 BELÉM, Brazil – The Honorable Julie Dabrusin, Minister of Environment and Climate Change, issued this statement at the conclusion of the 30th Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Belém, Brazil… “…Canada’s delegation worked with counterparts from around the world … to advocate for measures to confront the urgent realities of a rapidly changing climate and the need to accelerate climate action globally. Throughout the negotiations, Canada worked with countries to strengthen multilateralism; foster dialogue; build consensus; and advance evidence-based, inclusive climate action. …As the world moves rapidly toward net zero, Canada is well positioned to lead. …the science is clear that we need to do more, faster and together, to keep 1.5 °C of warming within reach. …one of Canada’s top priorities for COP30 was to push for more collective action to reduce emissions …to meet the Paris Agreement’s temperature goals.
BELÉM, Brazil – The Honorable Julie Dabrusin, Minister of Environment and Climate Change, issued this statement at the conclusion of the 30th Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Belém, Brazil… “…Canada’s delegation worked with counterparts from around the world … to advocate for measures to confront the urgent realities of a rapidly changing climate and the need to accelerate climate action globally. Throughout the negotiations, Canada worked with countries to strengthen multilateralism; foster dialogue; build consensus; and advance evidence-based, inclusive climate action. …As the world moves rapidly toward net zero, Canada is well positioned to lead. …the science is clear that we need to do more, faster and together, to keep 1.5 °C of warming within reach. …one of Canada’s top priorities for COP30 was to push for more collective action to reduce emissions …to meet the Paris Agreement’s temperature goals.

 Canada’s latest federal budget has earmarked tens of billion dollars over the next decade to kick-start the country’s clean economy. But according to a national association of accountants, it has failed to adopt national climate disclosure standards to transparently assess what will work. The latest federal budget lays out federal government spending through a new Climate Competitiveness Strategy. It earmarks a rolling $2 billion toward a Critical Minerals Sovereign Fund and $6 billion for a Build Communities Stronger Fund (over 10 years) to build and retrofit local infrastructure and clean energy projects. …It also seeks to create and expand investment tax credits for clean electricity, technology and critical minerals. …But on Tuesday, Chartered Professional Accountants Canada CEO Pamela Steer warned the lack of consistent and verifiable financial disclosure measures means there’s no reliable way to understand how government spending truly reduces emissions.
Canada’s latest federal budget has earmarked tens of billion dollars over the next decade to kick-start the country’s clean economy. But according to a national association of accountants, it has failed to adopt national climate disclosure standards to transparently assess what will work. The latest federal budget lays out federal government spending through a new Climate Competitiveness Strategy. It earmarks a rolling $2 billion toward a Critical Minerals Sovereign Fund and $6 billion for a Build Communities Stronger Fund (over 10 years) to build and retrofit local infrastructure and clean energy projects. …It also seeks to create and expand investment tax credits for clean electricity, technology and critical minerals. …But on Tuesday, Chartered Professional Accountants Canada CEO Pamela Steer warned the lack of consistent and verifiable financial disclosure measures means there’s no reliable way to understand how government spending truly reduces emissions. Greenwashing experts are cautiously optimistic that Ottawa’s plan to roll back nearly half of Canada’s anti-greenwashing rules does not represent a wholesale abandonment of federal efforts to curb climate disinformation following comments by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne. …Champagne did not elaborate on what could be included in the standard. A Department of Finance official told Canada’s National Observer in a statement that the “provisions are creating investment uncertainty and having the opposite of the desired effect with some parties slowing or reversing efforts to protect the environment.” …Announced this month in the 2026 budget, the changes ditched a requirement that companies prove their green claims using international, though unspecified, standards. The changes also prevent third parties from filing a greenwashing complaint with the Competition Bureau. …The budget claims the provisions were “creating investment uncertainty and having the opposite of the desired effect with some parties slowing or reversing efforts to protect the environment.” [A National Observer subscription may be required for story access]
Greenwashing experts are cautiously optimistic that Ottawa’s plan to roll back nearly half of Canada’s anti-greenwashing rules does not represent a wholesale abandonment of federal efforts to curb climate disinformation following comments by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne. …Champagne did not elaborate on what could be included in the standard. A Department of Finance official told Canada’s National Observer in a statement that the “provisions are creating investment uncertainty and having the opposite of the desired effect with some parties slowing or reversing efforts to protect the environment.” …Announced this month in the 2026 budget, the changes ditched a requirement that companies prove their green claims using international, though unspecified, standards. The changes also prevent third parties from filing a greenwashing complaint with the Competition Bureau. …The budget claims the provisions were “creating investment uncertainty and having the opposite of the desired effect with some parties slowing or reversing efforts to protect the environment.” [A National Observer subscription may be required for story access]
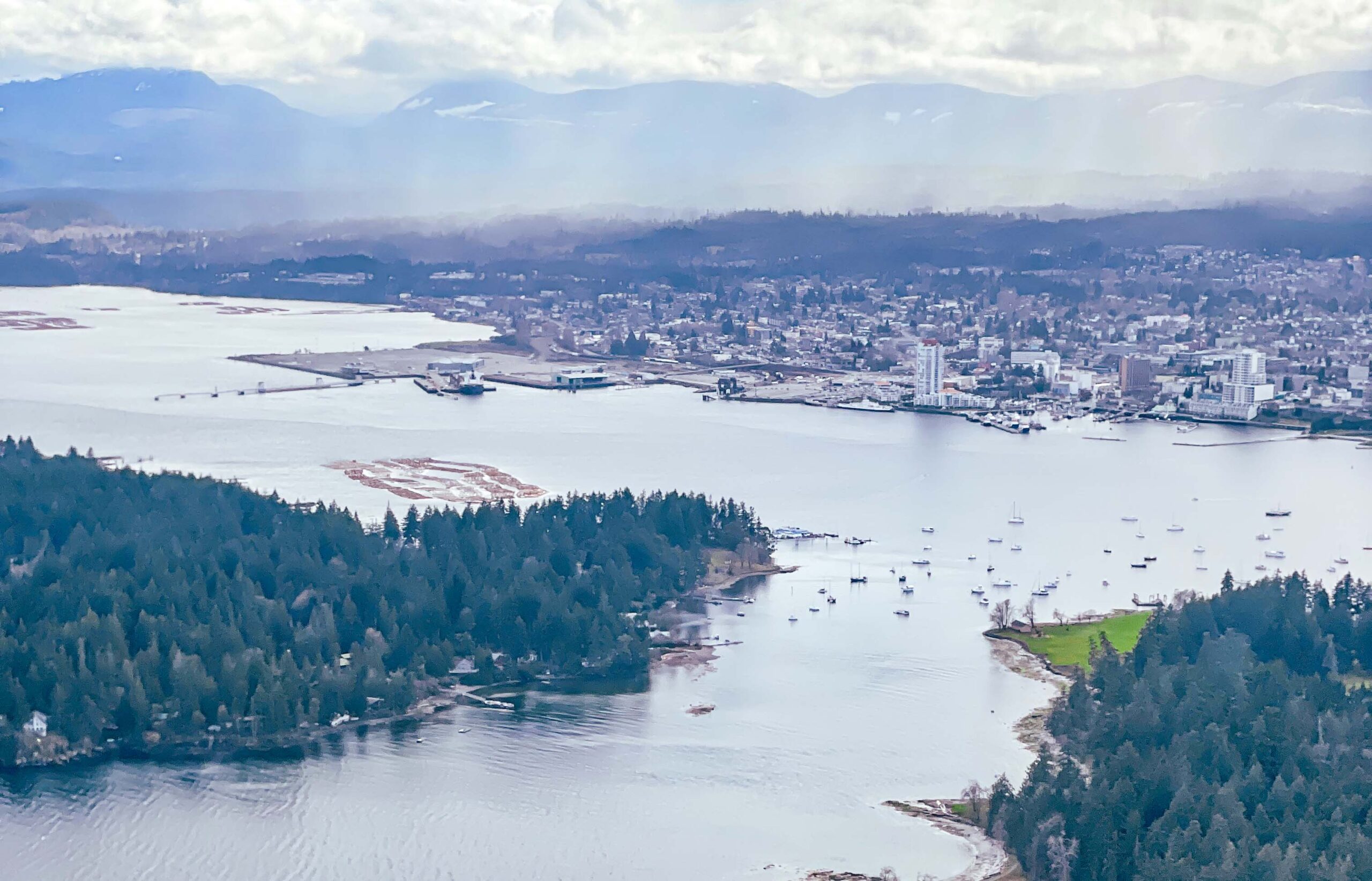
 Nanaimo city council Coun. Paul Manly tabled a motion that asked staff to prepare a report with options for a zoning amendment for industrial lands that would exclude emissions-intense heavy industry such as “waste energy, incinerators, chemical plants, thermal electrical generators, petroleum refineries and [liquefied] natural gas export facilities” from existing industrial zones in order to require site-specific zoning. …Ryan Prontack, a manager for Harmac Pacific, Nanaimo Forest Products, also appeared as a delegation. He said Harmac is looking to diversify its operations and has about 61 hectares of industrial-zoned land ready to develop. “While this motion represents many different activities we currently do, it also represent many that we have plans to diversify in the future,” Protack said. Manly said the motion does not affect Harmac’s current operations and is not about “blocking industry uses in perpetuity” but is about ensuring the city has a democratic process to evaluate project proposals.
Nanaimo city council Coun. Paul Manly tabled a motion that asked staff to prepare a report with options for a zoning amendment for industrial lands that would exclude emissions-intense heavy industry such as “waste energy, incinerators, chemical plants, thermal electrical generators, petroleum refineries and [liquefied] natural gas export facilities” from existing industrial zones in order to require site-specific zoning. …Ryan Prontack, a manager for Harmac Pacific, Nanaimo Forest Products, also appeared as a delegation. He said Harmac is looking to diversify its operations and has about 61 hectares of industrial-zoned land ready to develop. “While this motion represents many different activities we currently do, it also represent many that we have plans to diversify in the future,” Protack said. Manly said the motion does not affect Harmac’s current operations and is not about “blocking industry uses in perpetuity” but is about ensuring the city has a democratic process to evaluate project proposals. Drax power plant has continued to burn 250-year-old trees sourced from some of Canada’s oldest forests despite growing scrutiny of its sustainability claims, forestry experts say. A new report suggests it is “highly likely” that Britain’s biggest power plant sourced some wood from ecologically valuable forests as recently as this summer. Drax, Britain’s single biggest source of carbon emissions, has received billions of pounds in subsidies from burning biomass derived largely from wood. The report, by Stand.earth, claims that a subsidiary of Drax Group received hundreds of truckloads of whole logs at its biomass pellet sites throughout 2024 and into 2025, which were likely to have included trees that were hundreds of years old. The report could raise fresh questions for the owner of the North Yorkshire power plant, which has been forced in recent years to defend its sustainability claims while receiving more than £2m a day in green energy subsidies from UK bill payers.
Drax power plant has continued to burn 250-year-old trees sourced from some of Canada’s oldest forests despite growing scrutiny of its sustainability claims, forestry experts say. A new report suggests it is “highly likely” that Britain’s biggest power plant sourced some wood from ecologically valuable forests as recently as this summer. Drax, Britain’s single biggest source of carbon emissions, has received billions of pounds in subsidies from burning biomass derived largely from wood. The report, by Stand.earth, claims that a subsidiary of Drax Group received hundreds of truckloads of whole logs at its biomass pellet sites throughout 2024 and into 2025, which were likely to have included trees that were hundreds of years old. The report could raise fresh questions for the owner of the North Yorkshire power plant, which has been forced in recent years to defend its sustainability claims while receiving more than £2m a day in green energy subsidies from UK bill payers.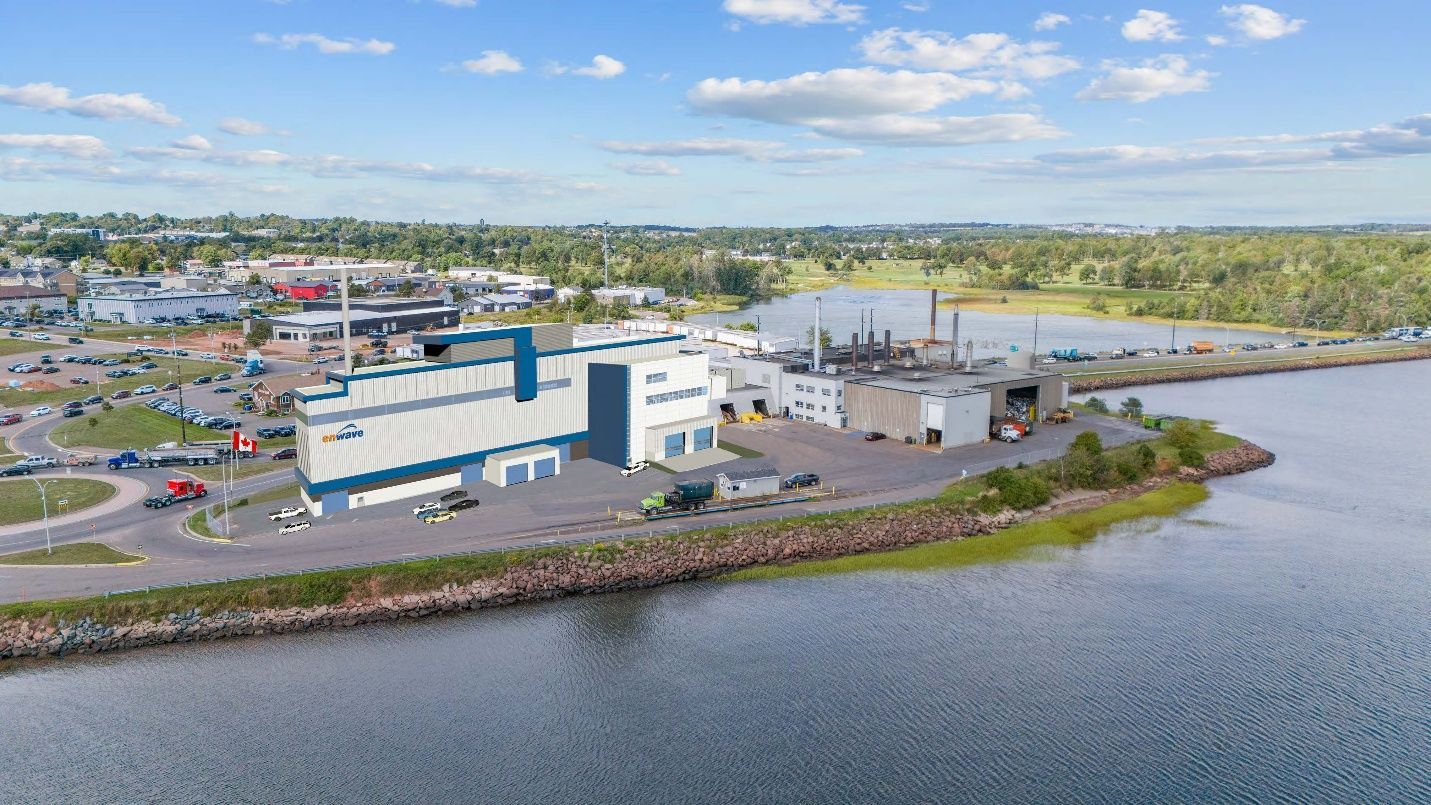
 WASHINGTON – The U.S. Department of Agriculture directed its staff to identify grants for possible termination in the early months of the second Trump administration by searching for more than two dozen specific words and phrases related to diversity and climate change, according to documents seen by Reuters. The effort was undertaken as part of a broad campaign across federal agencies to comply with President Donald Trump’s directives to end diversity, equity and inclusion efforts and climate regulation in the federal government. Trump … has called climate change a “con job.” The documents, obtained by legal advocacy group FarmSTAND … show the breadth of that effort… The topics and terms included “climate modeling,” “climate and emission analysis,” …”carbon pricing and market mechanics,” “renewable energy modernization that does not directly benefit farmers,” “climate adaption (sic) and resilience planning” and “biodiversity and ecosystem resilience related to climate change”.
WASHINGTON – The U.S. Department of Agriculture directed its staff to identify grants for possible termination in the early months of the second Trump administration by searching for more than two dozen specific words and phrases related to diversity and climate change, according to documents seen by Reuters. The effort was undertaken as part of a broad campaign across federal agencies to comply with President Donald Trump’s directives to end diversity, equity and inclusion efforts and climate regulation in the federal government. Trump … has called climate change a “con job.” The documents, obtained by legal advocacy group FarmSTAND … show the breadth of that effort… The topics and terms included “climate modeling,” “climate and emission analysis,” …”carbon pricing and market mechanics,” “renewable energy modernization that does not directly benefit farmers,” “climate adaption (sic) and resilience planning” and “biodiversity and ecosystem resilience related to climate change”.
 BRUSSELS — The European Commission has unveiled a new plan to end the dominance of planet-heating fossil fuels in Europe’s economy — and replace them with trees. The
BRUSSELS — The European Commission has unveiled a new plan to end the dominance of planet-heating fossil fuels in Europe’s economy — and replace them with trees. The  Africa’s forests have turned from a carbon sink into a carbon source, according to research that underscores the need for urgent action to save the world’s great natural climate stabilisers. The alarming shift, which has happened since 2010, means all of the planet’s three main rainforest regions – the South American Amazon, south-east Asia and Africa – are now part of the problem. Human activity is the primary cause of the problem. Farmers are clearing more land for food production. Infrastructure projects and mining are exacerbating the loss of vegetation and global heating – caused by the burning of gas, oil and coal – thereby degrading the resilience of ecosystems. …The worst affected were the tropical moist broadleaf forests in Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar and parts of west Africa. The study,
Africa’s forests have turned from a carbon sink into a carbon source, according to research that underscores the need for urgent action to save the world’s great natural climate stabilisers. The alarming shift, which has happened since 2010, means all of the planet’s three main rainforest regions – the South American Amazon, south-east Asia and Africa – are now part of the problem. Human activity is the primary cause of the problem. Farmers are clearing more land for food production. Infrastructure projects and mining are exacerbating the loss of vegetation and global heating – caused by the burning of gas, oil and coal – thereby degrading the resilience of ecosystems. …The worst affected were the tropical moist broadleaf forests in Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar and parts of west Africa. The study,  In response to an article published by The Guardian regarding our Canadian sustainable biomass operations, Miguel Veiga-Pestana, Drax’s Chief Sustainability Officer, wrote this response: The environmental non-profit Stand.earth fails to see the wood from the trees when it comes to the Canadian forestry industry and Drax’s limited role within it (
In response to an article published by The Guardian regarding our Canadian sustainable biomass operations, Miguel Veiga-Pestana, Drax’s Chief Sustainability Officer, wrote this response: The environmental non-profit Stand.earth fails to see the wood from the trees when it comes to the Canadian forestry industry and Drax’s limited role within it (

 A new
A new 

 While the summit launched new financial instruments and strengthened the recognition of Indigenous rights, the final binding text is conspicuously silent on the one commitment that matters most right now: a concrete, mandatory roadmap to halt deforestation. …The Brazilian Presidency pushed hard for two ambitious roadmaps: one to phase out fossil fuels and one to halt deforestation. The strategy was to link them, acknowledging the obvious: we cannot save the Amazon if the world keeps warming. …The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change process proved unable to digest the complexity of the forest–climate nexus. We have effectively moved from a consensus-based approach to a plurilateral one, where progress rests on voluntary clubs of nations rather than global law. …If the political outcome disappointed, the financial and rights-based elements provide a measure of hope: The Tropical Forests Forever Faculty—a mechanism that pays nations for standing forests as an asset class, not just for avoided deforestation.
While the summit launched new financial instruments and strengthened the recognition of Indigenous rights, the final binding text is conspicuously silent on the one commitment that matters most right now: a concrete, mandatory roadmap to halt deforestation. …The Brazilian Presidency pushed hard for two ambitious roadmaps: one to phase out fossil fuels and one to halt deforestation. The strategy was to link them, acknowledging the obvious: we cannot save the Amazon if the world keeps warming. …The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change process proved unable to digest the complexity of the forest–climate nexus. We have effectively moved from a consensus-based approach to a plurilateral one, where progress rests on voluntary clubs of nations rather than global law. …If the political outcome disappointed, the financial and rights-based elements provide a measure of hope: The Tropical Forests Forever Faculty—a mechanism that pays nations for standing forests as an asset class, not just for avoided deforestation.
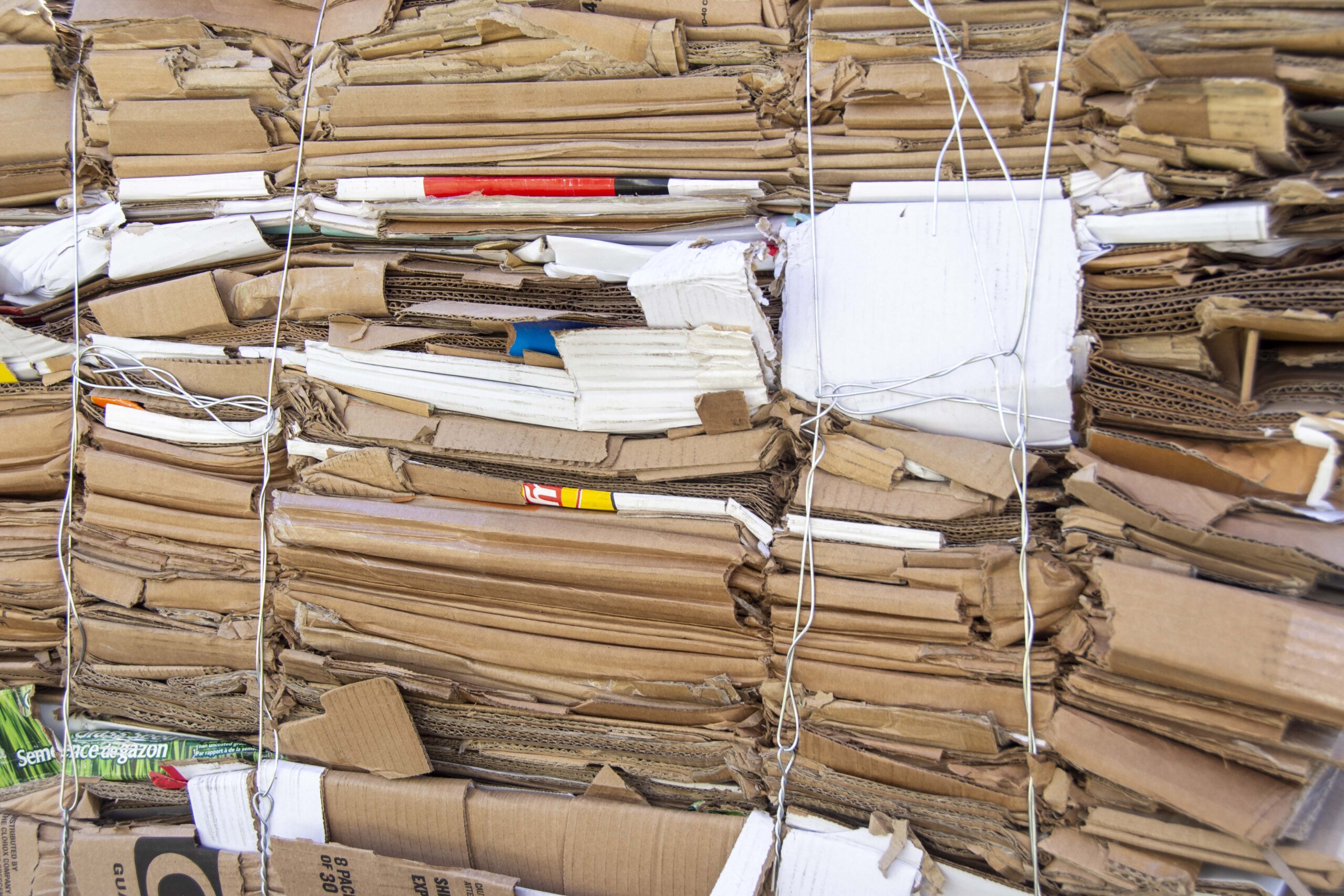 A new study has shown for the first time that waste cardboard can be used as an effective source of biomass fuel for large scale power generation. Engineers from the University of Nottingham have provided the first comprehensive characterisation of cardboard as a potential fuel source and created a new method to assess the composition of the material providing a practical tool for fuel assessment for cardboards. The study has been published in the journal Biomass and Bioenergy. This research demonstrates that cardboard shows differences in physical and chemical properties, including lower carbon content, reduced heating value, and a high prevalence of calcium carbonate fillers, particularly in printed grades. The researchers have also developed a new technique to analyse the calcium carbonate content of cardboard. Calcium carbonate is added to cardboard to improve its optical properties and stiffness, but forms ash during combustion which can reduce a boilers performance.
A new study has shown for the first time that waste cardboard can be used as an effective source of biomass fuel for large scale power generation. Engineers from the University of Nottingham have provided the first comprehensive characterisation of cardboard as a potential fuel source and created a new method to assess the composition of the material providing a practical tool for fuel assessment for cardboards. The study has been published in the journal Biomass and Bioenergy. This research demonstrates that cardboard shows differences in physical and chemical properties, including lower carbon content, reduced heating value, and a high prevalence of calcium carbonate fillers, particularly in printed grades. The researchers have also developed a new technique to analyse the calcium carbonate content of cardboard. Calcium carbonate is added to cardboard to improve its optical properties and stiffness, but forms ash during combustion which can reduce a boilers performance. BRAZIL — More than 30 years after the world first came together in Brazil to tackle climate change, global temperatures are still rising and so is impatience with talk over action. …For decades, protecting forests felt like an uphill struggle. Now, that’s changing. Forest nations and partners around the world are rewriting the economics of conservation, turning forest stewardship into an engine of prosperity and sustainable growth. In Guyana, our pioneering system for high-integrity carbon credits has shown how trees can be worth more standing than cut down. Brazil’s leadership on the new Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF) is creating a predictable, long-term finance reward for countries to preserve their forests and direct proceeds to Indigenous Peoples and local communities. Across the world, investors are beginning to recognise that keeping forests standing is not just good for the planet, it’s good for their bottom line.
BRAZIL — More than 30 years after the world first came together in Brazil to tackle climate change, global temperatures are still rising and so is impatience with talk over action. …For decades, protecting forests felt like an uphill struggle. Now, that’s changing. Forest nations and partners around the world are rewriting the economics of conservation, turning forest stewardship into an engine of prosperity and sustainable growth. In Guyana, our pioneering system for high-integrity carbon credits has shown how trees can be worth more standing than cut down. Brazil’s leadership on the new Tropical Forests Forever Facility (TFFF) is creating a predictable, long-term finance reward for countries to preserve their forests and direct proceeds to Indigenous Peoples and local communities. Across the world, investors are beginning to recognise that keeping forests standing is not just good for the planet, it’s good for their bottom line.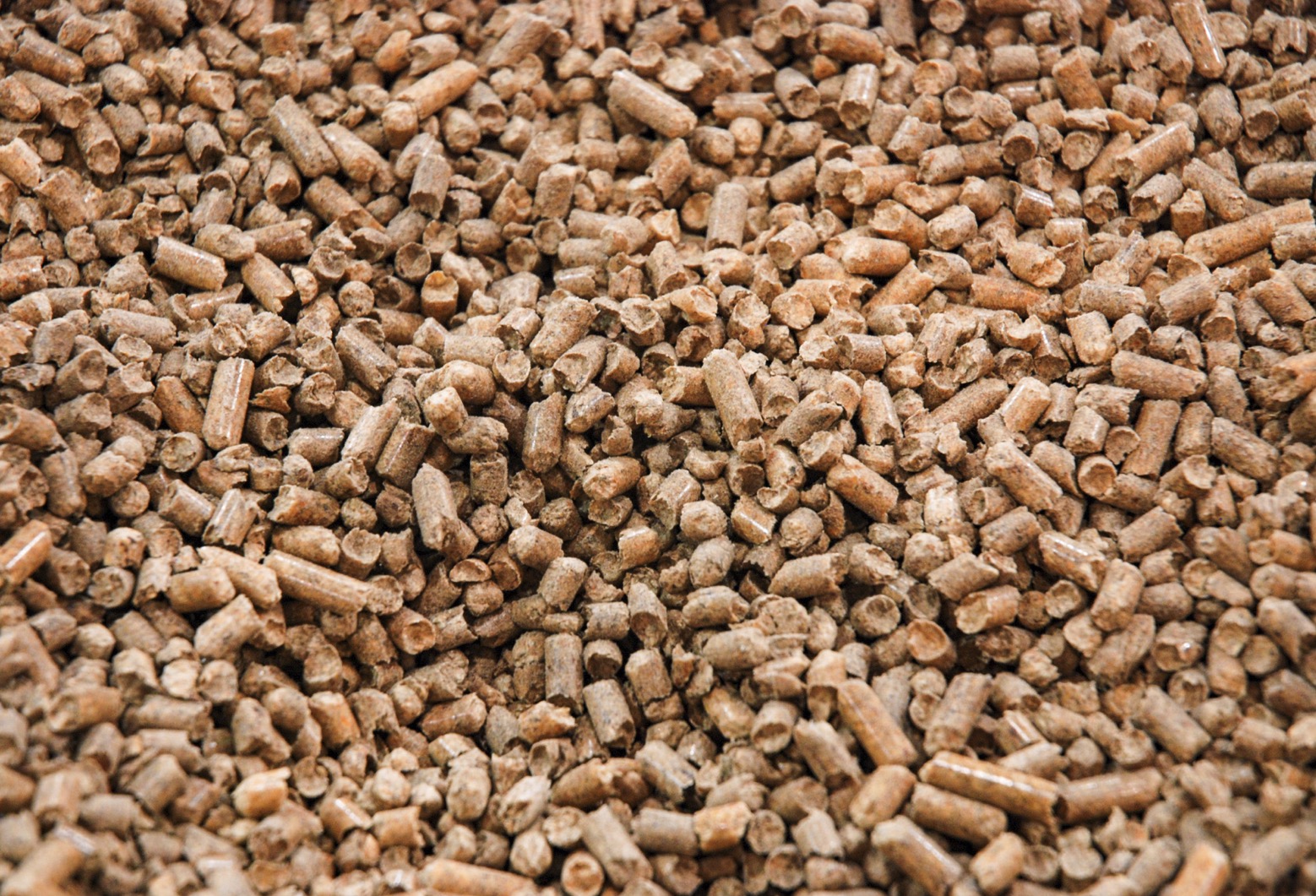 Britain’s biggest power plant will continue to earn more than £1m a day from burning wood pellets under a new government subsidy contract designed to halve its financial support, according to analysts. The Drax power plant in North Yorkshire is in line to earn £458.6m a year between 2027 and 2031 after the government agreed to extend its subsidies beyond 2026, according to analysts at Ember, a climate thinktank. The earnings are well below the £869m in subsidies handed to the Drax power plant last year for generating about 5% of the UK’s electricity from burning biomass after the government promised to curb the use of biomass in Britain’s power system. Under the contract, Drax will be paid to run just over a quarter of the time, down sharply from almost two-thirds of time currently. But the price it will earn for each unit of electricity generated will rise.
Britain’s biggest power plant will continue to earn more than £1m a day from burning wood pellets under a new government subsidy contract designed to halve its financial support, according to analysts. The Drax power plant in North Yorkshire is in line to earn £458.6m a year between 2027 and 2031 after the government agreed to extend its subsidies beyond 2026, according to analysts at Ember, a climate thinktank. The earnings are well below the £869m in subsidies handed to the Drax power plant last year for generating about 5% of the UK’s electricity from burning biomass after the government promised to curb the use of biomass in Britain’s power system. Under the contract, Drax will be paid to run just over a quarter of the time, down sharply from almost two-thirds of time currently. But the price it will earn for each unit of electricity generated will rise.
 Panama – Unveiled today at its General Assembly, the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) reports a sharp slide in public concern for climate change, even after the hottest year on record. The 2025 Global Consumer Awareness Survey – conducted with Ipsos across 50 countries and 40,000+ respondents – find war and conflict (52%) now dominate public worries while climate change trails at 31%. That is a 21-point gap in the 2025 snapshot. Looking only at the 32 countries surveyed in both 2022 and 2025, the concern gap has widened from 12 points in 2022 – where economic hardship was on top position – to 16 points in 2025. …While ‘climate change’ may rank lower as an abstract global issue in the 50-country snapshot, across the forestry module markets, the impacts felt through forests –wildfires, droughts, floods, and biodiversity loss – rank among the top concerns within the forestry sector.
Panama – Unveiled today at its General Assembly, the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) reports a sharp slide in public concern for climate change, even after the hottest year on record. The 2025 Global Consumer Awareness Survey – conducted with Ipsos across 50 countries and 40,000+ respondents – find war and conflict (52%) now dominate public worries while climate change trails at 31%. That is a 21-point gap in the 2025 snapshot. Looking only at the 32 countries surveyed in both 2022 and 2025, the concern gap has widened from 12 points in 2022 – where economic hardship was on top position – to 16 points in 2025. …While ‘climate change’ may rank lower as an abstract global issue in the 50-country snapshot, across the forestry module markets, the impacts felt through forests –wildfires, droughts, floods, and biodiversity loss – rank among the top concerns within the forestry sector.