 VANCOUVER — The Forest Innovation & Bioeconomy Conference (FIBC 2025) returns May 6-8, 2025, at the Westin Bayshore in Vancouver, bringing together industry, researchers, policymakers, investors, and First Nations leaders to explore the future of forest sector innovation. Hosted by the B.C. Ministry of Forests, the University of British Columbia’s BioProducts Institute, and Foresight Canada, this international event will focus on forest product innovation, diversification, and the commercialization of high value bioproducts. Early Bird Registration – Save by registering early by March 31, 2025.
VANCOUVER — The Forest Innovation & Bioeconomy Conference (FIBC 2025) returns May 6-8, 2025, at the Westin Bayshore in Vancouver, bringing together industry, researchers, policymakers, investors, and First Nations leaders to explore the future of forest sector innovation. Hosted by the B.C. Ministry of Forests, the University of British Columbia’s BioProducts Institute, and Foresight Canada, this international event will focus on forest product innovation, diversification, and the commercialization of high value bioproducts. Early Bird Registration – Save by registering early by March 31, 2025.
Key Highlights
- Lab-to-Market: The Pathway to Commercialization
- Horizon Europe & Canada Collaboration
- Europe Bioeconomy Cluster Development
- B.C.’s Forest Bioeconomy & Sector Diversification .
- Business to Business Matchmaking
 As the cross-border trade war escalates, Canada’s softwood lumber industry has an advantage on its side that no tariff can completely erase – its product is objectively better than much of the timber harvested from US forests. Softwood supplies, especially from BC and Alberta, are widely viewed as more desirable for wood framing because the growth rings are tighter than those found in lumber in the US South. In the milder climate of the U.S. South, the growing season is much faster. It takes about 35 years before southern yellow pine (SYP) trees are harvested. …Canada’s secret weapon, however, is hiding in plain sight. Tighter growth rings tend to result in quality two-by-four or two-by-six SPF boards for home builders, meaning walls that will stay straight. Compared with American SYP lumber, Canadian SPF is also lighter in weight. …Eastern SYP is currently selling at lower prices when compared with SPF. “SYP is an imperfect substitute for SPF,” RBC Capital Markets analyst Matthew McKellar said. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
As the cross-border trade war escalates, Canada’s softwood lumber industry has an advantage on its side that no tariff can completely erase – its product is objectively better than much of the timber harvested from US forests. Softwood supplies, especially from BC and Alberta, are widely viewed as more desirable for wood framing because the growth rings are tighter than those found in lumber in the US South. In the milder climate of the U.S. South, the growing season is much faster. It takes about 35 years before southern yellow pine (SYP) trees are harvested. …Canada’s secret weapon, however, is hiding in plain sight. Tighter growth rings tend to result in quality two-by-four or two-by-six SPF boards for home builders, meaning walls that will stay straight. Compared with American SYP lumber, Canadian SPF is also lighter in weight. …Eastern SYP is currently selling at lower prices when compared with SPF. “SYP is an imperfect substitute for SPF,” RBC Capital Markets analyst Matthew McKellar said. [to access the full story a Globe & Mail subscription is required]
 This year, Canadian forest companies and their employees continued to navigate a rapidly changing political, economic, and trade environment. Customers, investors, and local communities have a shared interest in good environmental outcomes and sustaining and growing family-supporting jobs. As a global leader in sustainable forest management and responsible sourcing, Canada’s forest sector and its people have met these challenges head-on. In 2024, FPAC and its members continued to make meaningful strides on climate action, biodiversity conservation, and expanded partnerships with Indigenous Peoples and inclusion of Indigenous knowledge into Sustainable Forest Management. Buyers of Canadian forest products can be confident that measures to improve environmental performance, strengthen relationships with Indigenous Peoples, and provide the highest quality of products are being implemented across our operations and throughout the country – ensuring that forestry practices in Canada contribute to maintaining and supporting the ecosystems, wildlife, and people that rely on them now and for generations to come.
This year, Canadian forest companies and their employees continued to navigate a rapidly changing political, economic, and trade environment. Customers, investors, and local communities have a shared interest in good environmental outcomes and sustaining and growing family-supporting jobs. As a global leader in sustainable forest management and responsible sourcing, Canada’s forest sector and its people have met these challenges head-on. In 2024, FPAC and its members continued to make meaningful strides on climate action, biodiversity conservation, and expanded partnerships with Indigenous Peoples and inclusion of Indigenous knowledge into Sustainable Forest Management. Buyers of Canadian forest products can be confident that measures to improve environmental performance, strengthen relationships with Indigenous Peoples, and provide the highest quality of products are being implemented across our operations and throughout the country – ensuring that forestry practices in Canada contribute to maintaining and supporting the ecosystems, wildlife, and people that rely on them now and for generations to come.

 Legislation has been introduced to strengthen BC’s ability to respond quickly to threats of tariffs imposed on Canada by the US, to grow a more self-reliant economy, and to defend workers and businesses. …If passed, the act will enable the BC government to be nimble in its response, giving government time to develop more long-term responses. A focus on expanding interprovincial trade and moving procurement away from American vendors will help encourage greater reliance on goods and services made in Canada. …The act will automatically be repealed by 2027 at the latest. …The legislation allows government to: 1. Temporarily modify the application or effect of BC laws and regulations to defend BC from challenges brought on by the continued tariff and sovereignty threats. …2. Reduce or eliminate barriers to interprovincial trade. …3. Impose tolls/fees on specified vehicles using provincial public infrastructure such as highways …4. Provide procurement directives to public bodies.
Legislation has been introduced to strengthen BC’s ability to respond quickly to threats of tariffs imposed on Canada by the US, to grow a more self-reliant economy, and to defend workers and businesses. …If passed, the act will enable the BC government to be nimble in its response, giving government time to develop more long-term responses. A focus on expanding interprovincial trade and moving procurement away from American vendors will help encourage greater reliance on goods and services made in Canada. …The act will automatically be repealed by 2027 at the latest. …The legislation allows government to: 1. Temporarily modify the application or effect of BC laws and regulations to defend BC from challenges brought on by the continued tariff and sovereignty threats. …2. Reduce or eliminate barriers to interprovincial trade. …3. Impose tolls/fees on specified vehicles using provincial public infrastructure such as highways …4. Provide procurement directives to public bodies.

 Trump’s escalating trade tariffs will hit world growth and raise inflation, the OECD has predicted. Canada and Mexico are forecast to see the biggest impact as they have had the harshest tariffs imposed on them, but US growth is also expected to be hit. …Trump has imposed 25% tariffs on all steel and aluminium imports. The US has also imposed 25% tariffs on other imports from Mexico and Canada – with some exemptions – and a 20% levy on Chinese goods. Canada and the EU have announced retaliatory tariffs. …Canada’s economy is predicted to grow by just 0.7% this year and in 2026, compared with the previous forecast of 2% for both years. Mexico is now forecast to contract by 1.3% this year and shrink a further 0.6% next year, instead of growing by 1.2% and 1.6%. Growth in the US has also been downgraded, with growth of 2.2% this year and 1.6% in 2025, down from previous forecasts of 2.4% and 2.1% China’s growth forecast will fall slightly to 4.8%.
Trump’s escalating trade tariffs will hit world growth and raise inflation, the OECD has predicted. Canada and Mexico are forecast to see the biggest impact as they have had the harshest tariffs imposed on them, but US growth is also expected to be hit. …Trump has imposed 25% tariffs on all steel and aluminium imports. The US has also imposed 25% tariffs on other imports from Mexico and Canada – with some exemptions – and a 20% levy on Chinese goods. Canada and the EU have announced retaliatory tariffs. …Canada’s economy is predicted to grow by just 0.7% this year and in 2026, compared with the previous forecast of 2% for both years. Mexico is now forecast to contract by 1.3% this year and shrink a further 0.6% next year, instead of growing by 1.2% and 1.6%. Growth in the US has also been downgraded, with growth of 2.2% this year and 1.6% in 2025, down from previous forecasts of 2.4% and 2.1% China’s growth forecast will fall slightly to 4.8%. The Trump administration’s tariffs on imported goods from Canada, Mexico and China — some already in place, others set to take effect in a few weeks — are already driving up the cost of building materials used in new residential construction and home remodeling projects. The tariffs are projected to raise the costs that go into building a single-family home in the U.S. by US$7,500 to US$10,000, according to the NAHB. We Buy Houses in San Francisco, which purchases foreclosed homes and then typically renovates and sells them, is increasing prices on its refurbished properties between 7% and 12%. That’s even after stockpiling 62% more Canadian lumber than usual. …The timing of the tariffs couldn’t be worse as this is typically the busiest time of year for home sales. …Confusion over the timing and scope of the tariffs, and their impact on the economy, could have a bigger chilling effect on the new-home market than higher prices.
The Trump administration’s tariffs on imported goods from Canada, Mexico and China — some already in place, others set to take effect in a few weeks — are already driving up the cost of building materials used in new residential construction and home remodeling projects. The tariffs are projected to raise the costs that go into building a single-family home in the U.S. by US$7,500 to US$10,000, according to the NAHB. We Buy Houses in San Francisco, which purchases foreclosed homes and then typically renovates and sells them, is increasing prices on its refurbished properties between 7% and 12%. That’s even after stockpiling 62% more Canadian lumber than usual. …The timing of the tariffs couldn’t be worse as this is typically the busiest time of year for home sales. …Confusion over the timing and scope of the tariffs, and their impact on the economy, could have a bigger chilling effect on the new-home market than higher prices.


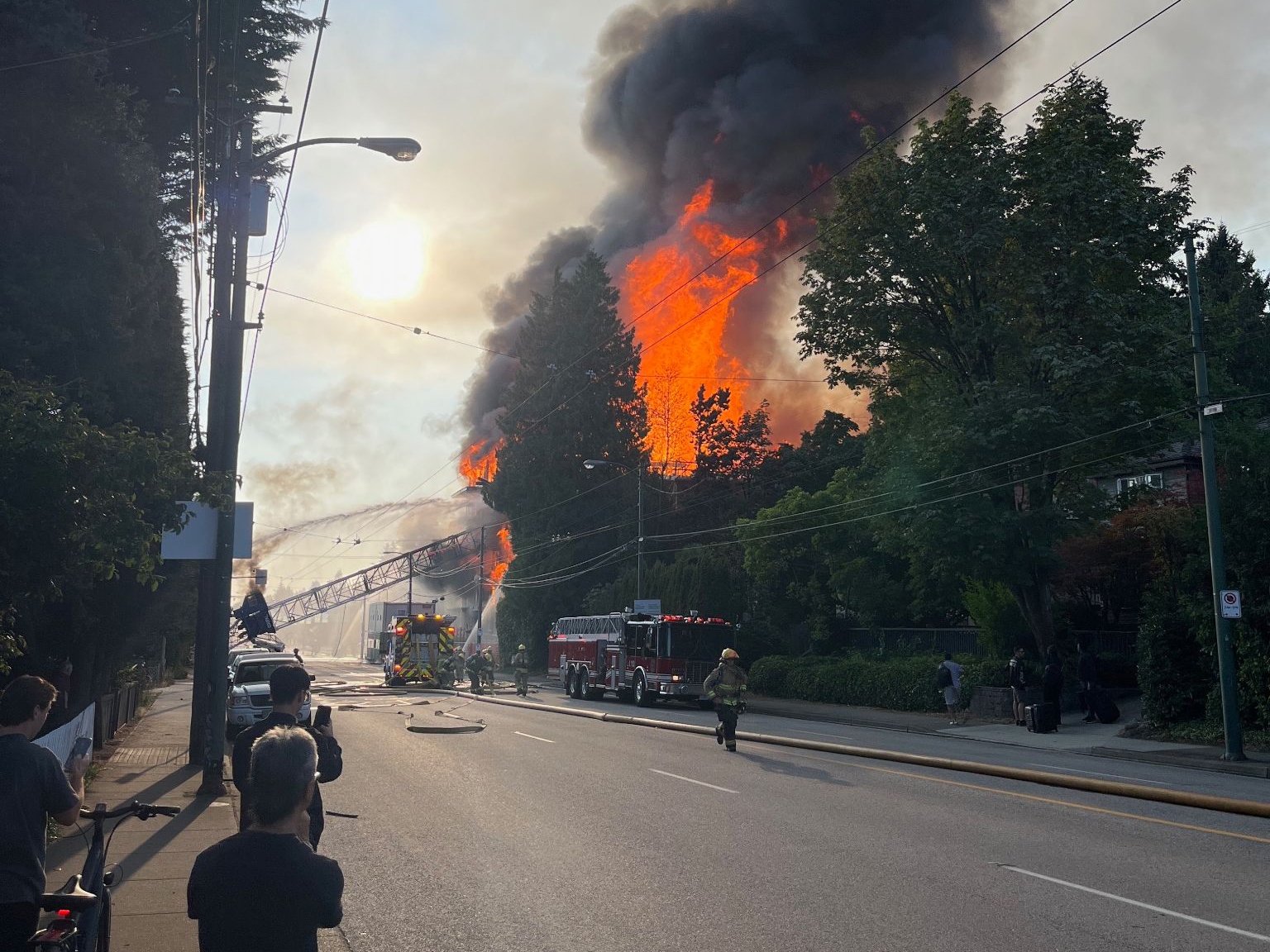
 VANCOUVER, BC — T
VANCOUVER, BC — T


 The Chisholm Awards for Innovation in Forestry program is a national competition for young researchers who are passionate about a range of activities relevant to forest-based science, products using forest-based raw materials, process improvements, or other innovations throughout the forest sector value chain. The Chisholm Awards for Innovation in Forestry are not just about rewarding research and development – they are also about showcasing the work of students and young researchers who are passionate about climate positive forestry and forest products, clean manufacturing, and the forest bioeconomy. Winners will be celebrated to coincide with The Twentieth Session of the United Nations’ Forum on Forests on May 5-9, 2025. Winners will receive a cash prize of CAD$2,500.00 along with local, regional, national, and social media promotion. Eligible applicants must be students or researchers who are 30 years old or younger as of March 1, 2025. Deadline to apply is April 4 by 11:59pm EDT.
The Chisholm Awards for Innovation in Forestry program is a national competition for young researchers who are passionate about a range of activities relevant to forest-based science, products using forest-based raw materials, process improvements, or other innovations throughout the forest sector value chain. The Chisholm Awards for Innovation in Forestry are not just about rewarding research and development – they are also about showcasing the work of students and young researchers who are passionate about climate positive forestry and forest products, clean manufacturing, and the forest bioeconomy. Winners will be celebrated to coincide with The Twentieth Session of the United Nations’ Forum on Forests on May 5-9, 2025. Winners will receive a cash prize of CAD$2,500.00 along with local, regional, national, and social media promotion. Eligible applicants must be students or researchers who are 30 years old or younger as of March 1, 2025. Deadline to apply is April 4 by 11:59pm EDT.






 If forest fires burn organic matter, and biochar is created by burning of organic matter shouldn’t forest soils be full of biochar? Not exactly. There is a difference between the burnt product of wildfire and biochar. Forest fires do produce charcoal, but while both charcoal and biochar are types of pyrogenic carbon, they’re not quite the same thing… Forests in Alberta have been affected by the mountain pine beetle, leaving behind dead trees that act as easy fuel for fires. These dead, dry trees are extremely flammable. The Canadian government has looked into using these dead trees as biofuels and some companies do use them to create biochar. Another source of organic matter for biochar is the material removed from forests as part of fuel management… Both of these methods help manage wildfire and could potentially increase the carbon sequestration of forests if the resulting biochar was added back into the forest’s soil.
If forest fires burn organic matter, and biochar is created by burning of organic matter shouldn’t forest soils be full of biochar? Not exactly. There is a difference between the burnt product of wildfire and biochar. Forest fires do produce charcoal, but while both charcoal and biochar are types of pyrogenic carbon, they’re not quite the same thing… Forests in Alberta have been affected by the mountain pine beetle, leaving behind dead trees that act as easy fuel for fires. These dead, dry trees are extremely flammable. The Canadian government has looked into using these dead trees as biofuels and some companies do use them to create biochar. Another source of organic matter for biochar is the material removed from forests as part of fuel management… Both of these methods help manage wildfire and could potentially increase the carbon sequestration of forests if the resulting biochar was added back into the forest’s soil.
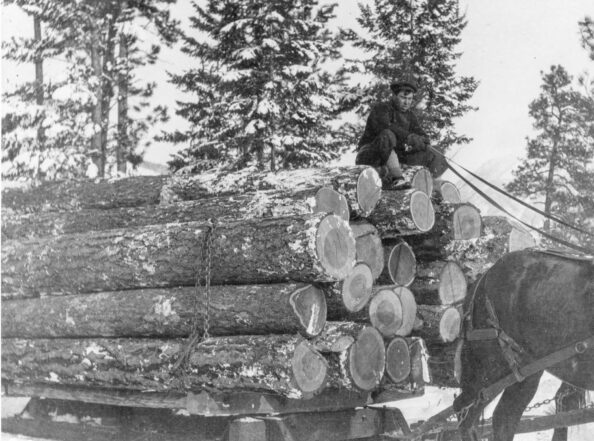
 Among the wave of humanity that came to Canada in the 19th century were hundreds of thousands of Irish, some of whom ended up in Bradford. …Between 1815 and 1840, about 450,000 Irish migrated to the British North American colonies. Cheap labour was needed in lumber camps and for construction of the Welland Canal and the Rideau Canal. Canada represented a new hope. Irish migration was encouraged by leaflets circulated by Canadian lumber merchants and the British government. For their part, lumber merchants realized money could be made in loading their vessels with would-be settlers on the return trip from Britain. …Irish migration to Canada increased when Ireland was struck by the Potato Famine due to widespread starvation. During this period, more than one million Irish died from starvation and resultant diseases. Even more fled overseas, many to Canada. …In 1847 alone, at least 110,000 Irish left Irish and British ports for Canada. The tragedy is many didn’t make it. …On this St. Patrick’s Day, raise a toast to them.
Among the wave of humanity that came to Canada in the 19th century were hundreds of thousands of Irish, some of whom ended up in Bradford. …Between 1815 and 1840, about 450,000 Irish migrated to the British North American colonies. Cheap labour was needed in lumber camps and for construction of the Welland Canal and the Rideau Canal. Canada represented a new hope. Irish migration was encouraged by leaflets circulated by Canadian lumber merchants and the British government. For their part, lumber merchants realized money could be made in loading their vessels with would-be settlers on the return trip from Britain. …Irish migration to Canada increased when Ireland was struck by the Potato Famine due to widespread starvation. During this period, more than one million Irish died from starvation and resultant diseases. Even more fled overseas, many to Canada. …In 1847 alone, at least 110,000 Irish left Irish and British ports for Canada. The tragedy is many didn’t make it. …On this St. Patrick’s Day, raise a toast to them.