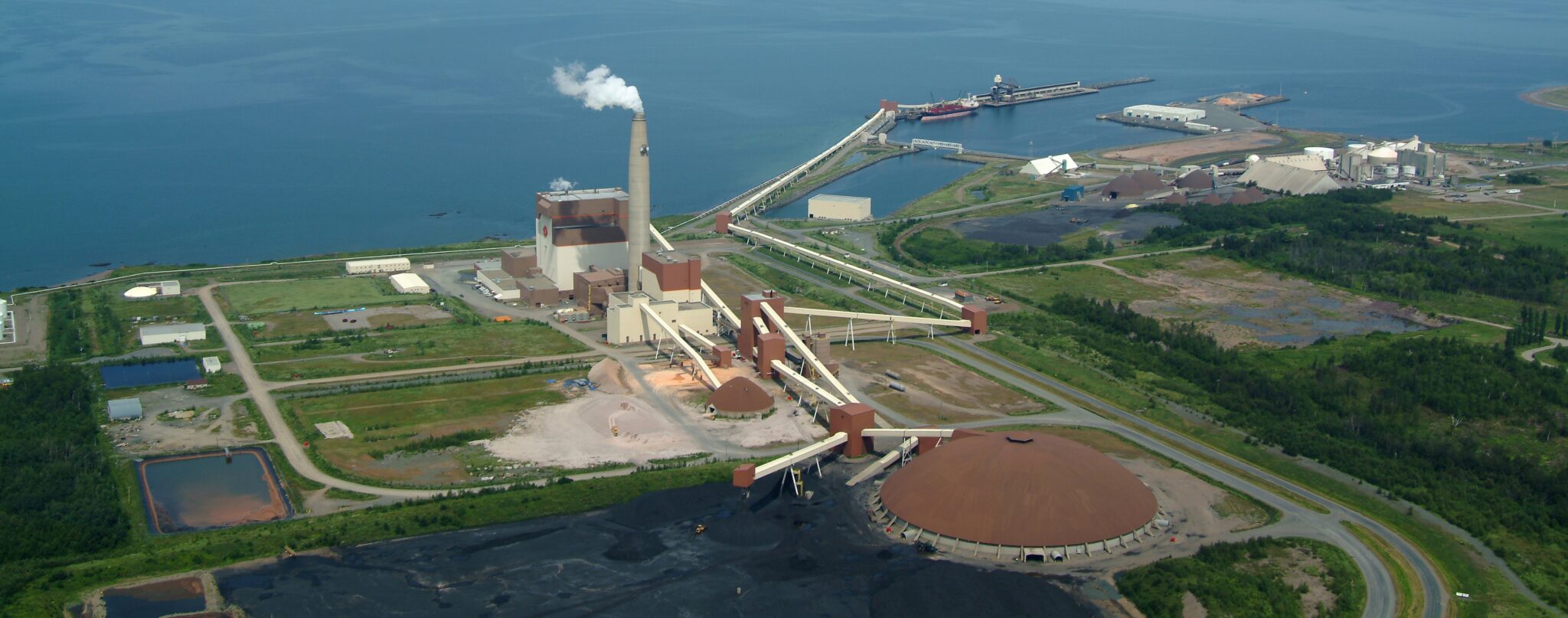
 In New Brunswick, NB Power’s plan to convert the Belledune coal-fired electric power station to black pellets presents an exciting opportunity for Canada. One that could strengthen the economics of the Canadian lumber sector, ensure better use of existing harvests and support rural communities across Atlantic Canada, while ensuring the power station complies with Canada’s 2030 coal phase-out regulation. With the right federal support, all of Belledune’s fuel supply can come from within Canada — specifically, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec and Ontario. This is “buy Canadian” in practice: Canadian fibre turned into Canadian pellets for Canadian electricity. Thermally treated pellets, often referred to as “black pellets,” are emerging as one of the most promising renewable fuels in Canada’s energy transition. They mimic coal in energy production, are compatible with existing coal infrastructure, easier to pulverize than white pellets and can be stored outdoors without degrading.
In New Brunswick, NB Power’s plan to convert the Belledune coal-fired electric power station to black pellets presents an exciting opportunity for Canada. One that could strengthen the economics of the Canadian lumber sector, ensure better use of existing harvests and support rural communities across Atlantic Canada, while ensuring the power station complies with Canada’s 2030 coal phase-out regulation. With the right federal support, all of Belledune’s fuel supply can come from within Canada — specifically, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec and Ontario. This is “buy Canadian” in practice: Canadian fibre turned into Canadian pellets for Canadian electricity. Thermally treated pellets, often referred to as “black pellets,” are emerging as one of the most promising renewable fuels in Canada’s energy transition. They mimic coal in energy production, are compatible with existing coal infrastructure, easier to pulverize than white pellets and can be stored outdoors without degrading.


 OTTAWA, ON – Canada’s emissions progress flatlined in 2024, according to the latest Early Estimate of National Emissions (EENE) from 440 Megatonnes, a project of the Canadian Climate Institute. With emissions essentially unchanged from 2023, at 694 megatonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (Mt), the new data shows that previous years’ improvements have stalled. Further, emissions trends indicate Canada’s 2030 emissions reduction target is now out of reach given weakening policy momentum across the country. That’s despite years of disruptive and costly wildfires, extreme weather and other climate-related disasters that increasingly threaten Canadians’ security and drive up the cost of living. …While some sectors—including electricity and buildings—continued to cut emissions in 2024, progress was modest and more than countered by rising emissions from oil and gas, particularly oil sands production.
OTTAWA, ON – Canada’s emissions progress flatlined in 2024, according to the latest Early Estimate of National Emissions (EENE) from 440 Megatonnes, a project of the Canadian Climate Institute. With emissions essentially unchanged from 2023, at 694 megatonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (Mt), the new data shows that previous years’ improvements have stalled. Further, emissions trends indicate Canada’s 2030 emissions reduction target is now out of reach given weakening policy momentum across the country. That’s despite years of disruptive and costly wildfires, extreme weather and other climate-related disasters that increasingly threaten Canadians’ security and drive up the cost of living. …While some sectors—including electricity and buildings—continued to cut emissions in 2024, progress was modest and more than countered by rising emissions from oil and gas, particularly oil sands production.
 THUNDER BAY — A number of stakeholders, largely from the forestry and energy sectors, got to provide regional input into a series of ongoing cross-province talks about energy policy. The Vaughn and Thunder Bay Chambers of Commerce held a roundtable discussion in the city on Oct. 2. The goal was for regional interests to provide requested input into an issues paper on energy being developed by the Toronto-based business lobby. …In Northwestern Ontario, she said, that includes longstanding sources like hydroelectricity and natural gas, but also continually-emerging opportunities connected to forestry and biomass. “We also talked a lot about the opportunities through the forest sector and biomass and the many things that can be created by harnessing forest products into energy,” Robinson said. “I think the most important thing was talking about how, from a forestry perspective, it really does check all the boxes.”
THUNDER BAY — A number of stakeholders, largely from the forestry and energy sectors, got to provide regional input into a series of ongoing cross-province talks about energy policy. The Vaughn and Thunder Bay Chambers of Commerce held a roundtable discussion in the city on Oct. 2. The goal was for regional interests to provide requested input into an issues paper on energy being developed by the Toronto-based business lobby. …In Northwestern Ontario, she said, that includes longstanding sources like hydroelectricity and natural gas, but also continually-emerging opportunities connected to forestry and biomass. “We also talked a lot about the opportunities through the forest sector and biomass and the many things that can be created by harnessing forest products into energy,” Robinson said. “I think the most important thing was talking about how, from a forestry perspective, it really does check all the boxes.”


 Given market sentiment and operating rates, in addition to recent mill closures and curtailments, how has demand for wood fiber changed recently and over the past 10 years? …Total capacity of the wood-using U.S. pulp and paper sector declined 18% in the past 10 years. This decline is specific to wood-using mills, excluding facilities that rely exclusively on recycled fiber, but the sector reported drops in all end uses, with reductions in printing and writing capacity falling 49%. This represented over half of the lost capacity nationwide. Newsprint, household/sanitary, and market pulp segments also had notable declines, each representing 10%-16% of the lost capacity. Regionally, capacity reductions in the U.S. South accounted for most of the volume lost (64%), with the U.S. West and North each representing 18%. The West experienced the largest and most severe drop in capacity for a given region, with pulp and paper mill closures and reductions decreasing capacity by 26%.
Given market sentiment and operating rates, in addition to recent mill closures and curtailments, how has demand for wood fiber changed recently and over the past 10 years? …Total capacity of the wood-using U.S. pulp and paper sector declined 18% in the past 10 years. This decline is specific to wood-using mills, excluding facilities that rely exclusively on recycled fiber, but the sector reported drops in all end uses, with reductions in printing and writing capacity falling 49%. This represented over half of the lost capacity nationwide. Newsprint, household/sanitary, and market pulp segments also had notable declines, each representing 10%-16% of the lost capacity. Regionally, capacity reductions in the U.S. South accounted for most of the volume lost (64%), with the U.S. West and North each representing 18%. The West experienced the largest and most severe drop in capacity for a given region, with pulp and paper mill closures and reductions decreasing capacity by 26%.
 At New York Climate Week, a coalition of 34 national governments unveiled a decisive blueprint called the Forest Finance Roadmap for Action, aimed at closing the substantial funding shortfall undermining global efforts to halt deforestation. The plan, developed in partnership with Brazil and backed by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), targets the estimated $66.8 billion annual finance gap in tropical nations. The roadmap distinguishes itself as the first unified framework to bring together governments from both the Global North and South under a shared agenda for forest finance, according to an announcement made by the Forest & Climate Leaders’ Partnership (FCLP). It seeks to move beyond pledge-making toward deployable, investment-ready strategies aligned with the COP30 Action Agenda and the Glasgow Leaders’ Declaration.
At New York Climate Week, a coalition of 34 national governments unveiled a decisive blueprint called the Forest Finance Roadmap for Action, aimed at closing the substantial funding shortfall undermining global efforts to halt deforestation. The plan, developed in partnership with Brazil and backed by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), targets the estimated $66.8 billion annual finance gap in tropical nations. The roadmap distinguishes itself as the first unified framework to bring together governments from both the Global North and South under a shared agenda for forest finance, according to an announcement made by the Forest & Climate Leaders’ Partnership (FCLP). It seeks to move beyond pledge-making toward deployable, investment-ready strategies aligned with the COP30 Action Agenda and the Glasgow Leaders’ Declaration. WASHINGTON — Evidence that climate change harms public health is “beyond scientific dispute,” the independent National Academy of Sciences said in response to the Trump administration’s efforts to revoke a landmark U.S. government finding to that effect that underpins key environmental regulations. The NAS, a non-governmental nonprofit set up to advise the government on science, said human activity is releasing greenhouse gases that are warming the planet, increasing extreme temperatures and changing the oceans, all dangerous developments for the health and welfare of the United States public. Evidence to that effect has only grown stronger since 2009, the group said. In July, the Trump administration proposed revoking what’s known as the 2009 “endangerment” finding, the concept that climate change is a threat. Overturning it could pave the way for cutting a range of rules that limit pollution from cars, power plants and other sources.
WASHINGTON — Evidence that climate change harms public health is “beyond scientific dispute,” the independent National Academy of Sciences said in response to the Trump administration’s efforts to revoke a landmark U.S. government finding to that effect that underpins key environmental regulations. The NAS, a non-governmental nonprofit set up to advise the government on science, said human activity is releasing greenhouse gases that are warming the planet, increasing extreme temperatures and changing the oceans, all dangerous developments for the health and welfare of the United States public. Evidence to that effect has only grown stronger since 2009, the group said. In July, the Trump administration proposed revoking what’s known as the 2009 “endangerment” finding, the concept that climate change is a threat. Overturning it could pave the way for cutting a range of rules that limit pollution from cars, power plants and other sources.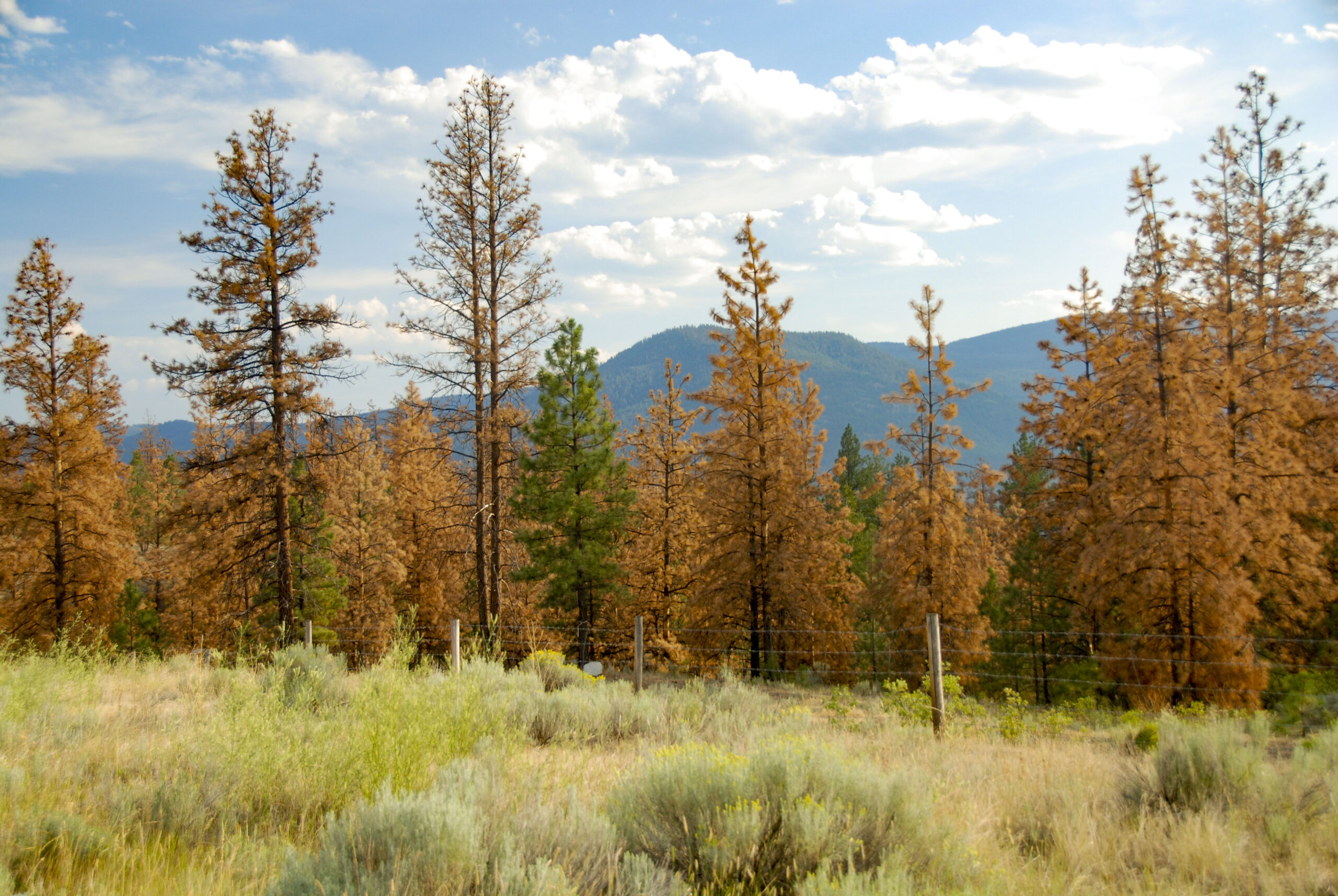 The American Biomass Energy Association and Pellet Fuels Institute are among 400-plus associations, businesses and landowners representing the forest products sector that sent a letter to President Donald Trump on Sept. 8 urging immediate action to stabilize the U.S. forestry sector and its access to markets in the face of mounting mill closures, devastating natural disasters, pests and diseases, and unfair foreign trade practices. “Together, these forces are pushing many landowners to exit forestry altogether,” the groups wrote. “If forests are abandoned or converted, the consequences for our domestic timber supply, as well as markets for housing, infrastructure, consumer products, energy, rural livelihoods, and environmental security, will be severe. …The letter outlines four immediate steps the Trump administration can take to spark job creation and economic growth. This includes promoting the use of biomass for electricity and expanding the definition of qualifying wood biomass under the Renewable Fuel Standard.
The American Biomass Energy Association and Pellet Fuels Institute are among 400-plus associations, businesses and landowners representing the forest products sector that sent a letter to President Donald Trump on Sept. 8 urging immediate action to stabilize the U.S. forestry sector and its access to markets in the face of mounting mill closures, devastating natural disasters, pests and diseases, and unfair foreign trade practices. “Together, these forces are pushing many landowners to exit forestry altogether,” the groups wrote. “If forests are abandoned or converted, the consequences for our domestic timber supply, as well as markets for housing, infrastructure, consumer products, energy, rural livelihoods, and environmental security, will be severe. …The letter outlines four immediate steps the Trump administration can take to spark job creation and economic growth. This includes promoting the use of biomass for electricity and expanding the definition of qualifying wood biomass under the Renewable Fuel Standard.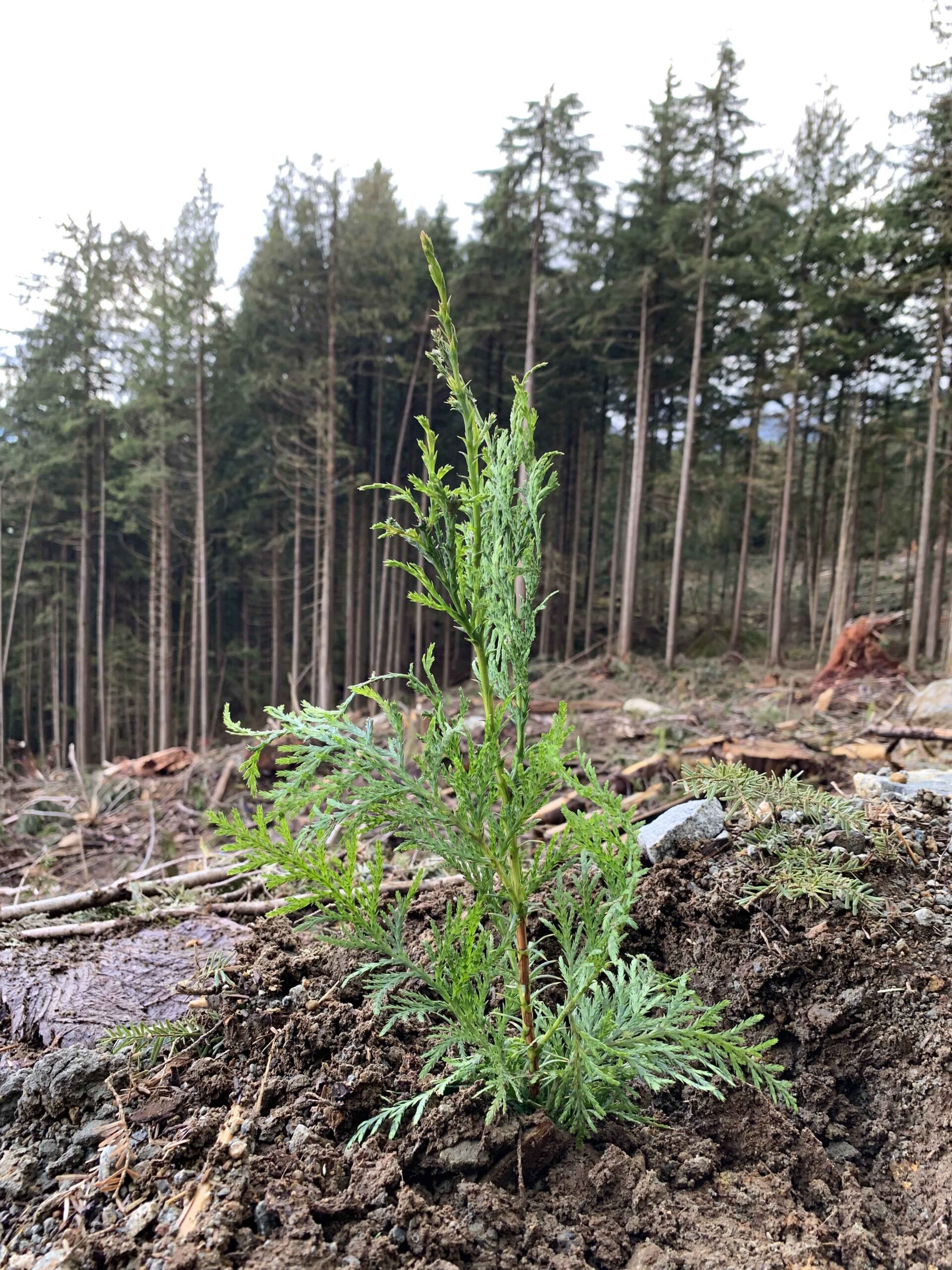  As the planet heats up, we need to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. …‘nature-based climate solutions’ are human interventions that utilize natural processes to draw down carbon from the atmosphere. According to William Anderegg, director of the Wilkes Center for Climate Science and Policy at the University of Utah, planting forests is an especially promising option. “The central opportunity here is that we can leverage nature,” Anderegg says, “and forests globally have pretty large potential to help with climate change mitigation.” [However], Anderegg says …there are many problems with the programs that seek to plant forests as a climate solution.
As the planet heats up, we need to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. …‘nature-based climate solutions’ are human interventions that utilize natural processes to draw down carbon from the atmosphere. According to William Anderegg, director of the Wilkes Center for Climate Science and Policy at the University of Utah, planting forests is an especially promising option. “The central opportunity here is that we can leverage nature,” Anderegg says, “and forests globally have pretty large potential to help with climate change mitigation.” [However], Anderegg says …there are many problems with the programs that seek to plant forests as a climate solution.  BILLINGS, Montana — A federal judge on Wednesday dismissed a lawsuit from young climate activists seeking to block President Donald Trump’s executive orders promoting fossil fuels and discouraging renewable energy. U.S. District Judge Dana Christensen said the plaintiffs showed overwhelming evidence climate change affects them and that it will worsen as a result of Trump’s orders. But Christensen concluded their request for the courts to intervene was “unworkable” because it was beyond the power of the judiciary to create environmental policies. The 22 plaintiffs included youths who prevailed in a landmark climate trial against the state of Montana in 2023. …Legal experts said the young activists and their lawyers from the environmental group Our Children’s Trust faced long odds in the federal case. …The climate activists will appeal Wednesday’s ruling, said Julia Olson, chief legal counsel at Our Children’s Trust.
BILLINGS, Montana — A federal judge on Wednesday dismissed a lawsuit from young climate activists seeking to block President Donald Trump’s executive orders promoting fossil fuels and discouraging renewable energy. U.S. District Judge Dana Christensen said the plaintiffs showed overwhelming evidence climate change affects them and that it will worsen as a result of Trump’s orders. But Christensen concluded their request for the courts to intervene was “unworkable” because it was beyond the power of the judiciary to create environmental policies. The 22 plaintiffs included youths who prevailed in a landmark climate trial against the state of Montana in 2023. …Legal experts said the young activists and their lawyers from the environmental group Our Children’s Trust faced long odds in the federal case. …The climate activists will appeal Wednesday’s ruling, said Julia Olson, chief legal counsel at Our Children’s Trust.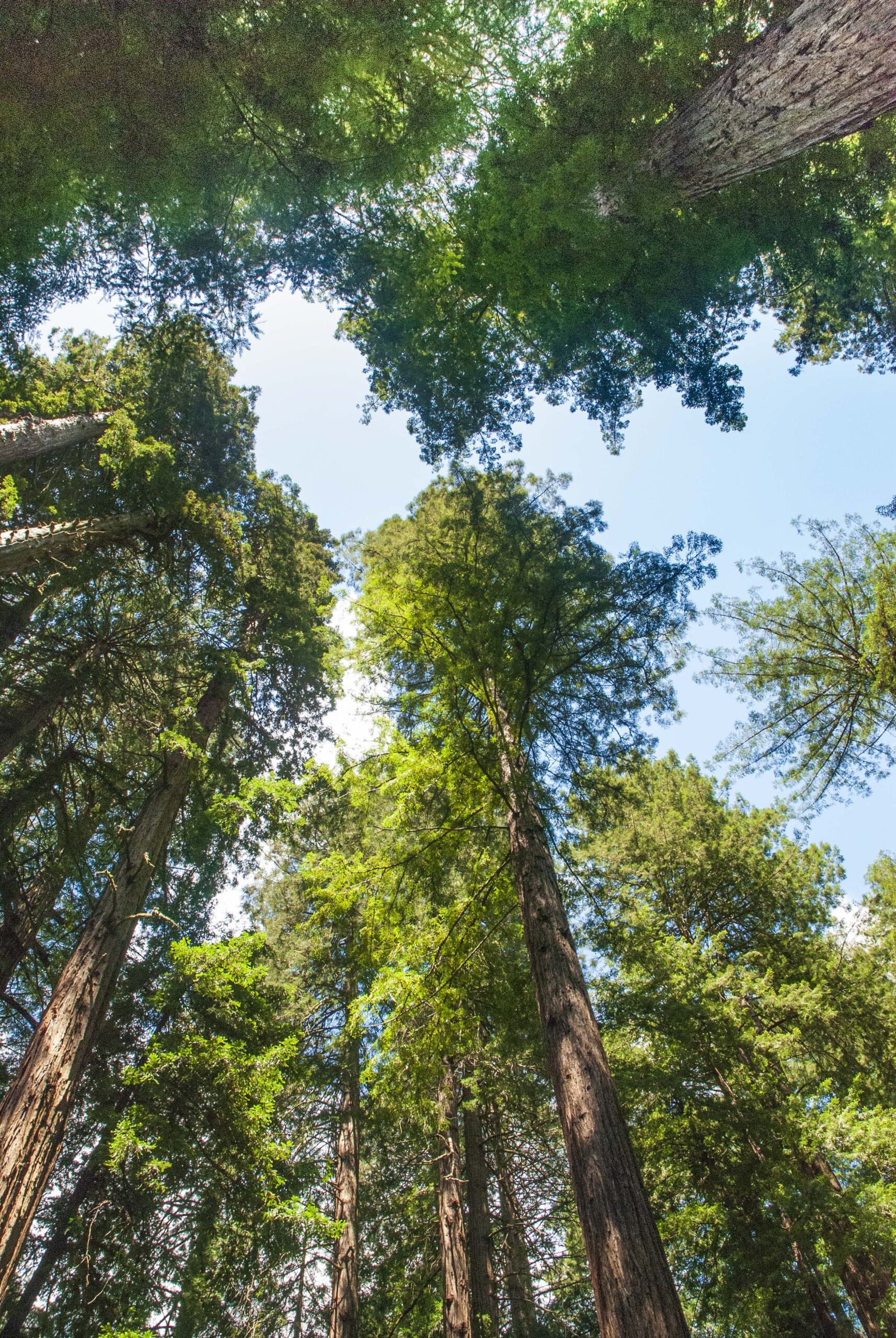 Storing carbon in forests is an essential, nature-based buffer against climate change. Yet forests packed with too many trees increase the threat of severe wildfires… A team of UC Merced and collaborating researchers evaluated the tradeoffs between two seemingly opposing scenarios: Trees are critical because they pull carbon dioxide from the air, preventing carbon from adding to greenhouse effects that trap heat and warm the atmosphere; and the increasing severity and danger of wildfires call for the thinning of overly dense forests. The researchers found that the best approach is a combination of both.
Storing carbon in forests is an essential, nature-based buffer against climate change. Yet forests packed with too many trees increase the threat of severe wildfires… A team of UC Merced and collaborating researchers evaluated the tradeoffs between two seemingly opposing scenarios: Trees are critical because they pull carbon dioxide from the air, preventing carbon from adding to greenhouse effects that trap heat and warm the atmosphere; and the increasing severity and danger of wildfires call for the thinning of overly dense forests. The researchers found that the best approach is a combination of both.  PASCAGOULA, Mississippi — A fire is burning inside one of the wood pellet domes at the Port of Pascagoula. The fire started Monday afternoon inside one of the two Enviva domes at the port. Jackson County Emergency Management Director Earl Etheridge said there is no danger of explosion. Jackson County firefighters are on scene to assist Enviva and port crews. The fire started Monday afternoon inside one of the two Enviva domes at the port. …Etheridge says that Enviva is injecting the dome with pressurized nitrogen to suppress the fire. The fire is contained to the dome. Crews are working to offload the 20,000 metric tons of wood pellets.
PASCAGOULA, Mississippi — A fire is burning inside one of the wood pellet domes at the Port of Pascagoula. The fire started Monday afternoon inside one of the two Enviva domes at the port. Jackson County Emergency Management Director Earl Etheridge said there is no danger of explosion. Jackson County firefighters are on scene to assist Enviva and port crews. The fire started Monday afternoon inside one of the two Enviva domes at the port. …Etheridge says that Enviva is injecting the dome with pressurized nitrogen to suppress the fire. The fire is contained to the dome. Crews are working to offload the 20,000 metric tons of wood pellets.  A study finds that replacing natural gas with electric and biomass power, along with improved energy efficiency, could help some pulp and paper mills reach zero net emissions. Researchers began with a simulation of mills defined by two characteristics: whether they used virgin or recycled fibers, and whether they were integrated or not. A virgin mill creates pulp and paper from fresh wood… while a recycled fiber mill re-uses fibers which may have been previously processed. A mill is considered integrated if it has the capability to turn wood and other biomass into pulp and paper on site, whereas a non-integrated mill uses pulp produced and dried off site. …The final strategy researchers analyzed was the use of low-carbon alternatives, like using waste wood in boilers instead of fossil fuels. The effectiveness changed depending on whether or not the mill was integrated, but all types saw reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
A study finds that replacing natural gas with electric and biomass power, along with improved energy efficiency, could help some pulp and paper mills reach zero net emissions. Researchers began with a simulation of mills defined by two characteristics: whether they used virgin or recycled fibers, and whether they were integrated or not. A virgin mill creates pulp and paper from fresh wood… while a recycled fiber mill re-uses fibers which may have been previously processed. A mill is considered integrated if it has the capability to turn wood and other biomass into pulp and paper on site, whereas a non-integrated mill uses pulp produced and dried off site. …The final strategy researchers analyzed was the use of low-carbon alternatives, like using waste wood in boilers instead of fossil fuels. The effectiveness changed depending on whether or not the mill was integrated, but all types saw reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. WISCONSIN — Lawmakers from northern and north-central Wisconsin are circulating a bill supporting Johnson Timber Corp. in Hayward to build a processing plant for aviation fuel made from logging debris to establish a processing plant in Wisconsin. The legislation would reward the company with a $60 million tax credit and access to $150 million in borrowing through Wisconsin’s bonding authority. Republican lawmakers wrote in a memo circulated Monday seeking cosponsors that the proposal would create 150 jobs and generate $1.2 billion a year in income after three years of operation. The processing plant in Hayward would be built by Johnson Timber Corp., in partnership with a German company… Synthec Fuels. Wisconsin along with Michigan and Minnesota are all vying for the project, Felzkowski said, “and the state that helps will be the first state” to get the facility and probably the headquarters for the overall processing operation.
WISCONSIN — Lawmakers from northern and north-central Wisconsin are circulating a bill supporting Johnson Timber Corp. in Hayward to build a processing plant for aviation fuel made from logging debris to establish a processing plant in Wisconsin. The legislation would reward the company with a $60 million tax credit and access to $150 million in borrowing through Wisconsin’s bonding authority. Republican lawmakers wrote in a memo circulated Monday seeking cosponsors that the proposal would create 150 jobs and generate $1.2 billion a year in income after three years of operation. The processing plant in Hayward would be built by Johnson Timber Corp., in partnership with a German company… Synthec Fuels. Wisconsin along with Michigan and Minnesota are all vying for the project, Felzkowski said, “and the state that helps will be the first state” to get the facility and probably the headquarters for the overall processing operation.

 Google has announced plans to address greenhouse gases beyond carbon dioxide by purchasing credits to support the emerging market for removing short-lived but highly potent “superpollutants.” The company will buy up to 25,000 tonnes of superpollutant-destruction credits by 2030 from two organisations, Recoolit and Cool Effect—equivalent to about one million tonnes of CO₂ removal over the long term. While carbon dioxide remains a key focus, Google said gases such as methane, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrous oxide have a much greater near-term warming impact. “It’s the right thing to do for the planet,” said Randy Spock, Google’s carbon credits and removals lead. “CO₂ is obviously very important… but if we think only about CO₂, then we’re just looking at one piece of the puzzle.” …Sam Abernethy, a climate scientist at Spark Climate Solutions, said: “Superpollutants only get a few percent of climate finance… that’s a misallocation given their importance.”
Google has announced plans to address greenhouse gases beyond carbon dioxide by purchasing credits to support the emerging market for removing short-lived but highly potent “superpollutants.” The company will buy up to 25,000 tonnes of superpollutant-destruction credits by 2030 from two organisations, Recoolit and Cool Effect—equivalent to about one million tonnes of CO₂ removal over the long term. While carbon dioxide remains a key focus, Google said gases such as methane, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrous oxide have a much greater near-term warming impact. “It’s the right thing to do for the planet,” said Randy Spock, Google’s carbon credits and removals lead. “CO₂ is obviously very important… but if we think only about CO₂, then we’re just looking at one piece of the puzzle.” …Sam Abernethy, a climate scientist at Spark Climate Solutions, said: “Superpollutants only get a few percent of climate finance… that’s a misallocation given their importance.”
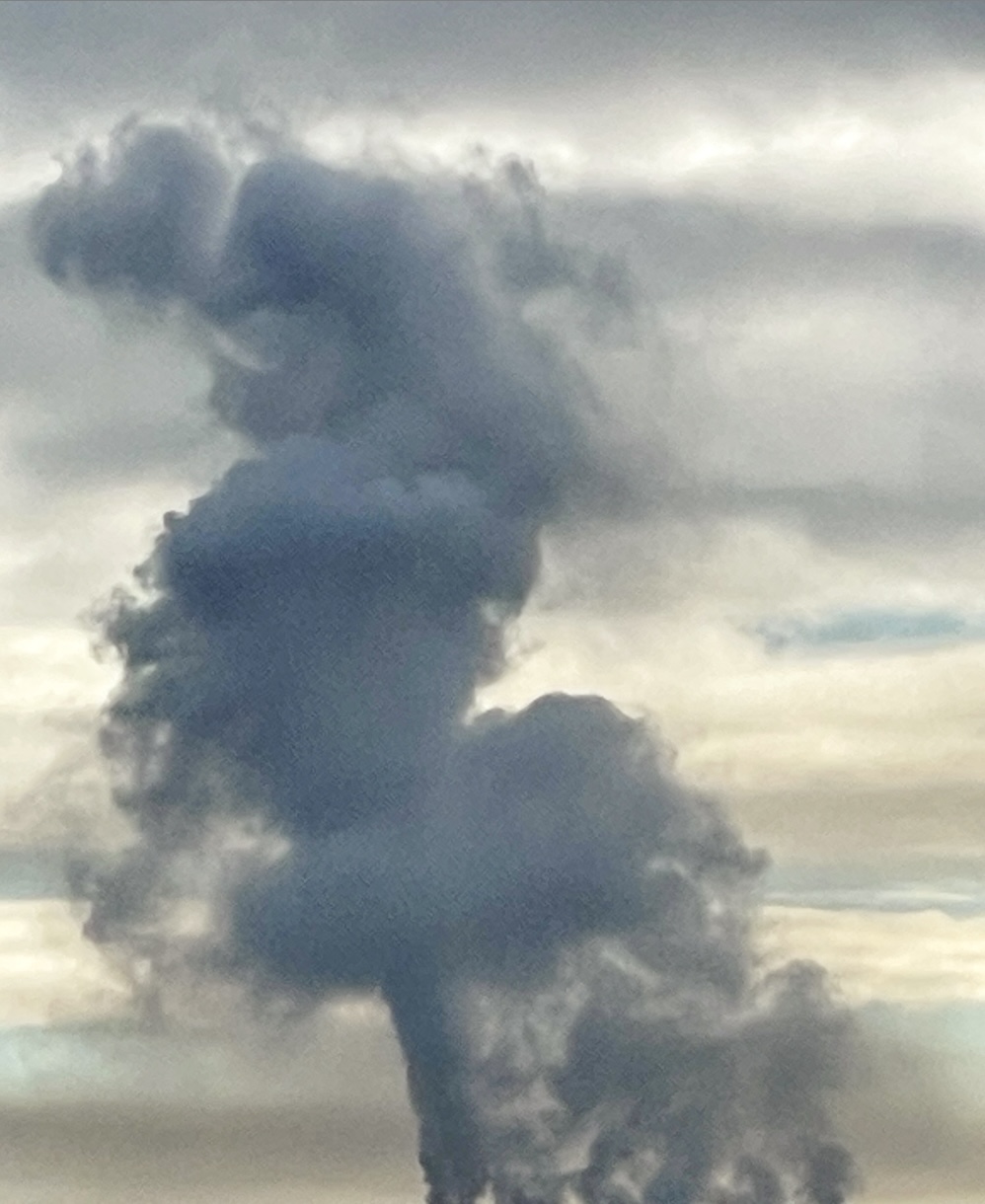 GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.
GENEVA — Heat-trapping carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere jumped by the highest amount on record last year, soaring to a level not seen in human civilization and “turbo-charging” the Earth’s climate and causing more extreme weather, the United Nations weather agency said Wednesday. The World Meteorological Organization said in its latest bulletin on greenhouse gases, an annual study released ahead of the U.N.’s annual climate conference, that CO2 growth rates have now tripled since the 1960s, and reached levels that existed more than 800,000 years ago. Emissions from burning coal, oil and gas, alongside more wildfires, have helped fan a “vicious climate cycle,” and people and industries continue to spew heat-trapping gases while the planet’s oceans and forests lose their ability to absorb them, the WMO report said.
 In 2024, the Amazon Rainforest underwent its most devastating forest fire season in more than two decades. According to a new study by the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre, the fire-driven forest degradation released an estimated 791 million metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2024, a sevenfold increase compared with the previous two years. The carbon emissions from fires in 2024 surpassed those from deforestation for the first time on record. Brazil was the largest contributor, accounting for 61% of these emissions, followed by Bolivia with 32%, the study found. “The escalating fire occurrence, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use, threatens to push the Amazon towards a catastrophic tipping point,” the authors write. …The researchers estimated that the total emissions from deforestation and fire-driven degradation in the Amazon in 2024 was 1,416 million metric tons of CO2. This is higher than Japan’s CO2 emissions in 2022, which ranked fifth after China, the U.S., India and Russia.
In 2024, the Amazon Rainforest underwent its most devastating forest fire season in more than two decades. According to a new study by the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre, the fire-driven forest degradation released an estimated 791 million metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2024, a sevenfold increase compared with the previous two years. The carbon emissions from fires in 2024 surpassed those from deforestation for the first time on record. Brazil was the largest contributor, accounting for 61% of these emissions, followed by Bolivia with 32%, the study found. “The escalating fire occurrence, driven by climate change and unsustainable land use, threatens to push the Amazon towards a catastrophic tipping point,” the authors write. …The researchers estimated that the total emissions from deforestation and fire-driven degradation in the Amazon in 2024 was 1,416 million metric tons of CO2. This is higher than Japan’s CO2 emissions in 2022, which ranked fifth after China, the U.S., India and Russia. The failure of carbon offsets to cut planet-heating pollution is “not due to a few bad apples”, a
The failure of carbon offsets to cut planet-heating pollution is “not due to a few bad apples”, a  Josep “Pep” Canadell, executive director of the Global Carbon Project, says he believes countries large and small need to think twice before pledging to collectively plant billions of trees as a primary emissions-reduction strategy to meet climate action goals. “We have somehow sold reforestation as an easier path [to fighting climate change], and it’s not easy at all,” Canadell said. “In my view, it’s not even easier than carbon capture and storage, a technology we’re still developing. That’s because when you bring humans into landscapes and try managing these landscapes, this stuff becomes very complex.” Canadell is the co-author of a
Josep “Pep” Canadell, executive director of the Global Carbon Project, says he believes countries large and small need to think twice before pledging to collectively plant billions of trees as a primary emissions-reduction strategy to meet climate action goals. “We have somehow sold reforestation as an easier path [to fighting climate change], and it’s not easy at all,” Canadell said. “In my view, it’s not even easier than carbon capture and storage, a technology we’re still developing. That’s because when you bring humans into landscapes and try managing these landscapes, this stuff becomes very complex.” Canadell is the co-author of a  The biggest trees in the Amazon are growing larger and more numerous, according to a new study that shows how an intact rainforest can help draw carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and sequester it in bark, trunk, branch and root. Scientists said
The biggest trees in the Amazon are growing larger and more numerous, according to a new study that shows how an intact rainforest can help draw carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and sequester it in bark, trunk, branch and root. Scientists said  EUROPE — Climate change has large economic costs for society. An important effect is the disruption of natural resource supply by climate-mediated disturbances such as wildfires, pest outbreaks and storms. Here we show that disturbance-induced losses for Europe’s timber-based forestry could increase from the current €115 billion to €247 billion under severe climate change. This would diminish the timber value of Europe’s forests by up to 42% and reduce the current gross value added of the forestry sector by up to 15%. Central Europe emerges as a continental hotspot of disturbance costs, with projected future costs of up to €19,885 per hectare. Simultaneous climate-related increases in forest productivity could offset future economic losses from disturbances in Northern and Central Europe but not in Southern Europe. We find high disturbance-related cost of unmitigated warming, highlighting that climate change adaptation in forestry is not only an ecological but also an economic imperative.
EUROPE — Climate change has large economic costs for society. An important effect is the disruption of natural resource supply by climate-mediated disturbances such as wildfires, pest outbreaks and storms. Here we show that disturbance-induced losses for Europe’s timber-based forestry could increase from the current €115 billion to €247 billion under severe climate change. This would diminish the timber value of Europe’s forests by up to 42% and reduce the current gross value added of the forestry sector by up to 15%. Central Europe emerges as a continental hotspot of disturbance costs, with projected future costs of up to €19,885 per hectare. Simultaneous climate-related increases in forest productivity could offset future economic losses from disturbances in Northern and Central Europe but not in Southern Europe. We find high disturbance-related cost of unmitigated warming, highlighting that climate change adaptation in forestry is not only an ecological but also an economic imperative.