 Work on climate change has largely focused on preventing it from getting worse, but as a new RBC report points out, businesses are also starting to think more about potential spending on adaptation and preparation as the costs of disasters pile up. The report says that extreme weather and natural disaster costs already totalled US$368 billion last year, 14 per cent above the long-term average since 2000, and that this year could match or exceed the total. The trend is expected to get worse, because as the report notes there’s expected to be a 2.7 degree rise in average temperatures by 2100 based on current global policies and actions, while an optimistic scenario pegs the rise at 1.9 degrees. The costs stemming from rising temperatures are leading to more attention in boardrooms, with the report noting mentions of climate change on the rise in both U.S. and Asia.
Work on climate change has largely focused on preventing it from getting worse, but as a new RBC report points out, businesses are also starting to think more about potential spending on adaptation and preparation as the costs of disasters pile up. The report says that extreme weather and natural disaster costs already totalled US$368 billion last year, 14 per cent above the long-term average since 2000, and that this year could match or exceed the total. The trend is expected to get worse, because as the report notes there’s expected to be a 2.7 degree rise in average temperatures by 2100 based on current global policies and actions, while an optimistic scenario pegs the rise at 1.9 degrees. The costs stemming from rising temperatures are leading to more attention in boardrooms, with the report noting mentions of climate change on the rise in both U.S. and Asia.




 Join us in Halifax, Nova Scotia, September 23-24, 2025 for Biomass for a Low-Carbon Future. As the world moves toward a low-carbon future, biomass and wood pellets play a key role in ensuring Canada has renewable and responsible energy. Join us to explore the numerous opportunities biomass presents, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to supporting economic growth in the transition to a net-zero economy. Who Should Attend? Anyone interested in advancing electrification, including pellet producers, customers, First Nations and government officials, policymakers, regulators at every level, researchers, safety specialists, logistics personnel and equipment manufacturers.
Join us in Halifax, Nova Scotia, September 23-24, 2025 for Biomass for a Low-Carbon Future. As the world moves toward a low-carbon future, biomass and wood pellets play a key role in ensuring Canada has renewable and responsible energy. Join us to explore the numerous opportunities biomass presents, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to supporting economic growth in the transition to a net-zero economy. Who Should Attend? Anyone interested in advancing electrification, including pellet producers, customers, First Nations and government officials, policymakers, regulators at every level, researchers, safety specialists, logistics personnel and equipment manufacturers.
 Earlier this year, Burnaby’s Svante Technologies made inroads in Alberta. The move eastward is partially powered by a newly formed partnership with Mercer International. The Canadian cleantech’s carbon capture project is targeting biogenic CO2 emissions from Mercer’s Peace River pulp mill. …One of the strategies the firm intends to adopt in Canada is carbon sequestration. Within Alberta, carbon sequestration is a sensible tactic to apply, according to Mercer International’s chief executive officer, Juan Carlos Bueno. “The reason why we’re doing it there is because the mill is located in Alberta, where you have geological formations that are suitable for sequestering CO2,” Bueno informed Andrew Snook of Pulp & Paper Canada. …Finalizing investment in the project, however, is no small consideration. There is a price tag north of $500 million and moving forward would require extensive support from both the Province of Alberta and Government of Canada.
Earlier this year, Burnaby’s Svante Technologies made inroads in Alberta. The move eastward is partially powered by a newly formed partnership with Mercer International. The Canadian cleantech’s carbon capture project is targeting biogenic CO2 emissions from Mercer’s Peace River pulp mill. …One of the strategies the firm intends to adopt in Canada is carbon sequestration. Within Alberta, carbon sequestration is a sensible tactic to apply, according to Mercer International’s chief executive officer, Juan Carlos Bueno. “The reason why we’re doing it there is because the mill is located in Alberta, where you have geological formations that are suitable for sequestering CO2,” Bueno informed Andrew Snook of Pulp & Paper Canada. …Finalizing investment in the project, however, is no small consideration. There is a price tag north of $500 million and moving forward would require extensive support from both the Province of Alberta and Government of Canada.


 Climate change has put Western Canada’s glaciers on track for devastating loss over the coming decades, with the southern half of BC expected to lose nearly 75% of the alpine ice — even if warming stops today, a new study has found. The planet has so far warmed an average of about 1.2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial temperatures. If that increase climbs to 1.5 degrees C, 81% of Western Canadian and US glacier mass would melt, according to the study published Thursday in the journal Science. …Harry Zekollari, the study’s lead author and a glaciologist at Belgium’s Vrije Universiteit Brussel, said the international research team used eight glacier computer models to analyze the potential long-term evolution of the year-round ice. The results painted a dire picture for the world’s glaciers, as the planet has already locked in enough warming to melt 40% of the Earth’s year-round ice by the end of the century.
Climate change has put Western Canada’s glaciers on track for devastating loss over the coming decades, with the southern half of BC expected to lose nearly 75% of the alpine ice — even if warming stops today, a new study has found. The planet has so far warmed an average of about 1.2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial temperatures. If that increase climbs to 1.5 degrees C, 81% of Western Canadian and US glacier mass would melt, according to the study published Thursday in the journal Science. …Harry Zekollari, the study’s lead author and a glaciologist at Belgium’s Vrije Universiteit Brussel, said the international research team used eight glacier computer models to analyze the potential long-term evolution of the year-round ice. The results painted a dire picture for the world’s glaciers, as the planet has already locked in enough warming to melt 40% of the Earth’s year-round ice by the end of the century.
 WASHINGTON — On behalf of the American Wood Council (AWC) and the American Forest & Paper Association (AF&PA), AF&PA Vice President of Public Policy Paul Noe gave oral testimony before the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, Subcommittee on Environment in their hearing titled, “Short-Circuiting Progress: How the Clean Air Act Impacts Building Necessary Infrastructure and Onshoring American Innovation.” In his testimony, Noe applauded legislation that would allow the paper and wood products industry to make capital investments to modernize their manufacturing facilities. …discussion was heard by the committee on two bills that would make critical revisions to the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) setting and implementation process that would reduce the type of permit gridlock created when the particulate matter NAAQS was significantly lowered by the previous administration. “We strongly support Congressmen Rick Allen and Buddy Carter in their efforts to address the impacts of air permitting issues on U.S. manufacturing,” said Noe.
WASHINGTON — On behalf of the American Wood Council (AWC) and the American Forest & Paper Association (AF&PA), AF&PA Vice President of Public Policy Paul Noe gave oral testimony before the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, Subcommittee on Environment in their hearing titled, “Short-Circuiting Progress: How the Clean Air Act Impacts Building Necessary Infrastructure and Onshoring American Innovation.” In his testimony, Noe applauded legislation that would allow the paper and wood products industry to make capital investments to modernize their manufacturing facilities. …discussion was heard by the committee on two bills that would make critical revisions to the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) setting and implementation process that would reduce the type of permit gridlock created when the particulate matter NAAQS was significantly lowered by the previous administration. “We strongly support Congressmen Rick Allen and Buddy Carter in their efforts to address the impacts of air permitting issues on U.S. manufacturing,” said Noe.  Replanting forests can help cool the planet even more than some scientists once believed, especially in the tropics. But even if every tree lost since the mid-19th century is replanted, the total effect won’t cancel out human-generated warming. …In a new study
Replanting forests can help cool the planet even more than some scientists once believed, especially in the tropics. But even if every tree lost since the mid-19th century is replanted, the total effect won’t cancel out human-generated warming. …In a new study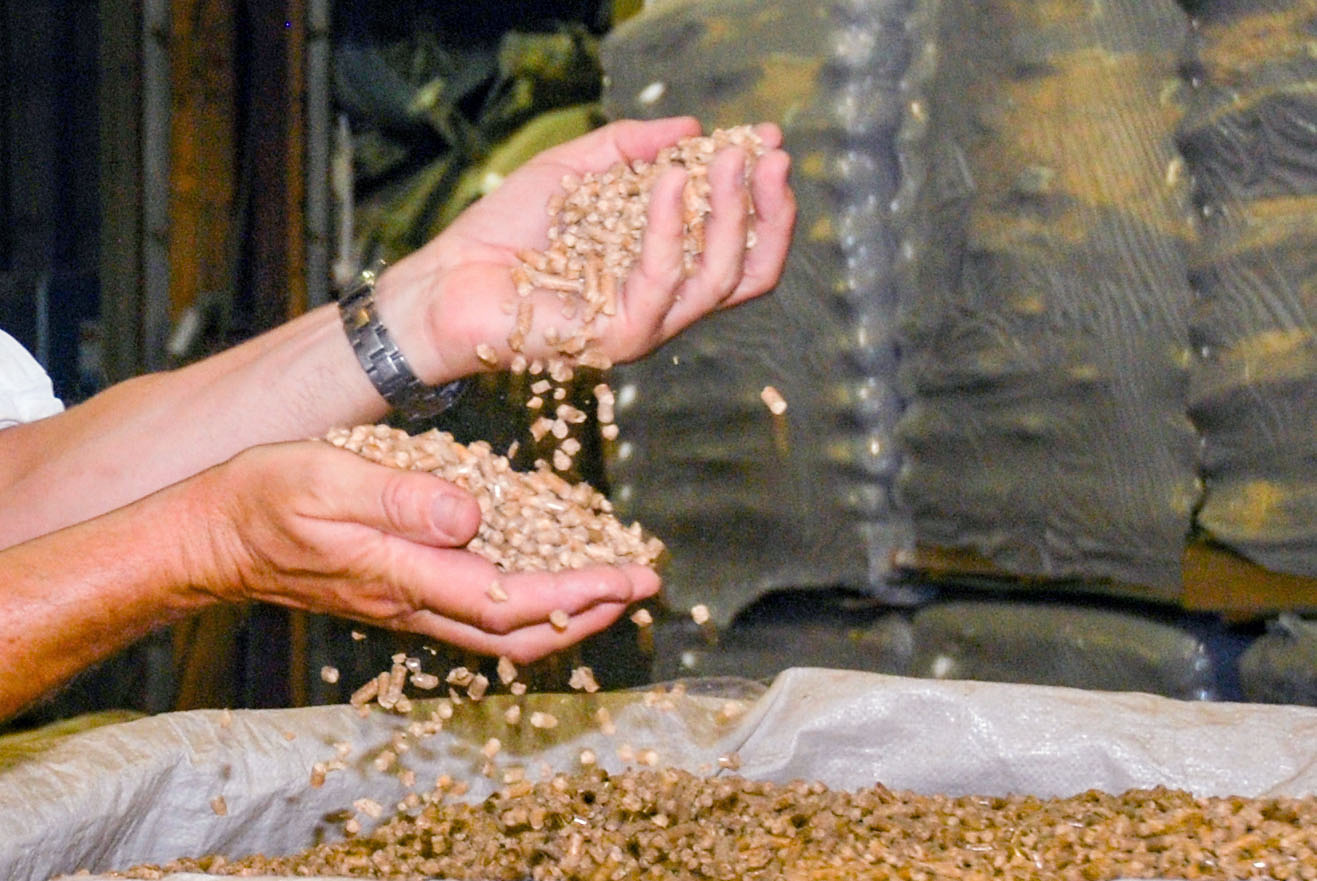  In an energy conversation dominated by buzzwords and breakthroughs, it’s easy to overlook the quiet, proven solutions that are already delivering results. Exhibit A: wood pellets. These compact cylinders aren’t flashy or trend on social media. For the uninitiated, they are carriers of renewable carbon and energy, sourced from responsibly managed forests; a real, scalable, domestic resource that delivers energy security, climate value, and rural jobs while sustaining and growing forests. Wood pellets are emerging as one of the smartest plays in America’s energy and climate portfolio. …Every year, America’s 360 million acres of privately-owned forests grow more wood than we harvest. …Responsible forest management, the kind that thins out fuel for wildfires, not only keeps forests healthy but also supplies feedstock for wood pellets. …This is climate action with a hard hat, not a hashtag. …Wood pellets are real, scalable, renewable and a true American resource.
In an energy conversation dominated by buzzwords and breakthroughs, it’s easy to overlook the quiet, proven solutions that are already delivering results. Exhibit A: wood pellets. These compact cylinders aren’t flashy or trend on social media. For the uninitiated, they are carriers of renewable carbon and energy, sourced from responsibly managed forests; a real, scalable, domestic resource that delivers energy security, climate value, and rural jobs while sustaining and growing forests. Wood pellets are emerging as one of the smartest plays in America’s energy and climate portfolio. …Every year, America’s 360 million acres of privately-owned forests grow more wood than we harvest. …Responsible forest management, the kind that thins out fuel for wildfires, not only keeps forests healthy but also supplies feedstock for wood pellets. …This is climate action with a hard hat, not a hashtag. …Wood pellets are real, scalable, renewable and a true American resource.

 A
A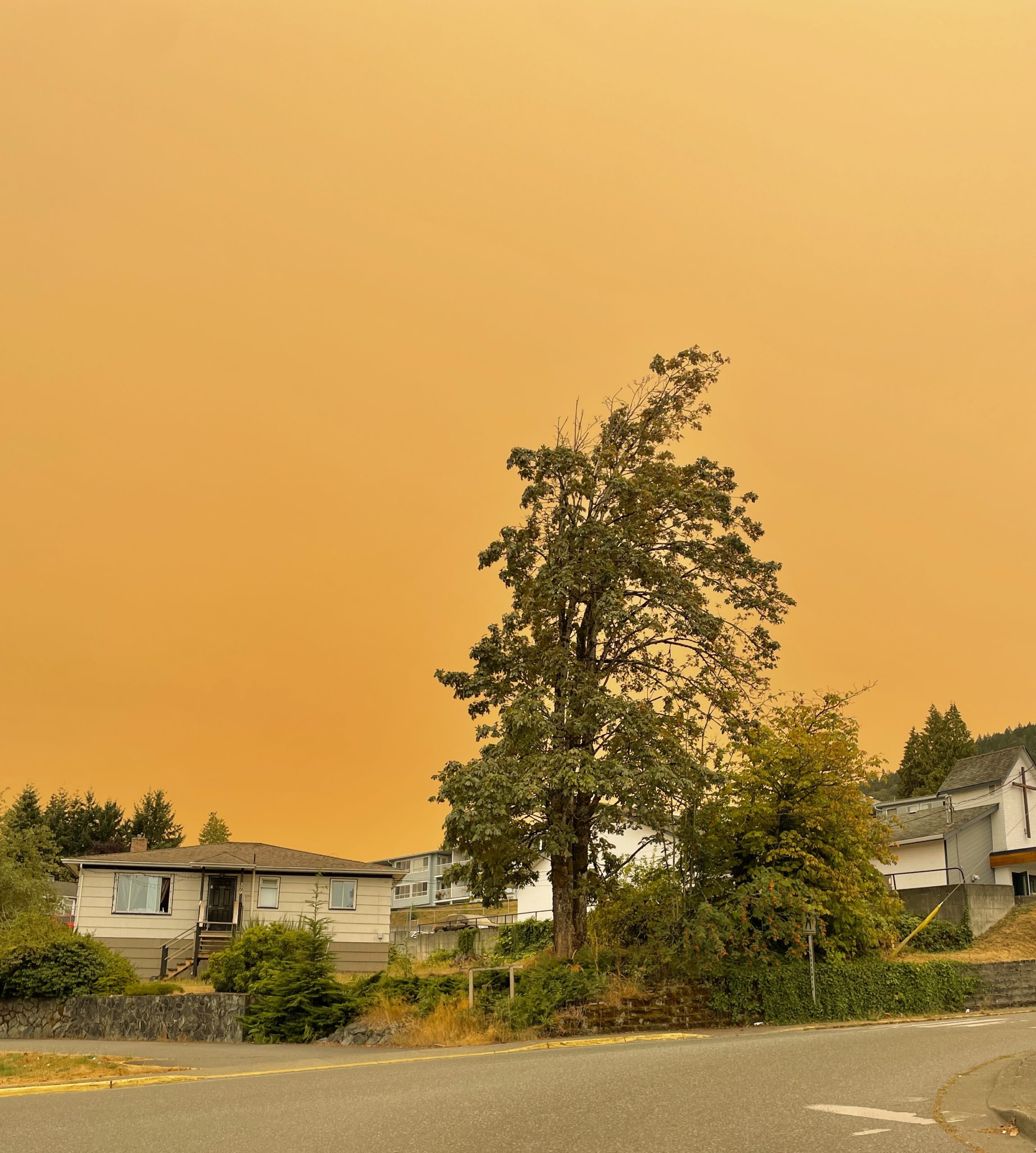  Even if you live far from the boreal forests in Canada and Siberia, you’ve likely noticed an increase in smoke from their forest fires. During major blazes in 2023, the smoke oranged the New York sky and drifted as far south as New Orleans. These blazes have surged in the last decade due to the effects of climate change — warmer summers, less snow cover in the spring, and the loss of sea ice. Experts expect that trend to continue. Yet recent climate change projection models have not accounted for the increase. For instance, the widely used sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Project, or CMIP6, released in the late 2010s, kept these fires constant at a relatively low severity. A new University of Washington-led study projects that in the next 35 years these increasing boreal fires will actually slow warming by 12% globally and 38% in the Arctic.
Even if you live far from the boreal forests in Canada and Siberia, you’ve likely noticed an increase in smoke from their forest fires. During major blazes in 2023, the smoke oranged the New York sky and drifted as far south as New Orleans. These blazes have surged in the last decade due to the effects of climate change — warmer summers, less snow cover in the spring, and the loss of sea ice. Experts expect that trend to continue. Yet recent climate change projection models have not accounted for the increase. For instance, the widely used sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Project, or CMIP6, released in the late 2010s, kept these fires constant at a relatively low severity. A new University of Washington-led study projects that in the next 35 years these increasing boreal fires will actually slow warming by 12% globally and 38% in the Arctic.
 TEXAS — A plan to open a bioenergy plant in Newton County has reached a new milestone with a landmark deal to supply wood for the site in Bon Wier. Mike Lout with KJAS, reports Nick Andrews, President and CEO of the Scottsdale, Arizona-based USA Bioenergy, announced on Tuesday that his company has
TEXAS — A plan to open a bioenergy plant in Newton County has reached a new milestone with a landmark deal to supply wood for the site in Bon Wier. Mike Lout with KJAS, reports Nick Andrews, President and CEO of the Scottsdale, Arizona-based USA Bioenergy, announced on Tuesday that his company has  GEORGETOWN, South Carolina — Over 650 Georgetown residents have signed a petition opposing a proposed biomass plant at the site of the International Paper mill that closed last year. The group Citizens for Georgetown says it is working to revitalize the town’s waterfront through “thoughtful redevelopment.” 653 people are opposing the plant that would generate energy for Santee Cooper from tree waste. …Citizens for Georgetown Chairman Tom Swatzel. “Now, we face a critical choice: leave decades of pollution in the land and water, continue with heavy industry OR clean up the site and reimagine these properties into a vibrant, sustainable future that benefits all residents.” …State Sen. Stephen Goldfinch expressed cautious optimism over the proposed plant, saying that it could involve an investment of nearly $4 billion and create new jobs.
GEORGETOWN, South Carolina — Over 650 Georgetown residents have signed a petition opposing a proposed biomass plant at the site of the International Paper mill that closed last year. The group Citizens for Georgetown says it is working to revitalize the town’s waterfront through “thoughtful redevelopment.” 653 people are opposing the plant that would generate energy for Santee Cooper from tree waste. …Citizens for Georgetown Chairman Tom Swatzel. “Now, we face a critical choice: leave decades of pollution in the land and water, continue with heavy industry OR clean up the site and reimagine these properties into a vibrant, sustainable future that benefits all residents.” …State Sen. Stephen Goldfinch expressed cautious optimism over the proposed plant, saying that it could involve an investment of nearly $4 billion and create new jobs. A law signed by Gov. Janet Mills last week
A law signed by Gov. Janet Mills last week  Of the two dozen people who showed up for a meeting to talk about a proposed biomass energy plant in Georgetown, five were from conservation groups. Another five were reporters.
Of the two dozen people who showed up for a meeting to talk about a proposed biomass energy plant in Georgetown, five were from conservation groups. Another five were reporters.



 DS Smith has brought online a €90 million biomass boiler at its Rouen paper mill in Normandy, France – one of Europe’s largest mill energy transitions to date. The new system replaces the site’s coal-fired boiler with a low-carbon, circular solution powered by locally sourced biomass waste. The project is expected to cut CO₂ emissions by 99,000 tonnes annually – equivalent to removing 40,000 cars from the road or powering 13,000 French homes each year. The boiler will process around 94,000 tonnes of biomass fuel each year, including industrial and municipal waste wood – mainly from the Paris and Normandy regions – as well as paper production by-products. Up to 70,000 tonnes of wood waste will be diverted from landfill annually, supporting DS Smith’s 2030 zero-landfill target.
DS Smith has brought online a €90 million biomass boiler at its Rouen paper mill in Normandy, France – one of Europe’s largest mill energy transitions to date. The new system replaces the site’s coal-fired boiler with a low-carbon, circular solution powered by locally sourced biomass waste. The project is expected to cut CO₂ emissions by 99,000 tonnes annually – equivalent to removing 40,000 cars from the road or powering 13,000 French homes each year. The boiler will process around 94,000 tonnes of biomass fuel each year, including industrial and municipal waste wood – mainly from the Paris and Normandy regions – as well as paper production by-products. Up to 70,000 tonnes of wood waste will be diverted from landfill annually, supporting DS Smith’s 2030 zero-landfill target. The Phillipines sits on a goldmine of forest and carbon wealth. But an unclear and short-sighted property rights regime is choking its potential; existing rules are partially to be blamed.
The Phillipines sits on a goldmine of forest and carbon wealth. But an unclear and short-sighted property rights regime is choking its potential; existing rules are partially to be blamed.  Hundreds of top environment lawyers are suing the New Zealand government over what they say is its “dangerously inadequate” plan to reduce emissions to net zero by 2050. It is the first time the country’s emissions reduction plan has faced litigation, and the lawyers believe it is the first case globally that challenges the use of forestry to offset emissions. …two groups representing more than 300 lawyers filed judicial review proceedings against the government in Wellington’s high court on Tuesday. The groups … claim … the government has abandoned dozens of tools to tackle emissions, failed to adequately consult the public, and too heavily relies on high-risk carbon capture strategies such as forestry. …They claim that the government is relying on “high risk” methods such as planting hundreds of thousands of hectares of introduced pine trees to offset emissions, and capturing carbon underground, with few alternatives to fall back on if something goes wrong.
Hundreds of top environment lawyers are suing the New Zealand government over what they say is its “dangerously inadequate” plan to reduce emissions to net zero by 2050. It is the first time the country’s emissions reduction plan has faced litigation, and the lawyers believe it is the first case globally that challenges the use of forestry to offset emissions. …two groups representing more than 300 lawyers filed judicial review proceedings against the government in Wellington’s high court on Tuesday. The groups … claim … the government has abandoned dozens of tools to tackle emissions, failed to adequately consult the public, and too heavily relies on high-risk carbon capture strategies such as forestry. …They claim that the government is relying on “high risk” methods such as planting hundreds of thousands of hectares of introduced pine trees to offset emissions, and capturing carbon underground, with few alternatives to fall back on if something goes wrong.
 Researchers from the University of Nottingham and CSIRO Australia have developed a pioneering combined milling and combustion performance model to improve the selection of low carbon fuels for power generation. Published in the
Researchers from the University of Nottingham and CSIRO Australia have developed a pioneering combined milling and combustion performance model to improve the selection of low carbon fuels for power generation. Published in the  Rio Tinto has started growing pongamia trees in northern Australia, as part of a biofuels project aimed at reducing the mining giant’s reliance on fossil fuels. Pongamia trees are native to Australia and produce oil-rich seeds that can be processed into renewable diesel… Earlier this year, Rio Tinto trialled 10 million litres of renewable diesel — created from used cooking oil — across its Pilbara iron ore operations in Western Australia. The biofuel got used across the supply chain, featuring in Rio Tinto’s rail, marine, haul trucks, surface mining equipment and light vehicles… Forestry Industry Association of the Northern Territory (FIANT) manager Hanna Lillicrap said it was great to see a major mining company getting involved in the forestry sector. “It reflects a growing recognition of the role forestry can play as a climate-positive solution in emissions reduction strategies,” she said. “It’s great to see serious investment going into research to better understand the species and its potential,” she said.
Rio Tinto has started growing pongamia trees in northern Australia, as part of a biofuels project aimed at reducing the mining giant’s reliance on fossil fuels. Pongamia trees are native to Australia and produce oil-rich seeds that can be processed into renewable diesel… Earlier this year, Rio Tinto trialled 10 million litres of renewable diesel — created from used cooking oil — across its Pilbara iron ore operations in Western Australia. The biofuel got used across the supply chain, featuring in Rio Tinto’s rail, marine, haul trucks, surface mining equipment and light vehicles… Forestry Industry Association of the Northern Territory (FIANT) manager Hanna Lillicrap said it was great to see a major mining company getting involved in the forestry sector. “It reflects a growing recognition of the role forestry can play as a climate-positive solution in emissions reduction strategies,” she said. “It’s great to see serious investment going into research to better understand the species and its potential,” she said. Even if conversations are dominated by electrification, Toyota is working on a different course to keep combustion engines relevant. A recent Nikkei Asia report reveals that Japanese automakers led by Toyota have opened a bioethanol facility in Fukushima, aiming to slash the carbon footprint of conventional engines with a new kind of “better biofuel”. …What sets this project apart is its focus on second-generation biofuels: non-edible plants and agricultural waste serve as the feedstock, rather than food crops like corn or sugarcane. By avoiding feedstocks that compete with food supply, Toyota’s program addresses a key criticism of traditional biofuels. …The choice of Fukushima for the facility is symbolic. The site reuses land in an area devastated by the 2011 nuclear disaster, turning “disaster zones” into productive, green-energy facilities. In doing so, Toyota’s project ties regional recovery to climate innovation. …Feedstock: Uses non-food biomass (e.g. wood chips, rice straw, plant waste) instead of edible crops.
Even if conversations are dominated by electrification, Toyota is working on a different course to keep combustion engines relevant. A recent Nikkei Asia report reveals that Japanese automakers led by Toyota have opened a bioethanol facility in Fukushima, aiming to slash the carbon footprint of conventional engines with a new kind of “better biofuel”. …What sets this project apart is its focus on second-generation biofuels: non-edible plants and agricultural waste serve as the feedstock, rather than food crops like corn or sugarcane. By avoiding feedstocks that compete with food supply, Toyota’s program addresses a key criticism of traditional biofuels. …The choice of Fukushima for the facility is symbolic. The site reuses land in an area devastated by the 2011 nuclear disaster, turning “disaster zones” into productive, green-energy facilities. In doing so, Toyota’s project ties regional recovery to climate innovation. …Feedstock: Uses non-food biomass (e.g. wood chips, rice straw, plant waste) instead of edible crops.