 Real gross domestic product (GDP) was essentially unchanged in November, following a 0.3% decline in October, as contractions in goods-producing industries offset expansions in services-producing industries. Goods-producing industries declined 0.3% in November, down for the third time in four months, driven by contractions in the manufacturing and agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting sectors in the month. …The manufacturing sector fell 1.3% in November, with decreases in both durable-goods and non-durable-goods manufacturing industries. …The agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting sector declined 1.1% in November, following a 0.6% decrease in October, as nearly all subsectors were down in November. …Forestry and logging (-2.8%) declined for the third straight month in November. This was the subsector’s largest contraction since May 2023, bringing activity to a record low level, as timber harvesting companies scaled back production in response to sawmill production cutbacks and weak lumber markets.
Real gross domestic product (GDP) was essentially unchanged in November, following a 0.3% decline in October, as contractions in goods-producing industries offset expansions in services-producing industries. Goods-producing industries declined 0.3% in November, down for the third time in four months, driven by contractions in the manufacturing and agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting sectors in the month. …The manufacturing sector fell 1.3% in November, with decreases in both durable-goods and non-durable-goods manufacturing industries. …The agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting sector declined 1.1% in November, following a 0.6% decrease in October, as nearly all subsectors were down in November. …Forestry and logging (-2.8%) declined for the third straight month in November. This was the subsector’s largest contraction since May 2023, bringing activity to a record low level, as timber harvesting companies scaled back production in response to sawmill production cutbacks and weak lumber markets.

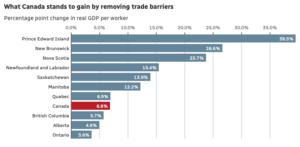 Canada’s economy could gain nearly 7%, or $210 billion, in real GDP over a gradual period by fully removing internal trade barriers between the country’s 13 provinces and territories, according to a report published Tuesday by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). On average, regulation-related barriers are the equivalent of a 9% tariff nationally, estimates the report, which was co-authored by IMF researchers Federico J. Diez and Yuanchen Yang with contributions from University of Calgary economist Trevor Tombe. …Because of the trade barriers between provinces, “Canada isn’t really one economy. It’s really 10 economies,” said Alicia Planincic, director of policy and economics at the Business Council of Alberta in Calgary. …The report points to finance, telecom, transportation and professional services as far-reaching sectors that “ripple through the economy” and raise costs for all of the businesses they touch.
Canada’s economy could gain nearly 7%, or $210 billion, in real GDP over a gradual period by fully removing internal trade barriers between the country’s 13 provinces and territories, according to a report published Tuesday by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). On average, regulation-related barriers are the equivalent of a 9% tariff nationally, estimates the report, which was co-authored by IMF researchers Federico J. Diez and Yuanchen Yang with contributions from University of Calgary economist Trevor Tombe. …Because of the trade barriers between provinces, “Canada isn’t really one economy. It’s really 10 economies,” said Alicia Planincic, director of policy and economics at the Business Council of Alberta in Calgary. …The report points to finance, telecom, transportation and professional services as far-reaching sectors that “ripple through the economy” and raise costs for all of the businesses they touch.  The Bank of Canada held its overnight interest rate steady at 2.25 per cent on Wednesday in a move widely expected by economists. The announcement comes amid ongoing trade uncertainty, with increased focus on the negotiation of the Canada-U.S.-Mexico Agreement and a murky outlook for the Canadian economy later in the year. Ahead of the announcement, economists polled by Reuters were unanimous in their expectations for a hold today, and nearly 75% forecast the central bank will stay on hold through 2026. In its December decision the Bank also held its policy rate stable. …“While this rate hold provides some stability, other factors such as economic uncertainty, potential job loss and affordability are continuing to put downward pressure on the housing market,” Rates.ca mortgage and real estate expert Victor Tran said in a statement following today’s decision.”
The Bank of Canada held its overnight interest rate steady at 2.25 per cent on Wednesday in a move widely expected by economists. The announcement comes amid ongoing trade uncertainty, with increased focus on the negotiation of the Canada-U.S.-Mexico Agreement and a murky outlook for the Canadian economy later in the year. Ahead of the announcement, economists polled by Reuters were unanimous in their expectations for a hold today, and nearly 75% forecast the central bank will stay on hold through 2026. In its December decision the Bank also held its policy rate stable. …“While this rate hold provides some stability, other factors such as economic uncertainty, potential job loss and affordability are continuing to put downward pressure on the housing market,” Rates.ca mortgage and real estate expert Victor Tran said in a statement following today’s decision.” In November, the volume of cargo carried by Canadian railways was up slightly (+0.5%) from November 2024 to 31.4 million tonnes. Higher volumes of intermodal shipments (mainly containers) as well as higher carloadings of wheat largely contributed to the increase in November 2025. The overall freight volume in November was on par with the five-year average of 31.5 million tonnes for the month. …Growth in non-intermodal freight loadings in November was moderated by declines in several commodities. Loadings of other oil seeds and nuts, and other agricultural products were down sharply by 35.4% (-312 000 tonnes) year over year—the largest drop in tonnage since December 2018. In November 2025, loadings of iron ores and concentrates decreased 6.4% (-287 000 tonnes) compared with November 2024, while loadings of lumber were down 22.1% (-143 000 tonnes), a fourth consecutive month of year-over-year decline.
In November, the volume of cargo carried by Canadian railways was up slightly (+0.5%) from November 2024 to 31.4 million tonnes. Higher volumes of intermodal shipments (mainly containers) as well as higher carloadings of wheat largely contributed to the increase in November 2025. The overall freight volume in November was on par with the five-year average of 31.5 million tonnes for the month. …Growth in non-intermodal freight loadings in November was moderated by declines in several commodities. Loadings of other oil seeds and nuts, and other agricultural products were down sharply by 35.4% (-312 000 tonnes) year over year—the largest drop in tonnage since December 2018. In November 2025, loadings of iron ores and concentrates decreased 6.4% (-287 000 tonnes) compared with November 2024, while loadings of lumber were down 22.1% (-143 000 tonnes), a fourth consecutive month of year-over-year decline.
 TORONTO — The review of North America’s free trade agreement will play a large part in determining the trajectory of the Canadian economy, as one strategist says he is optimistic that certain concessions could help achieve a positive outcome. Ashish Dewan, a senior investment strategist at Vanguard, said the Canadian economy is still significantly reliant on US trade despite attempts to diversify its trading partners. He said Canada currently has a “trade advantage,” due to a lower effective tariff rate compared with other nations, sitting around six per cent compared with about 16 to 19 per cent faced by other nations. “What’s really having a negative impact on the Canadian economy are those Section 232 sectoral tariffs,” Dewan said. Tariffs covered by Section 232 of the U.S. Trade Expansion Act of 1962 cover a wide range of products like steel, aluminum and lumber and are generally not exempt under the Canada-U.S.-Mexico Agreement, better known as CUSMA.
TORONTO — The review of North America’s free trade agreement will play a large part in determining the trajectory of the Canadian economy, as one strategist says he is optimistic that certain concessions could help achieve a positive outcome. Ashish Dewan, a senior investment strategist at Vanguard, said the Canadian economy is still significantly reliant on US trade despite attempts to diversify its trading partners. He said Canada currently has a “trade advantage,” due to a lower effective tariff rate compared with other nations, sitting around six per cent compared with about 16 to 19 per cent faced by other nations. “What’s really having a negative impact on the Canadian economy are those Section 232 sectoral tariffs,” Dewan said. Tariffs covered by Section 232 of the U.S. Trade Expansion Act of 1962 cover a wide range of products like steel, aluminum and lumber and are generally not exempt under the Canada-U.S.-Mexico Agreement, better known as CUSMA. Canada’s six largest CMAs recorded a 3.9% rise in housing starts in 2025, driven by a 58% jump in Montréal and record starts in Calgary and Edmonton, while Toronto fell 31% and Vancouver slipped 3%, CMHC said. CMHC said the metro gains helped lift the national annual total for all areas in Canada to 259,028 housing starts in 2025, up 5.6% from 245,367 in 2024 and ranking as the fifth highest annual total on record. …The year-over-year increase was driven by a second consecutive year of record rental housing starts, which made up just over half of all housing starts in Canada’s urban centres, CMHC said. …Among Canada’s three largest cities, CMHC said all posted year-over-year increases in December. Toronto recorded a 151% increase, driven by higher multi-unit starts. Montréal posted a 123% increase, driven by higher starts across all dwelling types. Vancouver reported a +17% increase, also driven by multi-unit starts.
Canada’s six largest CMAs recorded a 3.9% rise in housing starts in 2025, driven by a 58% jump in Montréal and record starts in Calgary and Edmonton, while Toronto fell 31% and Vancouver slipped 3%, CMHC said. CMHC said the metro gains helped lift the national annual total for all areas in Canada to 259,028 housing starts in 2025, up 5.6% from 245,367 in 2024 and ranking as the fifth highest annual total on record. …The year-over-year increase was driven by a second consecutive year of record rental housing starts, which made up just over half of all housing starts in Canada’s urban centres, CMHC said. …Among Canada’s three largest cities, CMHC said all posted year-over-year increases in December. Toronto recorded a 151% increase, driven by higher multi-unit starts. Montréal posted a 123% increase, driven by higher starts across all dwelling types. Vancouver reported a +17% increase, also driven by multi-unit starts. Canada’s annual inflation rate ticked up to 2.4% in December compared to the same period last year, when the federal government implemented a GST break that brought some prices down, Statistics Canada said. The temporary tax cut, which began on Dec. 14, 2024, lasted for two months. It reverberated through monthly inflation data for part of 2025 but officially fell out of the year-over-year movement last month, sending price growth accelerating, according to the data agency. December’s rate was a smidge higher than the 2.2% rate seen in November. It was partly offset by a year-over-year decline in gas prices. With energy excluded, inflation rose to 3% in December. …”The main takeaway here is that after a year of some wide divergences, almost all of the main measures of inflation are now very close to [2.5%], in tune with the Bank of Canada’s view on the pace of underlying inflation,” wrote BMO’s Douglas Porter.
Canada’s annual inflation rate ticked up to 2.4% in December compared to the same period last year, when the federal government implemented a GST break that brought some prices down, Statistics Canada said. The temporary tax cut, which began on Dec. 14, 2024, lasted for two months. It reverberated through monthly inflation data for part of 2025 but officially fell out of the year-over-year movement last month, sending price growth accelerating, according to the data agency. December’s rate was a smidge higher than the 2.2% rate seen in November. It was partly offset by a year-over-year decline in gas prices. With energy excluded, inflation rose to 3% in December. …”The main takeaway here is that after a year of some wide divergences, almost all of the main measures of inflation are now very close to [2.5%], in tune with the Bank of Canada’s view on the pace of underlying inflation,” wrote BMO’s Douglas Porter.
 There are solid reasons to expect near-term strength in the US and Canadian construction markets. In the US, rapid technological progress and supportive federal policies are driving major investments in semiconductor fabrication, AI-related data centers, and energy infrastructure, with growing momentum toward nuclear power. In Canada, federal and provincial governments are promoting “nation-building” projects that emphasize LNG export capacity, port expansions, and new mines for critical minerals required by the digital economy. Both nations recognize that housing supply must rise substantially to meet population needs, signaling a long-term boost in residential construction. Yet, 2025 proved disappointing for overall construction performance, especially in employment. …Housing activity revealed a sharper divide between the two nations. U.S. housing starts in November 2025 dropped to an annualized 1.246 million units, the lowest since the pandemic. Most analysts believe the country needs at least 1.5 million starts per year to meet demand.
There are solid reasons to expect near-term strength in the US and Canadian construction markets. In the US, rapid technological progress and supportive federal policies are driving major investments in semiconductor fabrication, AI-related data centers, and energy infrastructure, with growing momentum toward nuclear power. In Canada, federal and provincial governments are promoting “nation-building” projects that emphasize LNG export capacity, port expansions, and new mines for critical minerals required by the digital economy. Both nations recognize that housing supply must rise substantially to meet population needs, signaling a long-term boost in residential construction. Yet, 2025 proved disappointing for overall construction performance, especially in employment. …Housing activity revealed a sharper divide between the two nations. U.S. housing starts in November 2025 dropped to an annualized 1.246 million units, the lowest since the pandemic. Most analysts believe the country needs at least 1.5 million starts per year to meet demand. 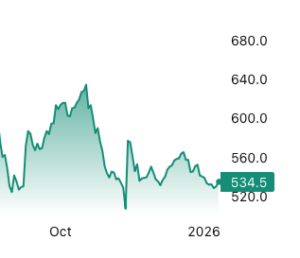 Lumber futures rose toward $535 per thousand board feet, rebounding from the September low of $528 reached on January 7th after a low liquidity holiday sell off unwound, improving seasonal demand expectations and longer term supply tightening. Renewed engagement from market participants, signaled that forced selling and the thin trading conditions that pushed prices to multi month lows have faded. Seasonal demand expectations have strengthened as builders begin positioning ahead of the spring construction period, when consumption typically improves following year end destocking. Industry forecasts point to a modest pickup in US housing starts and repair and remodel activity in 2026 as interest rates ease and trade uncertainty recedes, supporting demand after a weak finish to 2025. At the same time, longer term supply growth remains constrained by ongoing tariffs on Canadian softwood and slower capacity expansion across North American sawmills, limiting surplus.
Lumber futures rose toward $535 per thousand board feet, rebounding from the September low of $528 reached on January 7th after a low liquidity holiday sell off unwound, improving seasonal demand expectations and longer term supply tightening. Renewed engagement from market participants, signaled that forced selling and the thin trading conditions that pushed prices to multi month lows have faded. Seasonal demand expectations have strengthened as builders begin positioning ahead of the spring construction period, when consumption typically improves following year end destocking. Industry forecasts point to a modest pickup in US housing starts and repair and remodel activity in 2026 as interest rates ease and trade uncertainty recedes, supporting demand after a weak finish to 2025. At the same time, longer term supply growth remains constrained by ongoing tariffs on Canadian softwood and slower capacity expansion across North American sawmills, limiting surplus. VANCOUVER, BC – Canfor Pulp Products announced the expiration of the go-shop period provided for in the previously announced arrangement agreement dated December 3, 2025 between Canfor Pulp and Canfor Corporation, pursuant to which Canfor Corp will acquire all of Canfor Pulp’s issued and outstanding common shares not already owned by Canfor Corp and its affiliates. Under the terms of the Arrangement Agreement, each shareholder of Canfor Pulp will have the option to receive: 0.0425 of a common share of Canfor Corp per Canfor Pulp Share held, or $0.50 in cash per Canfor Pulp Share held. …During the Go-Shop Period, Canfor Pulp was permitted to actively solicit, evaluate and enter into negotiations with third parties that expressed an interest in acquiring Canfor Pulp. …The Go-Shop Period expired on January 19, 2026. Canfor Pulp did not receive any Acquisition Proposals.
VANCOUVER, BC – Canfor Pulp Products announced the expiration of the go-shop period provided for in the previously announced arrangement agreement dated December 3, 2025 between Canfor Pulp and Canfor Corporation, pursuant to which Canfor Corp will acquire all of Canfor Pulp’s issued and outstanding common shares not already owned by Canfor Corp and its affiliates. Under the terms of the Arrangement Agreement, each shareholder of Canfor Pulp will have the option to receive: 0.0425 of a common share of Canfor Corp per Canfor Pulp Share held, or $0.50 in cash per Canfor Pulp Share held. …During the Go-Shop Period, Canfor Pulp was permitted to actively solicit, evaluate and enter into negotiations with third parties that expressed an interest in acquiring Canfor Pulp. …The Go-Shop Period expired on January 19, 2026. Canfor Pulp did not receive any Acquisition Proposals.





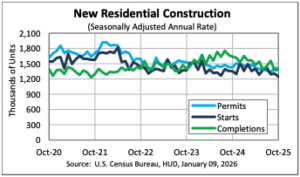
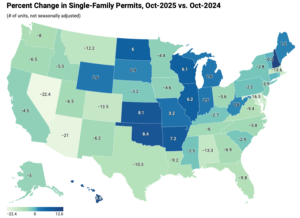 In October, single-family building permits weakened, reflecting continued caution among builders amid affordability constraints and financing challenges. In contrast, multifamily permit activity remained steady and continued to perform relatively well. Together, these trends suggest that while demand for new housing persists, builders are adjusting residential construction activity in response to evolving market conditions. Because permits typically precede construction starts, these patterns offer insight into the near-term outlook for residential building activity. Over the first ten months of 2025, the number of single-family permits issued nationwide reached 787,122. On a year-over-year basis, this represents a 7.0 percent decline compared with the October 2024 year-to-date total of 846,446. Multifamily permitting activity was stronger, with 426,352 permits issued nationwide, marking a 5.7 percent increase from the same period last year.
In October, single-family building permits weakened, reflecting continued caution among builders amid affordability constraints and financing challenges. In contrast, multifamily permit activity remained steady and continued to perform relatively well. Together, these trends suggest that while demand for new housing persists, builders are adjusting residential construction activity in response to evolving market conditions. Because permits typically precede construction starts, these patterns offer insight into the near-term outlook for residential building activity. Over the first ten months of 2025, the number of single-family permits issued nationwide reached 787,122. On a year-over-year basis, this represents a 7.0 percent decline compared with the October 2024 year-to-date total of 846,446. Multifamily permitting activity was stronger, with 426,352 permits issued nationwide, marking a 5.7 percent increase from the same period last year.
 Global markets plunged Tuesday after President Trump reignited fears of a US trade war with the European Union, America’s largest trading partner. The president showed no signs of backing off his threat from Saturday to hit seven EU countries and the United Kingdom with new tariffs unless they supported his push for American control of Greenland. Asked if he would be willing to use force to seize the semi-autonomous Danish territory, Trump replied, “No comment,” on Monday. The S&P 500 sold off by around 1.3% in early trading, while the Nasdaq Composite plunged 1.7%. The Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped more than 600 points. The S&P 500 has erased its gains for the year so far. Investors also sold off U.S. government bonds, driving up interest rates. Rising returns on US treasuries usually translate into higher mortgage rates and interest on new personal loans.
Global markets plunged Tuesday after President Trump reignited fears of a US trade war with the European Union, America’s largest trading partner. The president showed no signs of backing off his threat from Saturday to hit seven EU countries and the United Kingdom with new tariffs unless they supported his push for American control of Greenland. Asked if he would be willing to use force to seize the semi-autonomous Danish territory, Trump replied, “No comment,” on Monday. The S&P 500 sold off by around 1.3% in early trading, while the Nasdaq Composite plunged 1.7%. The Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped more than 600 points. The S&P 500 has erased its gains for the year so far. Investors also sold off U.S. government bonds, driving up interest rates. Rising returns on US treasuries usually translate into higher mortgage rates and interest on new personal loans.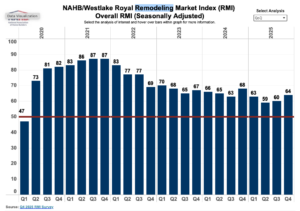 In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB remodeling index (RMI) posted a reading of 64, increasing four points compared to the previous quarter. Most remodelers are finding reasonably strong market conditions, even with the normal seasonal slowdown during the holidays. The major headwinds the industry is experiencing continue to be rising costs and potential customers hesitating due to policy and economic uncertainty. Demand for remodeling is being supported by an aging housing stock, strong homeowner equity and increasing need for aging-in-place improvements. …In the fourth quarter of 2025, the Current Conditions Index averaged 71, increasing three points from the previous quarter. …The Future Indicators Index averaged 56, up four points from the previous quarter.
In the third quarter of 2025, the NAHB remodeling index (RMI) posted a reading of 64, increasing four points compared to the previous quarter. Most remodelers are finding reasonably strong market conditions, even with the normal seasonal slowdown during the holidays. The major headwinds the industry is experiencing continue to be rising costs and potential customers hesitating due to policy and economic uncertainty. Demand for remodeling is being supported by an aging housing stock, strong homeowner equity and increasing need for aging-in-place improvements. …In the fourth quarter of 2025, the Current Conditions Index averaged 71, increasing three points from the previous quarter. …The Future Indicators Index averaged 56, up four points from the previous quarter. 



 Southern Pine lumber exports (treated and untreated) are almost equal to 2024 year to date through October 2025 at 488 MMBF, according to October 2025 data from the USDA’s Foreign Agriculture Services’ Global Agricultural Trade System. October 2025’s 60 MMBF of exports were up 47% over October 2024 and up 33% compared to September 2025. When looking at the report by dollar value, Southern Pine exports are up 4% YTD ($190 million) compared to 2024. Meanwhile, the October value of $25 million is the highest mark since June 2022, when the value hit $29 million. Mexico leads the way YTD 2025 at $56 million, followed by the Dominican Republic at $39 million, and India at $18 million. Treated lumber exports, meanwhile, are down 4% through the first 10 months of the year compared to 2024. The Leeward-Windward Islands market leads the way through October at $18 million, followed by Jamaica at $16 million, and Belize at $10 million. Softwood lumber imports are running 8% behind 2024 levels.
Southern Pine lumber exports (treated and untreated) are almost equal to 2024 year to date through October 2025 at 488 MMBF, according to October 2025 data from the USDA’s Foreign Agriculture Services’ Global Agricultural Trade System. October 2025’s 60 MMBF of exports were up 47% over October 2024 and up 33% compared to September 2025. When looking at the report by dollar value, Southern Pine exports are up 4% YTD ($190 million) compared to 2024. Meanwhile, the October value of $25 million is the highest mark since June 2022, when the value hit $29 million. Mexico leads the way YTD 2025 at $56 million, followed by the Dominican Republic at $39 million, and India at $18 million. Treated lumber exports, meanwhile, are down 4% through the first 10 months of the year compared to 2024. The Leeward-Windward Islands market leads the way through October at $18 million, followed by Jamaica at $16 million, and Belize at $10 million. Softwood lumber imports are running 8% behind 2024 levels. Tokyo — Housing starts in Japan fell 6.5% from the previous year to 740,667 units in 2025, down for the third straight year and hitting a 62-year low, the land ministry said Friday. The drop reflected deterioration in consumer sentiment amid rising prices, as well as falling demand due to the country’s shrinking population. Of the total, owner-occupied houses dropped 7.7% to 201,285 units, down for the fourth consecutive year. Housing for rent fell 5.0% to 324,991 units, down for the third year in a row. Condominiums and houses for sale decreased 7.6% to 208,169 units, down for the third consecutive year. The results can also be attributed to a law revision in April that led to delays in construction starts for wooden homes with energy-saving features.
Tokyo — Housing starts in Japan fell 6.5% from the previous year to 740,667 units in 2025, down for the third straight year and hitting a 62-year low, the land ministry said Friday. The drop reflected deterioration in consumer sentiment amid rising prices, as well as falling demand due to the country’s shrinking population. Of the total, owner-occupied houses dropped 7.7% to 201,285 units, down for the fourth consecutive year. Housing for rent fell 5.0% to 324,991 units, down for the third year in a row. Condominiums and houses for sale decreased 7.6% to 208,169 units, down for the third consecutive year. The results can also be attributed to a law revision in April that led to delays in construction starts for wooden homes with energy-saving features.
 HÀ NỘI — Despite unprecedented challenges from global markets and the growing impacts of climate change, 2025 marked a historic milestone for Việt Nam’s wood industry, as export turnover of timber and wood products surpassed US$17 billion for the first time. According to data from Việt Nam Customs, exports of timber and wood products reached nearly $1.7 billion in December 2025 alone, bringing total export value for the year to $17.2 billion – an increase of nearly 6 per cent compared with 2024. In 2025, exports of timber and wood products to the US totalled $9.46 billion, up 4.4 per cent year on year and accounting for approximately 55 per cent of the industry’s total export turnover. Việt Nam continued to maintain its position as the largest supplier of wooden furniture to the US market. …Việt Nam’s market share of wooden furniture in the US increased significantly, rising from 40.5 per cent in the first eight months of 2024 to 45.3 per cent in the same period of 2025.
HÀ NỘI — Despite unprecedented challenges from global markets and the growing impacts of climate change, 2025 marked a historic milestone for Việt Nam’s wood industry, as export turnover of timber and wood products surpassed US$17 billion for the first time. According to data from Việt Nam Customs, exports of timber and wood products reached nearly $1.7 billion in December 2025 alone, bringing total export value for the year to $17.2 billion – an increase of nearly 6 per cent compared with 2024. In 2025, exports of timber and wood products to the US totalled $9.46 billion, up 4.4 per cent year on year and accounting for approximately 55 per cent of the industry’s total export turnover. Việt Nam continued to maintain its position as the largest supplier of wooden furniture to the US market. …Việt Nam’s market share of wooden furniture in the US increased significantly, rising from 40.5 per cent in the first eight months of 2024 to 45.3 per cent in the same period of 2025.
Deposits $10.6 Billion CAD + Interest 2.6 Billion + FX Gain 0.5 Billion = Total $13.7 Billion
Canadian softwood lumber exporters are currently paying a combined duty deposit rate of 45.16% on lumber imported into the United States.