 years’ worth of data,
Woody trunks and branches of trees in the wet tropical rainforests of Queensland are losing their ability to absorb excess carbon dioxide. That’s according to an analysis of 49 years’ worth of data, 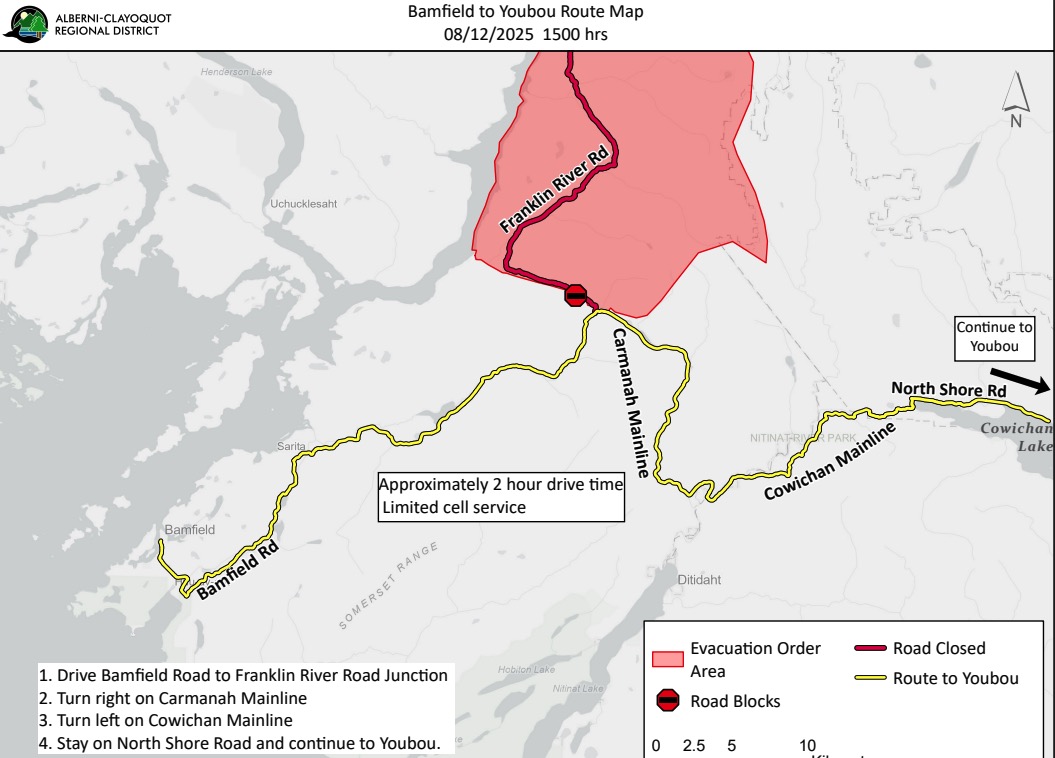 Since Aug. 11, the Bamfield Main Road has been closed. …When the Mount Underwood wildfire broke out, that road had to be closed because of a blaze raging nearby. …Bamfield-area residents have to travel more than four hours to get to Port Alberni. …Another point of frustration for the people on the other side of the closure is the existence of a logging road owned by Mosaic Forest Management, a section of that road goes around the Bamfield Main Road closure. Harrison said she and a small group of other people drove the road to check it out. …”The Youbou Road is 100 times worse than that little 20-minute bypass road,” claimed resident Sherry Harrison. …The ministry said the road owned by Mosaic is private and public use is up to the discretion of the company, but added those logging roads were not built and are not maintained for public use.
Since Aug. 11, the Bamfield Main Road has been closed. …When the Mount Underwood wildfire broke out, that road had to be closed because of a blaze raging nearby. …Bamfield-area residents have to travel more than four hours to get to Port Alberni. …Another point of frustration for the people on the other side of the closure is the existence of a logging road owned by Mosaic Forest Management, a section of that road goes around the Bamfield Main Road closure. Harrison said she and a small group of other people drove the road to check it out. …”The Youbou Road is 100 times worse than that little 20-minute bypass road,” claimed resident Sherry Harrison. …The ministry said the road owned by Mosaic is private and public use is up to the discretion of the company, but added those logging roads were not built and are not maintained for public use. GLOSTER, Miss. — A group of Gloster residents has filed a federal lawsuit against Drax Biomass and its subsidiaries, alleging that the company’s Amite BioEnergy wood pellet facility in the town has unlawfully released massive amounts of toxic pollutants into their community, violating the federal Clean Air Act and Mississippi law. According to a statement from the law firm that filed the claim, Singleton Schreiber, the lawsuit seeks “injunctive relief, civil penalties, and damages for the harm plaintiffs have suffered, including diminished property values, and the loss of safe use and enjoyment of their homes.” Drax responded to inquiries with the following statement: “We are aware of the lawsuit filed in Mississippi. While we cannot comment on the details of ongoing legal matters, our commitment to the communities where we operate remains unchanged. We strive to be a good neighbor in our communities and to support their wellbeing and prosperity.”
GLOSTER, Miss. — A group of Gloster residents has filed a federal lawsuit against Drax Biomass and its subsidiaries, alleging that the company’s Amite BioEnergy wood pellet facility in the town has unlawfully released massive amounts of toxic pollutants into their community, violating the federal Clean Air Act and Mississippi law. According to a statement from the law firm that filed the claim, Singleton Schreiber, the lawsuit seeks “injunctive relief, civil penalties, and damages for the harm plaintiffs have suffered, including diminished property values, and the loss of safe use and enjoyment of their homes.” Drax responded to inquiries with the following statement: “We are aware of the lawsuit filed in Mississippi. While we cannot comment on the details of ongoing legal matters, our commitment to the communities where we operate remains unchanged. We strive to be a good neighbor in our communities and to support their wellbeing and prosperity.”