 A pause on some tariffs creates a window for Canadian companies to re-examine their risk profiles and work with brokers to secure needed coverage. Both Bay Street and Wall Street are cheering the ruling from the US Court of International Trade that, at least temporarily, tamps down the 10% tariffs the White House imposed on most countries, and drug-related emergency orders setting 25% tariffs on some goods from Canada and Mexico. …Some companies may use tariff lulls to stock up on certain key materials. …Construction companies, for example, often import flooring products from the US, even though Canadian builders have good access to lumber. For them, stockpiling those materials reduces the economic impacts of both US tariffs and Canadian retaliatory tariffs. …Additional optimism arrived via King Charles III’s Speech from the Throne this week. The document opening Canada’s parliament commits to major economic initiatives, including large-scale increases in housing construction.
A pause on some tariffs creates a window for Canadian companies to re-examine their risk profiles and work with brokers to secure needed coverage. Both Bay Street and Wall Street are cheering the ruling from the US Court of International Trade that, at least temporarily, tamps down the 10% tariffs the White House imposed on most countries, and drug-related emergency orders setting 25% tariffs on some goods from Canada and Mexico. …Some companies may use tariff lulls to stock up on certain key materials. …Construction companies, for example, often import flooring products from the US, even though Canadian builders have good access to lumber. For them, stockpiling those materials reduces the economic impacts of both US tariffs and Canadian retaliatory tariffs. …Additional optimism arrived via King Charles III’s Speech from the Throne this week. The document opening Canada’s parliament commits to major economic initiatives, including large-scale increases in housing construction.
 Canada’s inflation rate eased to 1.7% in April, driven by a drop in prices after the federal government removed the consumer carbon tax, according to Statistics Canada. The slowdown came after the inflation rate hit 2.3% in March. Lower crude oil prices were also a factor in the decline, the data agency said. Despite the decline in headline inflation, core inflation measures all rose in April, some above three per cent — well above the Bank of Canada’s two per cent target rate. The central bank watches those numbers closely because they strip out volatile sectors and don’t factor in one-offs like the removal of the carbon tax. …The central bank is set to make its next interest rate decision on June 4. Porter still expects that the Bank of Canada will cut, given the outlook for weak economic growth in 2025, but said the bank might need more time to see how inflation plays out.
Canada’s inflation rate eased to 1.7% in April, driven by a drop in prices after the federal government removed the consumer carbon tax, according to Statistics Canada. The slowdown came after the inflation rate hit 2.3% in March. Lower crude oil prices were also a factor in the decline, the data agency said. Despite the decline in headline inflation, core inflation measures all rose in April, some above three per cent — well above the Bank of Canada’s two per cent target rate. The central bank watches those numbers closely because they strip out volatile sectors and don’t factor in one-offs like the removal of the carbon tax. …The central bank is set to make its next interest rate decision on June 4. Porter still expects that the Bank of Canada will cut, given the outlook for weak economic growth in 2025, but said the bank might need more time to see how inflation plays out. Tariff discussions about reducing US dependence on foreign goods became a focus for the second Trump administration. …However, the US forest products industry’s reliance on Canadian wood raises questions about eliminating Canadian wood imports entirely. This piece is the second in a two-part series by the Fastmarkets team.
Tariff discussions about reducing US dependence on foreign goods became a focus for the second Trump administration. …However, the US forest products industry’s reliance on Canadian wood raises questions about eliminating Canadian wood imports entirely. This piece is the second in a two-part series by the Fastmarkets team. 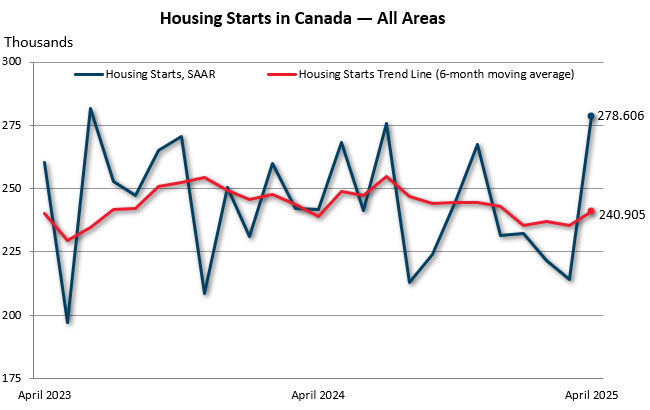

 The effects have been felt by building industries in terms of increased costs, disrupted supply chains and economic uncertainty. Last week’s webinar, “Trump’s Tariffs: Transition or Turmoil?… focused on the near-term effects of tariffs, how trade environments have shifted in response, and what the next steps of the Trump Administration might be. …Ari Hawkins, a Politico trade reporter, agreed that the administration is likely looking to the USMCA renegotiations to “really get into the weeds of a lot of these tariff disputes” with Canada. …Hawkins says that further Section 232 investigations could lead to new tariffs in the coming months on a range of products, including semiconductors, lumber and critical minerals. While the administration might make exemptions on materials like lumber before those investigations are completed, Hawkins says, they are still likely to face the Section 232 tariffs as part of the administration’s focus on incentivizing manufacturing and development within the US.
The effects have been felt by building industries in terms of increased costs, disrupted supply chains and economic uncertainty. Last week’s webinar, “Trump’s Tariffs: Transition or Turmoil?… focused on the near-term effects of tariffs, how trade environments have shifted in response, and what the next steps of the Trump Administration might be. …Ari Hawkins, a Politico trade reporter, agreed that the administration is likely looking to the USMCA renegotiations to “really get into the weeds of a lot of these tariff disputes” with Canada. …Hawkins says that further Section 232 investigations could lead to new tariffs in the coming months on a range of products, including semiconductors, lumber and critical minerals. While the administration might make exemptions on materials like lumber before those investigations are completed, Hawkins says, they are still likely to face the Section 232 tariffs as part of the administration’s focus on incentivizing manufacturing and development within the US. The downward price slide of recent weeks was unabated across most framing lumber species. Uncertainty surrounding the economy and potential new developments in US trade policy contributed to a cautious market tone. Many traders lamented that they anticipated at least a modest decline in mortgage interest rates by now that has not materialized. With discounts cutting deeper across most species, the Random Lengths Framing Lumber Composite Price tumbled $14. That’s the composite’s first double-digit drop since April 2024. Downward price pressure intensified across the South. …Competitively priced Western S-P-F crept deeper into traditional Southern Pine markets, especially lower grades, which contributed to the downward price pressure on SYP. …Lumber futures settled sharply higher on Thursday after a prolonged downward trend.
The downward price slide of recent weeks was unabated across most framing lumber species. Uncertainty surrounding the economy and potential new developments in US trade policy contributed to a cautious market tone. Many traders lamented that they anticipated at least a modest decline in mortgage interest rates by now that has not materialized. With discounts cutting deeper across most species, the Random Lengths Framing Lumber Composite Price tumbled $14. That’s the composite’s first double-digit drop since April 2024. Downward price pressure intensified across the South. …Competitively priced Western S-P-F crept deeper into traditional Southern Pine markets, especially lower grades, which contributed to the downward price pressure on SYP. …Lumber futures settled sharply higher on Thursday after a prolonged downward trend. Executives at two of North America’s lumber producers said they are bracing for volatile wood prices this building season before sharply higher US duties on Canadian lumber kick in. Despite President Trump’s threats, his April 2 tariff barrage didn’t hit Canadian lumber. Nonetheless, duties related to a long-running trade dispute are set to more than double later this year. Canfor and Interfor are not sure there won’t also be additional levies tied to Trump’s March 1 order for an investigation into the national security threat of imported wood. …Canfor’s Susan Yurkovich said “Either people won’t be able to access their products and there’ll be a slowdown… or there will be a price response, which also, of course, will have an impact on affordability.” …Interfor’s Bart Bender said he expects volatile pricing this spring and summer while sawmills figure out what sort of increases buyers will bear. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required]
Executives at two of North America’s lumber producers said they are bracing for volatile wood prices this building season before sharply higher US duties on Canadian lumber kick in. Despite President Trump’s threats, his April 2 tariff barrage didn’t hit Canadian lumber. Nonetheless, duties related to a long-running trade dispute are set to more than double later this year. Canfor and Interfor are not sure there won’t also be additional levies tied to Trump’s March 1 order for an investigation into the national security threat of imported wood. …Canfor’s Susan Yurkovich said “Either people won’t be able to access their products and there’ll be a slowdown… or there will be a price response, which also, of course, will have an impact on affordability.” …Interfor’s Bart Bender said he expects volatile pricing this spring and summer while sawmills figure out what sort of increases buyers will bear. [to access the full story a WSJ subscription is required] Interfor recorded a Net loss in Q1’25 of $35.1 million compared to a Net loss of $49.9 million and a Net loss of $72.9 million. Adjusted EBITDA was $48.6 million on sales of $735.5 million in Q1’25. …Notable items include: Lumber prices increased during Q1’25 as reflected in Interfor’s average selling price of $712 per mfbm, up $53 per mfbm versus Q4’24; lumber shipments totalled 863 million board feet, representing a 77 million board foot decrease over the prior quarter. The decrease primarily relates to the sale of the Quebec operations, weather-related curtailments and shipment delays resulting from tariff uncertainty. …The Company is well positioned with a diversified product mix…only about 24% of the Company’s total lumber production is exported from Canada to the US and exposed to a potential tariff. …Interfor expects that over the mid-term, lumber markets will continue to benefit from favourable underlying supply and demand fundamentals.
Interfor recorded a Net loss in Q1’25 of $35.1 million compared to a Net loss of $49.9 million and a Net loss of $72.9 million. Adjusted EBITDA was $48.6 million on sales of $735.5 million in Q1’25. …Notable items include: Lumber prices increased during Q1’25 as reflected in Interfor’s average selling price of $712 per mfbm, up $53 per mfbm versus Q4’24; lumber shipments totalled 863 million board feet, representing a 77 million board foot decrease over the prior quarter. The decrease primarily relates to the sale of the Quebec operations, weather-related curtailments and shipment delays resulting from tariff uncertainty. …The Company is well positioned with a diversified product mix…only about 24% of the Company’s total lumber production is exported from Canada to the US and exposed to a potential tariff. …Interfor expects that over the mid-term, lumber markets will continue to benefit from favourable underlying supply and demand fundamentals. New homes development got a shot in the arm this spring with April starts rising in Canada and the United States. Recent reports from TD Economics examined new home data in both markets, finding month-over-month rises in starts for April. In Canada, starts jumped 30 per cent month over month, marking the largest rise since June 2023. Driving growth was the multi-family family segment that saw starts rise 34 per cent, whereas single-family detached home starts gained six per cent from March. …TD noted the “bounce-back” in activity was not unsurprising given levels were so low to start the year. What’s more, housing starts could “be softening,” amid higher construction costs and lower immigration, it cautioned. In the U.S., activity was less robust by percentage growth. Starts there increased less than two per cent month over month.
New homes development got a shot in the arm this spring with April starts rising in Canada and the United States. Recent reports from TD Economics examined new home data in both markets, finding month-over-month rises in starts for April. In Canada, starts jumped 30 per cent month over month, marking the largest rise since June 2023. Driving growth was the multi-family family segment that saw starts rise 34 per cent, whereas single-family detached home starts gained six per cent from March. …TD noted the “bounce-back” in activity was not unsurprising given levels were so low to start the year. What’s more, housing starts could “be softening,” amid higher construction costs and lower immigration, it cautioned. In the U.S., activity was less robust by percentage growth. Starts there increased less than two per cent month over month. Weyerhaeuser Company and Firefighter Behavioral Health Alliance (FBHA) today announced an extension of their Fighting Fires Together campaign, a partnership that provides specialized mental health support for wildland firefighters and their families across the Pacific Northwest. Fighting Fires Together, now in its fourth year, addresses the often-overlooked mental health impacts of wildland firefighting in isolated, hazardous and highly stressful conditions. Through a free online resource hub, first responders can find specially designed content, including videos about Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, depression, anxiety and suicide prevention, along with mental health tips, educational articles and contacts for occupationally aware support groups and counselors in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia. Weyerhaeuser’s support for wildland firefighting efforts in the Pacific Northwest began in the aftermath of the Yacolt Burn in 1902, when the company began advocating for Washington’s first forest fire legislation and the funding of community fire prevention education and patrols.
Weyerhaeuser Company and Firefighter Behavioral Health Alliance (FBHA) today announced an extension of their Fighting Fires Together campaign, a partnership that provides specialized mental health support for wildland firefighters and their families across the Pacific Northwest. Fighting Fires Together, now in its fourth year, addresses the often-overlooked mental health impacts of wildland firefighting in isolated, hazardous and highly stressful conditions. Through a free online resource hub, first responders can find specially designed content, including videos about Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, depression, anxiety and suicide prevention, along with mental health tips, educational articles and contacts for occupationally aware support groups and counselors in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia. Weyerhaeuser’s support for wildland firefighting efforts in the Pacific Northwest began in the aftermath of the Yacolt Burn in 1902, when the company began advocating for Washington’s first forest fire legislation and the funding of community fire prevention education and patrols. 


 VANCOUVER, BC — Conifex Timber reported results for the first quarter ended March 31, 2025. EBITDA was $4.9 million for the quarter compared to EBITDA of negative $2.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and negative $0.5 million in the first quarter of 2024. Net income was $0.6 million for the quarter versus net loss of $7.8 million in the previous quarter and negative $4.5 million in the first quarter of 2024. …lumber production in the first quarter of 2025 totalled approximately 46.3 million board feet, representing operating rates of approximately 77% of annualized capacity. …Power Plant sold 47.6 GWh of electricity under our EPA with BC Hydro in the first quarter of 2025 representing approximately 88% of targeted operating rates.
VANCOUVER, BC — Conifex Timber reported results for the first quarter ended March 31, 2025. EBITDA was $4.9 million for the quarter compared to EBITDA of negative $2.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2024 and negative $0.5 million in the first quarter of 2024. Net income was $0.6 million for the quarter versus net loss of $7.8 million in the previous quarter and negative $4.5 million in the first quarter of 2024. …lumber production in the first quarter of 2025 totalled approximately 46.3 million board feet, representing operating rates of approximately 77% of annualized capacity. …Power Plant sold 47.6 GWh of electricity under our EPA with BC Hydro in the first quarter of 2025 representing approximately 88% of targeted operating rates. 
 The US economy shrank at a 0.2% annual pace from January through March, the first drop in three years, as President Trump’s trade wars disrupted business… a slight upgrade of its initial estimate. First-quarter growth was brought down by a surge in imports as companies in the United States hurried to bring in foreign goods before the president imposed massive import taxes. The January-March drop in gross domestic product — the nation’s output of goods and services — reversed a 2.4% gain in the fourth quarter of 2024. Imports grew at a 42.6% pace, fastest since third-quarter 2020, and shaved more than 5 percentage points off GDP growth. Consumer spending also slowed sharply. And federal government spending fell at a 4.6% annual pace, the biggest drop in three years. …From January through March, business investment surged 24.4%. An increase in inventories — as businesses stocked up ahead of the tariffs — added more than 2.6 percentage points to first-quarter GDP growth.
The US economy shrank at a 0.2% annual pace from January through March, the first drop in three years, as President Trump’s trade wars disrupted business… a slight upgrade of its initial estimate. First-quarter growth was brought down by a surge in imports as companies in the United States hurried to bring in foreign goods before the president imposed massive import taxes. The January-March drop in gross domestic product — the nation’s output of goods and services — reversed a 2.4% gain in the fourth quarter of 2024. Imports grew at a 42.6% pace, fastest since third-quarter 2020, and shaved more than 5 percentage points off GDP growth. Consumer spending also slowed sharply. And federal government spending fell at a 4.6% annual pace, the biggest drop in three years. …From January through March, business investment surged 24.4%. An increase in inventories — as businesses stocked up ahead of the tariffs — added more than 2.6 percentage points to first-quarter GDP growth.



 WASHINGTON, DC – Total single-family home sales are expected to close 2025 at 4.92 million units, with existing home sales accounting for 4.24 million of those units, according to the May 2025 Economic and Housing Outlook from the Fannie Mae Economic and Strategic Research (ESR) Group. Revisions to the home sales forecast were driven in part by the ESR Group’s lower expectations for mortgage rates, which it now forecasts to end 2025 and 2026 at 6.1% and 5.8%, respectively. The latest outlook also projects real gross domestic product growing at 0.7% in 2025 and 2.0% in 2026 on a Q4/Q4 basis. …We now expect the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to rise 3.5 percent Q4/Q4 in 2025, unchanged from our April forecast. Core CPI is expected to rise 3.8 percent Q4/Q4 in 2025 (down from 3.9 percent previously) and 2.6 percent in 2026 (unchanged).
WASHINGTON, DC – Total single-family home sales are expected to close 2025 at 4.92 million units, with existing home sales accounting for 4.24 million of those units, according to the May 2025 Economic and Housing Outlook from the Fannie Mae Economic and Strategic Research (ESR) Group. Revisions to the home sales forecast were driven in part by the ESR Group’s lower expectations for mortgage rates, which it now forecasts to end 2025 and 2026 at 6.1% and 5.8%, respectively. The latest outlook also projects real gross domestic product growing at 0.7% in 2025 and 2.0% in 2026 on a Q4/Q4 basis. …We now expect the Consumer Price Index (CPI) to rise 3.5 percent Q4/Q4 in 2025, unchanged from our April forecast. Core CPI is expected to rise 3.8 percent Q4/Q4 in 2025 (down from 3.9 percent previously) and 2.6 percent in 2026 (unchanged). Volatile lumber prices are once again rattling the U.S. housing market, squeezing builders and threatening to exacerbate an already dire affordability crisis. Softwood lumber prices in April surged 23% year-over-year, while futures rose sharply in early 2025 amid fears of increased U.S. duties and widespread sawmill closures across North America, according to the National Association of Home Builders. This has weighed heavily on major homebuilders such as Lennar, D.R. Horton and Toll Brothers, which have all seen their stocks slump this spring. …“The unpredictability of lumber prices adds serious complexity to planning and budgeting,” said Steve Martinez, of Idaho-based Tradewinds General Contracting. …Beyond homebuilding, higher lumber costs are hitting renovations, fencing and interiors. The US Forest Products annual market review found that U.S. lumber production inched up… but demand continues to outpace supply. Environmental regulations, aging forests and labor constraints compound the challenge.
Volatile lumber prices are once again rattling the U.S. housing market, squeezing builders and threatening to exacerbate an already dire affordability crisis. Softwood lumber prices in April surged 23% year-over-year, while futures rose sharply in early 2025 amid fears of increased U.S. duties and widespread sawmill closures across North America, according to the National Association of Home Builders. This has weighed heavily on major homebuilders such as Lennar, D.R. Horton and Toll Brothers, which have all seen their stocks slump this spring. …“The unpredictability of lumber prices adds serious complexity to planning and budgeting,” said Steve Martinez, of Idaho-based Tradewinds General Contracting. …Beyond homebuilding, higher lumber costs are hitting renovations, fencing and interiors. The US Forest Products annual market review found that U.S. lumber production inched up… but demand continues to outpace supply. Environmental regulations, aging forests and labor constraints compound the challenge.



 The Producer Price Index declined 0.5% in April, according to data released Thursday by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. However, of the 10 key commodities in the hardware and building supply space tracked below, only two (millwork and plywood) index lower compared to a year ago. And only one (plywood) declined from March to April. The softwood lumber index increased 8.6% year-over-year. A month ago, the increase was 12.6%. …Construction input prices decreased 0.1% in April compared to the previous month. Nonresidential construction input prices increased 0.2% for the month. “Construction input prices declined in April, but that was largely due to falling energy prices,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “Materials directly affected by tariffs saw sharp price increases for the month. Steel mill product prices, for instance, rose 5.9%, while copper wire and cable prices increased 5.0%.
The Producer Price Index declined 0.5% in April, according to data released Thursday by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. However, of the 10 key commodities in the hardware and building supply space tracked below, only two (millwork and plywood) index lower compared to a year ago. And only one (plywood) declined from March to April. The softwood lumber index increased 8.6% year-over-year. A month ago, the increase was 12.6%. …Construction input prices decreased 0.1% in April compared to the previous month. Nonresidential construction input prices increased 0.2% for the month. “Construction input prices declined in April, but that was largely due to falling energy prices,” said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. “Materials directly affected by tariffs saw sharp price increases for the month. Steel mill product prices, for instance, rose 5.9%, while copper wire and cable prices increased 5.0%.
 Builder confidence fell sharply in May on growing uncertainties stemming from elevated interest rates, tariff concerns, building material cost uncertainty and the cloudy economic outlook. However, 90% of the responses received in May were tabulated prior to the May 12 announcement that the US and China agreed to slash tariffs for 90 days to allow trade talks to continue. Builder confidence in the market for newly built single-family homes was 34 in May, down six points from April, according to the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI). This ties the November 2023 reading and is the lowest since the index hit 31 in December 2022. …All three of the major HMI indices posted losses in May. The HMI index gauging current sales conditions fell eight points in May to a level of 37, the component measuring sales expectations in the next six months edged one-point lower to 42 while the gauge charting traffic of prospective buyers dropped two points to 23.
Builder confidence fell sharply in May on growing uncertainties stemming from elevated interest rates, tariff concerns, building material cost uncertainty and the cloudy economic outlook. However, 90% of the responses received in May were tabulated prior to the May 12 announcement that the US and China agreed to slash tariffs for 90 days to allow trade talks to continue. Builder confidence in the market for newly built single-family homes was 34 in May, down six points from April, according to the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI). This ties the November 2023 reading and is the lowest since the index hit 31 in December 2022. …All three of the major HMI indices posted losses in May. The HMI index gauging current sales conditions fell eight points in May to a level of 37, the component measuring sales expectations in the next six months edged one-point lower to 42 while the gauge charting traffic of prospective buyers dropped two points to 23. While the Commerce Department released a report on Friday showing a rebound by new residential construction in the U.S. in the month of April, the report also showed a substantial pullback by building permits during the month. The Commerce Department said housing starts shot up by 1.6 percent to an annual rate of 1.361 million in April after plummeting by 10.1 percent to a revised rate of 1.339 million in March. However, economists had expected housing starts to surge by 3.5 percent to a rate of 1.370 million from the 1.324 million originally reported for the previous month. “Soft housing starts in April are another sign that builders are hitting the brakes this year in response to high uncertainty for costs and future demand,” writes Nationwide Senior Economist Ben Ayers. …The smaller than expected rebound by housing starts came as a sharp increase by multi-family starts was partly offset by a continued slump by single-family starts.
While the Commerce Department released a report on Friday showing a rebound by new residential construction in the U.S. in the month of April, the report also showed a substantial pullback by building permits during the month. The Commerce Department said housing starts shot up by 1.6 percent to an annual rate of 1.361 million in April after plummeting by 10.1 percent to a revised rate of 1.339 million in March. However, economists had expected housing starts to surge by 3.5 percent to a rate of 1.370 million from the 1.324 million originally reported for the previous month. “Soft housing starts in April are another sign that builders are hitting the brakes this year in response to high uncertainty for costs and future demand,” writes Nationwide Senior Economist Ben Ayers. …The smaller than expected rebound by housing starts came as a sharp increase by multi-family starts was partly offset by a continued slump by single-family starts.
 Inflation was slightly lower than expected in April as President Trump’s tariffs just began hitting the slowing US economy, according to a Labor Department report Tuesday. The consumer price index, which measures the costs for a broad range of goods and services, rose a seasonally adjusted 0.2% for the month, putting the 12-month inflation rate at 2.3%, its lowest since February 2021. The monthly reading was in line with the Dow Jones consensus estimate while the 12-month was a bit below the forecast for 2.4%. Markets reacted little to the news, with stock futures pointing flat to slightly lower and Treasury yields mixed. ″“Good news on inflation, and we need it given inflation shocks from tariffs are on their way,” said Robert Frick, at Navy Federal Credit Union. …Shelter prices again were the main culprit in pushing up the inflation gauge.
Inflation was slightly lower than expected in April as President Trump’s tariffs just began hitting the slowing US economy, according to a Labor Department report Tuesday. The consumer price index, which measures the costs for a broad range of goods and services, rose a seasonally adjusted 0.2% for the month, putting the 12-month inflation rate at 2.3%, its lowest since February 2021. The monthly reading was in line with the Dow Jones consensus estimate while the 12-month was a bit below the forecast for 2.4%. Markets reacted little to the news, with stock futures pointing flat to slightly lower and Treasury yields mixed. ″“Good news on inflation, and we need it given inflation shocks from tariffs are on their way,” said Robert Frick, at Navy Federal Credit Union. …Shelter prices again were the main culprit in pushing up the inflation gauge.  Economic uncertainty has produced a double whammy for the housing market: sluggish home sales and plodding construction. Last month was the slowest April for existing home sales in 16 years — a sharp rebuke to hopes that this spring the housing market would recover after two very sleepy years. In a May survey of builder confidence conducted by Wells Fargo and the National Association of Home Builders, home builder sentiment dropped to a level last seen in November 2023. The problem, as ever, is the cost of housing: Home prices are out of reach for many who would like to buy. And the tariff drama under President Trump has both made it more expensive to build new homes and made the future more unpredictable for would-be homebuyers. The result is a country where builders want to build, and buyers want to buy — but the future is too much in doubt.
Economic uncertainty has produced a double whammy for the housing market: sluggish home sales and plodding construction. Last month was the slowest April for existing home sales in 16 years — a sharp rebuke to hopes that this spring the housing market would recover after two very sleepy years. In a May survey of builder confidence conducted by Wells Fargo and the National Association of Home Builders, home builder sentiment dropped to a level last seen in November 2023. The problem, as ever, is the cost of housing: Home prices are out of reach for many who would like to buy. And the tariff drama under President Trump has both made it more expensive to build new homes and made the future more unpredictable for would-be homebuyers. The result is a country where builders want to build, and buyers want to buy — but the future is too much in doubt. Q1 2025 exports of Southern Pine lumber (treated and untreated) were 12% behind the same quarter in 2024 at 122 MMBF, but up 2% over the fourth quarter of 2024. On a monthly basis, Southern Pine lumber exports were down 20% in March over March 2024 but up 4.6% over February 2025. When looking at the report by dollar value, Southern Pine exports are down 7% to $50 million in the first quarter of 2025 compared to the same period in 2024, but down 17% over the fourth quarter of 2024. Mexico led the way at $13.2 million, followed by the Dominican Republic at $10.4 million, and Canada at $4.3 million. The total global value in March hit a six-month high of $18 million. Treated lumber exports, meanwhile, were down 19% compared to the first quarter of 2024 at $28 million and down 6% over the fourth quarter of 2024.
Q1 2025 exports of Southern Pine lumber (treated and untreated) were 12% behind the same quarter in 2024 at 122 MMBF, but up 2% over the fourth quarter of 2024. On a monthly basis, Southern Pine lumber exports were down 20% in March over March 2024 but up 4.6% over February 2025. When looking at the report by dollar value, Southern Pine exports are down 7% to $50 million in the first quarter of 2025 compared to the same period in 2024, but down 17% over the fourth quarter of 2024. Mexico led the way at $13.2 million, followed by the Dominican Republic at $10.4 million, and Canada at $4.3 million. The total global value in March hit a six-month high of $18 million. Treated lumber exports, meanwhile, were down 19% compared to the first quarter of 2024 at $28 million and down 6% over the fourth quarter of 2024.